by admin | Apr 14, 2021 | Software Testing, Blog |
Everything is going digital nowadays. If your business has not hopped onto the trend, you might lose the market’s interest or make their purchase inconvenient. If you want to make your business more convenient and explore ways to advance your business, a digital wallet would is a good starting point.
What You Should Know About Digital Wallets
A digital wallet or e-wallet stores the user’s payment information (their credit card information, passwords, other types of cards, coupons, or tickets). Some of the popular ones you probably have come across are Google Pay, Apple Pay, Amazon Pay, Android Pay, Paypal One Touch, Visa Checkout, and more.
These apps were developed so that users do not have to bring out their physical cards whenever they make an online or in-store purchase. Thanks to digital wallets, their payment information is safely stored. These apps secure the data by providing encryption, requesting passwords, or requiring fingerprint scans before people can purchase.
This technology makes purchasing a one-tap or one-click process. Aside from quick payment, it also stores loyalty details and online vouchers, placing financial information in one system.
Why You Should Consider It
If you are a retailer planning to build your digital wallet, you have made the right decision. Here are the advantages you could get from this option:
1. You Provide a More Secure Payment Platform for Your Customers
You may be thinking that having an e-wallet can give your customers a riskier experience. Digital wallets follow strict security protocols—one of which is biometric authentication.
Another one is by tokenization. The technology turns any sensitive information into data into a random string of characters that make it hard for hackers to decipher. When they make a payment, this series of characters get transported to the bank’s system. Even if their stored data is breached, it would be impossible for the hackers to find out people’s personal information with the key that unlocks the encryption.
2. Your Customers Enjoy Smaller Transaction Fees
When your customer pays directly to your digital wallet, it eliminates the additional expense and banking fees. Since they would pay you directly, the added step of banking transactions is eliminated in the process, saving them money and time.
At the same time, this technology also helps your business save on expenses. You no longer have to print out physical receipts, invoices, and other store expenses.
3. They Get an Enhanced Customer Experience
Digital wallets can speed up the online and in-store checkout process, which is always an added convenience. There is no need to line up or repeatedly enter payment information because you can already complete the transaction in one tap.
Moreover, most digital wallets are designed to allow retailers to provide special offers or discounts to their customers. All these are added benefits for the customer.
Conclusion
Launching a digital wallet for your business is not just a way to provide your customers with added convenience. It is also for the business’ low operating cost, payment security, and potentially increased sales. Digital wallets are specially designed to benefit all parties involved. If you would like your business to experience the enumerated advantages, consider setting this up for your business.
Once you have the software, make sure that it works in the best way possible. Let top software testing companies challenge it before you launch. Codoid is one of the top QA companies in the world. We provide automation testing, mobile app testing, performance testing, and data analytics testing to ensure that software would deliver. Contact us to learn more about how we can help.

by admin | Dec 11, 2020 | Software Testing, Blog |
At present, every techie has Agile, Continuous Delivery, and DevOps in their vocabulary. Everyone wants to be Agile, releasing software quickly, creating products that are innovative just like Silicon Valley startups and giants. A lot of points regarding the transformation are widely understood, and to a certain extent, have been adopted successfully. There is an area, however, where there are still adoption challenges as well as considerable confusion.
More specifically, it involves the testing process. As the release cycle of software shrinks from years to months, down to just weeks and days, or even quicker: how can the testing practices best be reshaped in order to ensure the released software—still in production—does not frustrate users? How do we make sure it does not break and cause disappointment?
This challenge is not uncommon, especially since most DevOps shops find that the most frustrating software production bottleneck is testing.
Understanding Continuous Testing
The answer lies in Continuous Testing, which is essentially the process of automated software testing as a service, a key part of software delivery that gives instant feedback on any risks from a software release candidate. While that sounds incredibly straightforward, there’s more nuance to it than that—the very magnitude, nature, and essence of transformation Continuous Testing gives.
Continuous Testing is basically about shifting testing from an event that is time-boxed amidst a process that is linear to having it embedded as an ongoing, fundamental part of all activities throughout the software delivery cycle.
End Goal
“In-sprint testing” should be the goal in agile environments of Continuous Testing. Whether or not your sprint is 2 weeks or 4 weeks, completing all types of testing within that sprint should be the goal. This is so that each sprint is able to end with ready-to-ship, fully tested software. The best continuous delivery practices show that it is incredibly impossible to do continuous delivery without continuous testing. If the sprint seems too short for comprehensive testing to be allowed, it is likely being looked into inaccurately.
The Process
The most important one is to define the tests even before a single line of code is written. Not having clarity in terms of requirements and interpretations that turn out to be wrong will lead to delays and reworking. It is also key to optimize coverage and tests, since some organizations end up defaulting to simultaneous testing. Unfortunately, all this accomplishes is prolonging test cycles and wasted resources.
For “in-sprint” testing to be developed, shift testing left in order for the tests to run earlier within the cycle of development. It’s also important for the test environment to be complete, since this is critical for continuous testing. Lower wait times and eliminate blocks through providing a test environment that is complete on demand, making sure that there are dev-friendly tools (as code, CI/CD integrations, supported open source). Don’t forget ephemeral environments, test data on demand, and virtual services!
Most importantly, make sure you have the right test data.
Conclusion
It is important to have cross-team collaboration and actionable analytics as well as feedback loops when it comes to continuous testing. While manual testing services have competencies, automation streamlines everything in a way that helps your organization much more efficiently. When in doubt, look to quality assurance professionals for assistance.
In search of automation testing companies you can rely on? Contact Codoid today! We are an industry leader in quality assurance with a brilliant team of engineers ready to help you.

by admin | Nov 30, 2020 | Software Testing, Fixed, Blog |
Chrome DevTools has several panels – Elements, Console, Sources, Network, Performance, Memory, Application, Security, and Audits. Today you are going to learn DevTools’ Console panel from a testing perspective.
What can you see in the Console panel? You can access error messages which are thrown by the parser. Sometimes the web application under test may not show errors on the UI. However, you may see JavaScript error messages in the console panel.
The errors are not show-stoppers or creating issues. Why should I bother? If the pages are error-free, there are some benefits you can reap.
- When a website is error-free, it will improve SEO.
- The errors may not create any issues now. However, when you add new snippets in the JavaScript files, it may produce unexpected issues. It is better to have an error-free Console panel for all the pages so that the developers can add new scripts confidently.
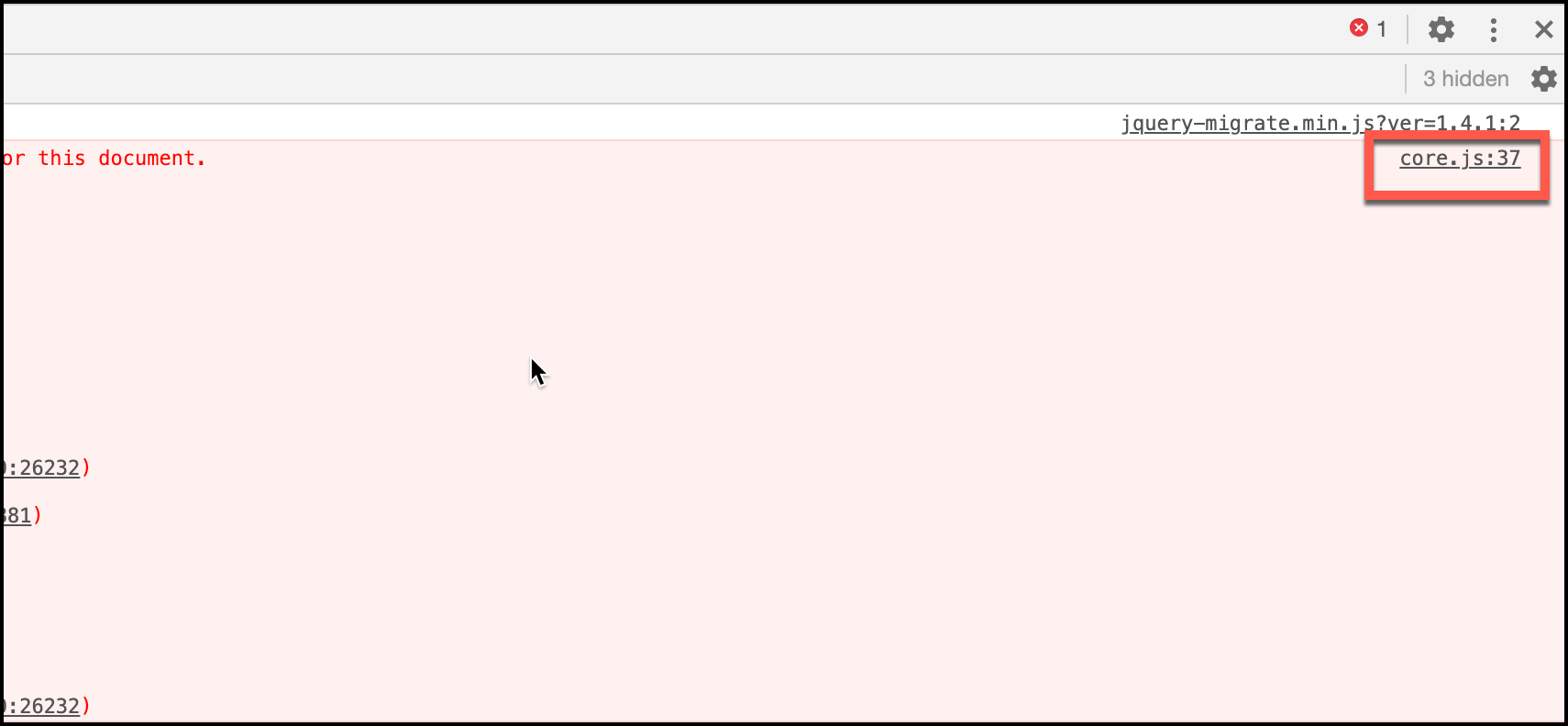
As a software tester, you must report JavaScript parser errors, which you see in the Chrome DevTools Console panel. When you notice an error, you will have to check from which JS file it is originated.
You can get the source file information at the right-side of the Console panel.
There are three types of messages Chrome DevTools shows – Informational, Warning, and Error. Informational Message is displayed without any background color. Warning message in Yellow and Error in Red background color.
If you want to view only Error messages, you can select ‘Errors’ in the ‘Default Levels’ drop-down.
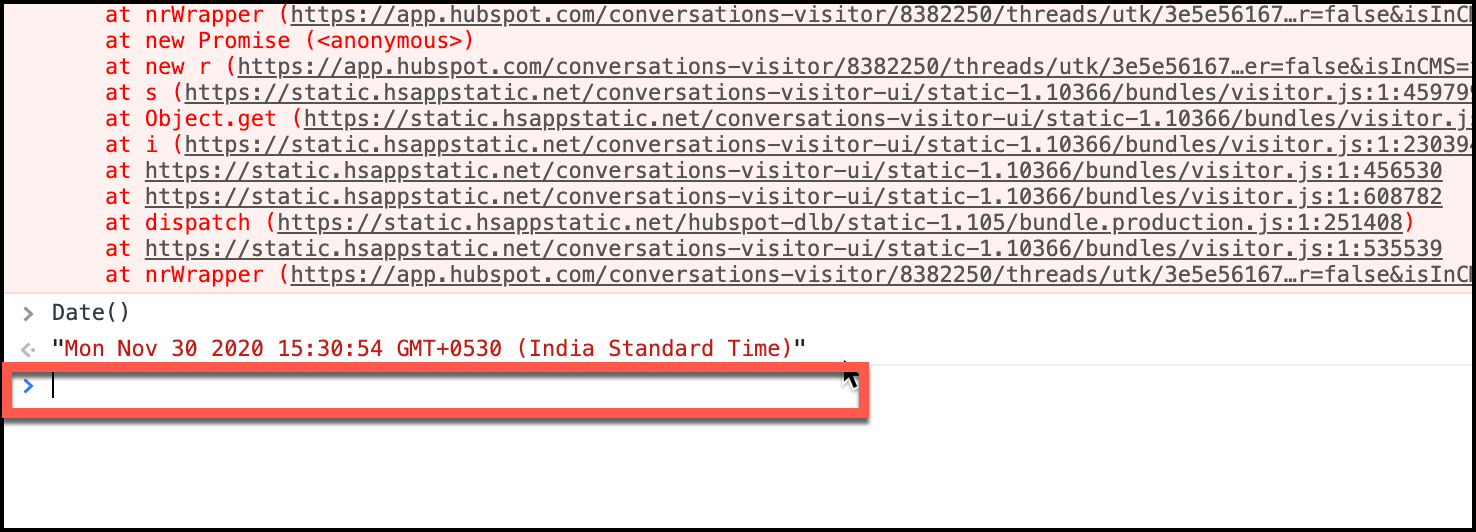
Console’s Command Prompt
Console panel has its Command prompt. It is a node command prompt. If you want to run any JavaScript snippets on a webpage, you can use this command prompt. Where can I find the command prompt? You can find the command line cursor below the log messages.
Selecting Elements
Everyone is aware that we can search elements in the Elements panel using XPath/CSS Selector. However, you can select an element in the DevTools Console panel as well. If you know about the ‘document.querySelector’ method, then it is straight-forward.
‘document.querySelector’ method accepts a CSS selector as an argument, and it selects only one element. If you want to select multiple elements, use the ‘document.querySelectorAll’ method in Console’s command prompt.
Using the ‘document.querySelector’ method, it returns one element, and you can focus on that element without any distraction. Whereas in Elements panel, it just highlights the selected element.
Selenium Chrome DevTools Protocol (CDP)
Now Selenium 4 has support to listen Console log messages. Manually, you can open the console panel and monitor the logs. However, in automation testing, there was no way to listen the logs.
DevTools devTools = driver.getDevTools();
devTools.createSessionIfThereIsNotOne();
devTools.clearListeners();
devTools.send(Log.enable());
devTools.addListener(Log.entryAdded(), logEntry -> {
System.out.println(logEntry.getText().contains("404"));
});
driver.get("https://codoid.com/fafafafsasf");
In Selenium 4, using Chrome DevTools Protocol, you can listen the logs. Refer to the below code. Note: Selenium 4 is not released yet. We have used Selenium 4 alpha version to accomplish the snippet.
In Conclusion
As a QA Company, we use the Chrome Console panel to access logs messages and report the errors to our clients’ developers. In the subsequent blog articles, we will be publishing on Chrome DevTools’ other panels.

by admin | Oct 19, 2020 | Software Testing, Fixed, Blog |
With the rapid changes in technology, the digitization across the business sectors had a tremendous impact on the retail industry. The retail sectors have been the most affected by the rapid digitization moves and changes among the business sectors. At the front end, the continuous Retail Testing Services includes stable and user-friendly customer experience. On the other hand, if we talk about the back end, then the Retail Testing Services has a transaction data load.
For the entire retail industry, the center of the business is primarily the customer experience. If the customer has a bad experience with the mobile app or storefront, it would significantly impact the customers’ experience. It will indeed affect the bottom line of the business as well.
The retail industry is continuously facing significant challenges due to the digitization process in today’s date. All businesses in the retail sector face many challenges. The challenges are met at both the application and the business level. Therefore, continuous testing in the retail industry is a must in order to fix all those challenges, thus ensuring the success of the retail industries.
What Is Continuous Testing?
Continuous testing is a process that involves the testing of the software at every stage of the software development cycle. The main and primary goal of continuous testing is to evaluate software quality at every step of the ongoing delivery process by testing often and testing early. Incorporating continuous testing in the retail industry is a great way to ensure that all the products are released to the market at the quality customer expect.
In other words, we can say that continuous testing is a software testing type in which the product is often and early evaluated throughout the entire ongoing delivery process. The process of constant testing enables constant feedback for the developers to fix all the bugs before being released to production. This process will increase the time to market for the retail industries but will also improve the quality that the customers expect.
Why Involve Continuous Testing In the Retail Industry
The testing of the omnichannel retailing model has increased the business via online technologies. It is essential for retailers to remain relevant in the present industry. The testing of the omnichannel and versatile retail sector is critical in order to deliver a consistent, reliable, and incorporated customer encounter.
Therefore, to create digital confidence among all the retail industry customers, it becomes essential to start with Retail Testing Services. If you want to know why to involve Continuous testing in the retail sector, then below mentioned are the reasons that will support its involvement:
Customer Experience Needs To Be Guaranteed: With the digital channels’ advancement, the customers find it really easy to access the products. Therefore, a retail industry needs to offer positive customer experience both on mobile application and in store. The customers’ main aim is to be able to shop anytime, anywhere without facing any issues. So, problems like slow apps, downtime, bugs, etc., will leave the customers with a bad experience.
Thus with continuous testing, it becomes very easy to check the software regressions, performance issues, and bugs. The outcome of catching bugs early will reduce the chances that these bugs will make it into production. Therefore, the process of continuous testing promises to offer an excellent customer experience with fewer bugs and enhanced performance.
Early Bug Detection Ensures Resource And Time Saving: The most important benefit offered by the process of continuous testing is that it helps in saving resources and time of the retail industry. The traditional approach of testing was very time consuming and confusing. The bugs can be detected by running the tests earlier under continuous testing before bundling up the new features. The early detection of bugs thus allows the developer to make necessary changes before time. Therefore the bugs can be corrected with less effort without wasting time on the other teams involves.
Thus, continuous testing helps the retail industry save their valuable resources and time by early bug detection.
Traditional Or Human Testing Is Not Sufficient: The human testing of the retailing industry software is not enough, and hence there arises the need for continuous testing. The changes in the software can have various unanticipated and unexpected side effects. Therefore, the testing must be utterly comprehensive in order to bring protection.
With each new release, it becomes essential to implement continuous testing throughout the entire pipeline. This will ultimately allow the retail industry to guarantee an excellent user experience prior to each of its releases. Therefore, with continuous testing, the test runs’ quality can be improved, thus improving the customer experience. It will altogether eliminate the need for traditional or human testing, which was very time consuming and creates many errors during the testing process.
Retail Industry Software Needs To Progress Constantly: As we all know, the advancement of technologies really calls for the need to develop and evolve the software continuously. One of the significant differences between the traditional product and the software is that it is always changing. With the variety of software products now, they are obligated to continuous evolvement after its release.
With continuous testing, you can make various changes and improvements even after the release, whether it involves redesigning the user interface or an improvement in the machine learning or artificial intelligence algorithms, all this with the primary motive of providing a flawless and unblemished customer experience.
Why Retail Industry Should Not Miss Out On Continuous Testing
With the digitization of services adding values to the retail industry, it is equally important to involve the process of software testing as well. The concept of continuous testing originated from the need to introduce the process of testing the software right from the beginning of the software development cycle and keep the software updated for frequent releases.
The retail industry should not miss out on continuous testing because of the following reasons:
- Continuous testing helps to reduce application bound risk
- Continuous testing enables the faster release
- Continuous testing helps in improving the test coverage
- Continuous testing helps in bringing consistency
- Continuous testing cuts the downtime taken for Code Review
- Continuous testing enables more transparency
The Bottom Line
As you have come to the article’s bottom line, have you realized how necessary continuous testing is? Be it a Retail industry or any other business industry, the process of constant testing plays a vital role at every step in the software development lifecycle. From bug detection to excellent customer experience continuous, testing holds major importance in the Retail Sector.

by admin | Oct 9, 2020 | Software Testing, Fixed, Blog |
Becoming a successful machine learning/artificial intelligence engineer, there are certain numbers of skills required to stir a prosperous career in the field of ML/AI. Having adept about the subject of matter, understanding essential requirements and the fundamentals necessary to build a successful career in the field of artificial intelligence or machine learning.
Machine learning is an innovative technology that employs logical algorithm and statistical models to carry out specific tasks, such tasks are being completely achieved through system self-learning of complex and important trends from a given dataset and drawing an inference for useful insights and conclusion. Whereas, artificial intelligence is a wider aspect of machine learning that employs human cleverness to machines in other to be able to autonomously process, learn, think and lastly make intelligent adjustments or corrections. Artificial intelligence was built to work autonomously without engaging the computer programmer for explicit coding of each part of the AI system.
Skills Required By Machine Learning Engineers
A quality and qualified engineer looking for an amazing career in the field of ML/AI needs to possess an in-depth knowledge of data science and statistical implementations; also, some fundamental know-how on software engineering and data handling. Some of the important skills required by aspiring ML/AI engineer includes:
Basic computer programming knowledge
A fundamental knowledge about software building and implementation ranging from linear programming, computer structural design, data architecture, to algorithm optimization as all needed as a ML/AI engineer. This engineer will also engage in simulating machines to carry out activities same way human beings does. An engineer without this basic programming knowledge will find it difficult.
Data handling and validation
Data handling skills is very important in ML/AI building and implementation. These skills is highly required by the intending engineers to perfectly identify different trends and patterns available of gathered datasets. Without this skills, proper data handling and validations can’t carry out.
Statistics and Probability
Data science was based on statistical modelling, a very crucial part of ML. An intending ML/AI engineer must be skilled in carrying out probability theories like Markov models, Bayesian principles, amongst others. Also, such an engineer must be capable of performing univariate and multivariate statistical analysis that forms the fundamental of ML models.
Software design
Long-term product of building a ML/AI system is incorporation into software either on PC or Smart phones. An engineer of ML/AI requires to have these skills for final representation and deployment of the developed model into software, this will provide a user-friendly interface for proper application.
Signal processing skills
Knowledge of signal processing is required to extract features and solve complex problems. This is a crucial aspect of ML that includes feature mining that will enable algorithms like Shearlets, Bandlets, and Wavelets perform theoretical analysis in solving multifaceted scenarios.
Architectures of Neural Network
Tasks that are beyond human capabilities are execute by Neural Networks. This network has demonstrated to be one of the most accurate ways of deciphering problems like Object recognition and classification, speech recognition, natural language processing, and many more.
Good understanding of Algebra and Calculus
Having an in-depth knowledge of Calculus, Matrices, Vector, Algebra, and others are very vital in understanding and representing some ML/AL concepts.
Physics
This is one of those basic knowledges required by ML engineer. It aids in the representation of complex situation and inferring of the situation.
Domain Knowledge
Knowledge of the field of subject matter, a machine learning engineer must be vast in of problem identification and solving to be able to design a nearly perfect model for useful insights and interpretation.
Fast Prototyping
The available for building and implementing an ML system is expected to be reduced to the barest minimum. This can only be achieved an engineer that knows how to select right model in carrying out certain excellently. It also includes weighing up different methods to achieve a faster model for implementation.

by admin | May 11, 2020 | Software Testing, Fixed, Blog |
We all are pretty much aware that Python is an object oriented programming language. A software tester should possess profound Programming Language skills and expert level Automation Tool knowledge before commencing scripting. Automation and coding patterns can be achieved when you are familiar with Oops concepts. For many automation testers, Oops concept is still a grey area. However, to setup test automation framework & excel in automation testing career, Object Oriented Programming Concepts are important. We, as a QA company, has a concrete career journey from automation tester to Test Automation Architect role. If you are familiar with Python Oops concept, you can create test automation libraries which are useful for your team to ease their automation scripting effort. This blog will provide you a sneak peek review of Python oops concepts.
Class Declaration
You can define class variable, instance variable, and methods in a class. Below snippet shows how to define a class.
Class with Constructor
Constructor is a special method which will be invoked when an instance is created. When Line #7 is executed, it will invoke ‘__init__’ method. i.e. constructor method. You may ask a question – Why are we passing ‘self’ as an argument in constructor method? Answer: ‘self’ represents the instance of the class.
#Class Definition
class SuperClass():
def __init__(self):
print("Constructor is called")
#Object Creation
obj = SuperClass()
Class Variable
Class variable which is stored in Class memory not in instance memory.
# Class Definition
class SuperClass():
counter = 0 #Class Variable
def __init__(self):
print("Constructor is called")
# Object Creation
obj1 = SuperClass()
obj2 = SuperClass()
obj1.counter +=1
obj1.counter +=1
print(obj1.counter)
print(obj2.counter)
In the above code, Line #14 prints 2 and Line #15 prints 0. However, as per the class variable paradigm it should print 2 for both the instances. The reason is line #11 & #12 change the values using its instances. To change class variable value, you need to use class name not instance. Please refer the below code. It changes class variable’s value using Class Name.
# Object Creation
obj1 = SuperClass()
obj2 = SuperClass()
SuperClass.counter +=1
SuperClass.counter +=1
print(obj1.counter)
print(obj2.counter)
Instance Variable
Instance variables are stored in Instance memory not in Class memory. Let’s see how to declare and use Instance variable.
# Class Definition
class SuperClass():
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
print("Constructor is called")
# Object Creation
obj1 = SuperClass("John", 40)
obj2 = SuperClass("Peter", 50)
In the above snippet, ‘name’ and ‘age’ are instance variables. When you create instance for SuperClass, memory will be allocated for ‘name’ & ‘age’ variables in instance memory.
Inheritance
#Super Class
class Animal():
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
#Sub class
class Cat(Animal):
def __init__(self, name, age):
super(Cat, self).__init__(name, age)
instance_1 = Cat("Kona", 2)
print(instance_1.name)
In Conclusion
Python oops concept is a vast topic. However, we wanted to keep this blog post precise and act as a quick start material to learn/recap Python Oops. As a test automation company we create useful test automation libraries with coding patterns and best practices. When you are aware of code design patterns and follow best practices, you can deliver quality test automation scripts with ease.