
by admin | Nov 29, 2021 | Automation Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
We live in a world where automation is already considered to be a huge advantage now for most companies. The same goes for testing mobile and web applications. You need to have the right tools that will help you automate many of the functions of testing so you can get a higher level of test coverage and execute them at a faster rate. Let’s look at some of the tools that quality teams are looking for when testing mobile apps and web apps.
Tools for Mobile App Testing
While most web developers and testers use the Selenium framework to write tests, there are many different tools for mobile app testing. The first question to ask when choosing a tool is whether it is open-sourced or closed-source. Since most mobile apps are built with open-source frameworks, it is best to select an open-source tool, if possible.
The next question is whether the tool runs on more than one OS or just on Android or just on iOS. You will probably write tests in a language that does not depend on OS, but you should remember that Android and iOS require different test frameworks.
Not every mobile app test framework is best for every application type: native apps, web apps with a mobile interface, and hybrid apps with heavy WebView use can require different tools.
If you are running into problems deciding which tool is best for your needs, keep in mind that many companies offer free trials or free versions of their products. Just do a little bit of research before you jump in headfirst.
Tools for Web App Testing
More and more businesses rely on their web applications to streamline their operations and improve their marketing efforts. The continuous, high load and growing market expectations require web apps to undergo a variety of tests to make sure that it’s compliant with the UI standards, as well as in terms of compatibility and usability. Web app testers need to use a variety of automated software testing tools that allow them to test their products from different perspectives.
Which Testing Tool to Use?
Before making a decision on which testing tool to use for your applications, you need to take into account all the other factors that could affect how your testing will go. Some of the questions you need to consider are:
- How many tests do you need to run?
- Who will run the tests?
- How frequently do you need to run them?
- How many users do you intend to simulate?
- What scripting languages do you have experience working with?
- What platforms and browsers do you need to cover?
- Are you testing a finished product or a pre-release version?
- How important is automation for you?
- Do you have a system of tracking and analyzing the results?
- How important is a visual reporting system for you?
Conclusion
Mobile and web app testing is a crucial step in software development where companies can’t afford to cut corners. The only way to make testing much more efficient is to use the right kind of tools for the job. This guide should help you decide what kind of tools you can use for testing that will help you automate many of its functions.
If you’re in need of a QA company with a seamless track record in web and mobile testing services, Codoid is your best choice. Every new software product deserves high-quality automation testing, and our team of highly skilled QA professionals can handle any job. When it comes to QA automation services, there’s no better choice than Codoid. Partner with us today!

by admin | Nov 12, 2021 | Automation Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
Robot Framework is an open-source Python-based automation framework used for Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and also for Acceptance Testing & Acceptances Test-Driven Development (ATDD). It is used with the keyword-driven testing approach for which testers can write automation test scripts easily. The Test cases are written using the keyword style in a tabular format making them easy to understand. Robot Framework does provide good support for external libraries. But Selenium library is the most popular library used with Robot Framework for web development and UI testing. As a leading mobile app testing service provider, we have been using Robot Framework in our various Android and iOS app testing projects. So we have written this end-to-end Robot Framework Tutorial that covers everything one has to know.
The Basic requirements for robot framework
Since the Robot framework is built based on Python, we have to install the latest version of Python by downloading it from their official site. After successful installation, set up the Path environment variable in your local system.
Steps to Install Robot Framework:-
1. You can check if the Python setup has been installed properly by opening Command Prompt and typing the below command.
2. Use the below command to check the pip version. (Pip is a Python package manager)
3. Now we’re all set to install the Robot framework
a. For a straightforward installation of the robot framework, you can use the command
pip install robotframework
b. If there is a need to install the robot framework without any cache, you can use this code instead.
pip install --no-cache-dir robotframework
c. If for any reason, you want to uninstall the Robot framework, then you can do so by using the below code.
pip uninstall robotframework
4. Just like how we verified Java, we can use the below commands to check it using Command Prompt.
(i)
This command will show the details of the robot framework and the framework location.
(ii.)
Once we enter this command, the desired result that should be displayed is “No broken requirements found.” If any other message apart from this (i.e.) a warning is displayed, we need to check the warning related to the setup and install it properly.
We can also verify if the Robot Framework has also been installed properly in our Local system.
Go to the Python folder > Lib > site-packages > verify if Robot Framework is installed.
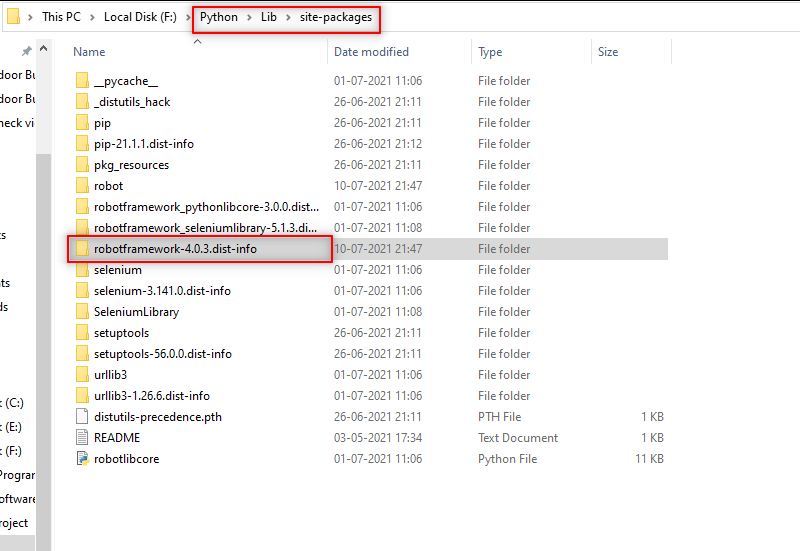
5. To verify the version of the installed Robot Framework, use this code
6. You might face a scenario where you would need to use a specific version of the Robot Framework, you can accomplish this by mentioning the specific version you need as shown below.
pip install robotframework==4.0.0 //mention the specific version
7. In time, you might want to upgrade the old version of the Robot Framework. You can use the below code to do it.
pip install --upgrade robotframework
8. In addition to verifying if the Robot Framework has been installed correctly, you might also have to check if the python libraries.
(i.)
This command will show all the python libraries installed with the robot framework version.
(ii.)
This command will show all the python libraries installed with their version numbers.
For writing automation test case:
In the Robot Framework Tutorial, we would be exploring how to perform web browser testing using Selenium Library. But for that to happen, we have to import the Selenium library file to this Robot project
Step 1: Enter the Command-Line to install Selenium
Step 2: To upgrade the pip installation with the Selenium library, enter the below-mentioned command
pip install --upgrade robotframework-seleniumlibrary
Step 3: Finally, you can check if the pip Robot framework Selenium library has been installed properly by using this command.
pip check robotframework-seleniumlibrary
IDE for the Robot framework:
We can conveniently use the following IDE’s to write the Robot Framework automation testing codes.
1. PyCharm
2. Eclipse with RED plugin
3. Visual Studio with one of the plugin
4. RIDE
In this Robot Framework Tutorial, we have used PyCharm with Selenium to write a website automation testing code.
PyCharm IDE Installation and a New Project Creation:-
Step 1: Go to https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/download/#section=windows
Step 2: Download the free Open-Source Community Version of the PyCharm .exe file.
Step 3: Once you run the .exe file of the PyCharm setup, you’ll see the ‘Install Location’ window. If you want to change the location from the default option, you can click on the “BROWSE” button, and select your own file setup location and click on the ‘Next’ button.
Step 4: In the 4th Window, select the 64-bit launcher and click the ‘NEXT’ button to move to the next window where you can directly click on the ‘INSTALL’ button to install all the files.
Step 5: Once the setup and jar files are properly installed and updated, tick the checkbox and finish by clicking on the “OK” button in the “Import Pycharm Settings” pop-up.
Step 6: Now, you will see the ‘Welcome to PyCharm’ window. Click on the “Create New Project” option and it will automatically generate a project fill location to set up the project. If you would like to change the location, then you may click on the file option to customize it as you please. Enter the “Project Name”, and click on the “CREATE” button.
Step 7: Finally the PyCharm Window will display with New Project.
In this Pycharm IDE, we are going to create a Robot framework for a website’s automation testing. So let’s explore how to generate a report and all the other essential actions in the upcoming topics of this Robot Framework Tutorial.
How to Create a New Robot Project and the required Setups:
In the Robot framework, we have to set up interpreters and add some plugins as well. Let see how to do those things now.
Step 1: You’ve already created the Initial Project for which you need to add the interpreters to work with the Selenium and Robot framework. So follow the below steps, and use the image as a reference if needed.
Go to File > Settings > Click on Project: “current project name” > Python Interpreter > + icon
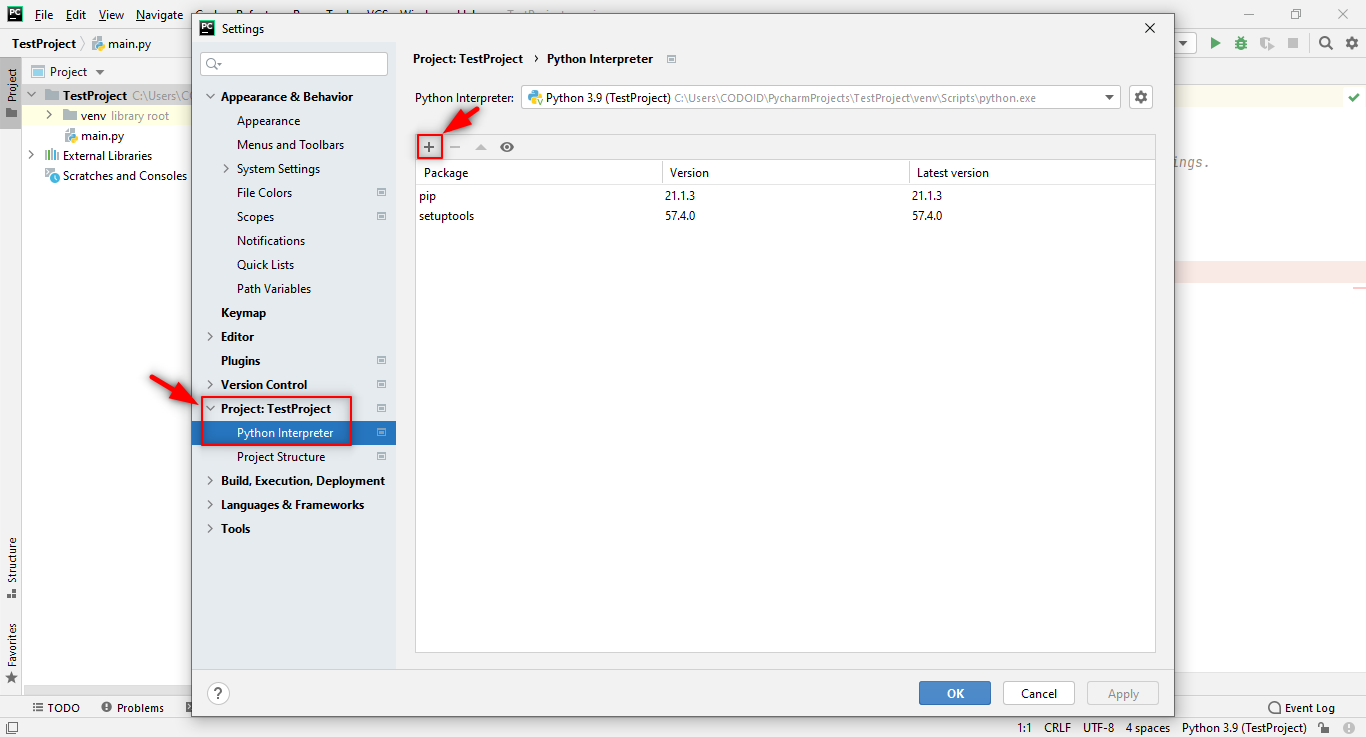
Step 2: You need to install the following packages for this project
i. Selenium
ii. robotframework
iii. robotframework-seleniumlibrary
You have to enter these three keywords one by one in the search input field and search for the packages. Once you find them, you have to click on the “Install Package” button and wait for a while for the packages to install in the back end. Once it is successfully installed, the highlighted message will appear and you can close the window by clicking on the “OK” button in the settings window.
Note: Make sure to close the window only after installing the three packages one by one.
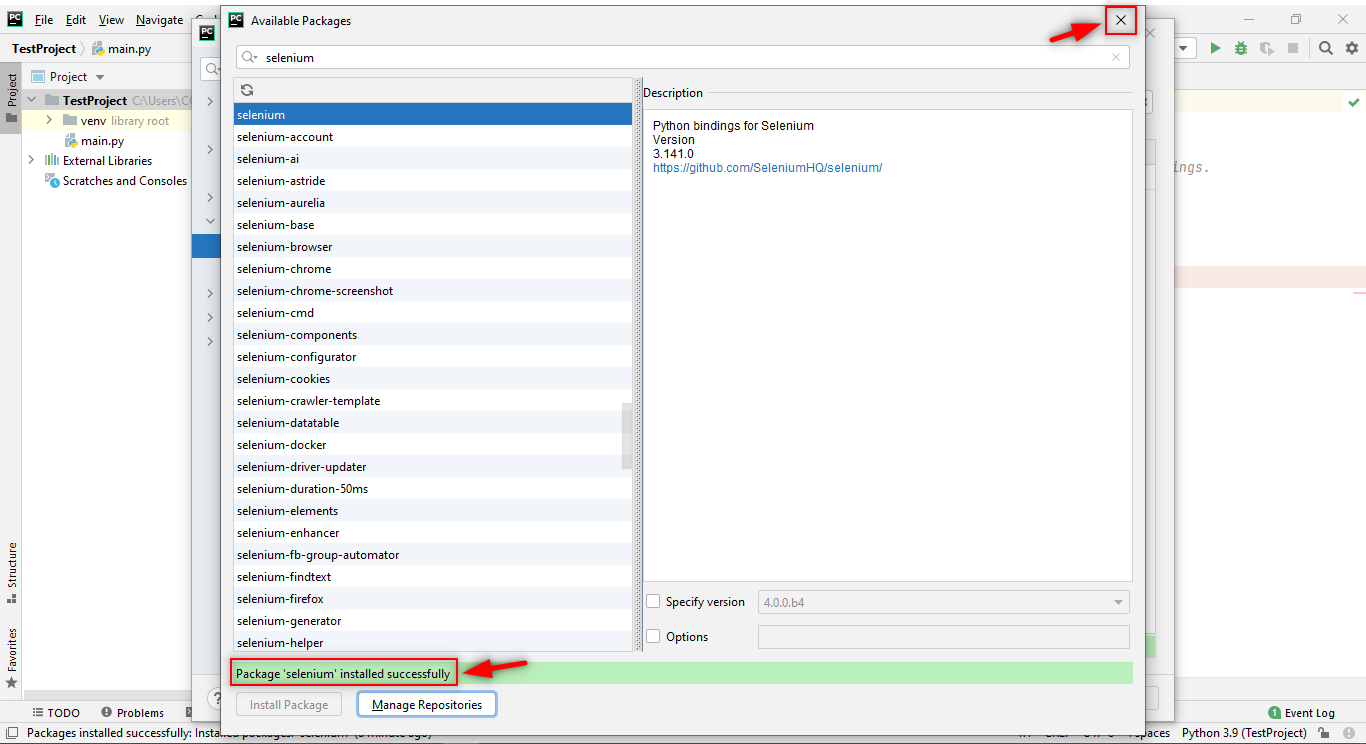
Step 3: Now, you have to add the “IntelliBot @SeleniumLibrary Patched” Plugin as it’ll help us find the Robot framework files and give auto suggestions for the keywords. So without this plugin, PyCharm will not be able to find the “.robot” files. The steps are as follows,
Settings > Plugin > Marketplace >Search “IntelliBot @SeleniumLibrary Patched” > Install
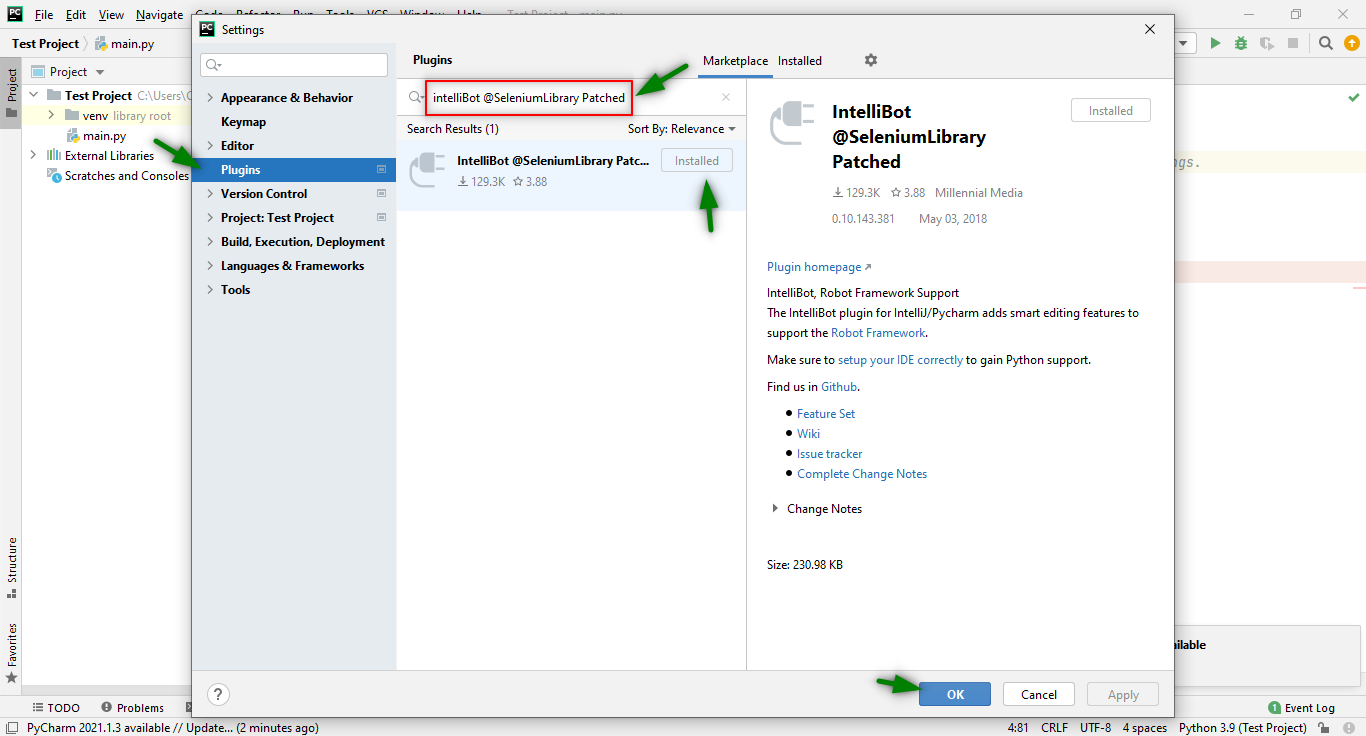
Once the Plugin has been installed, you have to restart the IDE for the initial configuration.
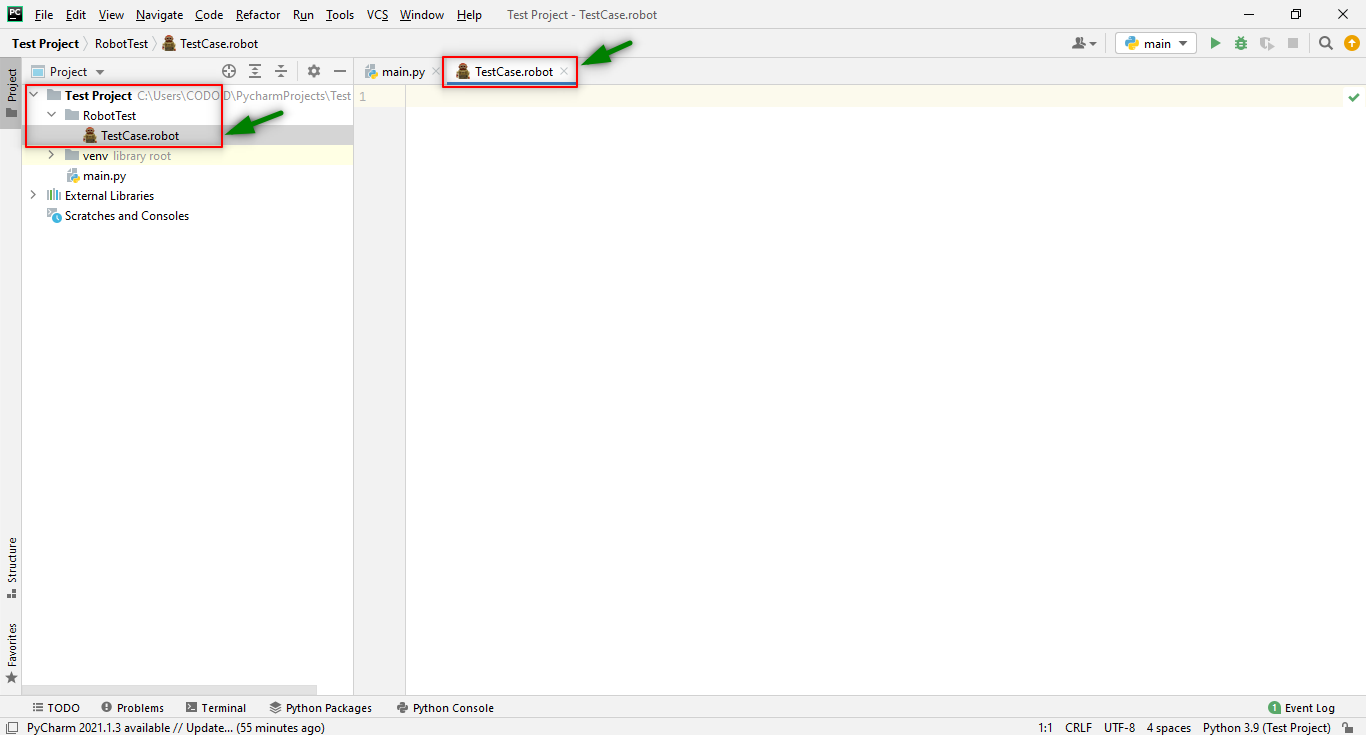
Step 4: Normally, the Project Structure contains multiple directories and each directory contains a similar kind of file. So in this Test project, we are going to create a test case inside the directory first.
Right-click Test Project > New > Directory > Enter the Directory Name
That directory will be created under the Test Project and so our Robot test cases can be created inside it.
Step 5: Create the “.robot” file under the created directory.
Right Click on Created Directory > New > File > Enter a File name that ends with “.robot”
Once the robot project has been created, the structure of the project will be how it’s shown in the following image.
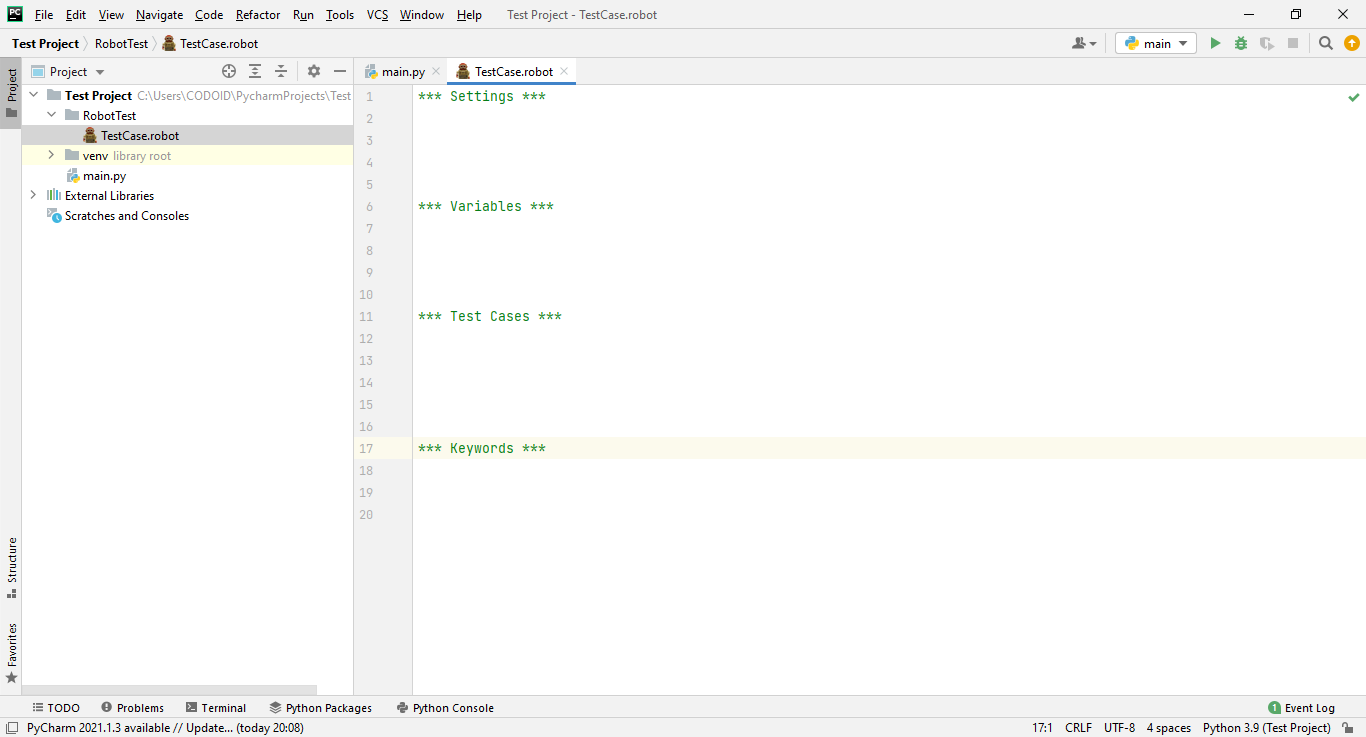
Prerequisites to run Automation Test Cases in the Robot Framework:
Whenever you write automation test cases in the Robot framework, 4 sections should be there. They are
- Settings
- Variables
- Test Cases
- Keywords
Note:
- These 4 sections are must-know aspects from a beginner’s point of view.
- Each and every section starts with ‘***’ and is followed by the Name of the Section. It also ends with ‘***’.
- One (or) Two Tab spaces are needed in between the Keyword and the Test data (or) Data (or) input data because indentation is very important in Python.
- When you’re about to write a test case, you should first write the test case name and then go to the next line to write the keyword after leaving a tab space.
Step 1: Settings
You are going to import the Selenium Library in this Test case.
The first line indicates the code block and the second line uses the “Library” keyword to import the “SeleniumLibrary”.
Syntax:
***Settings***
Keyword LibraryName
Step 2: Write the Test Cases
Now, you have to write exact test cases as per your requirements. First, you have to assign a test case name, and then enter the test case information in the next line. You can write these test cases using free defined Selenium Keywords. Being a leading QA Company, we wanted our Robot Framework Tutorial to be a comprehensive guide even for beginners. That is why we’re going through everything from scratch.
Syntax:
***Test Cases***
TestCase_Name
Keyword Locators(or)data Testdata
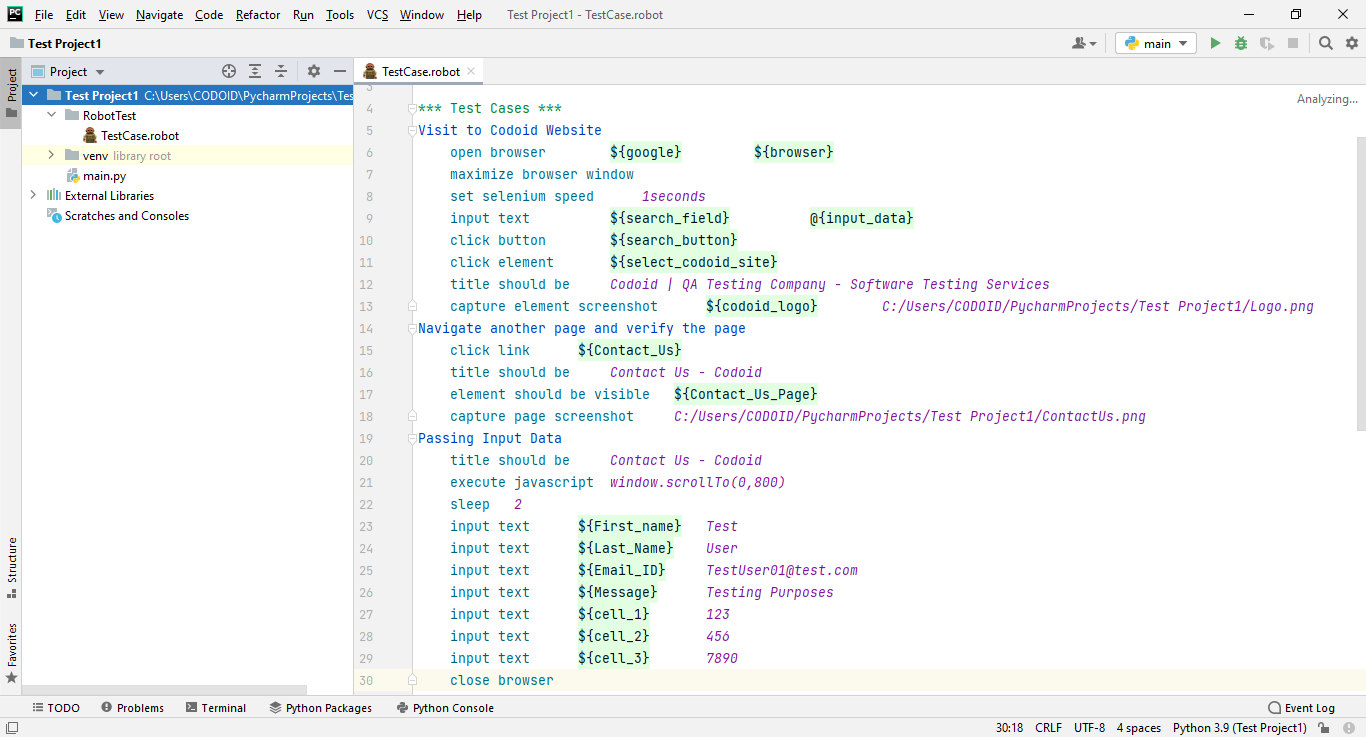
In this Robot Framework Tutorial, we are going to perform the following test cases:-
1. Visit the Codoid Website.
2. Navigate to another page and verify it.
3. Pass the Input data.
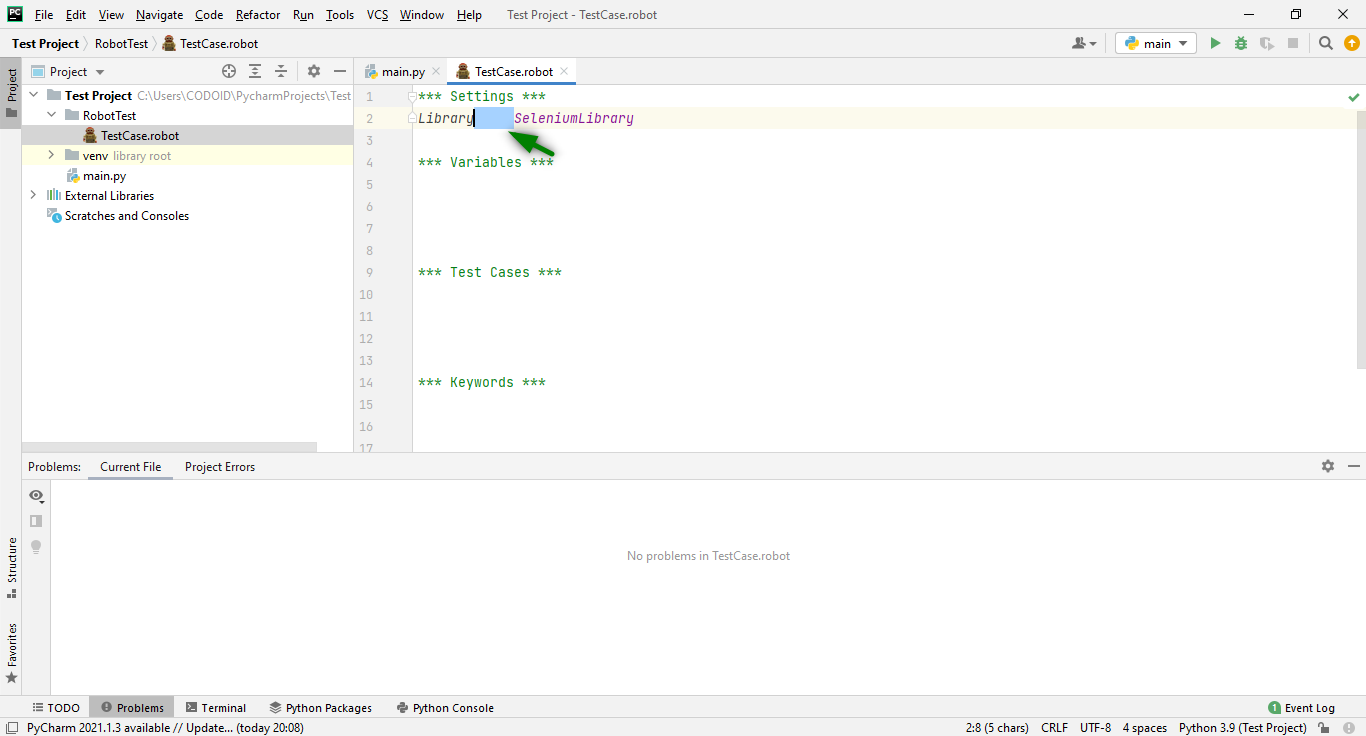
The first step towards automation is launching your browser. Based on the browser you are using (Chrome, Firefox, etc.), you have to download the various drivers. Once you have downloaded the drivers, you have to extract the downloaded file and copy the driver.exe file path. We will be using Chrome for our demonstration.
Syntax for the Chrome launch:
***Test Cases***
TestCase_Name
Keyword driver_name executable_path= “driver_path”
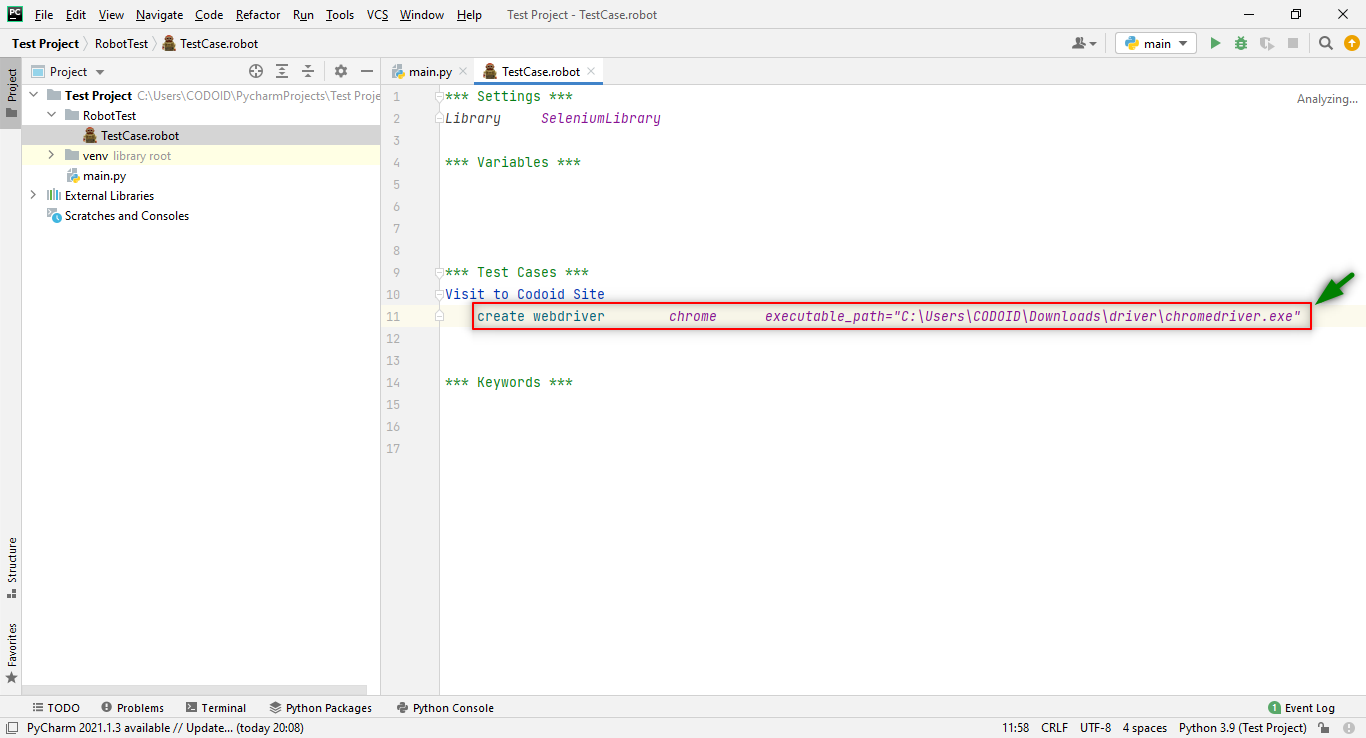
There is also another method that can help us save some valuable time by reducing the time to launch the browser. You can,
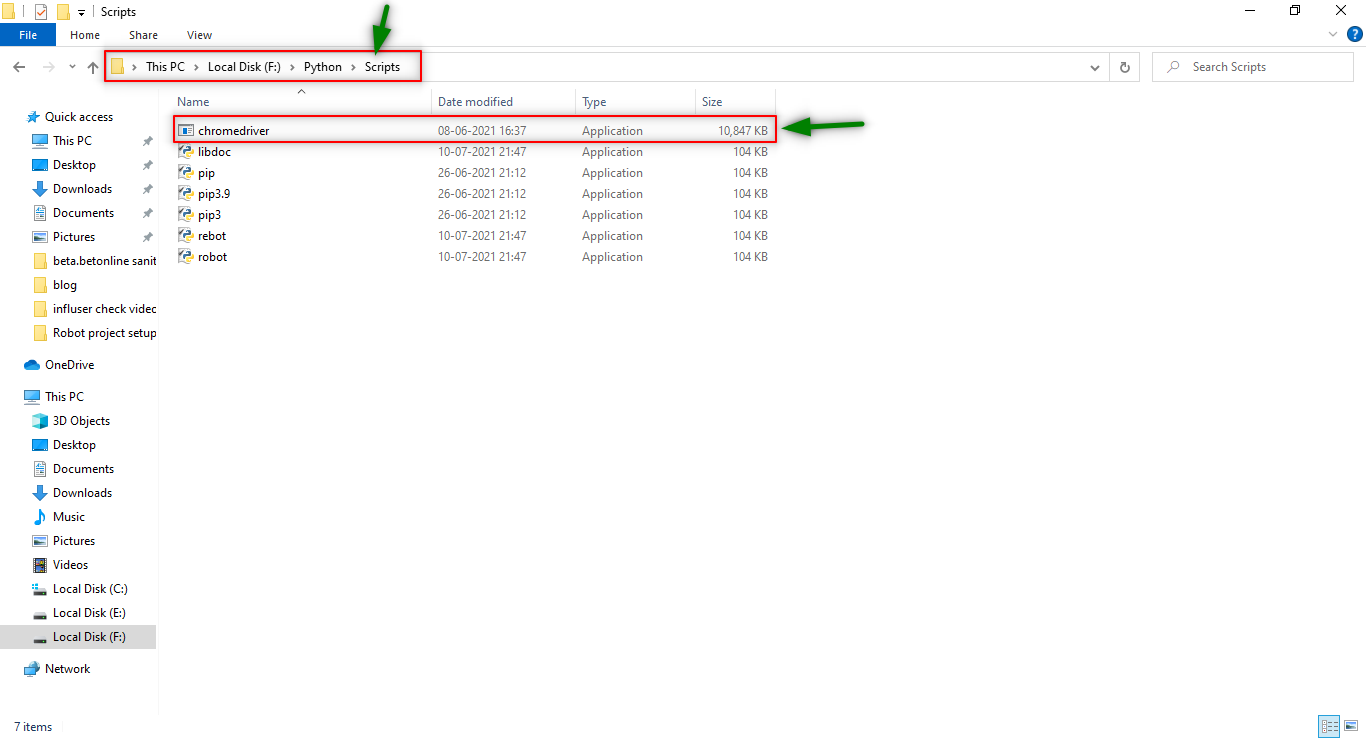
1. Copy or Cut “various_driver.exe” file from your local.
2. Paste them under the Python/Scripts page under your local system as shown below.
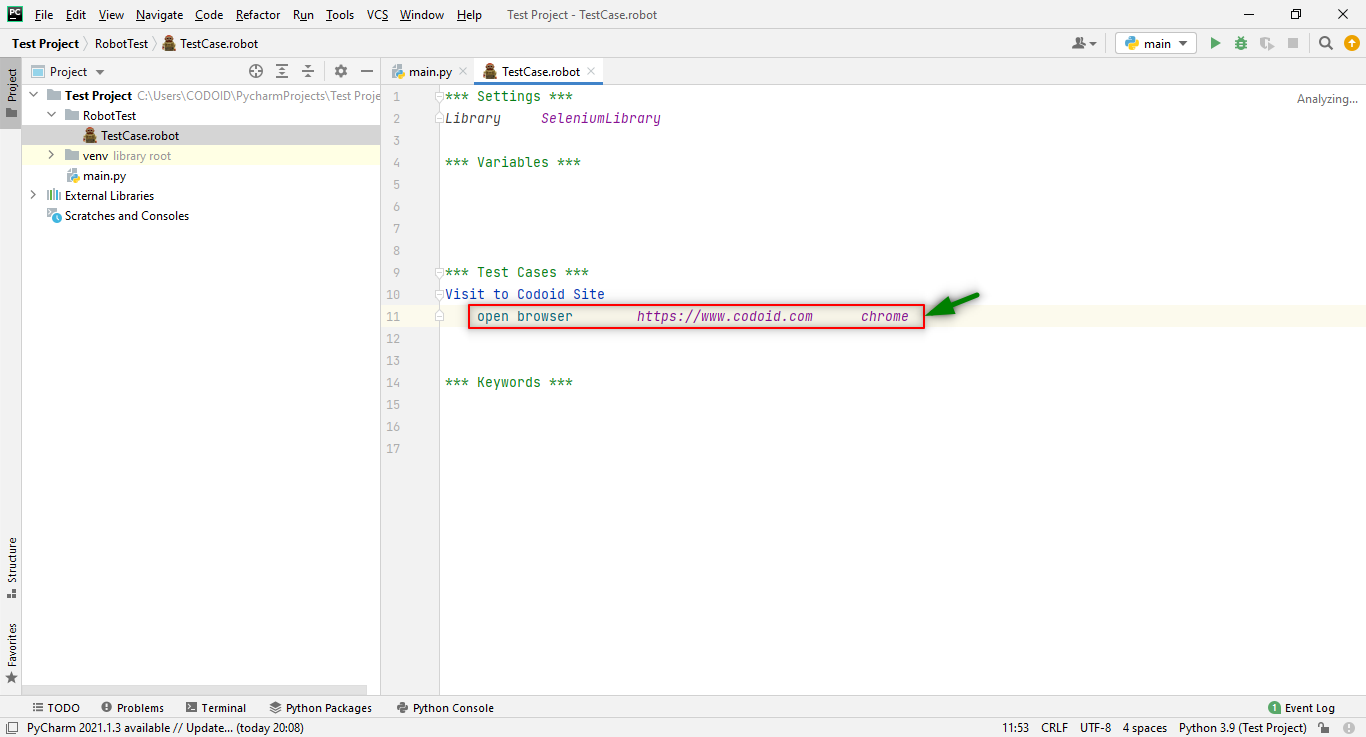
After this step, we can directly launch the browser without pointing to the driver location in the framework. We have to write the following syntax instead of using the “Create webdriver” keyword to set up the path.
Direct browser launching syntax:
***Test Cases***
TestCase_Name
Keyword input_data (or) URL driver_name
Based on the requirements, we have to write the test steps under the test case name with the Selenium Library Keywords and respected Locators along with the test data.
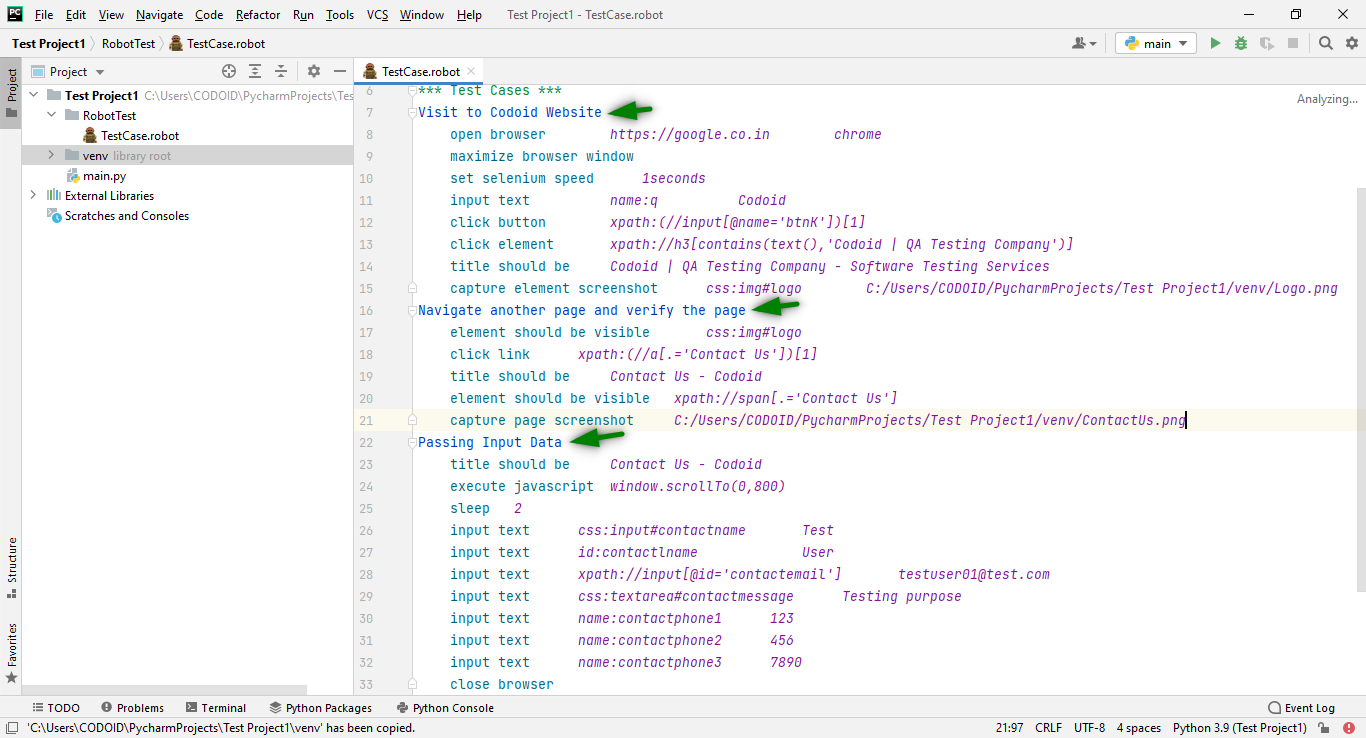
In this example, will be performing the test case with limited Selenium Keywords in the robot framework. For more Selenium Library keywords please visit their website.
Step 3: Define the Variable
The variables are elements used to store values which can be referred to by other elements.
Syntax:
***Variables ***
${URL} url
@{UserCredentials} inputs
Defined variables can be replaced in test cases and we can even reuse them anywhere in the test case when needed.
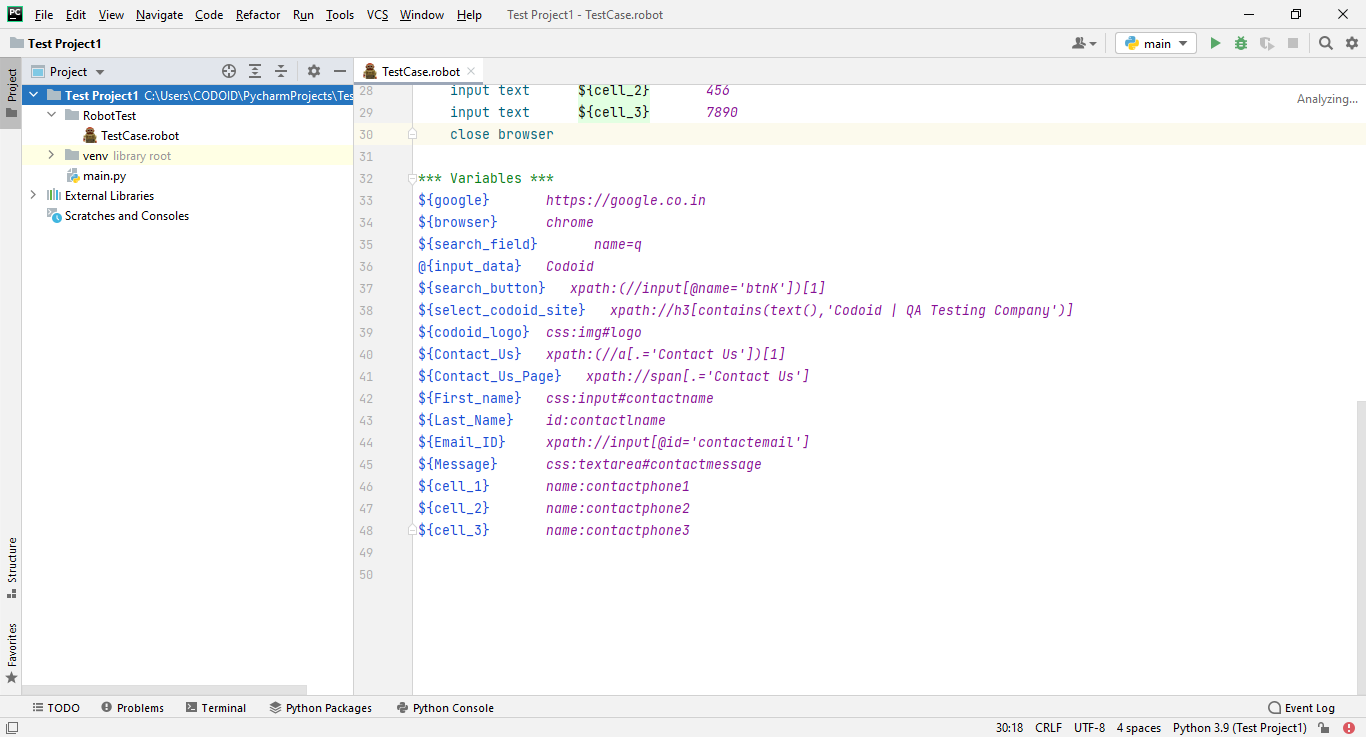
Apart from this, we have a lot of variables available in Robot Framework. We have mentioned only the required ones here
Step 4: Define the KEYWORDS
Since the keywords are reusable in the Robot framework, it helps manage the changes in a faster and efficient manner. You can even create our own keywords here.
Syntax:
***Keywords***
Keyword_Name
Selenium_keyword locators input_data
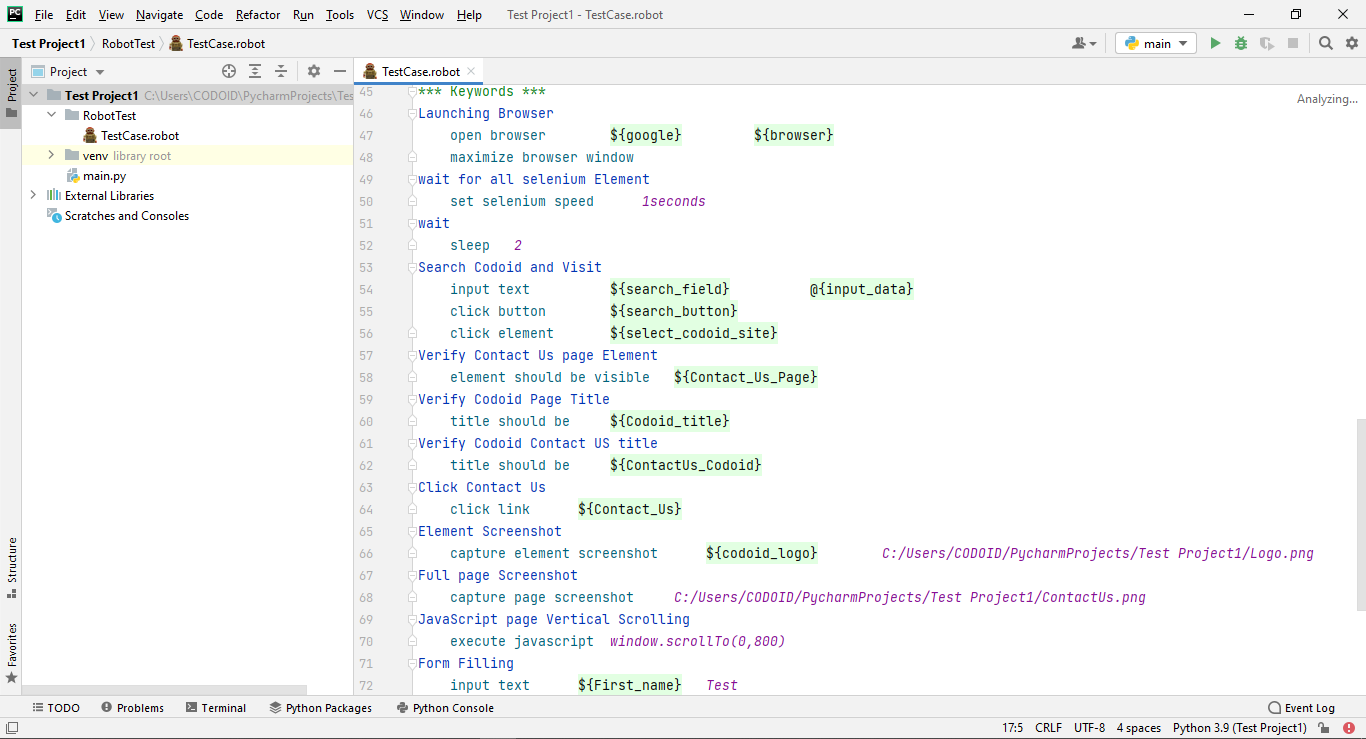
Once you write your own keyword, you can replace the test case steps with the keywords.
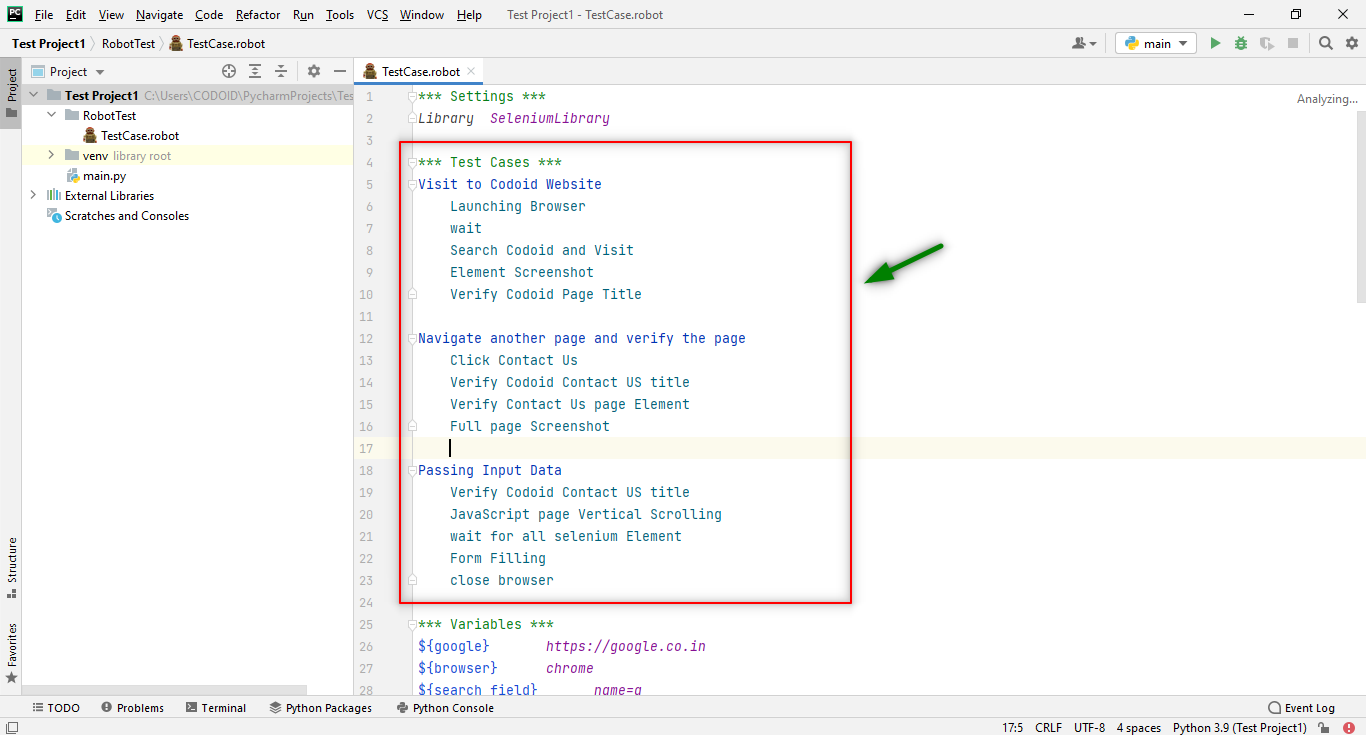
Even once all of this is done, we won’t be able to run our project directly in the PyCharm Robot framework. We would have to go to the Terminal and use the below command
robot directory_name\file_name.robot
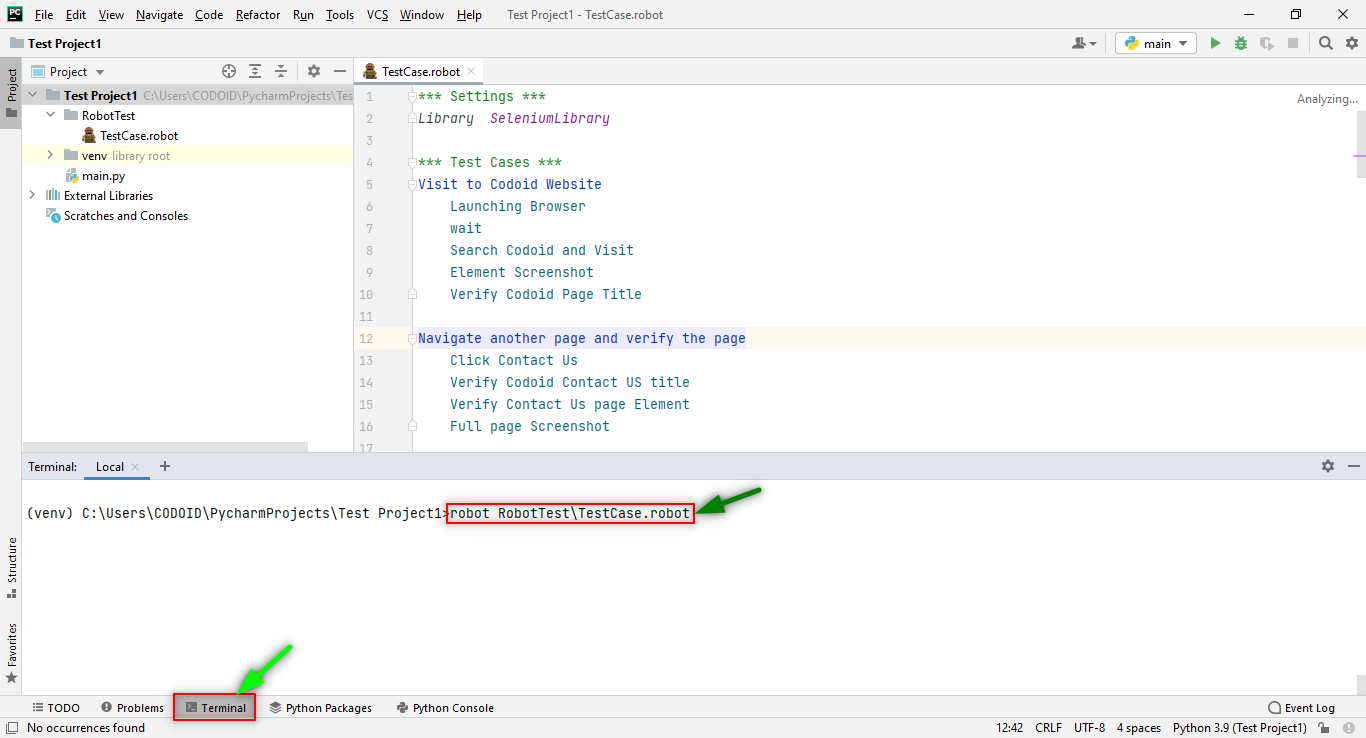
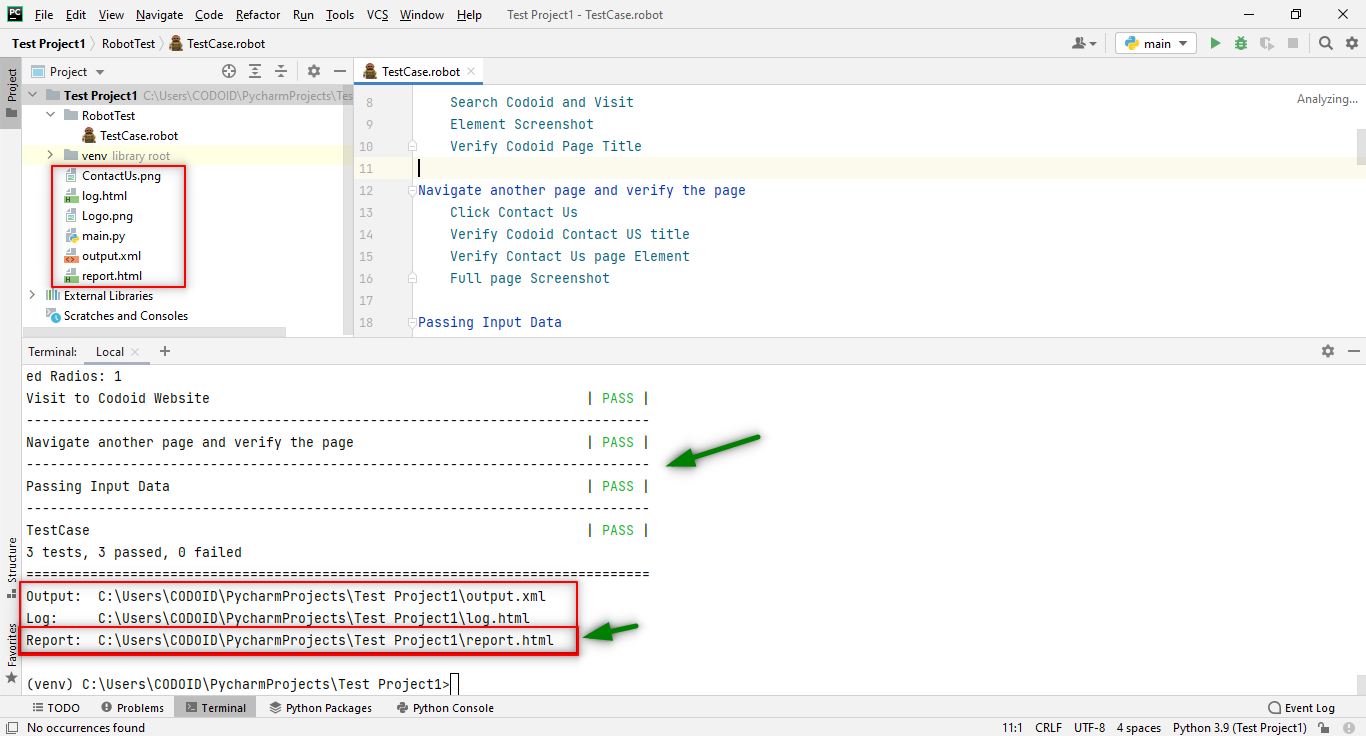
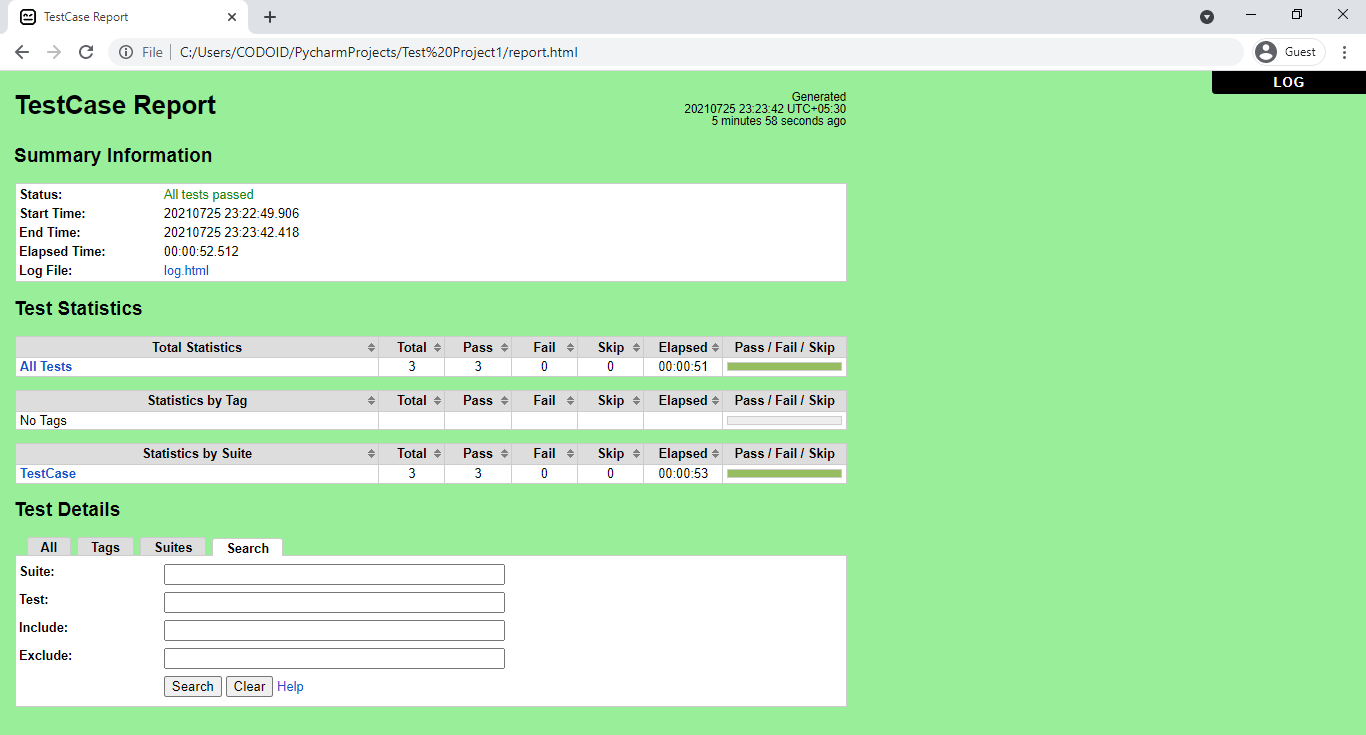
Once the project has been successfully executed, the output.html, the log.html, and the report.html files along with the screenshots for each test case will be automatically created in our project structure. So we can copy and paste it into any browser to check the report of the execution of our project.
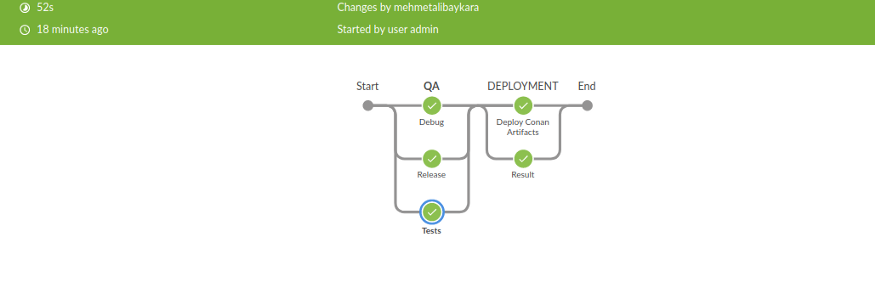
Here we have executed all the test cases. But if you are looking to run a separate test case, you can do so by using Tags. You should include the tags with the name of your choice inside the test cases section under the test case name as shown in the below image.
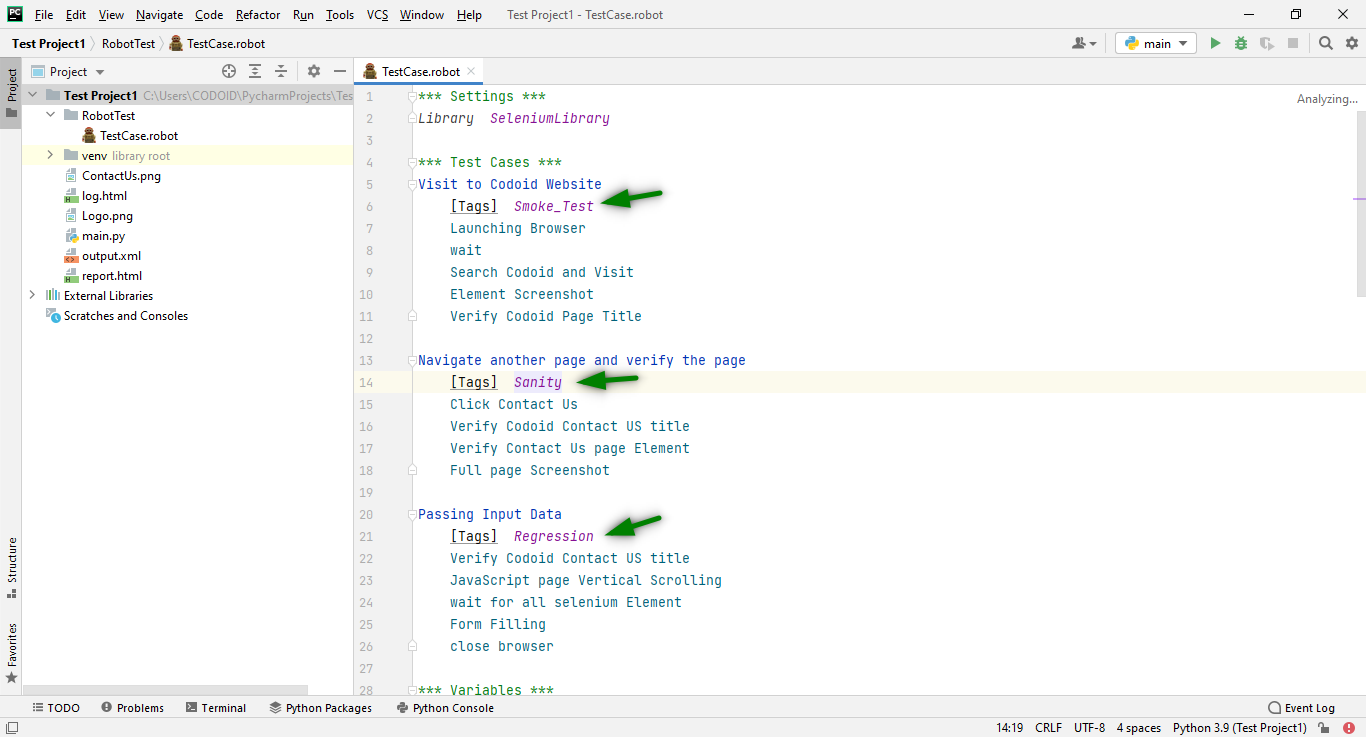
You can either run one or a particular set of test cases by using this command in the Terminal.
For one particular Tag:
robot --include=Tag_name directory_name\file_name.robot
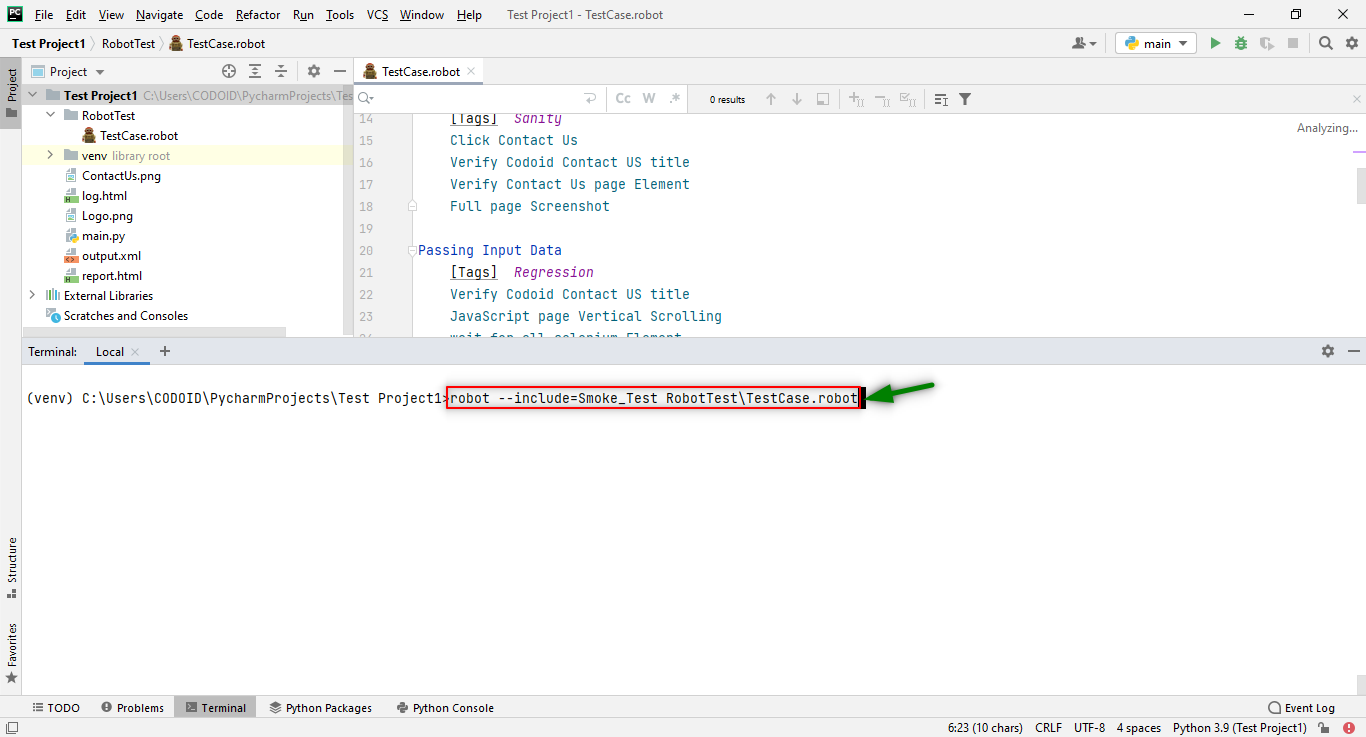
For Two Tags at a Time:
robot –i Tag_name -i Tag_name directory_name\file_name.robot
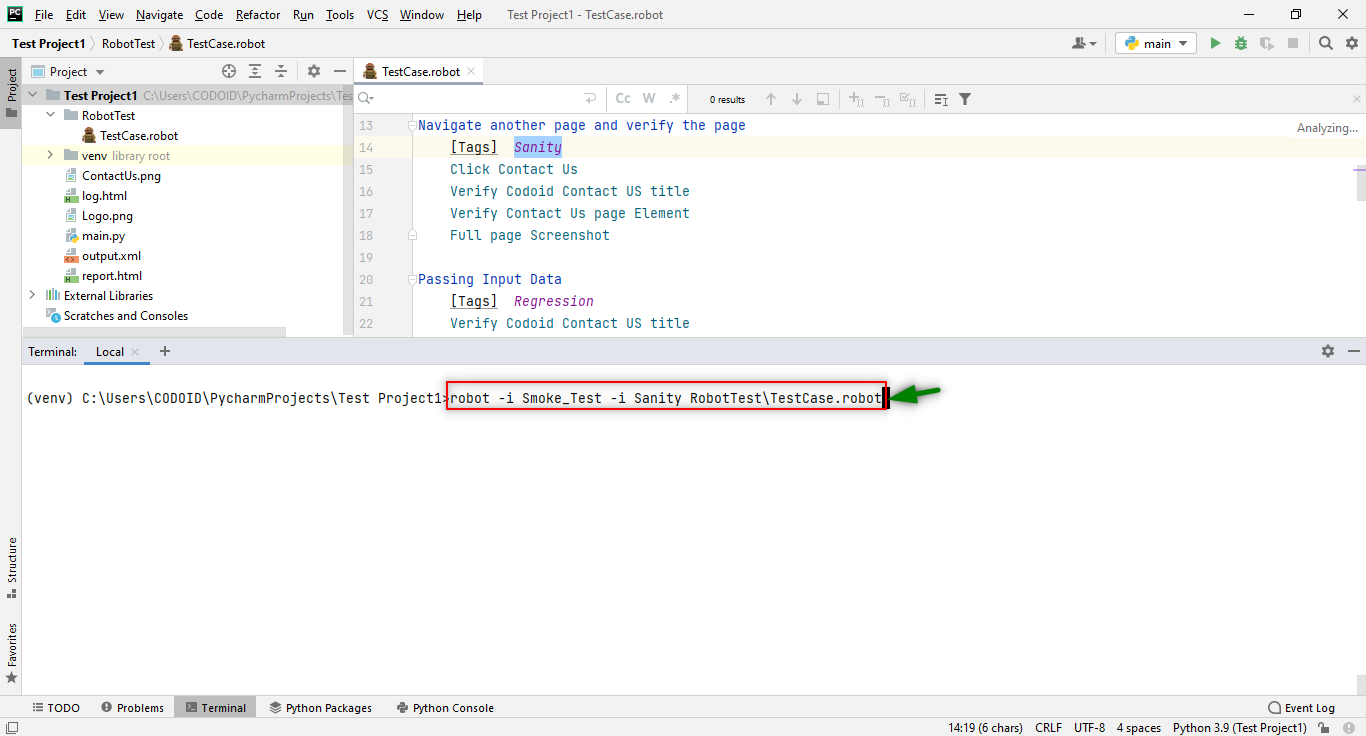
So using tags you will be able to get more concise reports as you can execute the test cases based on priorities. Refer to the following images to get a better understanding of what we mean.
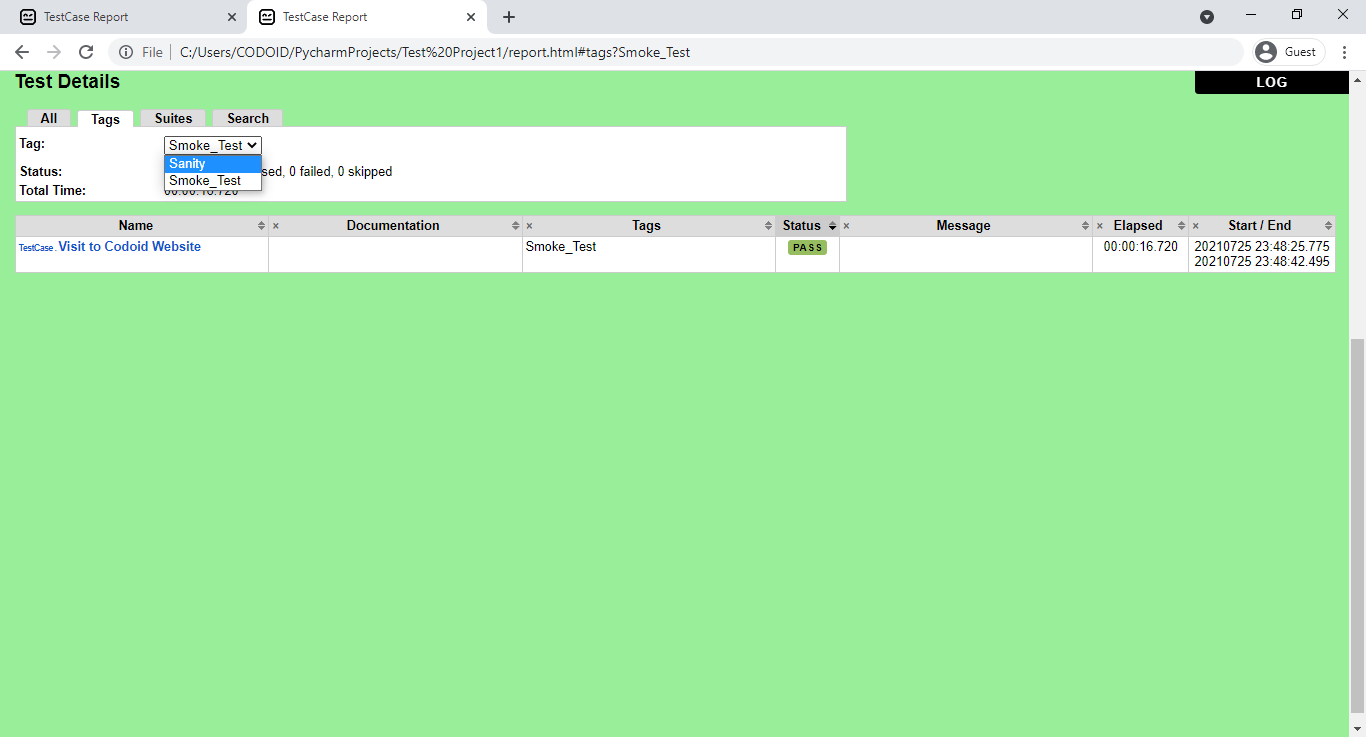
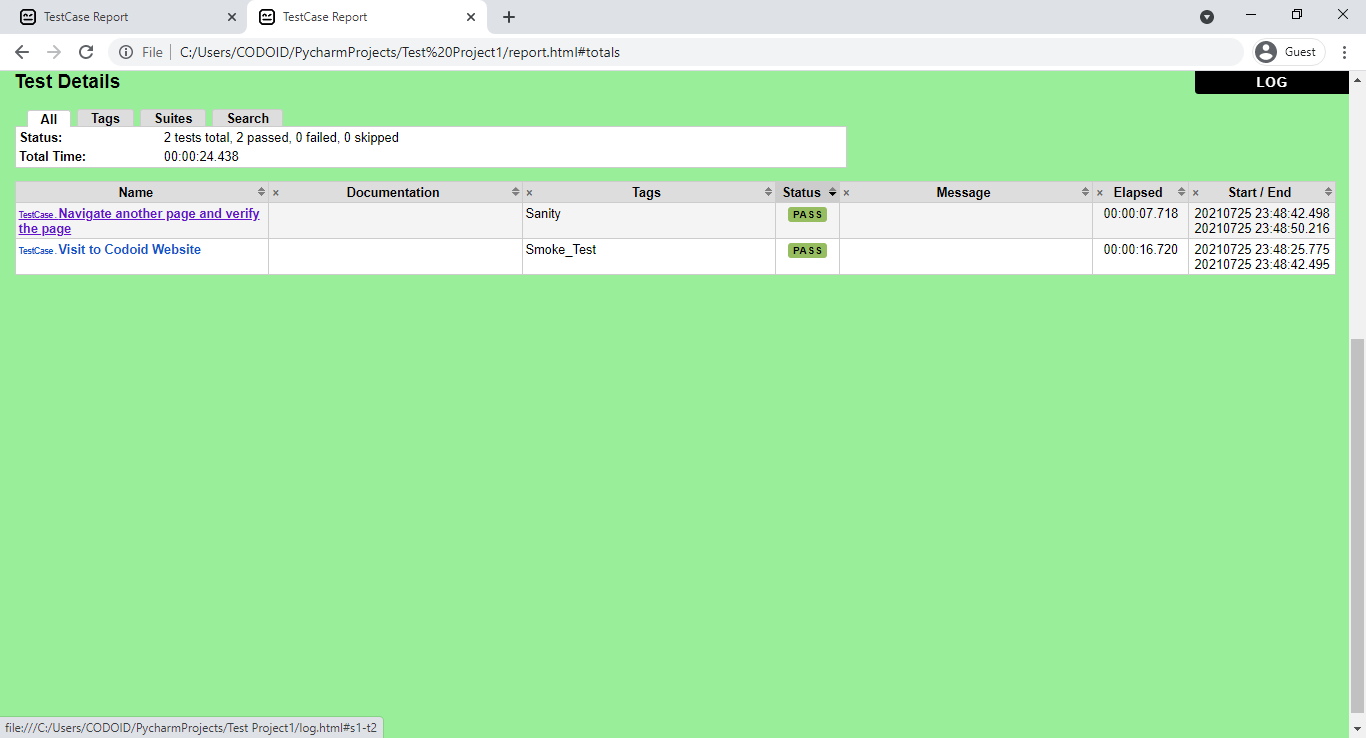
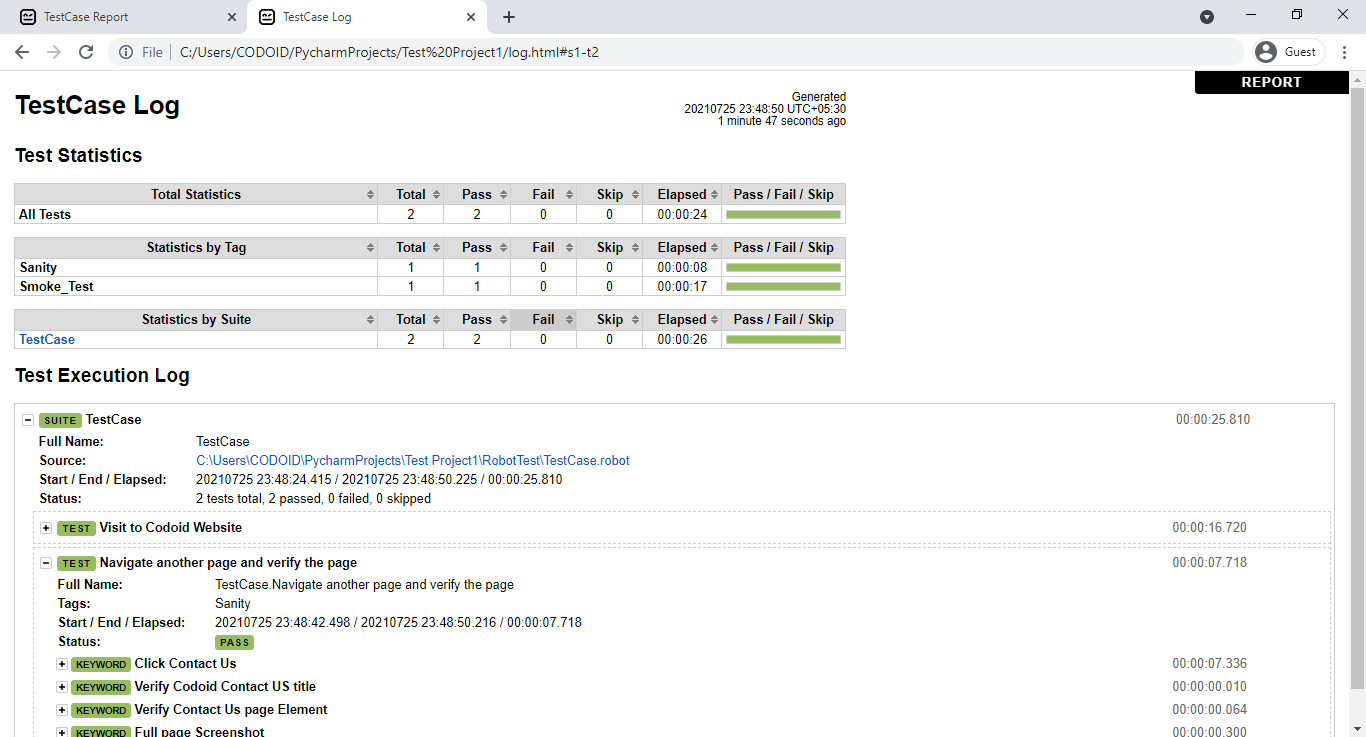
Conclusion:
We hope you have found our end-to-end Robot framework tutorial to be useful as the Robot framework is an easy-to-understand open-source tool that provides a modular interface to build custom automation test cases based on your varying requirements. So it has been widely adopted by various large organizations for this very purpose, and for good reason.

by admin | Nov 2, 2021 | Automation Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
Jenkins has risen to become an expert in Continuous Integration, Continuous Testing, & Continuous Delivery, and assumes a critical role in conveying great applications or items. It utilizes a component called the Jenkins pipeline for achieving Continuous Delivery (i.e.) the capacity to deliver applications routinely for a long stretch. This Jenkins pipeline guarantees that the product is consistently prepared for creation. As a leading QA Company, we have been using the Jenkins Pipeline and found it to be very effective. So if you are looking for a Jenkins Pipeline Tutorial that covers everything from the basics of the pipeline to learning how to perform parallel execution, you’ve found it.
What is a Jenkins Pipeline?
A pipeline in the Jenkins CI/CD can be defined as a series of events or even tasks that are interconnected to each other in a specific order. To put it in simpler terms, the Jenkins pipeline can also be characterized as a set of modules or plugins that enable the implementation & integration of the Continuous Delivery pipelines within Jenkins. It has an expandable automation system that can be used to build basic or complicated ‘template’ distribution pipelines via the Domain-specific language (DSL) used in the pipeline. Continuous Delivery in the Jenkins pipeline comprises 4 major states,
- Build
- Deploy
- Test
- Release
We will be taking a closer look at these states later on in the Jenkins Pipeline Tutorial, but first, let’s take a peek at the many advantages that the Jenkins pipeline CI/CD has to offer.
Advantages of the Pipeline:
- It can divide the jobs into parts (build /test /deploy) and each part can run in each agent.
- Parallel execution of stages is easy to configure and so it can be instrumental in saving time.
- Each stage can execute the different versions of JDK/MVN versions.
- It can be retriggered even from a failed stage.
- Visualizing the build flow becomes possible.
- The build can hold until the user gives the input.
- Version control and code reviews are made easier.
- We can pause and restart the build as and when we wish.
- It will automatically be created as sub-branches in a multi-branch pipeline script.
Pipeline’s Basic Keywords:
Knowing the basic keywords that will be used in the pipeline is the first step that we will be taking in our Jenkins Pipeline Tutorial. So let’s see what these keywords are and how you can use them in the pipeline. We’ll start with ‘Steps’.
Steps
- Steps have to be written inside the stage directive.
- Steps contains the command or scripts that we’ve used in the build.
-
- One step’s directive should be there in the stage directive.
Stage
- Stage defines a particular stage (build/test/deploy/..) of our job.
- There has to be a minimum of at least one stage.
- The name of the stage will be displayed on the Jenkins dashboard.
Stages
Stage and Stages are two different keywords that you shouldn’t confuse yourself with.
- It contains a sequence of the stages we saw earlier.
- There has to be at least one stage.
Agent
- It defines where we need to run our pipeline script. (Master/Slave/Container)
Stage color
So using color, we will be able to find out the current status of the stage.
- White – The stage hasn’t yet been executed.
- Green – The stage is a success.
- Blue Lines – The stage is being executed.
- Red Line or Red Lines – The stage has failed.
- Red (If in case few stages were a success and one failed, it will show red even if the few have been successful)
Types of Pipeline
1. Declarative pipeline
2. Scripted pipeline
So as seen above, there are two types of the pipeline, and the declarative pipeline is the recent addition that has the more simplified and opinionated syntax when compared to the scripted pipeline. Now let’s take a look at the syntax for these types.
Declarative Pipeline syntax:
Pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage(‘Build’) {
Steps {
}
}
stage(‘Test’){
steps {
}
}
stage(‘Deploy’){
steps {
}
}
}
}
Scripted Pipeline Syntax:
node {
stage(‘Build’) {
}
stage(Test’) {
}
stage(‘Deploy’) {
}
}
Variables in the pipeline:
What is a variable?
A variable is used to store values. There are two types of variables, and they are predefined and user-defined variables.
<variable name> = <variable value>
Predefined Variable:
pipeline{
agent any
stages{
stage('pre'){
steps{
echo " predefined variable $BUILD_NUMBER $WORKSPACE "
}
}
}
}
Output:
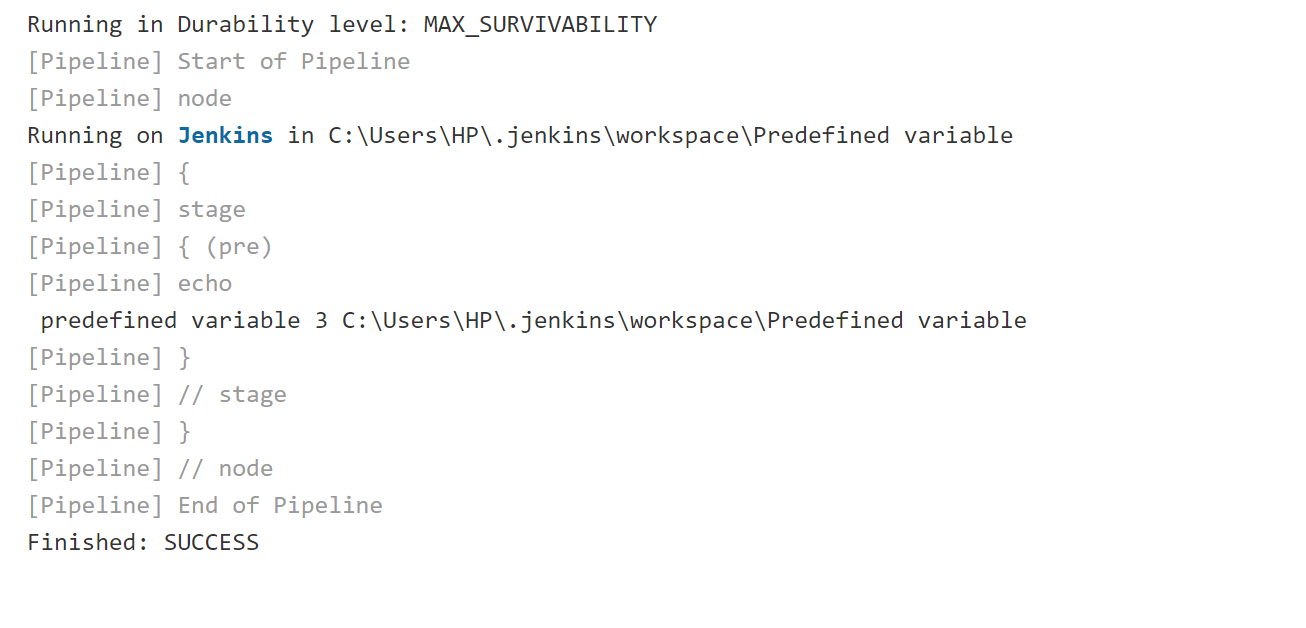
User-defined Variable:
User-defined Variable we can define in root level or stage level
pipeline {
agent any
environment{
MYHOME="Chennai"
}
stages{
stage('User'){
steps{
echo " userdefined variable $MYHOME "
}
}
}
}
Output:

Parameters in Pipeline:
Parameters are used to pass the following types of data dynamically.
- String
- Text
- Boolean
- Choice
- Password
- File
Implementation of Parameters in Pipeline:
pipeline{
agent any
parameters {
string(name: 'DEPLOY_ENV', defaultValue: 'staging', description: '')
text(name: 'DEPLOY_TEXT', defaultValue: 'RnD\nJenkins\nPipeline\n', description: '')
booleanParam(name: 'Are You Have Permission to Deploy', defaultValue: true, description: 'Toggle this value')
choice(name: 'CHOICE', choices: ['One', 'Two', 'Three'], description: 'Pick something')
file(name: 'FILE', description: 'Some file to upload')
password(name: 'PASSWORD', defaultValue: 'SECRET', description: 'A secret password')
}
stages{
stage('string'){
steps{
echo " string $DEPLOY_ENV"
}
}
stage('text'){
steps{
echo " text $DEPLOY_TEXT"
}
}
stage('booleanParam'){
steps{
script{
if(TOGGLE){
echo " now execute, booleann is true"
}else{
echo " Dont execute, boolean is true"
}
}
}
}
stage('choice'){
steps{
script{
if(DEPLOY_ENV=='staging'){
echo " choice $CHOICE"
}
}
}
}
stage('file'){
steps{
echo " file $FILE"
}
}
stage('password'){
steps{
echo " password $PASSWORD"
}
}
}
}
Output:
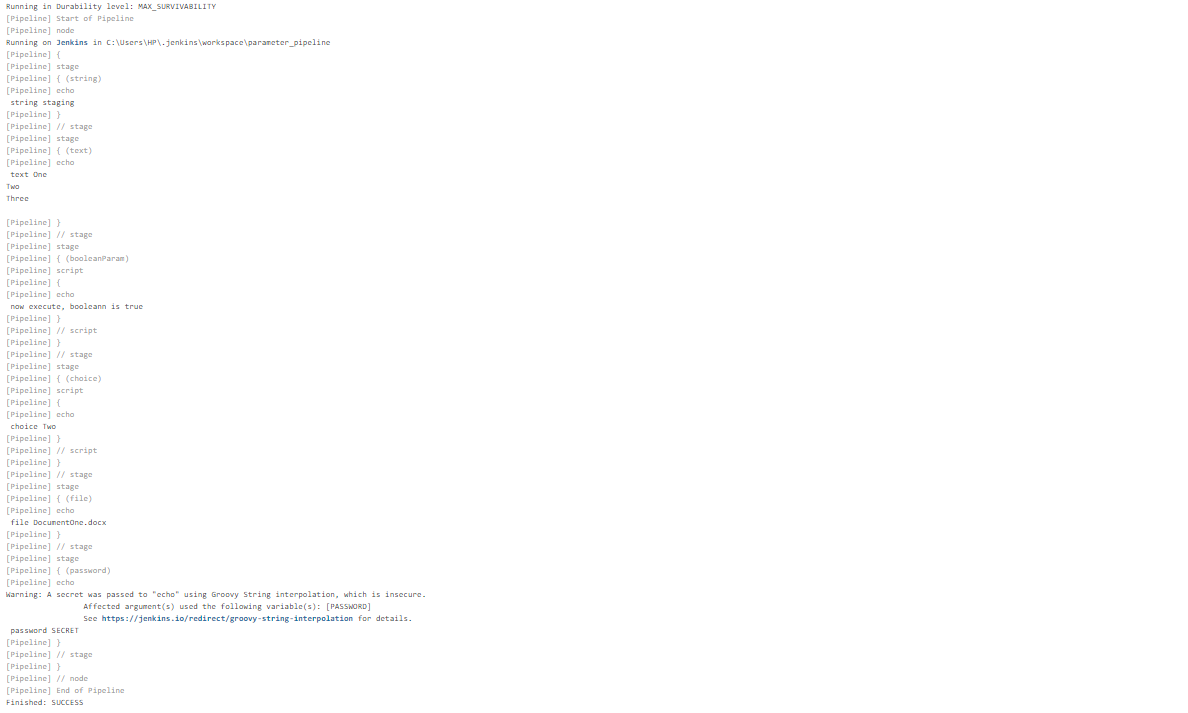
Parallel Execution in Jenkins pipeline:
We will be focusing on the parallel build using the Jenkins declarative pipeline in our Jenkins Pipeline Tutorial now. So you can trigger your build system by Jenkins if there are some steps that could possibly run at the same time since they have no dependencies. By following this method, you will speed up your build process and save time for other sequential steps. As one of the best automation testing service providers, we don’t just stop with using the best tools, we also focus on using them in the best way possible.
Parallel Execution:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage ('My Java Project Test Scenarios'){
parallel {
stage('Unite Test'){
steps {
echo 'Unit test Completed'
sleep 5
}
}
stage('Integration Test'){
steps {
echo 'Integration Completed'
sleep 5
}
}
stage('Security Test'){
steps {
echo 'Security Completed'
sleep 5
}
}
stage('Selenium UI Test'){
steps {
echo 'Selenium UI Test Completed'
sleep 5
}
}
}
}
}
}
Output:

Conclusion
We hope you enjoyed reading our Jenkins Pipeline Tutorial and found it to be informative at the same time. As promised we have covered everything including the basics of the Jenkins pipeline, seen its advantages, explored all the perquisites like variables and parameters that you will need to know to use it effectively. So make sure you don’t just try the Jenkins pipeline, make sure you use it effectively.

by admin | Oct 26, 2021 | Automation Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
Releasing software multiple times into production in a day to deploy the new features/fixes with high quality will need an automation testing setup in all the stages of your delivery pipeline. In DevOps, you have to automate as much as possible to enable continuous testing. So when a product is getting deployed into production more frequently, you have to test the product continuously. For you to proactively search for quality issues, continuous testing has to be enabled across all stages of your delivery pipeline. Since software Test Automation is the key enabler of Continuous Testing, we will be taking a look at the 6 steps that can help you achieve Continuous Testing.
Treating Test Code as Production Code
Whenever a change happens in the product, you have to update your test code to accommodate the change. Let’s say you have to make a change on a common page/screen, your test automation framework should enable you to update the change in that one place instead of updating all the scripts.
Implementing the best practices and design patterns in test automation ease script maintenance. So you have to design your framework in such a way that any script change can be added to the test suite quickly without any hassle.
Kick-off Test Execution for Every Code Commit
Every code commit to version control should kick off automated unit & acceptance tests. When you deliver fast, you will also be in need of quick feedback for the changes or fixes that you have made. Lack of code commit validations will lead to eventual quality issues and regression defects.
Test Automation Framework
You can’t just build the entire framework and immediately start the script creation for Continuous Testing. We have to use the Acceptance Test-Driven Automation (ATDA) approach to develop an automation testing framework. ATDA enables you to write automated test scripts from the very first day instead of waiting for the framework development phase to be completed.
In the past, automation testers used to spend at least two weeks, or even a month in certain cases to develop the test automation framework. The script development itself would begin only after that. So in order to achieve Continuous Testing, you have to start the script development from day one, and then go forward with the product development.
How can we develop scripts without a framework?
Let’s say your team is comfortable with Java. You can use JVM-Cucumber, Selenium, Maven, Appium, and IntelliJ Community edition to start writing automated test scripts from day one. If a script needs a new framework feature, you first have to develop the feature and complete the script. That is how you can evolve the framework and not hold up the script development during the framework development.
Avoid & remove Flaky Tests from CI
If an issue messes with the DevOps pipeline, the entire team should focus on the issue and fix it immediately. Similarly, if a script is flaky, it will make the pipeline unstable. Automation Testing Services is our core service, and we know for a fact that you’ll need a highly skilled team that follows the best practices and uses proper object locators to avoid flaky tests and achieve Continuous Testing.
So if some of your tests are flaky, you must quarantine, schedule, and run them separately, and bring them into the delivery pipeline only when it is fixed and stable.
Test Data Generation
Test data plays an important role in UI, Functional, Non-functional, and Integration Testing. So you have to park adequate test data for test execution. Make sure to avoid failures that can be caused by invalid or missing test data. You should also have an automated system that allocates the required test data and cleans up the consumed data during execution.
Setup the Tests for all the phases
Continuous Testing should be set up in all phases of your delivery pipeline starting from development to production. For example, if a feature is being actively used by the end-users on a daily basis for a particular period of time. You can write an automated test script to check the feature’s usage from the production monitoring data to proactively check for any quality issues. So make sure you don’t just focus on smoke and regression testing as you have to set up tests for different stages in the pipeline.
Conclusion
Being one of the best automation testing service providers, we, at Codoid, follow strict scripting practices and design patterns to avoid flaky tests and have helped many clients to enable Continuous Testing in their DevOps pipeline. Fast feedback is critical for DevOps. You also shouldn’t delay test code development. You have to add the test code as and when new features are deployed into the pipeline.

by admin | Oct 19, 2021 | Automation Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
Automation testing is not your departmental goal. Period. So when software testers or automation testers create automated test scripts, they should focus on how the tests will add value to the business or product instead of focusing on increasing the script count. Since analyzing the goals and objectives of automation testing before starting any project is very important, let’s learn about it in this blog.
A Confidence Booster
Automation test executions boost the confidence of your team to release a product. Testing a system manually on multiple browsers & devices is a tiring effort for a tester. Moreover, it is very much prone to errors. Whereas, if rightly done, automation scripts can execute your tests without any deviation. So this ultimately frees up the testers and lets them focus on the problem-solving activities.
In DevOps, there is always a need to automate as much as possible so that the testers can concentrate on Exploratory Testing to unearth bugs, identify new features, and capture edge cases for automation testing. So if there are no application issues, robust and reliable automated tests will run without any hassle, and the passing automated tests will boost the confidence of your team.
Avoid False Positives & Negatives
An automation test script should fail only when there is an application issue. But if your scripts are flaky, you will not be able to reap the benefits of automation testing, and your team will eventually lose confidence in the automated test scripts. That is why we have it in our top 3 objectives of the automation testing list. As a leading automated software testing company, we have seen success in our test automation by following the points.
How to avoid false positives & negatives:
- Recruit talented test automation engineers.
- Train your team to follow the best practices and coding patterns.
- Strictly avoid boilerplate codes.
- Enable the peer-review process.
- Quarantine flaky tests and bring them back to the execution pipeline only if & when they are stable & robust.
- Park the adequate test data required for automated test execution to avoid failures due to invalid data.
You need a highly skilled team to develop robust automated test scripts. We have been providing automation testing services to many of our clients over the years. During this period, we have revived many of the projects that had failed to reap the benefits of effective automation testing. We achieved it by trying to reuse the existing scripts and libraries. But at times, we have thrown away the poorly written automation test scripts into bins. So it is important to keep in mind that if the best practices and coding designs patterns are not followed when creating automation test scripts, you will have to suffer from such scripts forever.
Scripts fail due to invalid test data as well. But feeding the test data before starting the execution is a cumbersome task. In DevOps, automated test executions are kicked off as soon as product changes are pushed into master. So you cannot hold the execution for feeding the test data. Moreover, you will not be able to feed the data a day before the execution if your team is part of the continuous delivery pipeline as they will deliver changes into production multiple times a day.
So make sure to use a test data management tool to upload adequate test data for script executions. Your test automation scripts should be able to pick up the required data from the test data management tool.
Maintenance
When there is a change in the application, you have to accommodate the change in your script as well. If an automated test suite is not changed for a longer period, then it is going to perform the same testing again and again. You should have a process to obtain the below details constantly to keep your scripts up-to-date.
- You should know when a change is introduced in existing functionality.
- Note when a new feature is getting adding to the product.
- Note when an existing feature is removed from the system.
Conclusion
Adding more automated tests to improve coverage is a primary goal of an automation tester. However, if you do it without thinking about the system, goals, and objectives of automation testing, you will be missing out on the many benefits. Automation testing is not an isolated activity and it is pivotal for you to know how your scripting efforts are adding value to the system.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What are the objectives of Test Automation?
Test automation aims to optimize testing by increasing efficiency, speed, and accuracy, improving test coverage, and enhancing software quality. It achieves this by automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, reducing time and effort, and ensuring comprehensive test coverage.
-
What are the major benefits of Test Automation?
Test automation allows you to run a vast number of complex and lengthy test cases and brings in the necessary agility to testing which helps it to respond faster and more effectively to changes that would be impractical to run manually. It can enhance software quality by increasing the thoroughness of testing and reducing the likelihood of errors, without manual intervention.
-
What are the Challenges in Automation Testing?
Some of the challenges faced in automation testing are
1. Finding the right tools and frameworks that fit the project's requirements and technology stack.
2. Creating and maintaining reliable and efficient test scripts that can keep up with the constantly evolving application can also be difficult.
3. Ensuring that automated tests are accurately mimicking user behavior and covering all edge cases can be a time-consuming and complex task.
-
What is the future of Automation Testing?
Automation testing is evolving rapidly and is expected to become more sophisticated and intelligent with the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning. This can help create self-healing test scripts, improve test coverage, and increase the accuracy and reliability of test results. As companies increasingly adopt agile methodologies, cloud-based testing solutions, and continuous delivery, automation testing will remain a critical component of software development processes, ensuring high-quality releases and faster time-to-market.

by admin | Oct 15, 2021 | Automation Testing, Blog |
Developing software products for tech-driven businesses is dominating the landscape. As the digital transformation continues to reform several industries, setting a fool-proof test automation strategy becomes more important than ever.
Satisfying customers and offering products that can guarantee better functionality for different work settings are goals that every software company should reach; that’s why it’s worth putting the spotlight on one of the most critical stages in the process: automation testing.
This phase reveals your performance, effectiveness, and inefficiencies that need improvement, so it begs the question: what are the key elements that ensure your mobile app test automation strategy is results-driven and successful?
Powerful Pillars that Build a Stronger Testing Automation Strategy
Factor #1: The Right Automation Testing Tools
The automation tools you use for your project will set the tone for your testing efforts. With that in mind, the first step to enhance your test automation strategy is to implement the best tools that meet your unique needs—be it mobile app testing tools, web application automation testing, and more.
There are no hard rules when it comes to selecting the best tools; you only need to choose the ones that deliver the required features and functionality that matches your testing requirements. Some of the best performing and cost-effective tools for testing automation include Test Complete, WAPT, Ranorex, and Microsoft Test Manager.
Factor #2: Type of Tests Included in an Automated Test Suite
Not all scripts and sequences in a new automation test suite are applicable for all products; that’s why your team needs to assess your current operations and deploy the right elements that will yield better results for your project without disrupting the functionality of your software.
Creating a testing pyramid can reveal stages in the process that are relevant to your new test case—from testing levels, role distribution, task ownership, and the appropriate frequency for your tests.
Factor #3: Standardized Automation Scripts
Starting from scratch when automation testing different software can eat up plenty of time, money, and development efforts, so supplementing your testing with reusable automation scripts can maximize your process. If you’re working on projects that follow the same outline, then reusing a standardized framework can do wonders for easing your team’s workload.
The Bottom Line: Breaking Down the Building Blocks of an Effective Test Automation Strategy
Testing your mobile application’s performance, functionality, usability, and user engagement can be tricky, especially since the process can be time-consuming and complex in more ways than one.
Improving your test automation strategy is an essential step in ensuring your software products exceed the market’s expectations, so collaborating with testing companies like Codoid can supercharge your strategy by ensuring your end-to-end testing goes as smoothly as possible.
How Can Codoid Help You?
If you’re looking for performance testing companies, Codoid is here to help you.
We are an industry leader in QA, leading and guiding communities and clients with our passion for development and innovation. Our team of highly skilled engineers can help your team through software testing meetup groups, software quality assurance events, automation testing, and more.
Learn more about our services and how we can help you today!
























































