In modern software ecosystems, applications rarely operate in isolation. Instead, they function as part of complex, interconnected environments that span devices, platforms, vendors, networks, and cloud services. As a result, ensuring that these systems work together seamlessly has become one of the most critical challenges in software quality assurance. This is exactly where interoperability testing plays a vital role. At its simplest level, interoperability testing validates whether two or more systems can communicate and exchange data correctly. However, in enterprise environments, especially in Electric Vehicle (EV) and Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystems, its impact extends far beyond technical validation. It directly influences safety, reliability, scalability, regulatory compliance, and customer trust.
Moreover, as EV and IoT products scale across regions and integrate with third-party platforms, the number of dependencies increases dramatically. Vehicle hardware, sensors, mobile applications, backend services, cloud platforms, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, cellular networks, and external APIs must all function together flawlessly. Consequently, even a small interoperability failure can cascade into major operational issues, poor user experiences, or, in the worst cases, safety risks. Therefore, interoperability testing is no longer optional. Instead, it has become a strategic quality discipline that enables organizations to deliver reliable, user-centric, and future-proof connected products.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore:
- What interoperability testing is
- Different levels of interoperability
- Why interoperability testing is essential
- Tools used to perform interoperability testing
- Real-world EV & IoT interoperability testing examples
- Key metrics and best practices
- SEO-optimized FAQs for quick understanding
What Is Interoperability Testing?
Interoperability testing is a type of software testing that verifies whether a software application can interact correctly with other software components, systems, or devices. The primary goal of interoperability testing is to ensure that end-to-end functionality between communicating systems works exactly as defined in the requirements.
In other words, interoperability testing proves that different systems, often built by different vendors or teams, can exchange data, interpret it correctly, and perform expected actions without compatibility issues.
For example, interoperability testing can be performed between smartphones and tablets to verify seamless data transfer via Bluetooth. Similarly, in EV and IoT ecosystems, interoperability testing ensures smooth communication between vehicles, mobile apps, cloud platforms, and third-party services.
Unlike unit or functional testing, interoperability testing focuses on cross-system behavior, making it essential for complex, distributed architectures.
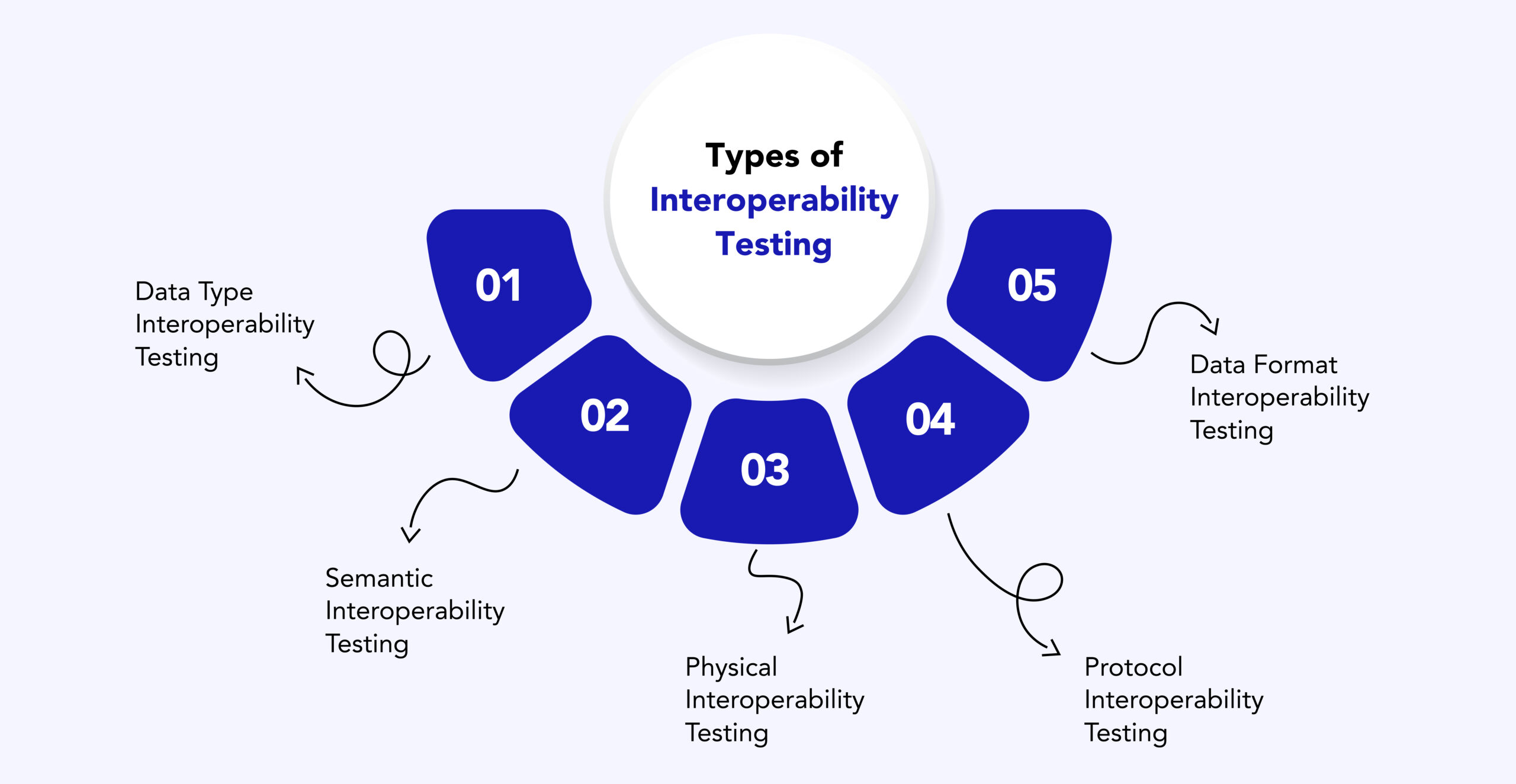
Different Levels of Software Interoperability
Interoperability testing can be categorized into multiple levels. Each level addresses a different dimension of system compatibility, and together they ensure holistic system reliability.
1. Physical Interoperability
Physical interoperability ensures that devices can physically connect and communicate with each other.
Examples include:
- Bluetooth connectivity between a vehicle and a mobile phone
- Physical connection between a charging station and an EV
Without physical interoperability, higher-level communication cannot occur.
2. Data-Type Interoperability
Data-type interoperability ensures that systems can exchange data in compatible formats and structures.
Examples include:
Failures at this level can lead to data corruption or incorrect system behavior.
3. Specification-Level Interoperability
Specification-level interoperability verifies that systems adhere to the same communication protocols, standards, and API contracts.
Examples include:
- REST or SOAP API compliance
- Versioned API compatibility
This level is especially critical when multiple vendors are involved.
4. Semantic Interoperability
Semantic interoperability ensures that the meaning of data remains consistent across systems.
For instance, when one system sends “battery level = 20%”, all receiving systems must interpret that value in the same way. Without semantic interoperability, systems may technically communicate but still behave incorrectly.
Why Perform Interoperability Testing?
Interoperability testing is essential because modern software products are built on integration, not isolation.
Key Reasons to Perform Interoperability Testing
- Ensures end-to-end service provision across products from different vendors
- Confirms that systems communicate without compatibility issues
- Improves reliability and operational stability
- Reduces post-release integration defects
Risks of Not Performing Interoperability Testing
When interoperability testing is neglected, organizations face several risks:
- Loss of data
- Unreliable performance
- Incorrect system operation
- Low maintainability
- Decreased user trust
Therefore, investing in interoperability testing early significantly reduces long-term cost and risk.
Tools for Interoperability Testing
We can perform interoperability testing with the help of specialized testing tools that validate communication across APIs, applications, and platforms.
Postman
Postman is widely used for testing API interoperability. It helps validate REST, SOAP, and GraphQL APIs by checking request-response behavior, authentication mechanisms, and data formats. Additionally, Postman supports automation, making it effective for validating repeated cross-system interactions.
SoapUI
SoapUI is designed for testing SOAP and REST APIs. It ensures that different systems follow API specifications correctly and handle errors gracefully. As a result, SoapUI is particularly useful when multiple enterprise systems communicate via standardized APIs.
Selenium
Selenium is used to test interoperability at the UI level. By automating browser actions, Selenium verifies whether web applications work consistently across browsers, operating systems, and environments.
JMeter
Although JMeter is primarily a performance testing tool, it can also support interoperability testing. JMeter simulates concurrent interactions between systems, helping teams understand how integrated systems behave under load.
Why Interoperability Testing Is Crucial for EV & IoT Systems
EV and IoT platforms are built on highly interconnected ecosystems that typically include:
- Vehicle ECUs and sensors
- Mobile companion apps (Android & iOS)
- Cloud and backend services
- Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and cellular networks
- Third-party APIs (maps, payments, notifications)
Because of this complexity, a failure in any single interaction can break the entire user journey. Therefore, interoperability testing becomes critical not only for functionality but also for safety and compliance.
Real-World EV & IoT Interoperability Testing Examples
Visual Use-Case Table (Enterprise View)
| S. No | Use Case | Systems Involved | What Interoperability Testing Validates | Business Impact if It Fails |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | EV Unlock via App | Vehicle, App, Cloud | Bluetooth pairing, auth sync, UI accuracy | Poor UX, high churn |
| 2 | Navigation Sync | App, Map APIs, ECU, GPS | Route transfer, rerouting, lifecycle handling | Safety risks |
| 3 | Charging Monitoring | Charger, BMS, Cloud, App | Real-time updates, alert accuracy | Loss of user trust |
| 4 | Network Switching | App, Network, Cloud | Fallback handling, feature degradation | App unusable |
| 5 | SOS Alerts | Sensors, GPS, App, Gateway | Location accuracy, delivery confirmation | Critical safety failure |
| 6 | Geofencing | GPS, Cloud, App, Vehicle | Boundary detection, alert consistency | Theft risk |
| 7 | App Lifecycle | OS, App Services, Vehicle | Reconnection, background sync | Stale data |
| 8 | Firmware Compatibility | Firmware, App, APIs | Backward compatibility | App crashes |
Detailed Scenario Explanations
1. EV ↔ Mobile App (Bluetooth & Cloud)
A user unlocks an electric scooter using a mobile app. Interoperability testing ensures Bluetooth pairing across phone models, permission handling, reconnection logic, and UI synchronization.
2. EV Navigation ↔ Map Services
Navigation is sent from the app to the vehicle display. Interoperability testing validates route transfer, rerouting behavior, and GPS dependency handling.
3. Charging Station ↔ EV ↔ App
Users monitor charging via the app. Testing focuses on real-time updates, alert accuracy, and synchronization delays.
4. Network Switching
Apps switch between 5G, 4G, and 3G. Interoperability testing ensures graceful degradation and user feedback.
5. Safety & Security Features
Features such as SOS alerts and geofencing rely heavily on interoperability across sensors, cloud rules, and notification services.
6. App Lifecycle Stability
When users minimize or kill the app, interoperability testing ensures reconnection and background sync.
7. Firmware & App Compatibility
Testing ensures backward compatibility when firmware and app versions differ.
Related Blogs
Key EV & IoT Interoperability Metrics
- Bluetooth reconnection time
- App-to-vehicle sync delay
- Network fallback behavior
- Data consistency across systems
- Alert delivery time
- Feature availability across versions
Best Practices for EV & IoT Interoperability Testing
- Test on real devices and vehicles
- Validate across multiple phone brands and OS versions
- Include network variation scenarios
- Test app lifecycle thoroughly
- Monitor cloud-to-device latency
- Automate critical interoperability flows
Conclusion
In EV and IoT ecosystems, interoperability testing defines the real user experience. From unlocking vehicles to navigation, charging, and safety alerts, every interaction depends on seamless communication across systems. As platforms scale and integrations increase, interoperability testing becomes a key differentiator. Organizations that invest in robust interoperability testing reduce risk, improve reliability, and deliver connected products users can trust.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is interoperability testing?
Interoperability testing verifies whether different systems, devices, or applications can communicate and function together correctly.
-
Why is interoperability testing important for EV and IoT systems?
Because EV and IoT platforms depend on multiple interconnected systems, interoperability testing ensures safety, reliability, and consistent user experience.
-
What is the difference between integration testing and interoperability testing?
Integration testing focuses on internal modules, while interoperability testing validates compatibility across independent systems or vendors.
-
Which tools are used for interoperability testing?
Postman, SoapUI, Selenium, and JMeter are commonly used tools for interoperability testing.

Planning to scale your EV or IoT platform? Talk to our testing experts to ensure seamless system integration at enterprise scale.
Talk to an Interoperability Expert






























Comments(0)