
by admin | Nov 26, 2021 | Software Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
Prevention is better than cure is a great saying that even applies to the software development lifecycle. But it is almost impossible to develop software without any bugs on the very first try. So in order to keep up with the ever-growing need for rapid software development, it is vital for us to minimize the time taken to fix a bug. So it is very important to know the different types of software bugs detected during software testing as the complete knowledge of the type of bug you are dealing with will be instrumental in helping you understand the severity and in turn sort your priorities accordingly.
But before we explore the various types of software bugs, let’s first look into what classifies as a software bug. A software bug can be defined as an error or a fault that can render a computer program or even an entire system to crash or malfunction. So you will not get the desired or expected output despite providing a valid input. Though a glitch is different from a software bug, few might assume both to be the same. Due to the random nature of software glitches, it can be very difficult to find the cause and solve it like a software bug. But you might get lucky as glitches are known to correct themselves.

Origin of the Term ‘Bug’
Before dive in to explore the different types of software bugs, let’s take a look at some interesting trivia related to the term ‘bug’. The first-ever bug in a computer was reported by Grace Hopper back in 1946 and there is an interesting story behind how the term ‘bug’ came into use.

But some records suggest that the term ‘bug’ was used years back to denote an issue in a system.

What are the Different Types of Software Bugs?
Let’s take a list of the various types of software bugs and then explore them one by one.
- Functionality Bugs
- Performance-based Bugs
- Usability Issues
- Safety Issues
- Compatibility Issues
- System-Level Integration Bugs
- Unit Level Bugs
Functionality Bugs
Every element in an application or a website will have a purpose for its existence. At times, it is possible for a few of these elements to not function as per the need or expectations. So such errors can be termed as functional bugs. The severity of these types of bugs could also be in different ranges. To bring that into perspective, a random non-functioning button that isn’t responding to clicks is also a functionality issue, and a malfunctioning login functionality that isn’t letting the users use the software is also a functionality issue. Owing to the broad nature of this type of bug, it is one of the most common bugs you will encounter. You have to be careful and not list every single bug you find under this category. Instead, you should take a closer look and classify it accordingly.
Performance-based Bugs
But just because a function works, doesn’t mean that everything is fine. According to a report, a delay of just one second decreases the customer’s satisfaction by 16%. Now, let’s say you are at the payment gateway and have entered your password or the OTP. The payment has to be verified and a success message has to be displayed in a very short span of time. If it takes 5 minutes for the success message to be displayed, then the user would be livid with your software. Similarly, if it works smoothly only once every 5 times, you would have to be counting on your luck to get that successful message. So speed, stability, resource consumption, etc. are a few performance issues that one might face.
Usability Issues
Over the years the number of fields in the sign-up form has been on the decline and usability is one of the major reasons. If it seems like too much work, users might shy away from creating an account or using the product altogether. You might have developed a great feature that can make a task easier for the user. But if the feature is hidden away in some menu making it hard for the user to find, it most probably will remain unused. There can also be workflow bugs that can make navigation through the software very difficult.
Accessibility issues are some of the most overlooked types of usability issues that make your product inaccessible to people with disabilities. As one of the leading QA companies, we provide the best web accessibility testing services and believe that everyone should have equal access to the various applications and websites in the market. Now let’s take a look at the few common accessibility issues that are usually found.
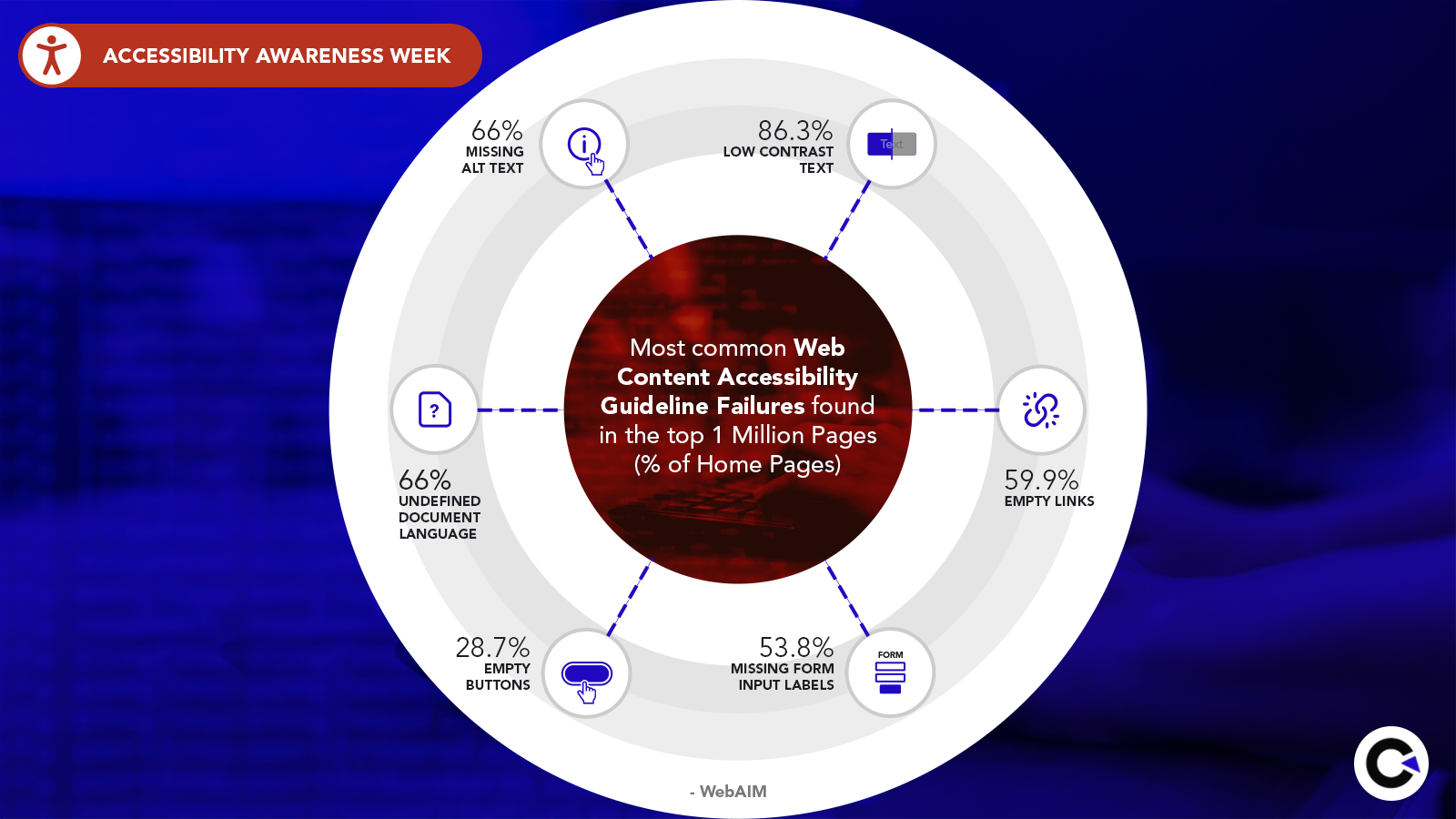
Safety Issues
With so much of our personal information at stake, safety and privacy have become major concerns for many users. The Covid-19 pandemic also resulted in a surge of security breaches as many products were left vulnerable due to their lack of focus on security. So make sure to look out for the following security issues.
- Encryption errors
- Buffer overflows
- Vulnerabilities in XSS
- Susceptibility to SQL injections
- Weak authentication
- Loopholes in role-based access
- Insecure deserialization
- Using components with known weaknesses
- Security misconfiguration
Compatibility Issues
If we take a mobile application as an example, compatibility is one mammoth challenge that the software development team has to overcome as there are so many mobile devices that are available in the market today. Each of these devices has its own display size & resolution, operating system, processors, and so on. So if you face any issues with a certain specification, then you would have to note it down. If you are developing a website, then you have to make sure it works fine across mobile devices, tabs, and computers. So just because everything works well in the defined circumstances, you can’t expect it to work the same way in real-world scenarios that have a lot of diversity.
System-Level Integration Bugs
Though the code for the different units of the software will be written by different software developers, it must all work together seamlessly. But it is not something that happens every time and you might encounter such issues when you are testing. You might something weird happening in the UI, or you might even witness memory overflow issues because of such bugs. So you can’t directly assume it is a UI issue as it might be caused due to the inconsistencies or incompatibilities across components. This makes it very hard to locate and resolve the issue as one would have to examine a larger chunk of code to identify the problem. So make sure to be extra careful when handling such complex issues.
Unit Level Bugs
Agile teams make use of unit tests to detect issues at the early stages of the software development so that they can be spotted and fixed easily. As a prominent agile testing services provider, we always focus on unit testing in all our projects. So it is highly important for you to know about unit-level bugs. If you are unaware of what unit tests are, they are nothing but the tests that are executed once a few models of the software have been developed. For example, if the sign-up page has been successfully developed, then the testers can verify that functionality alone with maximum coverage. Beyond the functionality, one could check if the data fields are accepting inputs as per the expectations. If the password must include both upper case and lower case letters, then it should not accept a password if this condition isn’t fulfilled.
The Other Different Types of Software Bugs
We have seen the major types of software bugs that you might come across while testing. Now we will be just skimming through the few other bugs that you should know about. The code might have syntax errors that prevent the code from compiling properly. Aspects like a missing character or bracket could cause such issues. Likewise, there might be unnecessary code duplication that is just making the software more bulky and slow. Apart from that, there could be logical errors in the code that can cause loss of functionality or even crash the application. Remember the example under the unit level bugs? You might face such out-of-bound bugs outside of unit testing too.
The Severity of the Different Software Bugs
By now you would have a pretty good idea of what types of software bugs will be severe and which ones have to be prioritized. Even if there is any confusion, the following example of a few bugs in an e-commerce website will help you get a crystal clear idea.
- Critical – If there is an issue that is preventing the users from even accessing the site due to a server issue or not allowing you to place an order, then that should be termed critical as all major functionalities have been blocked.
- High-level – This might also seem like a critical bug, but it is something that reduces functionality and not something that totally destroys it. For example, if you are able to access the site and place an order but not able to track the delivery. Here the main functionality is working, but still, there is a lot of inconveniences caused to the user while performing the main functionality (Shopping).
- Medium level – Minor or less important functionalities that impact a user’s experience with the product can be categorized here. A broken link or navigation issues are perfect examples.
- Low level – Bugs in this level will most probably be UI issues like alignment, typos, color issues, and so on.
Prioritization
Conventionally, many would assume that only the critical bugs should be resolved at the earliest. Though severity plays a major role in triaging which bugs to resolve first, complexity should also be considered. Critical bugs should get the main focus irrespective of how complex it is. But along with it, even small typos or issues that can be resolved much effort should also be fixed without any delay. It doesn’t matter if the bug is severe or not, a bug is still a bug and our plan should always be to fix it at the earliest. Highly severe bugs can be prioritized based on complexity. Whereas moderately severe bugs should be fixed by the next update.
Conclusion
We hope you had a good time reading our blog and now have a pretty good idea of the different types of software bugs you might have to deal with when testing. This is a list of the most common bugs you might face, there might be scenarios where you face bugs that are more complex or different in nature. But this list is a good place for you to start and then slowly up your skills as you move forward in your testing career.

by admin | Nov 19, 2021 | Software Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
Software testing is done to find anomalies in code that prohibit the product from performing as it should. These abnormalities are divided into specific groups to make debugging tasks more manageable for your team.
This article will explain the differences between bugs, errors, and issues so that QAs may be confident in cataloging, analyzing, and resolving these anomalies. Unfortunately, these flaws are guaranteed to appear while getting manual testing services for your website or app.
What is a Bug?
Any flaw in a software system that makes it act in unexpected and undesired ways is referred to as a bug. These might include unreasonable or inaccurate reactions, failed systems, and system crashes, among other things. It’s a programming fault that leads to software failure that can be discovered before the website or app is put into production.
Here are a few examples of bugs:
- Algorithm-related bugs
- Bugs that impair logic, such as infinite loops
- Uninitialized variables that cause bugs to appear
What is an Error?
Errors refer to coding or programming faults that are often caused by wrong syntax or erroneous loops. Inconsistencies or blatant fallacies in the underlying code structure cause errors to appear in the source code. Misconceptions, oversights, or misunderstandings on the developer’s part (engineers, testers, analysts, etc.) cause anomalies.
Errors come in a variety of forms:
- Calculation errors caused by incorrect formulas
- Errors in data handling due to the overwriting of required files
- Errors in configuration owing to a lack of storage capacity
What is an Issue?
The issue is a bit of a catch-all word. It signifies the presence of some abnormality in a software system that has to be resolved in software testing circles. As a result, an issue might be anything from a bug to missing or erroneous documentation, a feature request, or any other process that needs to be completed.
Issues are often assigned severity levels to be prioritized in the development and quality assurance hierarchy: high, medium, low, and cosmetic.
Clients and managers use the word “issue” to signify that something is wrong with the program at hand. It is often employed when the source of the problem is unknown. And once a problem has been identified, it must be investigated to determine its nature before being allocated to the appropriate team for remediation.
The Importance of Real Devices in Debugging and Problem-Solving
Identifying and removing any anomaly requires rigorous software testing on actual browsers and devices. Given the present state of browser-device fragmentation, every website or app must be accessible across various device-browser-OS combinations.
More than 4 billion people use various devices to access the internet, including:
- More than 9,000 different gadgets
- 21 distinct operating systems (vendor + version)
- Hundreds of browsers powered by eight primary browser engines
To ensure a favorable user experience across the board, there are 63,000 browser-platform-device combinations to test, and the number is continually growing. Due to the unique specifications of one particular browser, device, or OS, faults may appear on one combination but not on others. The program must be tested on various devices and browsers to guarantee that flaws and issues may be spotted across them.
Conclusion
Quality control operations include identifying defects, categorizing, reporting, and finally removing them. However, prevention is better than cure. The core of software quality assurance is to set up monitoring and inspection mechanisms at every level of the software development life cycle. Make sure to get optimal QA services to avoid any bug, error, or issue in your software.
Codoid is an industry leader in QA services. Our brilliant team of engineers is dedicated to helping clients overcome the challenges of complex manual testing services to grow a product. Contact us today!

by admin | Nov 8, 2021 | Software Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
Knowing each entity in depth is very important when it comes to testing banking applications that deal with corporate customers. Corporate Customers are the ones who are neither individuals nor micro-enterprises. With years of experience in providing the best software testing services to our clients, we are well-worse with everything a team will need to know about entities. So in this blog, we will be seeing an overview of entities on the whole as we will be learning what is an entity, exploring the Different Business Entities, and will also be covering how to test its intricacies.
What is an Entity?
An entity is a registered organization that processes and provides certain services to end consumers. It has its own goals & missions and a separate existence like humans. There are key representatives called the key principles of the organization who govern the entity. Now let’s take a look at the list of the different types of entities and explore them one by one.
The Different Business Entities:
- Public Limited Company
- Private Limited Company
- Partnership
- Sole proprietorship
- HUF
- Religious Establishment
- LLC
- Statutory Corporation
- Holding Company
- Trust
- Funds
- Non Profit Organizations
- Investment Vehicles
- State-Owned Entity
- Charitable Organizations
- Central Bank
- Sovereign Wealth Funds
- Clubs and Societies
Public Limited Company:
A public limited company offers shares of their stock to the general public by listing it on the stock exchange. The stakeholders are the owners of a PLC. It is referred to as PLC in the United Kingdom, as Inc in the United States, and as Ltd. In India. PLC requires a minimum number of 7 members, and there is no upper limit. It should also have at least 3 directors.
Private Limited Company:
A Private Limited Company can be listed in the stock exchange or need not be. Even if they hold shares, they cannot be sold to the general public. It requires a minimum of 2 members to start the company and it should have 2 or more directors. It is called LLC in the United States, PVT in the United Kingdom, and Pvt. Ltd in India.
Partnership:
A Partnership is a formal agreement between 2 or more parties to manage the business and share its profit or loss. Unlike Private Limited companies, partnership firms are not separate entities. A change in the partners leads to the formation of a new partnership firm while the old partnership firm would get dissolved. There should be a minimum of 2 partners, but the number should also not exceed 50.
Sole proprietorship:
When a company is owned and managed by a single owner, it is called a sole proprietorship. It is unincorporated by nature, meaning this company has no separate existence by itself. It is easy and inexpensive to establish when compared to the other entities as it has fewer regulations. The biggest challenge would be raising the required capital for the business from external sources. Small business owners mostly prefer sole proprietorships.
HUF
HUF is a family business that lends a way of saving taxes by clubbing the assets owned by the members of a family. Though it is an option available only in India, we wanted to be thorough in our proceedings. The senior-most member in the family will most probably be the head of their HUF. It is governed by Hindu Law. So the death of the senior member does not affect the existence of the business, the next senior-most male member becomes head.
Religious Establishment:
Temples, Churches, and Mosques are places of worship that can be termed as religious establishments. There are a lot of regulatory laws that help prevent the misuse of religious institutions as an unauthorized way of gaining money.
LLC (Limited Liability Company:
An LLC is a Legal Entity that helps its owners avoid personal responsibility for its debt and liabilities. LLCs do not pay tax as the profit or loss is passed to the owners who show it as their personal gain or loss. It is mostly incorporated, meaning the entity has a separate existence, unlike Sole Proprietary.
Statutory Corporation:
Statutory Corporations are companies owned by a government with the presence of other stakeholders. It is a cumbersome task to start such an entity as a lot of approvals are required. Once the policies governing this entity have been created, it is nearly impossible to change. So they are prone to wastage of capital & assets and inefficiency in operations compared to private establishments. It also suffers from political interference.
Holding Companies:
When multiple businesses are owned by a single person or by a group of people, they create a holding company which is called the ‘Parent Company’ to keep track of its subsidiaries. This holding company doesn’t usually perform any business activities, its primary purpose is to monitor the subsidiary businesses. So when the subsidiaries grow, their parent companies also grow in tandem. It receives dividends from its subsidiaries. The holding company either owns 100% of its subsidiary or at least 51% of its subsidiary to maintain control over it. This helps them to protect the interest of its subsidiary and helps to protect it from the creditors of the subsidiary to control the assets by investing less money.
Trust:
Trusts are owned by Banks or Financial Institutions and act as custodian for asset management, beneficial ownership registration, and so on. It acts on behalf of its client or beneficiary to make investment-related decisions.
Funds:
Funds are investment companies that focus on investing in securities. They employ portfolio managers to help manage the investment options offered by the firm.
Non Profit Organizations:
A non-profit organization can be a trust, a corporation, an association, a Limited Liability Company, or unincorporated. Since they are mainly created to serve a social cause, they will have tax exemption benefits.
To create a Non-Profit Organization, first, we have to decide if creating it as a non-profit is the right choice, create a mission statement, develop a business plan, build a board, and then file for the tax-exempt status.
Investment Vehicle:
An investment vehicle is a type of company that helps the investor grow their money by issuing bonds or investing in stocks or investing in real estate. Any mutual fund company that helps its investors diversify their portfolios is an example of an Investment Vehicle.
There is a special type of Investment Vehicle called the Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV). It is created by the parent company for the main purpose of undertaking some risky projects.
State-Owned Entity:
It is a company owned by the Government with the sole purpose of generating profits or helping the Government with certain activities that are vital to them.
Charitable Organizations:
It is a type of organization created with the sole purpose of aiding a social cause. It can be set up with the objective of safeguarding animals, protecting the environment, aiding in disaster recovery, and so on. The major difference between a charitable organization and an NGO is that it can run for profit. They accept funds from the general public for their survival.
Central Bank:
Central Bank is an entity that can be seen in every country and is called the Bank of Banks. They are responsible for the formulation of monetary policies and supervising or governing the other banks. It holds the privilege to issue currency notes for the nation. It eases or tightens the supply of money based on the demand to keep a nation’s economy on the positive side. It can be a lender when any financial institutions are in trouble.
Sovereign Wealth Funds:
It is an enterprise created by the Government to invest its surplus funds from any trade or budgeting. The sovereign wealth funds then invest that money in local industries to generate the return.
Clubs and Societies:
Based on the nature of Clubs and societies, it could be a non-profit or a profit-based entity whose profits go to the owner or can be saved by the club for a rainy day. Clubs can be established for fun & recreational activities, for people with similar interests, or even for social causes. They can grow to the extent of sponsoring an event or conducting a competition.
Testing Intricacies for the Different Business Entities:
Each entity type has its own intricacies based on its purpose and objective. We have mentioned the various testing considerations below.
Setting up an entity or type of Business
- Business rules pertaining to each of the entity types
- Nature of the business
- The process to add or modify the key owners or stakeholders of the entity.
- The type of registration that is required.
- Documentation requirements for setting up the entity.
- The workflow process for the approval or verification of an entity.
- Consider the variations in the country in which the setup is made based on and the country’s risk exposure as well.
- The economic condition of the country and its impact on the setup of the entity.
- Risk definition and approval mechanisms.
- The political influence and exposure of the business. (Could be added as a part of the Business Rules)
Below are the scenarios in which Testing should be mandated:
- When we need to create or set up an entity in a system, we are required to be aware of all the above areas and it has got its own influence on the setup. The primary focus area is on the Business Rules for each type of Entity.
- When we modify an entity type, we should again be careful to test all the above areas as business rules, country exposure, etc. might have different levels of impact.
- When there is new criteria or business rule imposed by a country, we need to do a round of post regression testing as the entity level rules change.
- When Risk exposure on a firm / Country / Region changes, we have to do another round of testing.
Since these entity setups mostly require multiple levels of approval and review, most of the applications will be standard workflow products like PEGA, IBM-BPM, TIBCO Business Studio, Appian, etc.
Conclusion
We hope you have found this blog to be informative and now have a clear picture of what an entity is, what the different types of entities are, and the intricacies you’ll have to know. As a leading QA company, we will be exploring such niche topics. So make sure to follow us on our social media handles to be updated with our blogs.

by admin | Oct 28, 2021 | Software Testing, Blog |
There has been an apparent shift in Software Engineering and software testing, remarkably how practices have changed from manual to automated. Due to the advancements in artificial technology, machine learning, and automation tools, many manual testers fear that automated testing will soon replace manual testing completely. However, that could not be further from the truth.
Why Manual Testing Is Still Necessary
Many technicians believe that the shift from manual to automated testing is practiced globally. However, automation can only really substitute manual testing to an extent, meaning the latter still has a relevant role that automated testing cannot do.
With that said, there remain critical areas that need manual supervision. Below are some instances of when manual testing is necessary and other situations when it can be replaced by automated testing.
Areas That Require Manual Testing
Manual testing must not be replaced when it is the requirement to create an ideal testing, such as the following:
User Experience
User experience (UX) is anchored on human interaction, so expert manual testing is crucial for imitating user behavior and analyzing software based on user needs and demands.
Using manual testing leads to a better UX, which is almost unattainable by automated testing unless with the help of a highly trained artificial intelligence (AI).
Small Projects
The cost of implementing automated testing is higher than traditional methods of manual testing. So, having high installation costs of automated testing for a small project means you’re wasting money and sacrificing efficiency.
Minute Details
Automation works best on predetermined testing procedures. Most of the time, it is not customizable. While the results can be faster, it can neglect tiny details that may negatively impact the software.
So, manual testing is used to remove any bugs that may have been ignored during automated testing. It’s important to catch these errors before the software goes live, which manual testing can do.
Maintenance Costs
Automated testing requires high maintenance costs, so automation might not fit the budget of a small organization. If that’s the case, manual testing is preferred over automated methods to escape high expenses.
Areas That Automated Testing Can Substitute For
Manual testing should be replaced with automation when it does not fit the requirements of ideal testing in quality assurance (QA), such as the following:
Repetitive Steps
Automated testing is ideal for repetitive steps that do not require manual expertise and supervision. Automating these steps within the testing process saves many QA companies time, workforce, and energy.
Elimination of Human Errors
A highly trained artificial intelligence can be superior to human intelligence, preventing any errors in the software testing process. This aspect makes automated testing more beneficial than manual testing, with the latter more prone to human mistakes.
Complicated Coding
Automated testing is designed to work on all kinds of programs and coding, especially complicated ones. That is another example of when manual testing is less effective and valuable, especially when coding is also new to the testers.
Conclusion
Manual and automated testing have their own advantages and disadvantages, but neither can replace the other to the full extent. While many QA companies favor automated over manual testing, the latter is still crucial in many areas and can never be totally replaced.
Codoid is an industry-leading QA company with A-grade software testing solutions. Our brilliant team of engineers loves to attend and speak at software testing meetup groups, forums, automation testing conferences, and software quality assurance events. We are your go-to software testing company, whether performance testing, analytics testing, agile testing, mobile app testing, or others. If you want QA testing done right, we’re the company to call. Get in touch with us today!

by admin | Oct 28, 2021 | Software Testing, Blog |
A few decades ago, the prominent testing practice revolved solely around websites to ensure they performed well on desktops and laptops. Today, thanks to the meteoric rise in the mobile ecosystem, mobile app testing has begun to dominate the market, requiring companies to focus most of their efforts on polishing their mobile apps. Although they have some similarities with web app testing, they are still different and use various metrics to ensure top performance.
Understanding the two processes will help you know what you need to ensure proper, thorough testing and help you develop well-working apps that offer substantial value to your target audience. Here is what you need to know about the differences between mobile app testing and web app testing:
The Different Applications
There are various applications you must familiarize yourself with to understand how they are different. Web applications are computer programs that deploy in a web browser, usually built through HTML5, CSS, and JavaScript. Web apps provide more interactivity than websites and are accessible via desktop or laptop. A few examples of web applications include online stores, online banking, and email.
Mobile applications are programs designed to be used on mobile devices like smartphones, tablets, and wearable technology. They are classified into mobile web, native, and hybrid apps. Mobile web apps are programs that you can access through a mobile browser, which means you don’t have to download them onto your device to use them. Like web apps, they’re built using CSS, JavaScript, and HTML5, although there isn’t any standard software kit. Web apps for mobile use are simpler to develop and test, although they’re often more primitive in their functions.
On the other hand, native applications are engineered to run on the device itself, requiring users to download them to use them. They’re specific to platforms, built using certain languages and integrated development environments or IDEs. Developers build native Android applications through Kotlin, Android Studio, Eclipse IDE, and Java. To develop an app for Apple devices, developers must use Objective-C, Swift, and the XCode IDE. Native apps are much more secure and seamlessly integrate with the hardware.
Lastly, hybrid applications feature a mix of characteristics of native and mobile web apps. They’re built using the standard web stack then wrapped in a native environment, allowing developers to use the same code for various platforms. They’re simpler to develop and maintain but are slower and have less advanced functionality.
The Different Types of Mobile App and Web App Testing
Whether you’re testing web or mobile applications, you’ll need to ensure that the app is user-friendly and works as intended under various situations, even when it’s in production. Both testing varieties include the following:
- Recovery testing
- Localization testing
- Functional testing
- Usability testing
- Compatibility testing
- Certification testing
- Performance testing
- Change-related testing
What Sets Mobile App Testing Apart From Web App Testing
A few factors separate mobile app testing from web app testing: user interaction, compatibility, and Internet connection.
User Interaction
Desktop browser-based applications are restricted to a mouse and keyboard, with all operations doable by clicking or pressing a specific key. On the other hand, mobile apps feature a more comprehensive range of options, with tapping, pulling, pinching, and swiping resulting in different actions. It is also not difficult to test, and you’ll have voice assistants and move commanders to add to your testing checklist.
Compatibility
Testing web apps against various browsers is crucial to ensure that all users benefit from the app. This quality must also apply to mobile web and hybrid counterparts. Web-based applications are easier to test due to a desktop’s functionality, but the testing procedure for mobile apps is more complicated due to the wide variety of mobile devices. For this reason, it is essential to check the technical specifications of each mobile device and how they impact your app’s behavior.
Internet Connection
Most web applications need an Internet connection to function, which also applies to mobile web apps. That is why it is vital to test your mobile app and check its performance under various Internet speeds. You’ll also have to verify if your native or hybrid mobile app works correctly in offline mode, how it responds to interrupted connection, and how it works with various Internet connectivity like 3G, 4G, 5G, and Wi-Fi.
Conclusion
Mobile app testing is a crucial part of refining your app and ensuring it functions properly. By understanding its differences with web app testing, you can determine your testing strategy and ensure the quality of your app.
Codoid is one of the top software testing companies. As an industry leader in quality assurance, we take pride in offering the best app testing services to ensure your product’s quality. Contact us today to learn more about what we can do for your app.
by admin | Oct 21, 2021 | Software Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
User Acceptance Testing is one of the last phases of testing in the software development lifecycle that involves the product being used by the end-user to see if it meets the business requirements and if it can handle real-world scenarios. So it goes without saying that intricate planning and disciplined execution are required as it assures the stakeholders that the software is ready for rollout. As one of the best software testing companies in India, we have vast experience when it comes to performing user acceptance testing. So in this User Acceptance Testing Tutorial, we will be explaining the important factors to consider when performing User Acceptance Tests.
Prerequisites
There are various reasons why user acceptance testing happens at the very end. For starters, we can start only when the application code has been fully developed without any major errors. To ensure that there are no major errors, we should have completed unit testing, system testing, integrated testing, and regression testing as well. The only acceptable errors are cosmetic errors as they don’t affect further processing of the application. The business requirements should also be available to design the test cases accurately. Apart from that, the environment for performing UAT should also be ready. Now that we have covered all the prerequisites, let’s explore how to get the job done.
The Stages of User Acceptance Testing
For an easier understanding of how to efficiently execute UAT, we have split the main process into different stages to indicate the purpose.
Strategic Planning
As in every process, we should start by coming up with a plan to perform UAT. To develop the most effective plan for your project, you should analyze the business requirements and define the main objectives of UAT. This is when you will also be defining the exit criteria for UAT. An exit criterion is nothing but the minimum goals that should be achieved when performing the planned User Acceptance Tests. Exit criteria can be defined by combining the system requirements along with user stories.
Designing effective Test Cases
Once the plan is ready, you will have a clear vision as to what has to be achieved for the business. So we will be using that to design test cases that cover all the functions that needed to be tested in real-world scenarios. You also have to be crystal clear about the expected result of each test and define the steps that have to be followed to get that result. This step doesn’t end here as you will also be needed to prepare the required test data required to perform such tests.
Choosing the right team
There are primarily two ways to go about UAT. Either you can have end-users sign up to beta test your application by making it available to them or you can create your own team. You can either execute it using an in-house team or you can also employ outsourcing software testing options. Irrespective of which way you choose, you have to make sure the right people are on the task. If you are choosing people for your beta program, then make sure they are people from the same demographic as the targeted users of the application. Make sure to check their knowledge of the business and ability to detect bugs as well.
User Acceptance Testing
All the groundwork has been laid for you to start with the tests. So in this part of the User Acceptance Testing Tutorial, we will be focusing on how to perform UAT. Make sure to follow all the steps from your test cases without any deviation. If you wish to test something else in a random manner, do it separately and not while performing a particular test case. Once you start, you will also have to create meticulous records of the results, remarks, and so on from each test. Then only it will be possible for the development team to fix all the bugs and issues that were discovered during the process. Once the bugs are fixed, you can rerun those tests to see if the changes have been made without any issues.
Sign-Off
This step is the final step and the name makes it self-explanatory as well. So once you have verified that the application meets all the business requirements, you can indicate to the team that the software is ready for rollout by sending a sign-off email.
General Tip: Using the right pools is also pivotal in yielding the best results. As a leading software testing services company, we use the best tools to make the process more efficient. Test data management can become a nightmare if you don’t monitor and feed the test data in a frequent manner. We use data management tools to feed all the required test data and remove the hassle from this process. Similarly, we also use bug reporting systems to keep track of all the bugs that were discovered and make sure everything is resolved in the most efficient manner.
Conclusion
We hope that our User Acceptance Testing Tutorial has helped you get a clear picture of the UAT process. Based on your specific project demands, you could make some tweaks to this process. Also, make sure to choose the appropriate tools to get the best results.






























