by Rajesh K | Sep 2, 2025 | Software Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
In software testing, test data is the lifeblood of reliable quality assurance. Whether you are verifying a login page, stress-testing a payment system, or validating a healthcare records platform, the effectiveness of your tests is directly tied to the quality of the data you use. Without diverse, relevant, and secure testdata, even the most well-written test cases can fail to uncover critical defects. Moreover, poor-quality testdata often leads to inaccurate results, missed bugs, and wasted resources. For example, imagine testing an e-commerce checkout system using only valid inputs. While the “happy path” works, what happens when a user enters an invalid coupon code or tries to process a payment with an expired credit card? Without including these scenarios in your testdata set, you risk pushing faulty functionality into production.
Therefore, investing in high-quality testdata is not just a technical best practice; it is a business-critical strategy. It ensures comprehensive test coverage, strengthens data security, and accelerates defect detection. In this guide, we will explore the different types of testdata, proven techniques for creating them, and practical strategies for managing testdata at scale. By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap to improve your testing outcomes and boost confidence in every release.
Understanding Test Data in Software Testing
What Is Test Data?
Testdata refers to the input values, conditions, and datasets used to verify how a software system behaves under different circumstances. It can be as simple as entering a valid username or as complex as simulating thousands of financial transactions across multiple systems.
Why Is It Important?
- It validates that the application meets functional requirements.
- It ensures systems can handle both expected and unexpected inputs.
- It supports performance, security, and regression testing.
- It enables early defect detection, saving both time and costs.
Example: Testing a banking app with only valid account numbers might confirm that deposits work, but what if someone enters an invalid IBAN or tries to transfer an unusually high amount? Without proper testdata, these crucial edge cases could slip through unnoticed.
Types of Test Data and Their Impact
1. Valid Test Data
Represents correct inputs that the system should accept.
Example: A valid email address during registration ([email protected]).
Impact: Confirms core functionality works under normal conditions.
2. Invalid Test Data
Represents incorrect or unexpected values.
Example: Entering abcd in a numeric-only field.
Impact: Validates error handling and resilience against user mistakes or malicious attacks.
3. Boundary Value Data
Tests the “edges” of input ranges.
Example: Passwords with 7, 8, 16, and 17 characters.
Impact: Exposes defects where limits are mishandled.
4. Null or Absent Data
Leaves fields blank or uses empty files.
Example: Submitting a form without required fields.
Impact: Ensures the application handles missing information gracefully.
Test Data vs. Production Data
| Feature |
Test Data |
Production Data |
| Purpose |
For testing in non-live environments |
For live business operations |
| Content |
Synthetic, anonymized, or subsets |
Real, sensitive user info |
| Security |
Lower risk, but anonymization needed |
Requires the highest protection |
| Regulation |
Subject to rules if containing PII |
Strictly governed (GDPR, HIPAA) |
Transition insight: While production data mirrors real-world usage, it introduces compliance and security risks. Consequently, organizations often prefer synthetic or masked data to balance realism with privacy.
Techniques for Creating High-Quality Test Data
Manual Data Creation
- Simple but time-consuming.
- Best for small-scale, unique scenarios.
Automated Data Generation
- Uses tools to generate large, realistic datasets.
- Ideal for load testing, regression, and performance testing.
Scripting and Back-End Injection
- Leverages SQL, Python, or shell scripts to populate databases.
- Useful for complex scenarios that cannot be easily created via the UI.
Strategies for Effective Test Data Generation
- Data Profiling – Analyze production data to understand patterns.
- Data Masking – Replace sensitive values with fictional but realistic ones.
- Synthetic Data Tools – Generate customizable datasets without privacy risks.
- Ensuring Diversity – Include valid, invalid, boundary, null, and large-volume data.
Key Challenges in Test Data Management
- Sensitive Data Risks → Must apply anonymization or masking.
- Maintaining Relevance → Test data must evolve with application updates.
- Scalability → Handling large datasets can become a bottleneck.
- Consistency → Multiple teams often introduce inconsistencies.
Best Practice Tip: Use Test Data Management (TDM) tools to automate provisioning, version control, and lifecycle management.
Industry-Specific Examples of Test Data
- Banking & Finance: Valid IBANs, invalid credit cards, extreme transaction amounts.
- E-Commerce: Valid orders, expired coupons, zero-price items.
- Healthcare: Anonymized patient data, invalid blood groups, and future birth dates.
- Telecom: Valid phone numbers, invalid formats, massive data usage.
- Travel & Hospitality: Special characters in names, invalid booking dates.
- Insurance: Duplicate claims, expired policy claims.
- Education: Invalid scores, expired enrollments, malformed email addresses.
Best Practices for Test Data Management
- Document test data requirements clearly.
- Apply version control to test data sets.
- Adopt “privacy by design” in testing.
- Automate refresh cycles for accuracy.
- Use synthetic data wherever possible.
Conclusion
High-quality test data is not optional; it is essential for building reliable, secure, and user-friendly applications. By diversifying your data sets, leveraging automation, and adhering to privacy regulations, you can maximize test coverage and minimize risk. Furthermore, effective test data management improves efficiency, accelerates defect detection, and ensures smoother software releases.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Can poor-quality test data impact results?
Yes. It can lead to inaccurate results, missed bugs, and a false sense of security.
-
What are secure methods for handling sensitive test data?
Techniques like data masking, anonymization, and synthetic data generation are widely used.
-
Why is test data management critical?
It ensures that consistent, relevant, and high-quality test data is always available, preventing testing delays and improving accuracy.

by Rajesh K | Jul 30, 2025 | Software Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
Have you ever wondered why some software teams are consistently great at handling unexpected issues, while others scramble whenever a bug pops up? It comes down to preparation and more specifically, software testing technique known as bebugging. You’re probably already familiar with traditional debugging, where developers identify and fix bugs that naturally occur during software execution. But bebugging takes this a step further by deliberately adding bugs into the software. Why would anyone intentionally introduce errors, you ask? Simply put, bebugging is like having a fire drill for your software. It prepares your team to recognize and resolve issues quickly and effectively. Imagine you’re about to launch a new app or software update. Wouldn’t it be comforting to know that your team has already handled many of the potential issues before they even arose?
In this detailed guide, you’ll discover exactly what bebugging is, why it’s essential for your development process, and how you can implement it successfully. Whether you’re a QA engineer, software developer, or tech lead, mastering bebugging will transform your team’s approach to troubleshooting and significantly boost your software’s reliability.
What Exactly Is Bebugging, and How Is It Different from Debugging?
Though they sound similar, bebugging and debugging have very different purposes:
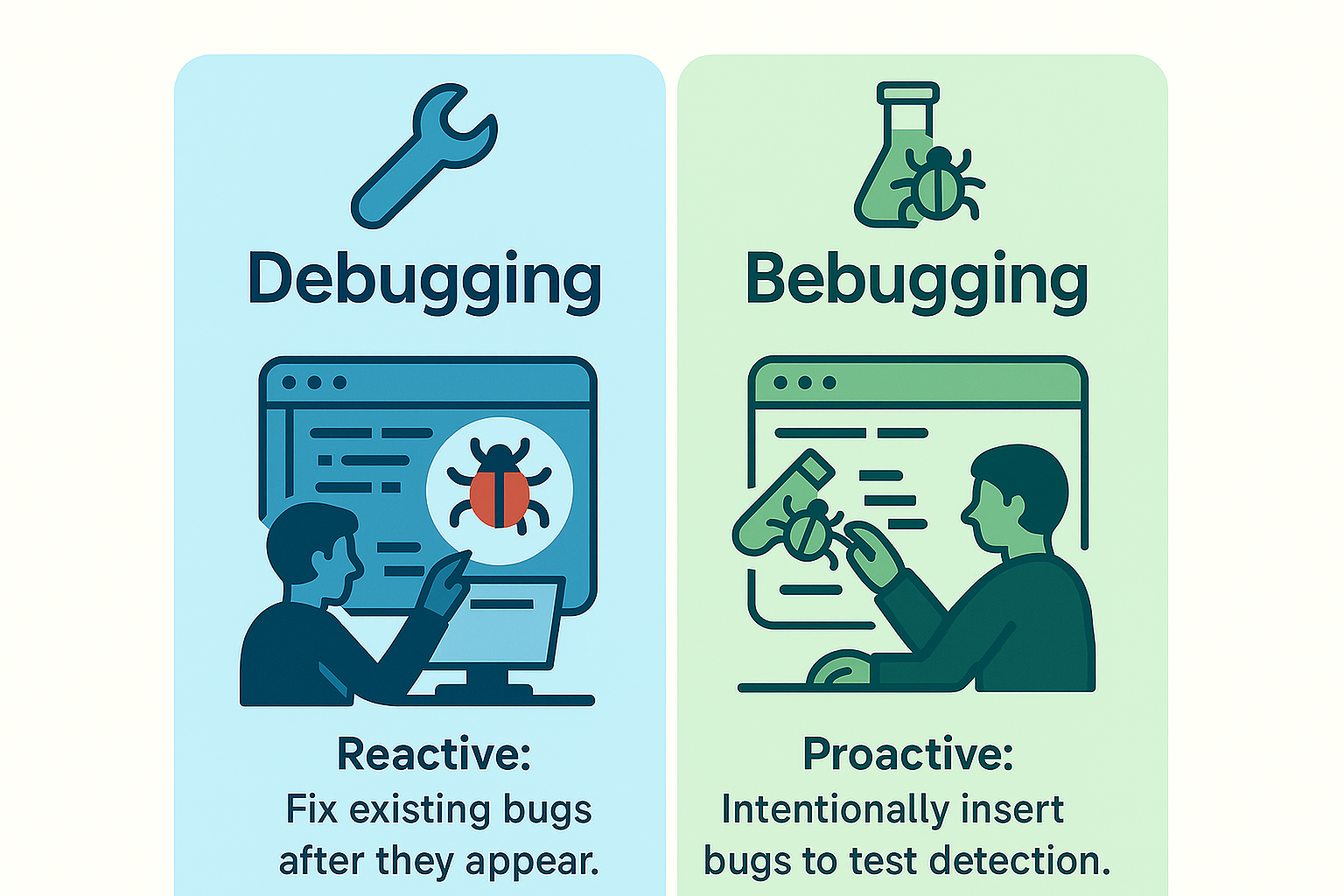
- Debugging is reactive. It involves locating and fixing existing software errors.
- Bebugging is proactive. It means intentionally inserting bugs to test how effectively your team identifies and resolves issues.
Think about it this way: debugging is like fixing leaks as you discover them in your roof. Bebugging, on the other hand, involves deliberately making controlled leaks to test whether your waterproofing measures are strong enough to handle real storms. This proactive practice encourages a problem-solving culture in your team, making them better prepared for real-world software challenges.
A Brief History: Where Did Bebugging Come From?
The term “debugging” famously originated with Admiral Grace Hopper in the 1940s when she literally removed a moth from a malfunctioning computer. Over the years, as software became increasingly complex, engineers realized that simply reacting to bugs wasn’t enough. In response, the concept of “bebugging” emerged, where teams began intentionally inserting errors to test their software’s reliability and their team’s readiness.
By the 1970s and 1980s, the practice gained traction, especially in large-scale projects where even minor errors could lead to significant disruptions. With modern development practices like Agile and CI/CD, bebugging has become a critical component in ensuring software quality.
Why Should Your Team Use Bebugging?
Bebugging isn’t just a quirky testing technique; it brings substantial benefits:
- Enhanced Troubleshooting Skills: Regularly handling intentional bugs improves your team’s ability to quickly diagnose and fix complex real-world issues.
- Better Preparedness: Your team will be better equipped to deal with unexpected problems, significantly reducing panic and downtime during critical periods.
- Improved Software Reliability: Regular bebugging ensures your software remains robust, reducing the likelihood of major issues slipping through to customers.
- Sharper Error Detection: It refines your team’s ability to spot subtle errors, enhancing overall testing effectiveness.
Key Techniques for Successful Bebugging
Error Seeding
Error seeding involves strategically placing known bugs within critical software components. It helps teams practice identifying and fixing errors in controlled scenarios, just like rehearsing emergency drills. For example, introducing bugs in authentication or payment processing modules can greatly enhance your team’s readiness for high-risk situations.
Automated Error Injection
Automation is a powerful tool in bebugging, particularly for larger or continuously evolving projects. AI-driven automated tools systematically introduce errors, allowing for consistent, repeatable testing without overwhelming your team. These tools often integrate with robust error tracking systems to monitor anomalies and improve detection accuracy.
Stress Testing Combined with Bebugging
Stress testing pushes your software to its limits to observe its behavior under extreme conditions. When combined with bebugging, intentionally adding bugs during these stressful scenarios, you’ll gain insight into potential vulnerabilities, allowing your team to proactively address issues before users encounter them.
How to Implement Bebugging Step-by-Step
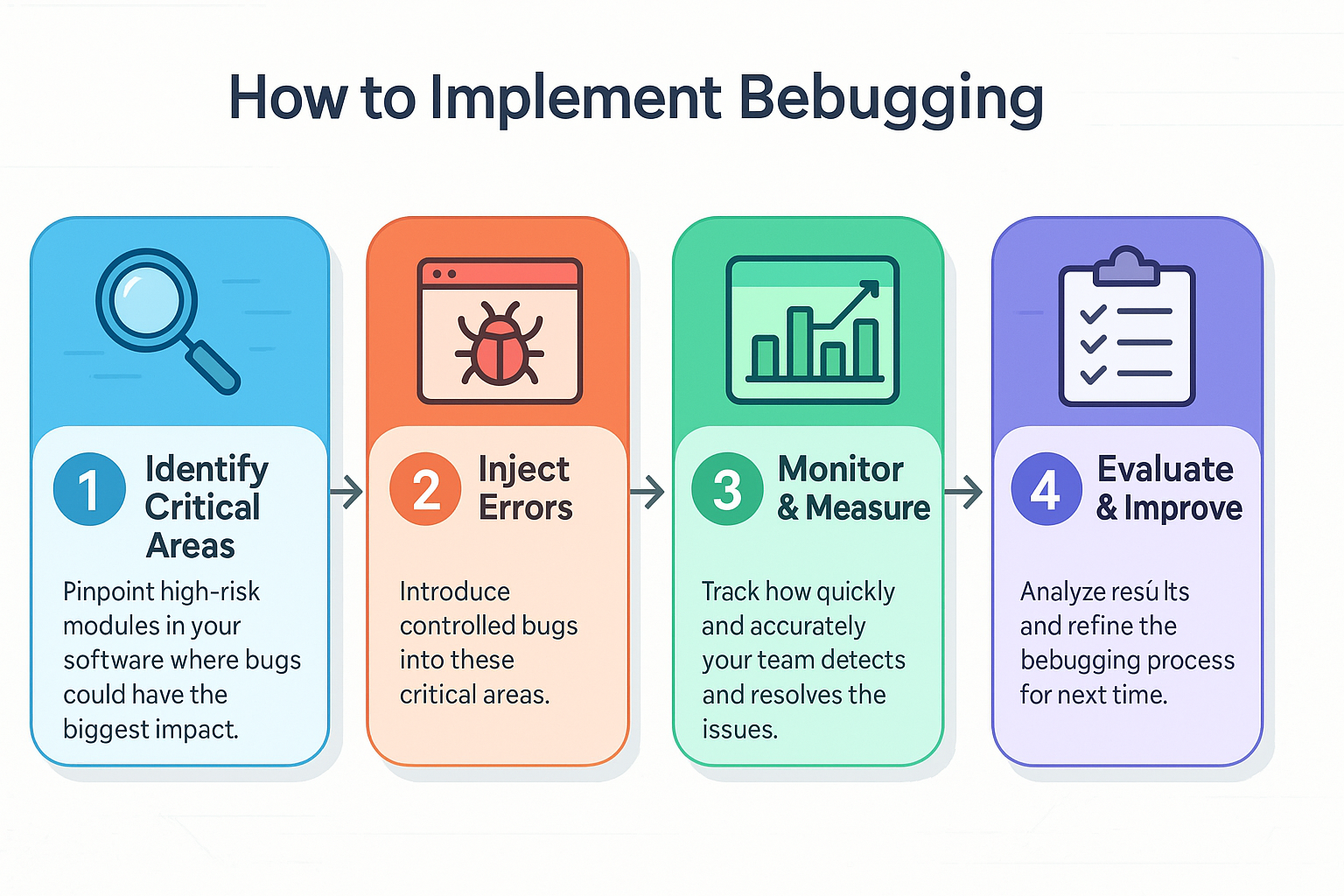
- Identify Critical Areas: Pinpoint areas within your software most susceptible to significant impacts if bugs arise.
- Plan and Inject Errors: Decide on the types of intentional errors, syntax errors, logical bugs, and runtime issues, and introduce them systematically.
- Monitor and Measure: Observe how effectively and swiftly your team identifies and fixes these injected bugs. Capture metrics like detection time and accuracy.
- Evaluate and Improve: Analyze your team’s performance, identify strengths and weaknesses, and refine your error-handling procedures accordingly.
Bebugging in Action: A Real-World Example
Consider a fintech company that adopted bebugging in their agile workflow. They intentionally placed logic and security errors in their payment processing software. Because they regularly practiced handling these issues, the team quickly spotted and resolved them. This proactive strategy significantly reduced future debugging time and helped prevent potential security threats, increasing customer trust and regulatory compliance.
Traditional Debugging vs. Bebugging
| Aspect |
Traditional Debugging |
Bebugging |
| Purpose |
Reactive error fixing |
Proactive error detection |
| Implementation |
Fixing existing errors |
Introducing intentional errors |
| Benefits |
Immediate bug resolution |
Enhanced long-term reliability |
| Suitability |
Post-development phase |
Throughout software development |
Why Rapid Bug Detection Matters to Your Business
Rapid bug detection is critical because unresolved issues harm your software’s performance, disrupt user experience, and damage your brand reputation. Quick detection helps you avoid:
- User Frustration: Slower software performance or crashes lead to dissatisfied customers.
- Data Loss Risks: Bugs can cause significant data issues, potentially costing your business heavily.
- Brand Damage: Persistent issues weaken customer trust and loyalty, negatively impacting your business.
Common Types of Bugs to Look Out For:
- Syntax Errors: Basic code mistakes, like typos or missing punctuation.
- Semantic Errors: Logic errors where the software works incorrectly despite being syntactically correct.
- Runtime Errors: Issues arising during the software’s actual execution, often due to unexpected scenarios.
- Concurrency Errors: Bugs related to improper interactions between parallel processes or threads, causing unpredictable results or crashes.
Conclusion
Bebugging isn’t just another testing practice, it’s a strategic move toward building reliable and robust software. It empowers your team to handle problems confidently, proactively ensuring your software meets the highest quality standards. At Codoid Innovations, we are committed to staying ahead of software testing challenges by continuously embracing innovative methods like bebugging. With our dedicated expertise in quality assurance and advanced testing strategies, we ensure your software is not just error-free but future-proof.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What's the key difference between debugging and bebugging?
Debugging reacts to errors after they appear, while bebugging proactively inserts errors to prepare teams for future issues.
-
Can we automate bebugging for large projects?
Absolutely! Automation tools using AI are perfect for systematic bebugging, especially in extensive or continuously evolving software projects.
-
Is bebugging good for all software?
While helpful in most cases, bebugging is especially beneficial in agile environments or complex software systems where rapid, continuous improvement is essential.
-
What tools are best for bebugging?
Integrated Development Environment (IDE) debuggers like GDB, combined with error-tracking tools like Sentry, Bugzilla, or JIRA, work effectively for bebugging practices.

by Rajesh K | Jul 23, 2025 | Software Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
Let’s be honest: building great software is hard, especially when everyone’s juggling shifting priorities, fast-moving roadmaps, and the demands of software testing. If you’ve ever been part of a team where developers, testers, designers, and business folks all speak different languages, you know how quickly things can go off the rails. This is where user stories become your team’s secret superpower. They don’t just keep you organized; they bring everyone together, centering the conversation on what really matters: the people using your product. User stories help teams move beyond technical checklists and buzzwords. Instead, they spark genuine discussion about the user’s world. The beauty? Even a simple, well-written story can align your developers, QA engineers, and stakeholders, making it clear what needs to be built, how it will be validated through software testing, and why it matters.
And yet, let’s be real: writing truly great user stories is more art than science. It’s easy to fall into the trap of being too vague (Let users do stuff faster!) or too prescriptive (Build exactly this, my way!). In this post, I’ll walk you through proven strategies, real-world examples, and practical tips for making user stories work for your Agile team, no matter how chaotic your sprint board might look today.
What Exactly Is a User Story?
Think of a user story as a mini-movie starring your customer, not your code. It’s a short, plain-English note that spells out what the user wants and why it matters.
Classic format:
As a [type of user], I want [goal] so that [benefit].
For example:
As a frequent traveler, I want to store multiple addresses in my profile to save time during bookings.
Why does this simple sentence matter so much? Because it puts real people at the center of your development process. You’re not just shipping features; you’re solving actual problems.
Real-life tip:
Next time your team debates a new feature, just ask, Who is this for? What do they want? Why? If you can answer those three, you’re already on your way to a great user story.
Who Really Writes User Stories?
If you picture a Product Owner hunched over a laptop, churning out stories in a vacuum, it’s time for a rethink. The best user stories come out of collaboration a little bit like a writers’ room for your favorite TV show.
Here’s how everyone pitches in:
- Product Owner: Sets the vision and makes sure stories tie back to business goals.
- Business Analyst: Adds detail and helps translate user needs into practical ideas.
- Developers: Spot technical hurdles early and help shape the story’s scope.
- QA Engineers: Insist on clear acceptance criteria, so you’re never guessing at done.
- Designers (UX/UI): Weave in the usability side, making sure stories match real workflows.
- Stakeholders and End Users: Their feedback and needs are the source material for stories in the first place.
- Scrum Master: Keeps conversations flowing, but doesn’t usually write the stories themselves.
What matters most is that everyone talks. The richest stories are refined together debated, improved, and sometimes even argued over. That’s not dysfunction; that’s how clarity is born.
A True Story: Turning a Stakeholder Wish Into a User Story
Let’s look at a situation most teams will recognize:
A hotel manager says, Can you let guests skip the front desk for check-in?
The Product Owner drafts:
As a tired traveler, I want mobile check-in so I can go straight to my room.
Then, during a lively backlog grooming session, each expert chimes in:
- Developer: We’ll need to hook into the keycard system for this to work.
- QA: Let’s be sure: guests get a QR code by email, and that unlocks their room?
- Designer: I’ll mock up a confirmation screen showing their room number and a map.
Suddenly, what started as a vague wish becomes a clear, buildable, and testable user story that everyone can rally behind.
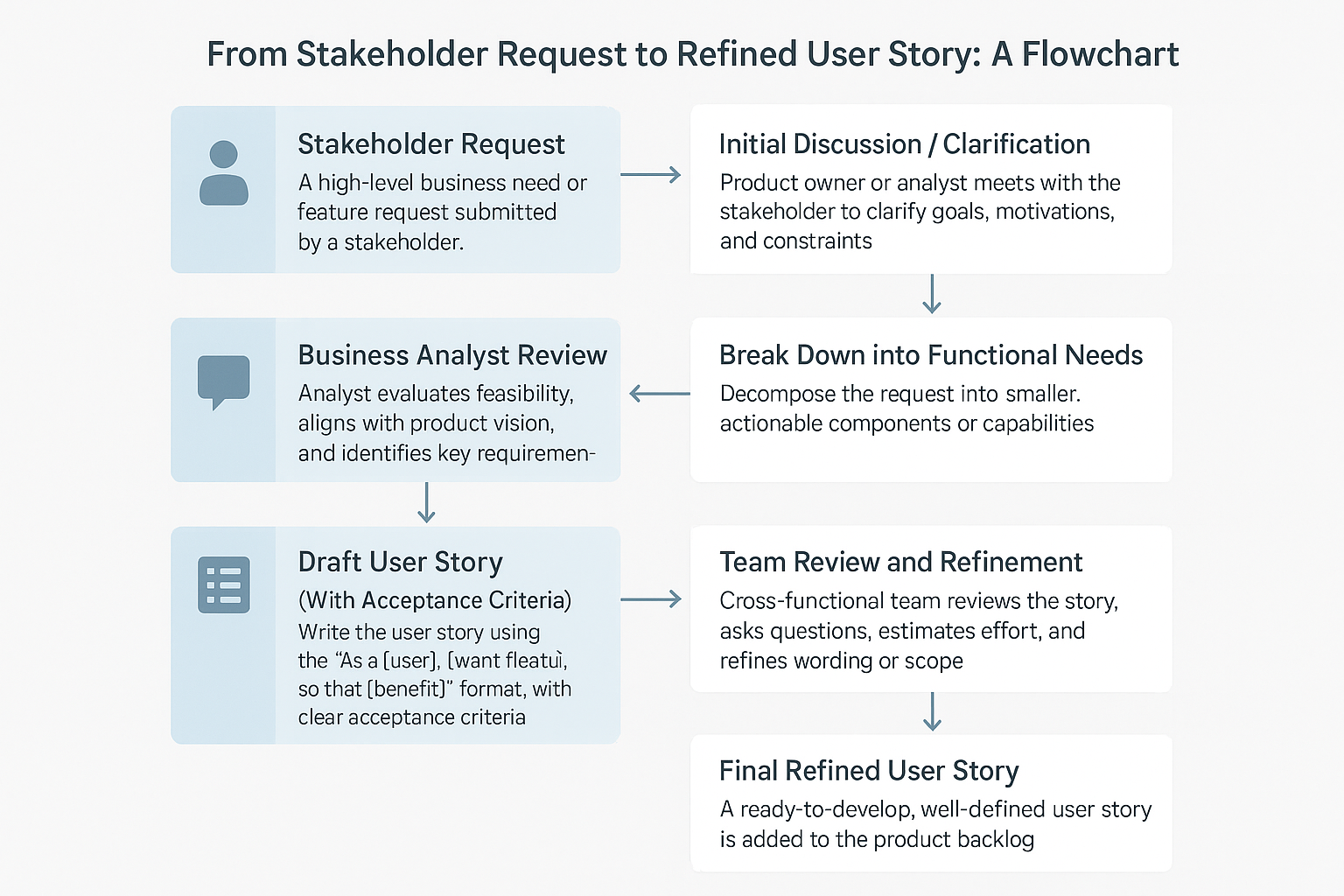
The INVEST Checklist: Your Go-To for User Story Quality
Ever feel like you’re not sure if a user story is good enough? The INVEST model can help. Here’s what each letter stands for and how you can apply it without getting bogged down in jargon:
| I |
N |
V |
E |
S |
T |
| Independent: Can this story stand on its own? |
Negotiable: Are we allowed to discuss and reshape it as we learn? |
Valuable: Will it deliver something users (or the business) care about? |
Estimable: Can the team size it up without endless debate? |
Small: Is it bite-sized enough to finish in one sprint? |
Testable: Could QA (or anyone) clearly say, Yes, we did this? |
Example:
As a user, I want to log my daily medication so I can track my health.
- Independent? Yes.
- Negotiable? Maybe we want more tracking options later.
- Valuable? Absolutely better health tracking.
- Estimable? Team can give a quick point estimate.
- Small? Just daily logging for now, not reminders.
- Testable? The log appears in the user’s history.
Why it matters:
Teams using INVEST avoid that all-too-common pain of stories that are either too tangled (But that depends on this other feature) or too fuzzy ( Did we really finish it? ).
User Stories, Tasks, and Requirements: Untangling the Mess
If you’re new to Agile, or even if you’re not, these words get tossed around a lot. Here’s a quick cheat sheet:
- User Story: A short description of what the user wants and why. The big picture.
Ex: As a caregiver, I want to assign a task to another family member so we can share responsibilities.
- Task: The building blocks or steps needed to turn that story into reality.
Ex: Design the UI for task assignment, code the backend API, add tests…
- Requirement: The nitty-gritty rules or constraints your system must follow.
Ex: Only assign tasks to users in the same group, Audit all changes for six months, Supports mobile and tablet.
How to use this:
Start with user stories to frame the why. Break them down into tasks for the how. Lean on requirements for the rules and edge cases.
Writing Great User Stories: How to Get the Goldilocks Level of Detail
Here’s the balancing act:
- Too vague? Everyone will interpret it differently. Chaos ensues.
- Too detailed? You risk stifling innovation or drowning in minutiae.
Here’s what works (in the real world):
- Stay user-focused:
As a [user], I want [goal] so that [benefit]. Always ask yourself: Would the real user recognize themselves in this story?
- Skip the tech for now:
The “how” is for planning sessions and tech spikes. The story itself is about need.
- Set clear acceptance criteria:
What does “done” look like? Write a checklist.
- Give just enough context:
If there are relevant workflows, mention them but keep it snappy.
- Save the edge cases:
Let your main story cover the core path. Put exceptions in separate stories.
Well-balanced story example:
As a caregiver, I want to assign a recurring task to a family member so that I can automate reminders for ongoing responsibilities.
Acceptance Criteria:
- The user can select “recurring” when creating a task
- Choose how often: daily, weekly, or monthly
- Assigned user gets reminders automatically
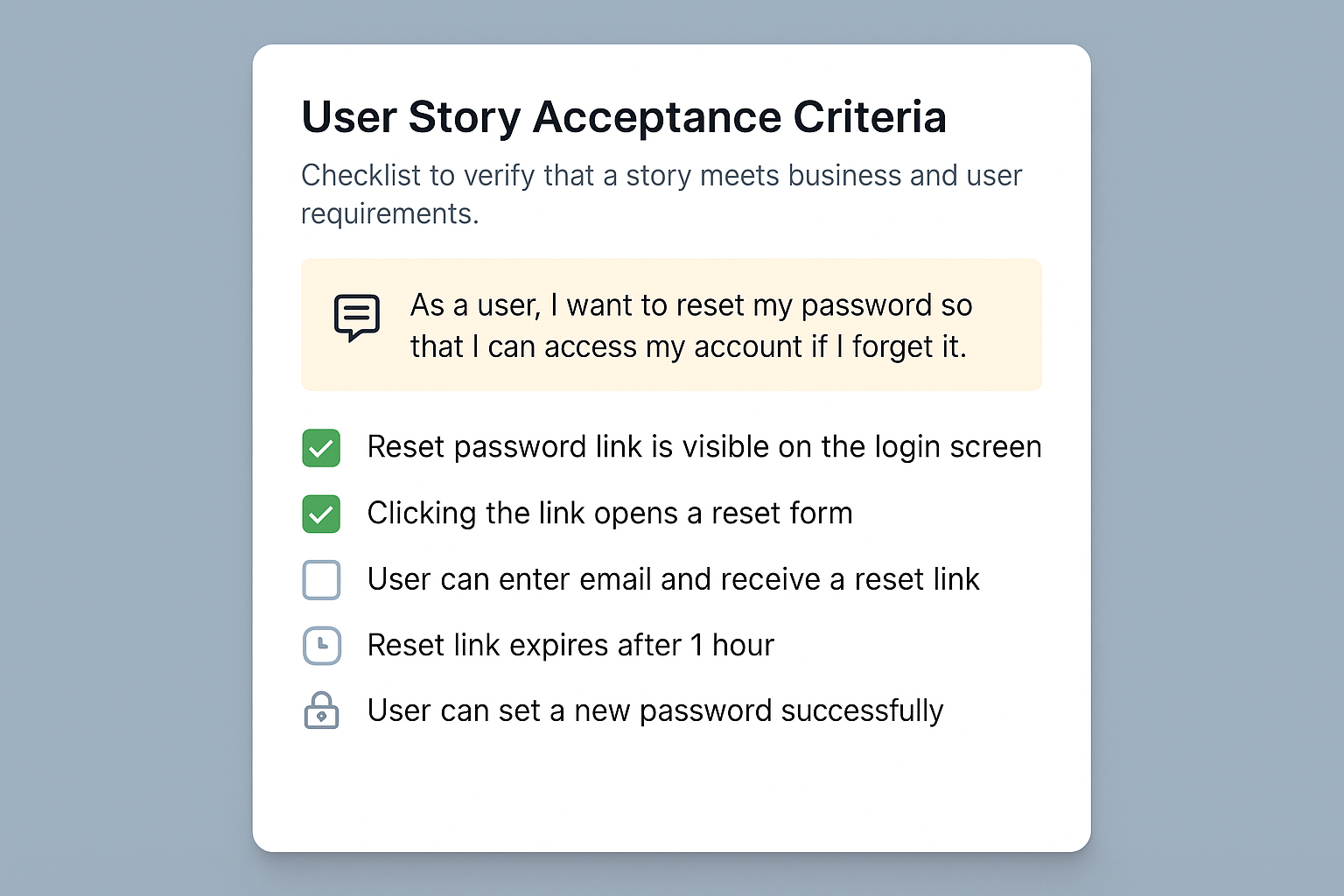
A Relatable Example: When User Stories Make All the Difference
Let’s say you’re building a health app. During a sprint review, a nurse on the team says, We really need a way to track each patient’s medication.You turn that need into: As a nurse, I want to log each patient’s medication so I can ensure adherence to treatment. Through team discussion, QA adds testable criteria and devs note integration needs. The story quickly moves from a wish list to something meaningful, testable, and, most importantly, useful in the real world.
Quick-Glance Table: Why Great User Stories Matter
| Sno |
Benefit |
Why Your Team Will Thank You |
| 1 |
Focuses everyone on user needs |
Features actually get used |
| 2 |
Improves estimates and planning |
No more surprise work mid-sprint |
| 3 |
Boosts cross-team communication |
Fewer meetings, more clarity |
| 4 |
Prevents rework and misunderstandings |
Less frustration, faster delivery |
| 5 |
Ensures testability and value |
QA and users both win |
| 6 |
Adapts easily to changing needs |
Your team stays agile literally |
Sample Code Snippet: User Story as a Jira Ticket
Title: Allow recurring tasks for caregivers
Story:
As a caregiver, I want to assign a recurring task to a family member so that I can automate reminders for ongoing responsibilities.
Acceptance Criteria:
- User can select “recurring” when creating a task
- Frequency options: daily, weekly, monthly
- Assigned user receives automated reminders
Conclusion: Take Your User Stories and Product to the Next Level
Writing great user stories isn’t just about following a template; it’s about fostering a culture of empathy, clarity, and collaboration. By focusing on real user needs, adhering to proven criteria like INVEST, and keeping stories actionable and testable, you empower your Agile team to deliver high-value software faster and with greater confidence. Partners like Codoid, with expertise in Agile testing and behavior-driven development (BDD), can help ensure your user stories are not only well-written but also easily testable and aligned with real-world outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What makes a user story different from a requirement?
User stories are informal, user-focused, and designed to spark discussion. Requirements are formal, detailed, and specify what the system must do—including constraints and rules.
-
How detailed should a user story be?
Enough to explain what’s needed and why, without dictating the technical implementation. Add acceptance criteria for clarity, but leave the “how” to the team.
-
Can developers write user stories?
Yes! While product owners typically own the process, developers, testers, and other team members can suggest or refine stories to add technical or practical insights.
-
What is the best way to split large user stories?
Break them down by workflow, user role, or acceptance criteria. Ensure each smaller story still delivers independent, testable value.
-
How do I know if my user story is “done”?
If it meets all acceptance criteria, passes testing, and delivers the intended value to the user, it’s done.
-
Should acceptance criteria be part of every user story?
Absolutely. Clear acceptance criteria make stories testable and ensure everyone understands what success looks like.
by Rajesh K | Jul 14, 2025 | Software Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
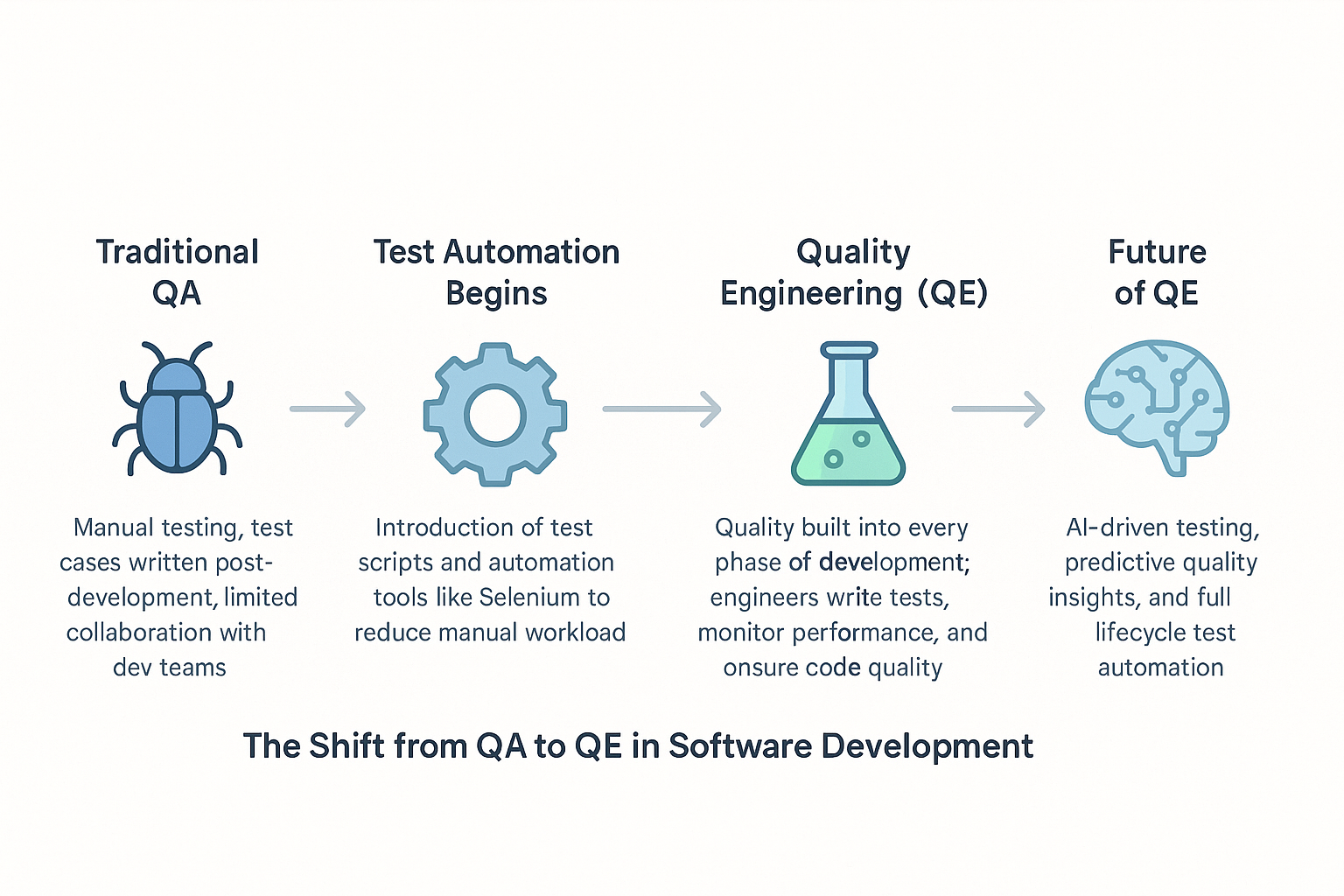
In the dynamic world of software development, the roles of Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Engineering (QE) have become increasingly significant. Although often used interchangeably, QA and QE represent two distinct philosophies and approaches to ensuring software quality. Understanding the difference between QA vs QE isn’t just a matter of semantics; it’s a strategic necessity that can impact product delivery timelines, customer satisfaction, and organizational agility. Quality Assurance has traditionally focused on maintaining standards and preventing defects through structured processes. In contrast, Quality Engineering emphasizes continuous improvement, leveraging automation, integration, and modern development methodologies to ensure quality is built into every stage of the development lifecycle.
As the demand for robust, reliable software grows, the pressure on development teams to produce high-quality products quickly has never been greater. This shift has led to the evolution from traditional QA to modern QE, prompting organizations to rethink how they define and implement quality.
This comprehensive guide will explore:
- Definitions and distinctions between QA and QE
- Historical evolution of both roles
- Key principles, tools, and methodologies
- How QA and QE impact the software development lifecycle
- Real-world applications and use cases
- Strategic advice for choosing and balancing both
Whether you’re a QA engineer looking to future-proof your skills or a tech lead deciding how to structure your quality teams, this post will provide the clarity and insights you need.
What is Quality Assurance (QA)?
Quality Assurance is a systematic approach to ensuring that software meets specified requirements and adheres to predefined quality standards. QA focuses on process-oriented activities that aim to prevent defects before they reach the end-user.
Key Objectives of QA:
- Detect and prevent defects early
- Ensure compliance with standards and regulations
- Improve the development process through audits and reviews
- Enhance customer satisfaction
Core Practices:
- Manual and automated test execution
- Risk-based testing
- Test case design and traceability
- Regression testing
Real-life Example: Imagine launching a healthcare application. QA processes ensure that critical features like patient data entry, billing, and compliance logging meet regulatory standards before deployment.
What is Quality Engineering (QE)?
Quality Engineering takes a broader and more proactive approach to software quality. It integrates quality checks throughout the software development lifecycle (SDLC), using automation, CI/CD pipelines, and collaboration across teams.
Key Objectives of QE:
- Embed quality throughout the SDLC
- Use automation to accelerate testing
- Foster continuous improvement and learning
- Improve time-to-market without compromising quality
Core Practices:
- Test automation and framework design
- Performance and security testing
- CI/CD integration
- Shift-left testing and DevOps collaboration
Example: In a fintech company, QE engineers automate tests for real-time transaction engines and integrate them into the CI pipeline. This ensures each code change is instantly verified for performance and security compliance.
A Historical Perspective: QA to QE
Origins of QA
QA finds its roots in manufacturing during the Industrial Revolution, where early pioneers like Frederick Winslow Taylor introduced methods to enhance production quality. It later evolved into statistical quality control and eventually into Total Quality Management (TQM).
Rise of QE
As software complexity increased, the need for more adaptive and continuous approaches led to the rise of QE. Emerging technologies like machine learning, cloud computing, and containerization demanded real-time testing and feedback mechanisms that QA alone couldn’t deliver.
Transitioning to QE allowed teams to scale testing, support agile methodologies, and automate redundant tasks.
QA vs QE: What Sets Them Apart?
| S. No |
Aspect |
Quality Assurance (QA) |
Quality Engineering (QE) |
| 1 |
Primary Focus |
Process consistency and defect prevention |
Continuous improvement and test automation |
| 2 |
Approach |
Reactive and checklist-driven |
Proactive and data-driven |
| 3 |
Testing Methodology |
Manual + limited automation |
Automated, integrated into CI/CD |
| 4 |
Tools |
ISO 9001, statistical tools |
Selenium, Jenkins, TestNG, Cypress |
| 5 |
Goal |
Ensure product meets requirements |
Optimize the entire development process |
| 6 |
Team Integration |
Separate from dev teams |
Embedded within cross-functional dev teams |
Methodologies and Tools
QA Techniques:
- Waterfall testing strategies
- Use of quality gates and defect logs
- Functional and non-functional testing
- Compliance and audit reviews
QE Techniques:
- Agile testing and TDD (Test-Driven Development)
- CI/CD pipelines with automated regression
- Integration with DevOps workflows
- Machine learning for predictive testing
How QA and QE Impact the SDLC
QA’s Contribution:
- Maintains documentation and traceability
- Ensures final product meets acceptance criteria
- Reduces production bugs through rigorous test cycles
QE’s Contribution:
- Reduces bottlenecks via automation
- Promotes faster delivery and frequent releases
- Improves developer-tester collaboration
Use Case: A SaaS startup that transitioned from traditional QA to QE saw a 35% drop in production defects and reduced release cycles from monthly to weekly.
Team Structures and Roles
QA Team Roles:
- QA Analyst: Designs and runs tests
- QA Lead: Manages QA strategy and reporting
- Manual Tester: Conducts exploratory testing
QE Team Roles:
- QE Engineer: Builds automation frameworks
- SDET (Software Development Engineer in Test): Writes code-level tests
- DevOps QA: Monitors quality metrics in CI/CD pipelines
Choosing Between QA and QE (Or Combining Both)
While QA ensures a strong foundation in risk prevention and compliance, QE is necessary for scalability, speed, and continuous improvement.
When to Choose QA:
- Regulatory-heavy industries (e.g., healthcare, aviation)
- Projects with fixed scopes and waterfall models
When to Embrace QE:
- Agile and DevOps teams
- High-release velocity environments
- Need for frequent regression testing
Ideal Approach: Combine QA and QE
- Use QA for strategic oversight and manual validations
- Use QE to drive test automation and CI/CD integration
Conclusion: QA vs QE Is Not a Battle It’s a Balance
As software development continues to evolve, so must our approach to quality. QA and QE serve complementary roles in the pursuit of reliable, scalable, and efficient software delivery. The key is not to choose one over the other, but to understand when and how to apply both effectively. Organizations that blend the disciplined structure of QA with the agility and innovation of QE are better positioned to meet modern quality demands. Whether you’re scaling your automation efforts or tightening your compliance protocols, integrating both QA and QE into your quality strategy is the path forward.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Is QE replacing QA in modern development teams?
No. QE is an evolution of QA, not a replacement. Both roles coexist to support different aspects of quality.
-
Can a QA professional transition to a QE role?
Absolutely. With training in automation, CI/CD, and agile methodologies, QA professionals can successfully move into QE roles.
-
Which role has more demand in the industry?
Currently, QE roles are growing faster due to the industry's shift toward DevOps and agile. However, QA remains essential in many sectors.
-
What skills are unique to QE?
Automation scripting, familiarity with tools like Selenium, Jenkins, and Docker, and understanding of DevOps pipelines.
-
How do I know if my organization needs QA, QE, or both?
Evaluate your current development speed, defect rates, and regulatory needs. If you're aiming for faster releases and fewer bugs, QE is essential. For process stability, keep QA.

by Rajesh K | Jul 11, 2025 | Software Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
In the fast-paced world of software development, teams are expected to deliver high-quality products quickly, often under shifting requirements. Enter Test Driven Development in Agile, a software testing strategy that flips traditional coding on its head by writing tests before the actual code. This preemptive approach ensures that every new feature is verified from the start, resulting in fewer bugs, faster feedback loops, and more maintainable code. TDD is especially powerful within Agile frameworks, where iterative progress, continuous feedback, and adaptability are core principles. By integrating software testing into the early stages of development, teams stay aligned with business goals, stakeholders are kept in the loop, and the software evolves with greater confidence and less rework.
But adopting TDD is more than just writing tests; it’s about transforming your development culture. Whether you’re a QA lead, automation tester, or product owner, understanding how TDD complements Agile can help you deliver robust applications that meet customer needs and business goals.
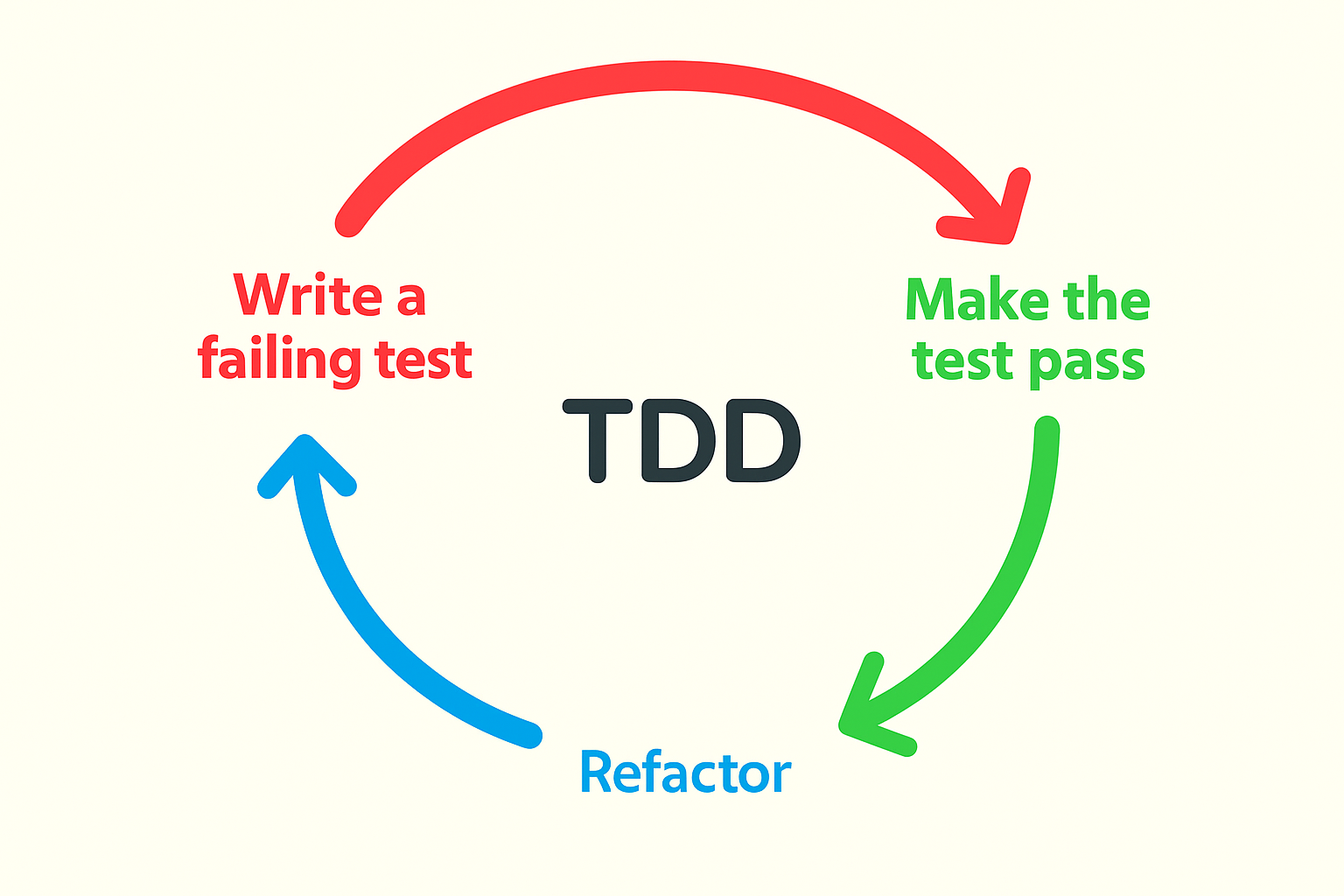
What is Test Driven Development (TDD)?
Test Driven Development (TDD) is a development methodology where tests are written before the actual code. This ensures that each unit of functionality is driven by specific requirements, resulting in focused, minimal, and testable code.
Core Principles of TDD:
- Write a test first for a new feature.
- Run the test and watch it fail (Red).
- Write just enough code to pass the test (Green).
- Refactor the code to improve the design while keeping tests green.
This process, known as the Red-Green-Refactor cycle, is repeated for every new feature or function.
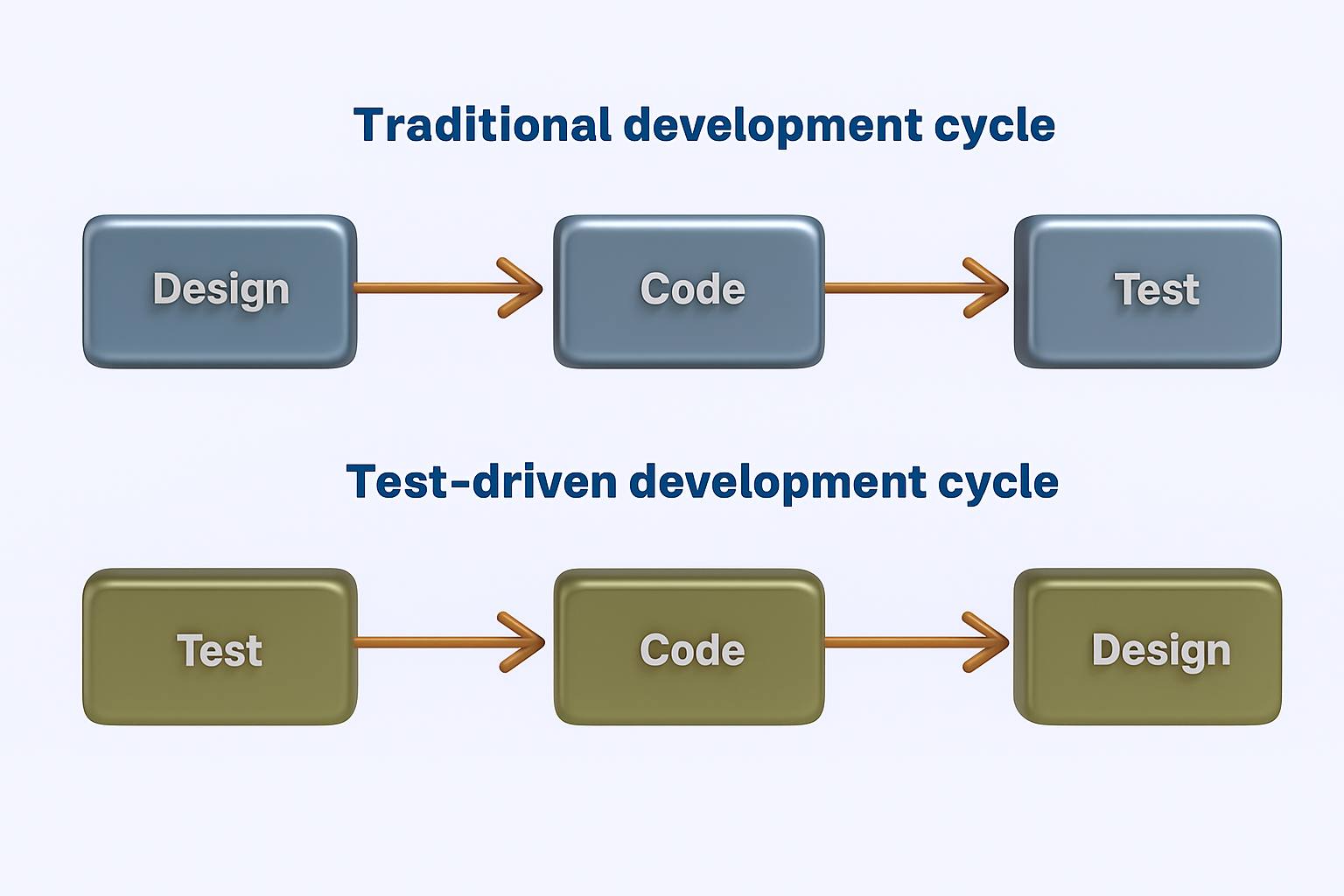
The Red-Green-Refactor Cycle Explained
Here’s a quick breakdown of how this loop works:
- Red: Write a unit test for a specific behavior. It should fail because the behavior doesn’t exist yet.
- Green: Write the minimum code necessary to make the test pass.
- Refactor: Clean up the code while keeping all tests passing.
This tight loop ensures fast feedback, minimizes overengineering, and leads to cleaner, more reliable code.
How TDD Integrates with Agile Methodologies
Agile promotes adaptability, transparency, and continuous delivery. TDD aligns perfectly with these values by embedding quality checks into each sprint and ensuring features are verified before they’re shipped.
TDD Enables Agile by:
- Ensuring code quality in short iterations
- Offering real-time validation of features
- Empowering cross-functional collaboration
- Supporting continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) pipelines
Example:
During a sprint, a development team writes tests based on the acceptance criteria of a user story. As they develop the functionality, the passing tests confirm adherence to requirements. If the criteria change mid-sprint, modifying tests keeps the team aligned with new priorities.
Key Benefits of TDD in Agile Teams
| S. No |
Benefit |
How It Helps Agile Teams |
| 1 |
Higher Code Quality |
Prevents bugs through test-first development |
| 2 |
Faster Feedback |
Reduces cycle time with instant test results |
| 3 |
Better Collaboration |
Shared understanding of feature requirements |
| 4 |
Safe Refactoring |
Enables confident changes to legacy code |
| 5 |
Improved Maintainability |
Modular, testable code evolves easily |
| 6 |
Supports Continuous Delivery |
Automated tests streamline deployment |
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
- Inadequate Test Coverage
Problem: Over-focus on unit tests might ignore system-level issues.
Solution: Complement TDD with integration and end-to-end tests.
- Initial Slowdown in Development
Problem: Writing tests first can feel slow early on.
Solution: ROI comes with time through reduced bugs and maintenance.
- Skill Gaps
Problem: Teams may lack test writing experience.
Solution: Invest in training and pair programming.
- Balancing Coverage and Speed
Focus on:
- High-risk areas
- Edge cases
- Critical user flows
Best Practices for Effective TDD in Agile
- Start Small: Begin with simple units before scaling to complex logic.
- Use the Inside-Out Approach: Write core logic tests before peripheral ones.
- Maintain Clean Test Code: Keep tests as clean and readable as production code.
- Document Test Intent: Comment on what the test verifies and why.
- Review and Refactor Tests: Don’t let test code rot over time.
Tools and Frameworks to Support TDD
| S. No |
Stack |
Frameworks |
CI/CD Tools |
| 1 |
Java |
JUnit, TestNG |
Jenkins, GitLab CI |
| 2 |
.NET |
NUnit, xUnit |
Azure DevOps, TeamCity |
| 3 |
JavaScript |
Jest, Mocha |
GitHub Actions, CircleCI |
| 4 |
Python |
PyTest, unittest |
Travis CI, Bitbucket Pipelines |
Advanced TDD Strategies for Scaling Teams
- Automate Everything: Integrate testing in CI pipelines for instant feedback.
- Mock External Systems: Use mocks or stubs for APIs and services to isolate units.
- Measure Test Coverage: Aim for 80–90%, but prioritize meaningful tests over metrics.
- Test Data Management: Use fixtures or factories to handle test data consistently.
Real-World Example: TDD in a Sprint Cycle
A product team receives a user story to add a “Forgot Password” feature.
Sprint Day 1:
QA and dev collaborate on writing tests for the expected behavior.
Tests include: email input validation, error messaging, and token generation.
Sprint Day 2–3:
Devs write just enough code to pass the tests.
Refactor and push code to CI. Tests pass.
Sprint Day 4:
Stakeholders demo the feature using a staging build with all tests green.
Outcome:
- No bugs.
- Code was released with confidence.
- Stakeholders trust the process and request more TDD adoption.
Conclusion
Test Driven Development in agile is not just a technical methodology; it’s a mindset shift that helps Agile teams deliver more reliable, maintainable, and scalable software. By placing testing at the forefront of development, TDD encourages precision, accountability, and collaboration across roles. It supports the core Agile values of responsiveness and continuous improvement, enabling teams to produce functional code with confidence. Whether you’re starting small or scaling enterprise-wide, implementing TDD can lead to significant improvements in your software quality, team efficiency, and stakeholder satisfaction. Start embedding TDD in your Agile workflow today to future-proof your development process.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the biggest advantage of TDD in Agile?
The biggest advantage is early bug detection and confidence in code changes, which aligns with Agile’s goal of fast, reliable delivery.
-
How much time should be spent on writing TDD tests?
Typically, 20–30% of development time should be reserved for writing and maintaining tests.
-
Is TDD suitable for large and complex applications?
Yes, especially when combined with integration and end-to-end testing. It helps manage complexity and enables safer refactoring.
-
Can TDD slow down initial development?
It might initially, but over time, it leads to faster and more stable releases.
-
What skills do developers need for TDD?
Strong knowledge of testing frameworks, good design practices, and experience with version control and CI/CD tools.

by Rajesh K | Jun 18, 2025 | Software Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
If software projects still followed a “code everything first, test at the end” model, modern teams would be drowning in last-minute bugs, missed launch dates, and emergency hot-fixes. Customers have little patience for broken features, and competitors ship improvements weekly sometimes daily. To keep pace, engineering leaders have embraced Shift Left Testing: moving software testing activities as far left on the project timeline as possible and running them continuously. Rooted in shift left testing principles, the idea is simple but powerful: find and fix defects while they are cheap and easy to fix, not after they have spread across the codebase or reached production. Studies show that a bug caught during development can cost up to thirty times less to remedy than the same bug discovered in production. Fixing it sooner also prevents domino-effect rework that can derail sprint commitments.
Shift Left isn’t only about cost; it changes culture. Developers and QA engineers collaborate from day one, agree on acceptance criteria, and build automated tests alongside the code. Testing stops being a painful gate at the end instead, it becomes a routine quality pulse that guides design choices and safeguards continuous delivery. Done well, Shift Left delivers three wins at once: higher product quality, faster release cycles, and lower overall cost. This guide explains how it works, which tests must run earliest, and how you can roll out a Shift Left strategy that sticks.
What Is Shift Left Testing?
Shift Left Testing means planning, designing, and executing tests earlier in the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) instead of waiting until coding is “finished.” The typical waterfall flow places requirements on the far left and testing on the far right. By “shifting left,” you embed testing tasks unit tests, integration checks, static analysis, security scans within each development stage.
Core principles include:
- Early Involvement – Include testing considerations in the initial requirements and design phases. Testers should collaborate with product owners and developers when user stories and features are being defined. By doing this, teams can spot ambiguity or potential problem areas up front and design better solutions. When developers write code, they already know the test cases and quality criteria it needs to satisfy.
- Continuous Testing – Make testing a continuous activity at every stage of development, not just a one-time phase . Every code change or build should trigger tests from unit tests to integration and even exploratory tests so that immediate feedback is available. This continuous feedback loop ensures any new bug is caught quickly, long before it can affect later stages . (For more on continuous testing in practice, read our Continuous Testing in DevOps guide (internal link).)
- Extensive Automation – Embrace automation to execute tests rapidly and repeatedly. Automated tests (unit, API, regression suites, etc.) can run in parallel with development, providing instant alerts if something breaks . Automation is crucial for Shift Left because it supports the high frequency of tests (especially in a CI/CD pipeline) without slowing down the team. It also frees up human testers to focus on complex scenarios and exploratory testing.
- Collaboration and Shared Ownership – Break down silos between developers, QA, and operations. Everyone is responsible for quality. Developers are encouraged to write and run unit tests and integration tests, while testers might get involved in reviewing code or designing test cases during development. This overlap fosters a “whole team” approach to quality where issues can be discussed and resolved collaboratively in real time . In Agile terms, think of it as turning QA into Quality Engineering (QE) – quality is built into the product with active contribution from all roles, rather than tested in at the end.
The outcome? Defects are prevented or caught right after they appear, long before they cause schedule slips or reach customers.
Shift Left vs. Traditional Testing (Comparison Table)
One of the best ways to understand the impact of Shift Left Testing is to compare it with a traditional testing approach. In conventional (waterfall-style) development, testing happens late often after all development is complete. In a Shift Left approach, testing happens early and throughout development. The biggest differences lie in when testing occurs, who is involved, and why it’s done. The table below summarizes the key differences between Traditional Testing and Shift Left Testing:
| S. No |
Aspect |
Traditional Testing (Test Late) |
Shift Left Testing (Test Early & Often) |
| 1 |
When Testing Occurs |
Primarily at the end of the SDLC (after development is finished). |
Throughout the SDLC, starting from requirements/design stages . Early tests (unit, integration) run in each iteration. |
| 2 |
Approach to Quality |
Reactive find and fix bugs right before release. Quality checks are a final gate. |
Proactive prevent and catch defects early. Quality is built-in from the beginning as part of design and coding. |
| 3 |
Team Involvement |
QA testers are mostly involved at the end. Little developer involvement in testing; silos between dev and test teams. |
Whole-team involvement. Developers, QA, and even Ops collaborate on testing from day one . Developers write tests, testers partake in requirements and design discussions. |
| 4 |
Tools & Automation |
Often relies on manual testing and separate QA environments towards project end. Automation may be minimal or late. |
Heavy use of test automation and CI/CD pipeline integration for continuous tests. Testing tools are in place from the start (unit testing frameworks, CI build checks, etc.). |
| 5 |
Defect Detection |
Bugs are found late, potentially after they’ve impacted large portions of code. Late defects often cause project delays and expensive fixes. |
Bugs are caught early, in small code units or components . This minimizes the impact and cost of defects, preventing late-stage surprises. |
| 6 |
Cost & Time Impact |
Higher cost of fixes (defects discovered at end might require major rework) and longer time to market . A bug found just before release can derail schedules. |
Lower cost of fixes (issues are resolved when easier/cheaper to fix ) and faster delivery. Few last-minute issues means ontime releases with less firefighting. |
As shown above, traditional testing defers quality checks to the “extreme right” of the timeline, whereas shift-left testing pushes them to the “left” (early stages) . In a traditional model, if testers find a critical bug at the end, the software must loop back to developers, causing delays and cost overruns . Shift Left flips this scenario: by testing early, issues are discovered when they’re smaller and easier to fix, so development can continue smoothly. In fact, it’s often said that “the difference lies in when the testing happens and why” shift-left aims to prevent issues early, whereas late testing often ends up just documenting issues after the fact.
To illustrate, consider how each approach handles a new feature. In a traditional process, developers might build the entire feature over weeks, then hand it to QA. QA finds bugs that send the feature back for rework, leading to surprise delays. In a shift-left approach, QA and dev work together from the start testers help define acceptance criteria, developers write unit tests as they code, and small increments are tested immediately. The feature is validated continuously, so by the time it’s “done,” there are no major surprises. This leads to fewer late-stage defects and a more predictable timeline. As a result, teams that shift left can deliver features faster without sacrificing quality, while traditional approaches often struggle with long test fix cycles toward the end of projects.
Benefits of Shifting Left: Why Test Early?
Adopting Shift Left Testing principles brings a host of tangible benefits to software teams and businesses. By catching issues sooner and baking quality into the process, organizations can achieve faster delivery, lower costs, and better products. Here are some key benefits of shifting left:
- Early Defect Detection & Prevention: The primary benefit is finding bugs earlier in the development process, which makes them much easier and cheaper to fix . Developers can address issues in their code before it integrates with larger systems, preventing small bugs from snowballing into major problems. Early testing essentially prevents defects from ever reaching production. As a result, teams avoid the nightmare of discovering critical issues right before a release or (worse) in front of customers. One study notes that fixing a bug during development could cost 30x less than fixing it in production so early bug detection has a huge ROI.
- Lower Costs & Less Rework: Because defects are caught when they’re simpler to resolve, the cost of quality issues drops dramatically. There’s less need for expensive, last-minute project rework or emergency patches. For example, if a security vulnerability in a payment app is only discovered after release, the company must spend significant time and money on hotfixes, customer support, and possibly downtime losses expenses that would have been far lower if the issue was caught earlier. By shifting left, teams fix bugs when they’re introduced (often in a single module or during a build) rather than refactoring broad swaths of completed work. This reduces the risk of project overruns and protects the budget. (One report even estimates network outage costs at $5,600 per minute reinforcing how critical early issue prevention can be.)
- Faster Time-to-Market: Shifting left can accelerate development cycles and delivery of features. It’s simple: when you start testing earlier, you uncover and address obstacles sooner, which means fewer delays later. Teams that integrate continuous testing report significantly shorter intervals between releases. Instead of a long test-fix period at the end, issues are resolved on the fly. This leads to a smoother, more parallel workflow where development and testing happen concurrently. Ultimately, features get to market faster because there’s no waiting on a big testing phase or extensive bugfix cycle at the end. As the saying goes, “the sooner you start, the sooner you finish” early bug fixing means you don’t pay for those bugs with added time before release . Many organizations have found that shifting left helped them ship updates quickly and frequently without compromising quality.
- Higher Software Quality: When testing is ingrained throughout development, the end product’s quality naturally improves. Shift Left Testing principles brings rigorous and frequent quality checks at every stage, leading to more stable and polished software . Issues are not only fixed earlier but also often found before code is merged, resulting in cleaner architecture and codebase. This proactive approach yields fewer defects escaping to production and a stronger code foundation. Frequent testing also improves test coverage more of the code and use cases get tested than in a last- minute rush. The outcome is a high-quality application with minimal patches and hotfixes needed down the line , which means users encounter far fewer bugs. In short, shift-left principles help deliver a product that meets requirements and user expectations from day one.
- Improved Team Collaboration & Efficiency: Shift Left fosters a culture of collaboration that can make teams more efficient and effective. Developers and testers working together from the start means better communication, shared understanding, and faster feedback loops . Instead of throwing work “over the wall,” everyone stays on the same page regarding quality goals. This can boost developer morale and ownership as well – developers get quick feedback on their code and can be confident in making changes, knowing that continuous tests have their back . Testers, on the other hand, become proactive contributors rather than last-minute gatekeepers, often gaining more technical skills (like scripting or using automation tools) in the process. Overall, the team spends less time in blame or scramble mode and more time steadily improving the product. The shared responsibility for quality means issues are addressed by the right people at the right time, with less back-and-forth.
- Customer Satisfaction & Stakeholder Confidence: By enabling on-time delivery of a reliable, high-quality product, Shift Left Testing principles ultimately leads to happier customers and stakeholders . When releases go out with fewer bugs (especially critical ones), user experience improves and trust in the product grows. Additionally, being able to hit delivery timelines (because you’re not derailed by late defects) boosts the confidence of project managers and executives. They can plan releases more predictably and meet market commitments. In a B2B context, demonstrating a robust testing process that catches issues early can be a selling point clients have confidence that the software will be stable. All of this translates to better business outcomes, whether it’s higher customer retention, fewer support calls, or a stronger reputation for quality.
How to Implement Shift Left Testing (Best Practices)
Shifting your testing approach leftward requires more than just a mandate, it involves process changes, cultural shifts, and tooling upgrades. Here are some best practices and practical steps to implement Shift Left Testing principles in your team:
1.Foster a Collaborative “Quality Culture”:
Begin by breaking the mindset that testing is solely QA’s job. Encourage developers, testers, and product owners to work together on quality from the outset. Include testers in early-stage activities for example, have QA representatives attend requirements gathering and design meetings. This ensures potential test scenarios and pitfalls are considered early . Likewise, encourage developers to participate in test planning or review test cases. The goal is to create a culture where everyone feels responsible for the product’s quality. When communication flows freely between dev and QA, bugs are caught and addressed faster. (Remember: shifting left isn’t a tool or a single step – it’s a team mindset shift.)
2.Start Testing from Day One (Plan for Early Testing):
Don’t wait until code is complete to think about testing. As soon as requirements are defined, start formulating a test plan and test cases. For each new feature or user story, ask “How will we test this?” up front. Adopting practices like Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) or writing acceptance criteria for each story can help bake testing into the planning. Developers can also practice Test-Driven Development (TDD) writing unit tests for a function before writing the function itself. TDD ensures that coding is guided by testing goals and that every unit of code has associated tests from the very beginning. By planning and writing tests early, you create a safety net that catches regressions as development progresses.
3.Integrate Testing into CI/CD Pipelines:
A technical backbone of Shift Left Testing is a robust Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) setup with automated tests. Make sure your team has a CI system (like Jenkins, GitLab CI, etc.) where every code commit triggers a build and run of your test suite. Start with automated unit tests developers should write and maintain unit tests for their code and have them run on each commit. Then include integration tests, API tests, and other automated checks as appropriate for your application. The idea is that by the time code reaches later stages (staging or pre-production), it has already passed a gauntlet of tests from earlier stages. Integrating static code analysis tools for security and code quality into CI is also advisable (this performs a kind of “automated code review” every time code is pushed). A well- implemented CI pipeline will provide immediate feedback if a developer introduces a bug, the pipeline fails within minutes, and they can fix it before moving on. This keeps defects from accumulating. Essentially, continuous testing through CI/CD is what enables shift-left at scale: it’s how you test “early and often” in practice.
4.Leverage Test Automation & Tools:
Manual testing alone can’t keep up with the speed of modern development, especially when shifting left. Invest in good test automation tools and frameworks that fit your tech stack (e.g., JUnit or PyTest for unit tests, Selenium or Cypress for UI tests, Postman or RestAssured for API tests, etc.). Automation is crucial for running repetitive tests quickly. Aim to automate not just functional tests, but also regression tests and smoke tests that can run whenever new code is integrated. Automated tests ensure consistency and speed they’ll catch if a new code change breaks an existing feature within minutes, which is vital for early detection. Additionally, consider tools for test data management (so you have fresh, relevant test data for early testing) and environment virtualization (like using Docker containers or service virtualization to simulate parts of the system that aren’t built yet, allowing testing in isolation). The more you can automate and simulate, the earlier in the pipeline you can run meaningful tests. Tip: Start small by automating the highest value tests (e.g. critical user flows or core units) and expand coverage iteratively.
5.Implement Fast Feedback Loops:
The effectiveness of Shift Left depends on getting feedback to the right people quickly. Ensure that when tests fail or issues are found, the team knows right away. This could be as simple as configuring CI to send alerts on test failures or having dashboards that track test results in real time. It’s also a good practice to conduct regular code reviews and peer testing for instance, developers can review each other’s code for potential issues (a form of shifting quality checks left into the coding stage itself) and even write unit tests for each other’s modules. Consider scheduling short “bug bash” sessions early in development sprints where the team collectively tests new features in a development environment to flush out issues. The idea is to create tight feedback loops: find issues, fix, and learn from them quickly. This might also involve refining requirements when testers or developers identify unclear or conflicting requirements early on. Some teams incorporate shift-left principles by adopting tools that provide instant code feedback (like linters or static analyzers in the IDE, which highlight potential bugs or security vulnerabilities as code is written).
6.Train and Empower Team Members:
Shifting left may require new skills or knowledge, especially for teams used to siloed roles. Provide training for developers on writing good automated tests and using testing frameworks. Similarly, train QA engineers on the development process and basic coding so they can participate more deeply (for example, writing simple automated tests or scripts). Encourage a cross-functional skill development: testers who can read code and developers who understand testing theory will collaborate much more effectively. It can also help to designate “quality champions” or mentors on the team to support others in following shift-left practices. Remember that implementing shift-left is an iterative journey – start with pilot projects or specific areas where early testing could show immediate improvements, then share those wins to get buy-in from the rest of the organization.
By following these steps, teams can gradually move toward a full shift-left testing approach. It’s often helpful to measure your progress track metrics like defect rates in production vs. in development, time taken to resolve bugs, or the percentage of test coverage at different stages. Many organizations see improvements in all these metrics as they implement shift-left practices. Moreover, industry experts advise that key enablers for shift-left success are a supportive culture and proper tooling. Integrating security checks (shift-left security) alongside testing is another emerging best practice – this means running security scans and threat modeling early as well, to catch vulnerabilities when they’re easiest to fix.
In summary, implementing Shift Left Testing principles is about people, process, and tools. Get your team on board with the philosophy of early testing, adjust your development workflow to embed testing steps from the beginning, and use automation to support the increased testing frequency. With these in place, you’ll significantly reduce the pain of late-stage bug fixes and pave the way for continuous delivery of high- quality software.
Key Testing Types in a Shift-Left Strategy
| Hierarchy Level |
Testing Type |
Why It Belongs Early |
Mandatory? |
| Level 1 |
Unit Tests
Static Code Analysis / Linting |
Validate each function or class as code is written.
Spot style issues, security flaws, and code smells instantly. |
Yes – baseline |
| Level 2 |
Component / Integration Tests
API Contract Tests |
Ensure modules interact correctly and contracts hold.
Verify request/response formats as services evolve. |
Highly recommended |
| Level 3 |
Security Scans (Dependencies, Secrets)
Performance Micro-Benchmarks |
Catch CVEs and leaked credentials before merge.
Flag major regressions in critical code paths early. |
Recommended |
| Level 4 |
UI Smoke Tests |
Lightweight checks that core screens render and flows work. |
Optional in early stages |
Practical tip:
- Run Level 1 on every commit.
- Gate merges with Level 2.
- Schedule Level 3 nightly.
- Add Level 4 where rapid UI feedback is valuable.
Benefits of Shifting Left
- Early Defect Detection – Bugs surface minutes after code is written, not weeks later.
- Lower Fix Cost – Simple, localized changes beat large-scale rework.
- Faster Delivery – No giant “test/fix” crunch at the end; sprints finish on time.
- Higher Quality – Continuous checks raise overall stability and user trust.
- Better Team Morale – Developers and testers collaborate, avoiding blame games.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction – Fewer production incidents keep users happy.
Real-World Example
A fintech team built a new payment feature. Under their old process, QA found a critical security flaw two days before launch, delaying release by a week and costing thousands in fixes. After adopting Shift Left testing principles:
- QA joined requirement workshops and identified risky input scenarios.
- Developers wrote unit and API tests plus static-analysis checks from day one.
- CI ran these tests on each commit; a vulnerability scan flagged an unsafe dependency immediately.
- The issue was fixed the same afternoon—long before staging.
Result: The feature shipped on schedule with zero security incidents post-release, saving the company money and reputation.
Shift Left in Agile and DevOps
- Agile: Testing fits inside each sprint; the definition of “done” requires passing automated checks.
- DevOps: Continuous integration pipelines fail fast if any unit or integration test breaks.
- DevSecOps: Security scanning shifts left alongside functional tests, enabling early threat mitigation.
These methodologies rely on Shift Left to sustain rapid, reliable delivery.
Conclusion
Shift Left Testing is more than a trend; it’s a strategic approach to building quality from the start. By testing early in the software development life cycle (SDLC), teams catch issues sooner, reduce rework, and accelerate delivery. Rooted in shift left testing principles, it fosters a proactive quality culture, minimizes late-stage surprises, and supports faster, more reliable releases. Whether you’re using Agile, DevOps, or CI/CD, adopting shift-left principles empowers your team to deliver better software more quickly. It may require change, but the long-term gains in efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction are well worth it.
Test early, fix faster, and release with confidence.
.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What does “shift left” mean in testing?
It means moving testing tasks from late stages to early stages of development so defects are found quickly.
-
Why is shift-left important for Agile and DevOps teams?
Short sprints and continuous delivery need rapid feedback; early automated tests keep quality high without slowing releases.
-
Which tests are absolutely mandatory when shifting left?
Unit tests and static code analysis they form the first safety net for every code change.
-
Does shift-left remove the need for final-stage testing?
No. You still run end-to-end or user-acceptance checks, but far fewer surprises remain because most bugs were prevented early.