by Rajesh K | Sep 19, 2025 | Software Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
When a company builds software, like a mobile app or a website, it’s not enough to just write the code and release it. The software needs to work smoothly, be easy to use, and meet users’ expectations. That’s where software testing, specifically Alpha and Beta Testing, comes in. These are two critical steps in the software development lifecycle (SDLC) that help ensure a product is ready for the world. Both fall under User Acceptance Testing (UAT), a phase where the software is checked to see if it’s ready for real users. This article explains Alpha and Beta Testing in detail, breaking down what they are, who does them, how they work, their benefits, challenges, and how they differ, with a real-world example to make it all clear.
What Is Alpha Testing?
Alpha Testing is like a dress rehearsal for software before it’s shown to the public. It’s an early testing phase where the development team checks the software in a controlled environment, like a lab or office, to find and fix problems. Imagine you’re baking a cake—you’d taste it yourself before serving it to guests. Alpha Testing is similar: it’s done internally to catch issues before external users see the product.
This testing happens toward the end of the development process, just before the software is stable enough to share with outsiders. It uses two approaches:
- White-box testing: Testers look at the software’s code to understand why something might break (like checking the recipe if the cake tastes off).
- Black-box testing: Testers use the software as a user would, focusing on how it works without worrying about the code (like judging the cake by its taste and look).
Alpha Testing ensures the software is functional, stable, and meets the project’s goals before moving to the next stage.
Who Conducts Alpha Testing?
Alpha Testing is an internal affair, handled by people within the company. The key players include:
- Developers: These are the coders who built the software. They test their own work to spot technical glitches, like a feature that crashes the app.
- Quality Assurance (QA) Team: These are professional testers who run detailed checks to ensure the software works as expected. They’re like editors proofreading a book.
- Product Managers: They check if the software aligns with the company’s goals, such as ensuring a shopping app makes buying easy for customers.
- Internal Users: Sometimes, other employees (not developers) test the software by pretending to be real users, providing a fresh perspective.
For example, in a company building a fitness app, developers might test the workout tracker, QA might check the calorie counter, and a product manager might ensure the app feels intuitive.
Objectives of Alpha Testing
Alpha Testing has clear goals to ensure the software is on the right track:
- Find and Fix Bugs: Catch errors, like a button that doesn’t work or a page that freezes, before users see them.
- Ensure Functionality: Confirm every feature (e.g., a login button or a search tool) works as designed.
- Check Stability: Make sure the software doesn’t crash or slow down during use.
- Meet User Needs: Verify the software solves the problems it was built for, like helping users book flights easily.
- Prepare for Beta Testing: Ensure the software is stable enough to share with external testers.
Think of Alpha Testing as a quality checkpoint that catches major issues early, saving time and money later.
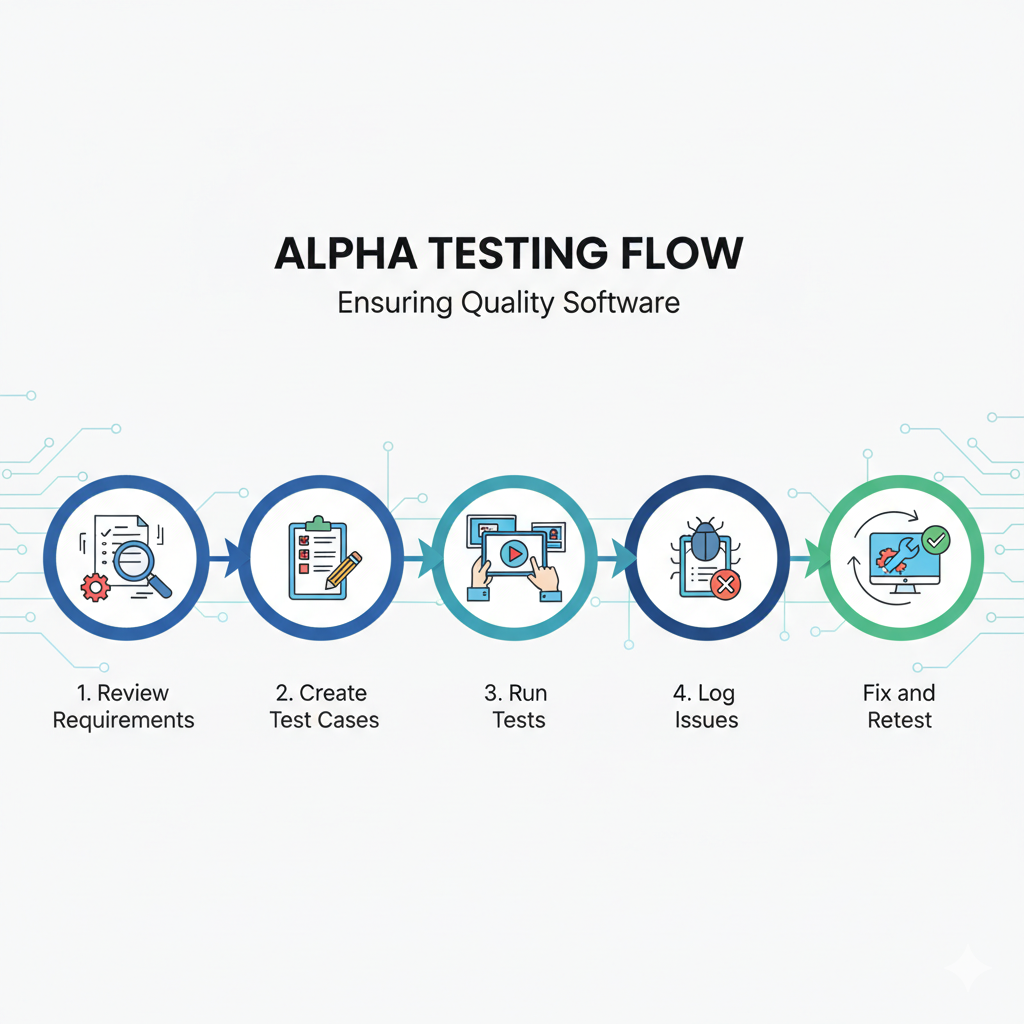
How Alpha Testing Works
Alpha Testing follows a structured process to thoroughly check the software:
- Review Requirements: The team looks at the project’s goals (e.g., “The app must let users save their progress”). This ensures tests cover what matters.
- Create Test Cases: Testers write detailed plans, like “Click the ‘Save’ button and check if data is stored.” These cover all features and scenarios.
- Run Tests: In a lab or controlled setting, testers use the software, following the test cases, to spot issues.
- Log Issues: Any problems, like a crash or a slow feature, are recorded with details (e.g., “App crashes when uploading a photo”).
- Fix and Retest: Developers fix the issues, and testers check again to confirm the problems are gone.
Phases of Alpha Testing
Alpha Testing is often split into two stages for efficiency:
- First Phase (Developer Testing): Developers test their own code using tools like debuggers to find obvious errors, such as a feature that doesn’t load. This is quick and technical, focusing on fixing clear flaws.
- Second Phase (QA Testing): The QA team takes over, testing the entire software using both white-box (code-level) and black-box (user-level) methods. They simulate user actions, like signing up for an account, to ensure everything works smoothly.
Benefits of Alpha Testing
Alpha Testing offers several advantages that make it essential:
- Catches Issues Early: Finding bugs in-house prevents bigger problems later, like a public app crash.
- Improves Quality: By fixing technical flaws, the software becomes more reliable and user-friendly.
- Saves Money: It’s cheaper to fix issues before release than to patch a live product, which might upset users.
- Gives Usability Insights: Internal testers can spot confusing features, like a poorly placed button, and suggest improvements.
- Ensures Goal Alignment: Confirms the software matches the company’s vision, like ensuring a travel app books hotels as promised.
- Controlled Environment: Testing in a lab avoids external distractions, making it easier to focus on technical details.
Challenges of Alpha Testing
Despite its benefits, Alpha Testing has limitations:
- Misses Real-World Issues: A lab can’t mimic every user scenario, like a weak internet connection affecting an app.
- Internal Bias: Testers who know the software well might miss problems obvious to new users.
- Time-Intensive: Thorough testing takes weeks, which can delay the project.
- Incomplete Software: Some features might not be ready, so testers can’t check everything.
- Resource-Heavy: It requires developers, QA, and equipment, which can strain small teams.
- False Confidence: A successful Alpha Test might make the team think the software is perfect, overlooking subtle issues.
What Is Beta Testing?
Beta Testing is the next step, where the software is shared with real users outside the company to test it in everyday conditions. It’s like letting a few customers try a new restaurant dish before adding it to the menu. Beta Testing happens just before the official launch and focuses on how the software performs in real-world settings, like different phones, computers, or internet speeds. It gathers feedback to fix final issues and ensure the product is ready for everyone.
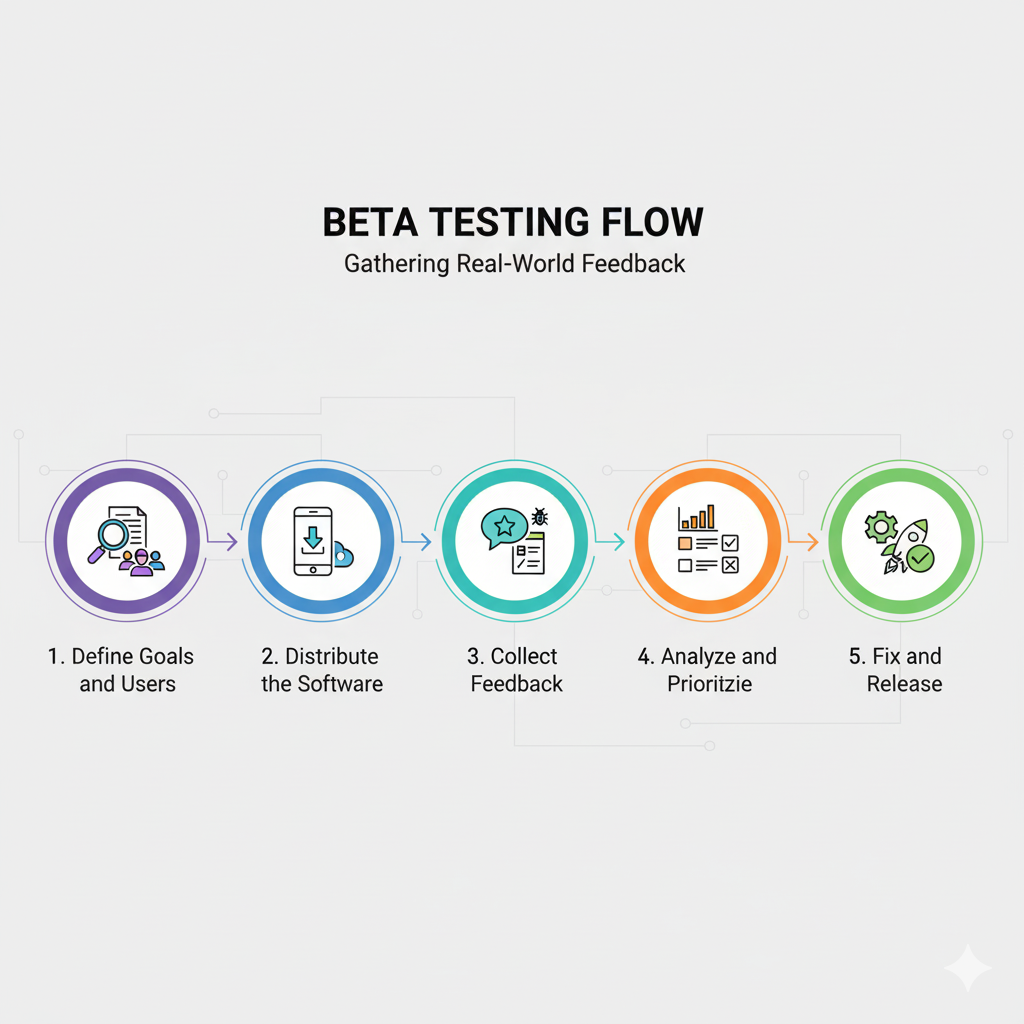
How Beta Testing Works
Beta Testing follows a structured process to thoroughly check the software:
- Define Goals and Users: First, you decide what you want to achieve with the beta test. Do you want to check for stability, performance, or gather feedback on new features? Then, you choose a group of beta testers. These are typically a small group of target users, either volunteers or people you select. For example, if you’re making a social media app for college students, you would recruit a group of students to test it.
- Distribute the Software: You provide the beta testers with the software. This can be done through app stores, a special download link, or a dedicated platform. It’s also important to give them clear instructions on what you want them to test and how to report issues.
- Collect Feedback: Beta testers use the software naturally in their own environment. They report any issues, bugs, or suggestions they have. This can be done through an in-app feedback tool, an online survey, or a dedicated communication channel.
- Analyse and Prioritise: You and your team collect all the feedback. You then analyse it to find common issues and prioritise which ones to fix. For example, a bug that makes the app crash for many users is more important to fix than a suggestion to change the colour of a button.
- Fix and Release: Based on the prioritised list, developers fix the most critical issues. After these fixes are implemented and re-tested, the product is ready for its final release to the public.
Why Is Beta Testing Important?
Beta Testing is vital for several reasons:
- Finds Hidden Bugs: Real users uncover issues missed in the lab, like a feature failing on older phones.
- Improves User Experience: Feedback shows if the software is easy to use or confusing, like a clunky checkout process.
- Tests Compatibility: Ensures the software works on different devices, browsers, or operating systems.
- Builds Customer Trust: Involving users makes them feel valued, increasing loyalty.
- Confirms Market Readiness: Verifies the product is polished and ready for a successful launch.
Characteristics of Beta Testing
Beta Testing has distinct traits:
- External Users: Done by customers, clients, or public testers, not company staff.
- Real-World Settings: Users test on their own devices and networks, like home Wi-Fi or a busy café.
- Black-Box Focus: Testers use the software like regular users, without accessing the code.
- Feedback-Driven: The goal is to collect user opinions on usability, speed, and reliability.
- Flexible Environment: No controlled lab users test wherever they are.
Types of Beta Testing
Beta Testing comes in different flavours, depending on the goals:
- Closed Beta Testing: A small, invited group (e.g., loyal customers) tests the software for targeted feedback. For example, a game company might invite 100 fans to test a new level.
- Open Beta Testing: The software is shared publicly, often via app stores, to get feedback from a wide audience. Think of a new app available for anyone to download.
- Technical Beta Testing: Tech-savvy users, like IT staff, test complex features, such as a software’s integration with other tools.
- Focused Beta Testing: Targets specific parts, like a new search feature in an app, to get detailed feedback.
- Post-Release Beta Testing: After launch, users test updates or new features to improve future versions.
Criteria for Beta Testing
Before starting Beta Testing, certain conditions must be met:
- Alpha Testing Complete: The software must pass internal tests and be stable.
- Beta Version Ready: A near-final version of the software is prepared for users.
- Real-World Setup: Users need access to the software in their normal environments.
- Feedback Tools: Systems (like surveys or bug-reporting apps) must be ready to collect user input.
Tools for Beta Testing
Several tools help manage Beta Testing and collect feedback:
- Ubertesters: Tracks how users interact with the app and logs crashes or errors.
- BetaTesting: Helps recruit testers and organizes their feedback through surveys.
- UserZoom: Records user sessions and collects opinions via videos or questionnaires.
- Instabug: Lets users report bugs with screenshots or notes directly in the app.
- Testlio: Connects companies with real-world testers for diverse feedback.
These tools make it easier to gather and analyse user input, ensuring no critical feedback is missed.
Uses of Beta Testing
Beta Testing serves multiple purposes:
- Bug Resolution: Finds and fixes issues in real-world conditions, like an app crashing on a specific phone.
- Compatibility Checks: Ensures the software works across devices, like iPhones, Androids, or PCs.
- User Feedback: Gathers opinions on ease of use, like whether a menu is intuitive.
- Performance Testing: Checks speed and responsiveness, such as how fast a webpage loads.
- Customer Engagement: Builds excitement and loyalty by involving users in the process.
Benefits of Beta Testing
Beta Testing offers significant advantages:
- Real-World Insights: Users reveal how the software performs in unpredictable settings, like spotty internet.
- User-Focused Improvements: Feedback helps refine features, making the product more intuitive.
- Lower Launch Risks: Fixing issues before release prevents bad reviews or crashes.
- Cost-Effective Feedback: Getting user input is cheaper than fixing a failed launch.
- Customer Loyalty: Involving users creates a sense of ownership and trust.
Challenges of Beta Testing
Beta Testing isn’t perfect and comes with hurdles:
- Unpredictable Environments: Users’ devices and networks vary, making it hard to pinpoint why something fails.
- Overwhelming Feedback: Sorting through many reports, some vague or repetitive, takes effort.
- Less Control: Developers can’t monitor how users test, unlike in a lab.
- Time Delays: Analyzing feedback and making fixes can push back the launch date.
- User Expertise: Some testers may not know how to provide clear, useful feedback.
Alpha vs. Beta Testing: Key Differences
| Sno |
Aspect |
Alpha Testing |
Beta Testing |
| 1 |
Who Does It |
Internal team (developers, QA, product managers) |
External users (customers, public testers) |
| 2 |
Where It Happens |
Controlled lab or office environment |
Real-world settings (users’ homes, devices) |
| 3 |
Testing Approach |
White-box (code-level) and black-box (user-level) |
Mostly black-box (user-level) |
| 4 |
Main Focus |
Technical bugs, functionality, stability |
Usability, real-world performance, user feedback |
| 5 |
Duration |
Longer, with multiple test cycles |
Shorter, often 1-2 cycles over a few weeks |
| 6 |
Issue Resolution |
Bugs fixed immediately by developers |
Feedback prioritized for current or future updates |
| 7 |
Setup Needs |
Requires lab, tools, and test environments |
No special setup; users’ devices suffice |
Case Study: A Real-World Example
Let’s look at FitTrack, a startup creating a fitness app to track workouts and calories. During Alpha Testing, their developers tested the app in-house on a lab server. They found a bug where the workout timer froze during long sessions (e.g., a 2-hour hike). The QA team also noticed that the calorie calculator gave wrong results for certain foods. These issues were fixed, and the app passed internal checks after two weeks of testing.
For Beta Testing, FitTrack invited 300 users to try the app on their phones. Users reported that the app’s progress charts were hard to read on smaller screens, and some Android users experienced slow loading times. The team redesigned the charts for better clarity and optimized performance for older devices. When the app launched, it earned a 4.7-star rating, largely because Beta Testing ensured it worked well for real users.
This case shows how Alpha Testing catches technical flaws early, while Beta Testing polishes the user experience for a successful launch.
Conclusion
Alpha and Beta Testing are like two sides of a coin, working together to deliver high-quality software. Alpha Testing, done internally, roots out technical issues and ensures the software meets its core goals. Beta Testing, with real users, fine-tunes the product by testing it in diverse, real world conditions. Both have challenges, like time demands in Alpha or messy feedback in Beta but their benefits far outweigh the drawbacks. By catching bugs, improving usability, and building user trust, these tests pave the way for a product that shines on launch day.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What’s the main goal of Alpha Testing?
Alpha Testing aims to find and fix major technical issues, like crashes or broken features, in a controlled setting before sharing the software with external users. It ensures the product is stable and functional.
-
Who performs Alpha Testing?
It’s done by internal teams, including developers who check their code, QA testers who run detailed tests, product managers who verify business goals, and sometimes internal employees acting as users.
-
What testing methods are used in Alpha Testing?
Alpha Testing uses white-box testing (checking the code to find errors) and black-box testing (using the software like a regular user) to thoroughly evaluate the product.
-
How is Alpha Testing different from unit testing?
Unit testing checks small pieces of code (like one function) in isolation. Alpha Testing tests the entire software system, combining all parts, to ensure it works as a whole in a controlled environment.
-
Can Alpha Testing make a product completely bug-free?
No, Alpha Testing catches many issues, but can’t cover every scenario, especially real-world cases like unique user devices or network issues. That’s why Beta Testing is needed.

by Rajesh K | Sep 16, 2025 | API Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
In today’s software, you will see that one task often needs help from more than one service. Have you ever thought about how apps carry out these steps so easily? A big part of the answer is API chaining. This helpful method links several API requests in a row. The result from one request goes right into the next one, without you needing to do anything extra. This makes complex actions much easier. It is also very important in automation testing. You can copy real user actions using just one automated chain of steps. With API chaining, your app can work in a simple, smart way where every step sets up the next through easy api requests.
- API chaining lets you link a few API requests, so they work together as one step-by-step process.
- The output from one API call is used by the next one in line. So, each API depends on what comes before it.
- You need tools like Postman and API gateways to set up and handle chaining API calls easily.
- API chaining helps with end-to-end testing. It shows if different services work well with each other.
- It helps find problems with how things connect early on. That way, applications are more reliable and strong.
Understanding API Chaining and Its Core Principles
At its core, api chaining means making a sequence of api calls that depend on each other. You can think of it like a relay race. One person hands to the next, but here, it is data that moves along. First, you do one api call. The answer you get is then sent into the next api. You then use that response for another api call, and keep going like this. In the end, the chaining of api calls helps you finish a bigger job in a smooth way.
This way works well for automated testing. It lets you test an entire workflow, not just single api requests. With chaining, you see how data moves between services. This helps you find issues early. The api gateway can handle this full workflow on the server. This makes things easier for the client app.
Now, let’s look at how this process works in a simple way. We will talk about the main ideas that you need to understand.
How API Chaining Works: Step-by-Step Breakdown
Running a sequence of API requests through chaining is simple to follow. It begins with the first API request. This one step starts the whole workflow. The response from this first API call is important. It gives you the data you need for the next API requests in the sequence.
For example, the process might look like this:
- Step 1: First Request: You send the first request to an API endpoint to set up a new user account. The server gets this request, works on it, and sends a response with a unique user ID in it.
- Step 2: Data Extraction: You take the user ID out from the response you get from your first request.
- Step 3: Second Request: You use the same user ID in the request body or in the URL to make a second request. You do this to get the user’s profile details from another endpoint.
This easy, three-step process shows how chaining can bring different api endpoints together as one unit. The main point is that the second call needs the first to finish and give its output. This makes the workflow with your endpoints automated and smooth.
Key Concepts: Data Passing, Dependencies, and Sequence
To master API chaining, you need to know about three key ideas. The first one is data passing. The second is dependencies. The third one is sequence. These three work together to make sure your chaining workflow runs well and does what you want it to do. This is how you make the api chaining strong and stable in your workflow.
The mechanics of chaining rely on these elements:
- Data Passing: This means taking some data from one API response, like an authentication token or a user id, and then using it in the next API request. This is what links the chain together in the workflow.
- Dependencies: Later API calls in the chain need the earlier calls to work first. If the first API call does not go through, the whole workflow does not work, because the needed data such as the user id does not get passed forward
- Sequence: You have to run the API calls in the right order. If you do not use the right sequence, the logic of the workflow will break. Making sure every API call goes in the proper order helps with validation of the process and keeps it working well.
It is important to manage these ideas well when you build strong chains. For security, you need to handle sensitive data like tokens with care. A good practice is to use environment variables or secure places to store them. You should always make sure you have the right authentication steps set up for every link in the chain.
What is API Chaining?
API chaining is a way in software development where you make several API calls, but you do them one after another in a set order. You do not make random or single requests. With chaining, each API call uses the result from the last call to work. This links all the api calls into one smooth workflow. So, the output from one API is used in the next one to finish one larger job. API chaining helps when there are many steps and each step needs to follow the one before it. This happens a lot in workflows in software development.
Think of this as making a multi-step process work on its own. For example, when you want to book a flight, the steps are to search for flights first, pick a seat next, and then pay. You need to make one API call for each action. By chaining these API calls, you connect the different endpoints together. This lets you use one smooth functionality. It makes things a lot easier for the client app, and it lowers the amount of manual work needed.
Let’s look at how you can use the Postman tool to do this in real life.
How to Create a Collection?
One simple way to begin with api chaining is to use Postman. Postman is a well-known tool for api testing. To start, you should put your api requests into a collection. A collection in Postman is a place where you can group api requests that are linked. This makes it easy to handle them and run them together.
Creating one is simple:
- In the Postman app, click the “New” button. Then choose “Collection.”
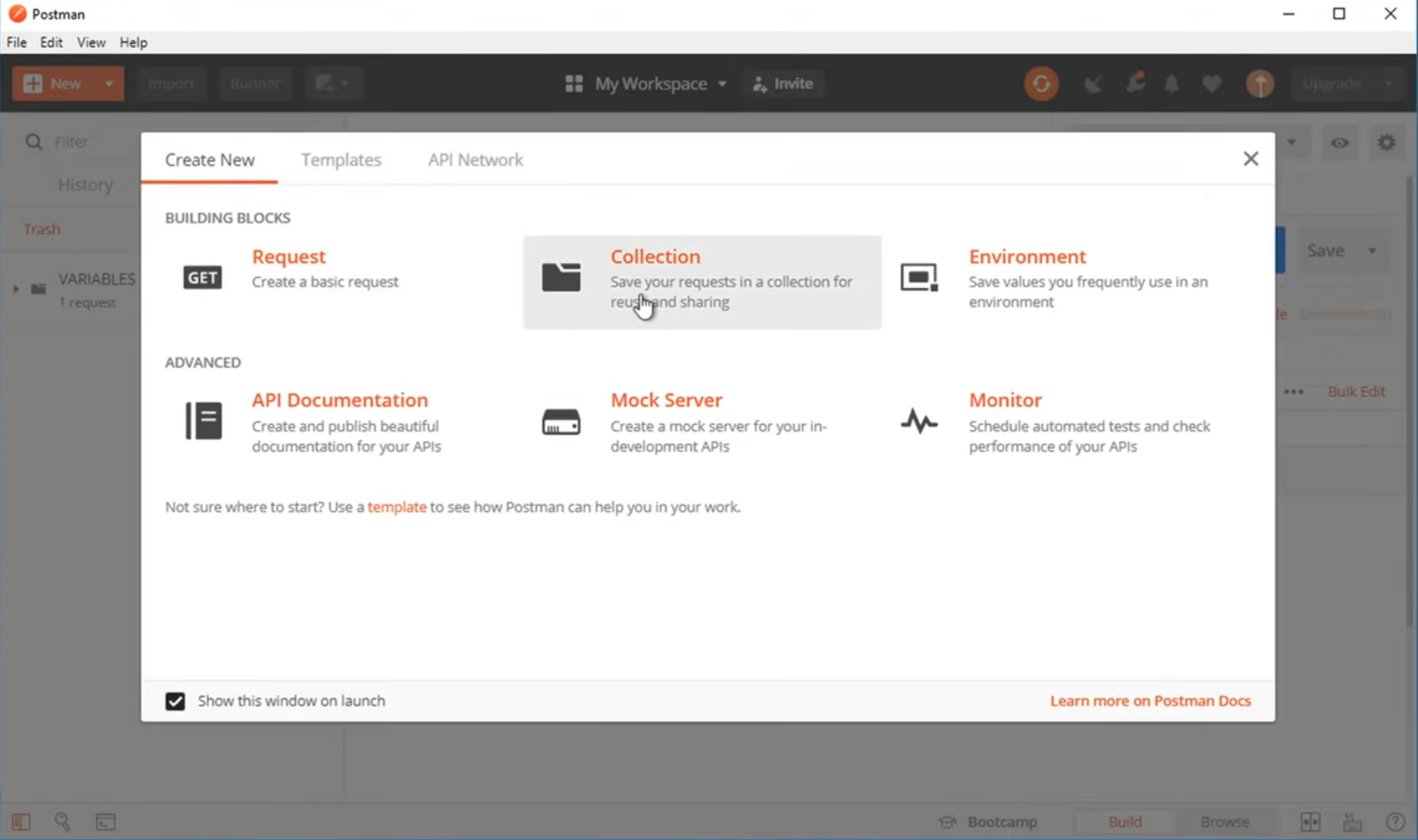
- Type a name that shows what the collection is for, like “User Workflow.” Click “Create.”.
After you make your collection, you will have your own space to start building your sequence. This is the base for setting up your chain API calls. Every request you need for your API workflow will stay here. You can set the order in which they go and manage any shared data needed to run the chain api calls or the whole API workflow.
Add 2 Requests in Postman
With your collection set up in Postman, you can now add each API call that you need for your workflow. Postman is a good REST API client, so this step is easy to do with it. Start with the first request, as this will begin the workflow and set things in motion.
Here’s how you can add two requests:
- First Request: Click “Add a request.” Name it “Create User.” Add the user creation URL and choose POST as the method. Running it will return a user ID.
- Second Request: Add another request called “Get User Details.” Use the ID from the first request to fetch the user’s details.
Right now, you have two different requests in your collection. The next thing you need to do is to link them by moving data from the first one to the second one. This step is what chaining is all about.
Use Environment variables to parameterize the value to be referred
To pass data between requests in Postman, you need to use environment variables. If you put things like IDs or tokens by hand, it is not the best way to do this. It is slow and makes things hard to change. Instead, environment variables let you keep and use data in a way that changes as you go, which works well for chaining your steps. They are also better for keeping important data safe.
Here’s how to set them up:
- Click the “eye” icon at the top-right corner of Postman to open the environment management section. Click “Add” to make a new environment and give it a name.
- In your new environment, you can set values you need several times. For example, you can make a variable named userID but leave its “Initial Value” and “Current Value” empty for now.
When you use {{userID}} in your request URL or in the request body, it tells Postman to get the value for this variable every time you run it. This way, you can send the same requests again and again. It also lets you get ready for data that changes, which you may get from the first call in your chain.
Update the Fetched Values in Environment Variables
After you run your first request, you need to catch what comes back and keep it in an environment variable. In Postman, you can do this by adding a bit of JavaScript code in the “Tests” tab for your request. This script will run after you get the response.
To change the userID variable, you can use this script:
- Parse the response: First, get the JSON response from the API call. Just type const responseData = pm.response.json(); to do it.
- Set the variable: Now get the ID from the the api response, and put it as an environment variable. Write pm.environment.set(“userID”, responseData.id); for this.
This easy script takes care of the main part of chaining. When you run the “Create User” request, it will save the new user’s id to the userID variable on its own. It is also a good spot to add some basic validation. This helps make sure the id was made the right way before you go on.
Run the Second Request
Now, your userID environment variable is set to update on its own. You can use this in your second request. This will finish the chaining process in Postman. Go to your “Get User Details” request and set it up.
Here’s how to finish the setup:
- In the URL space for the second request, use the variable you made before. For example, if your endpoint is api/users/{id}, then your URL in Postman should be api/users/{{userID}}.
- Make sure you pick your environment from the list at the top right.
When you run the collection in Postman, the tool sends the requests one after another. The first call makes a new user and keeps the user id for you. Then, the second request takes this id and uses it to get the user’s details. This simple workflow is a big part of api testing. It shows how you can set up an api system to run all steps in order with no manual work.
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing API Chaining in Automation Testing
Adding API chaining to your automation testing plan can help make things faster and cover more ground. Instead of having a different test for each API, you can set up full workflows that act like real users. The main steps are to find the right workflow, set up the sequence of API calls, and handle the data that moves from one call to the next.
The key is to make your tests change based on what happens. Start with the first API call. Get the needed info from its reply, like an authentication token or an ID. You will then use this info in all the subsequent requests that need it. It is also good to have validation checks after every call. This helps you know the workflow is going right. This way, you check each API and see if they work well together.
Real-World Use Cases for API Chaining
API chaining is used a lot in modern web applications. It helps make the user experience feel smooth. Any time you do something online that has more than one step, like ordering a product or booking a trip, there will be a chain of API calls working together behind the scenes. This is how these apps connect the steps for you.
In software development, chaining is a key technique when you need to build complex features in a fast and smooth way. For example, when you want to make an online store checkout system, you have to check inventory, process a payment, and create a shipping order. When you use chaining for these steps, it helps you manage the whole workflow as one simple transaction. This makes the process more reliable and also better in performance.
These are a few ways the chaining method can be used. Now, let us look at some cases in more detail.
Multi-Step Data Retrieval in Web Applications
In today’s web applications, getting data can take several steps. Sometimes, you want to find user information and then get the user’s recent activity from another service. You don’t have to make your app take care of both api requests. The api gateway can be set up to do this for you.
This is a good way to use a sequence of API calls. The workflow can go like this.
- The client makes one request to the api gateway.
- The api gateway first talks to a user service to get profile details for this user.
- The gateway then takes an id from that answer and uses it to call the activity service. The activity service gives back recent orders.
- After this, the gateway puts both answers together and sends all the data back to the client in one payload.
This way makes things easier on the client side. The server will handle the steps, so it can be faster and there will be less wait time. It is a good way to bring data together from more than one place.
Automated Testing and Validation Scenarios
API chaining is key in good automated testing. It lets testers do more than basic checks. With chaining, testers can check all steps of a business process from start to finish. This way, you can see if all linked services in the API do what they are meant to do. By following a user’s path through the app, you make sure every part works together, and the validation is done in the right way.
Common testing situations that use chain API calls include the following:
- User Authentication: A workflow to log in a user, get a token, and then use that token for a protected resource.
- E-commerce Order: A workflow where you add an item to the cart, move to checkout, and then confirm the order.
- Data Lifecycle: A workflow to make a resource, change it, and then remove it, checking at each step to see how it is.
These tests help a lot in software development. They find bugs when parts in software come together. Rest Assured is one tool that lets you build these tests with Java. It is easy to use. If you add it to the CI/CD pipeline, it helps the whole process work better. So, you can catch problems early and keep things running smooth.
Tools and Platforms for Simplifying API Chaining
| Tool/Platform |
How It Simplifies Chaining |
| Postman |
Graphical interface with collections and environment variables. |
| Rest Assured |
Programmatic chaining in Java for automated test suites. |
| API Gateway |
Handles orchestration of API calls on the server. |
Automating Chains with Postman and Rest Assured
For teams that want to start automation, Postman and Rest Assured are both good tools. Postman is easy to use because it lets you set up tasks visually. With its Collection Runner, you can run a list of requests one after the other. You can also use scripts to move data from one step to the next and to check facts along the way.
On the other hand, Rest Assured is a Java tool that helps with test automation. You can use it to chain API calls right in your own Java code. This makes it good for use in a CI/CD setup. Rest Assured helps make automation and testing of your API easy for you and your team.
- With Postman: You set up and manage your requests in a clear way using collections. You also use environment variables to connect your requests.
- With Rest Assured: You need to write code for each request. You read the value you get back from the first response, then use that value to make and send the next request.
Both tools are good for setting up a chain of calls. Rest Assured works well if you want it in your development pipeline. Postman is easy to use, and it helps you make and test things fast.
Leveraging API Gateways for Seamless Orchestration
API gateways give a strong and easy way, on the server, to handle API chaining. The client app does not need to make several calls. The gateway will do that for the client. This is called orchestration. In this setup, the server gateway works like a guide for all your backend services.
Here’s how it typically works:
- You set up a new route on your API gateway.
- In that route’s setup, you pick a pipeline or order for backend endpoints. These endpoints will be called in a set order.
When a client sends one request to the gateway’s route, the gateway goes through the whole chain of calls. The response moves from one service to the next, step by step. For example, Apache APISIX lets you build custom plugins for these kinds of pipeline requests. This helps make client code easier, cuts down network trips, and keeps your backend setup flexible.
Conclusion
To sum up, API chaining is a strong method that can help make complex API requests easier. It helps you get data and set up automation faster. When you understand the basics and use a clear plan, you can make your workflow more simple. It also makes testing better, and you will see smooth data interactions between several services. Using API chaining helps improve performance and brings more order when you handle dependencies and sequences. If you want to know more about api requests, chaining, and how api chaining can help with automation and your workflow, feel free to ask for a free consultation. This way, you can find solutions made just for you.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
How can I pass data between chained API requests securely?
For safe handling of data in chained api requests, it is best to not put important information straight into the code. You can use environment settings with tools like Postman. This keeps your login details away from your tests and keeps them safe. When it comes to api chaining on the server, an api gateway is helpful. It can manage how things move along, change the request body, and keep all sensitive data out before moving the data to the next service.
-
What challenges should I consider when designing API chaining workflows?
When you design api chaining workflows, the big challenges are dealing with how each api depends on the others and what to do if something goes wrong. If one api call fails in the chaining process, then the whole sequence can stop working. You need strong error handling to stop this from causing more problems down the line. It can also be hard to keep up with updates. A change to one api can affect other parts of the chain, so you may have to update several things at once. This helps you avoid manual intervention.
-
Can API chaining improve efficiency in test automation?
Absolutely. API chaining makes test automation much better by linking several endpoints. This lets you check end-to-end workflows instead of just single parts. You get more real-world validation for your app this way. It helps people find bugs in how different pieces work together, and automates steps that would take a lot of time to do by hand. API chaining is a good way to make automation stronger.

by Rajesh K | Sep 2, 2025 | Software Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
In software testing, test data is the lifeblood of reliable quality assurance. Whether you are verifying a login page, stress-testing a payment system, or validating a healthcare records platform, the effectiveness of your tests is directly tied to the quality of the data you use. Without diverse, relevant, and secure testdata, even the most well-written test cases can fail to uncover critical defects. Moreover, poor-quality testdata often leads to inaccurate results, missed bugs, and wasted resources. For example, imagine testing an e-commerce checkout system using only valid inputs. While the “happy path” works, what happens when a user enters an invalid coupon code or tries to process a payment with an expired credit card? Without including these scenarios in your testdata set, you risk pushing faulty functionality into production.
Therefore, investing in high-quality testdata is not just a technical best practice; it is a business-critical strategy. It ensures comprehensive test coverage, strengthens data security, and accelerates defect detection. In this guide, we will explore the different types of testdata, proven techniques for creating them, and practical strategies for managing testdata at scale. By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap to improve your testing outcomes and boost confidence in every release.
Understanding Test Data in Software Testing
What Is Test Data?
Testdata refers to the input values, conditions, and datasets used to verify how a software system behaves under different circumstances. It can be as simple as entering a valid username or as complex as simulating thousands of financial transactions across multiple systems.
Why Is It Important?
- It validates that the application meets functional requirements.
- It ensures systems can handle both expected and unexpected inputs.
- It supports performance, security, and regression testing.
- It enables early defect detection, saving both time and costs.
Example: Testing a banking app with only valid account numbers might confirm that deposits work, but what if someone enters an invalid IBAN or tries to transfer an unusually high amount? Without proper testdata, these crucial edge cases could slip through unnoticed.
Types of Test Data and Their Impact
1. Valid Test Data
Represents correct inputs that the system should accept.
Example: A valid email address during registration ([email protected]).
Impact: Confirms core functionality works under normal conditions.
2. Invalid Test Data
Represents incorrect or unexpected values.
Example: Entering abcd in a numeric-only field.
Impact: Validates error handling and resilience against user mistakes or malicious attacks.
3. Boundary Value Data
Tests the “edges” of input ranges.
Example: Passwords with 7, 8, 16, and 17 characters.
Impact: Exposes defects where limits are mishandled.
4. Null or Absent Data
Leaves fields blank or uses empty files.
Example: Submitting a form without required fields.
Impact: Ensures the application handles missing information gracefully.
Test Data vs. Production Data
| Feature |
Test Data |
Production Data |
| Purpose |
For testing in non-live environments |
For live business operations |
| Content |
Synthetic, anonymized, or subsets |
Real, sensitive user info |
| Security |
Lower risk, but anonymization needed |
Requires the highest protection |
| Regulation |
Subject to rules if containing PII |
Strictly governed (GDPR, HIPAA) |
Transition insight: While production data mirrors real-world usage, it introduces compliance and security risks. Consequently, organizations often prefer synthetic or masked data to balance realism with privacy.
Techniques for Creating High-Quality Test Data
Manual Data Creation
- Simple but time-consuming.
- Best for small-scale, unique scenarios.
Automated Data Generation
- Uses tools to generate large, realistic datasets.
- Ideal for load testing, regression, and performance testing.
Scripting and Back-End Injection
- Leverages SQL, Python, or shell scripts to populate databases.
- Useful for complex scenarios that cannot be easily created via the UI.
Strategies for Effective Test Data Generation
- Data Profiling – Analyze production data to understand patterns.
- Data Masking – Replace sensitive values with fictional but realistic ones.
- Synthetic Data Tools – Generate customizable datasets without privacy risks.
- Ensuring Diversity – Include valid, invalid, boundary, null, and large-volume data.
Key Challenges in Test Data Management
- Sensitive Data Risks → Must apply anonymization or masking.
- Maintaining Relevance → Test data must evolve with application updates.
- Scalability → Handling large datasets can become a bottleneck.
- Consistency → Multiple teams often introduce inconsistencies.
Best Practice Tip: Use Test Data Management (TDM) tools to automate provisioning, version control, and lifecycle management.
Industry-Specific Examples of Test Data
- Banking & Finance: Valid IBANs, invalid credit cards, extreme transaction amounts.
- E-Commerce: Valid orders, expired coupons, zero-price items.
- Healthcare: Anonymized patient data, invalid blood groups, and future birth dates.
- Telecom: Valid phone numbers, invalid formats, massive data usage.
- Travel & Hospitality: Special characters in names, invalid booking dates.
- Insurance: Duplicate claims, expired policy claims.
- Education: Invalid scores, expired enrollments, malformed email addresses.
Best Practices for Test Data Management
- Document test data requirements clearly.
- Apply version control to test data sets.
- Adopt “privacy by design” in testing.
- Automate refresh cycles for accuracy.
- Use synthetic data wherever possible.
Conclusion
High-quality test data is not optional; it is essential for building reliable, secure, and user-friendly applications. By diversifying your data sets, leveraging automation, and adhering to privacy regulations, you can maximize test coverage and minimize risk. Furthermore, effective test data management improves efficiency, accelerates defect detection, and ensures smoother software releases.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Can poor-quality test data impact results?
Yes. It can lead to inaccurate results, missed bugs, and a false sense of security.
-
What are secure methods for handling sensitive test data?
Techniques like data masking, anonymization, and synthetic data generation are widely used.
-
Why is test data management critical?
It ensures that consistent, relevant, and high-quality test data is always available, preventing testing delays and improving accuracy.

by Rajesh K | Aug 26, 2025 | Artificial Intelligence, Blog, Latest Post |
In the fast-moving world of software testing, creating and maintaining test cases is both a necessity and a burden. QA teams know the drill: requirements evolve, user stories multiply, and deadlines shrink. Manual test case creation, while thorough, simply cannot keep pace with today’s agile and DevOps cycles. This is where AI Test Case Generator enter the picture, promising speed, accuracy, and scale. From free Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Grok to specialized enterprise platforms such as TestRigor, Applitools, and Mabl, the options are expanding rapidly. Each tool has strengths, weaknesses, and unique pricing models. However, while cloud-based solutions dominate the market, they often raise serious concerns about data privacy, compliance, and long-term costs. That’s why offline tools like Codoid’s Tester Companion stand out, especially for teams in regulated industries.
This blog will walk you through the AI test case generator landscape: starting with free LLMs, moving into advanced paid tools, and finally comparing them against our own Codoid Tester Companion. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of which solution best fits your needs.
What Is an AI Test Case Generator?
An AI test case generator is a tool that uses machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP) to automatically create test cases from inputs like requirements, Jira tickets, or even UI designs. Instead of manually writing out steps and validations, testers can feed the tool a feature description, and the AI produces structured test cases.
Key benefits of AI test case generators:
- Speed: Generate dozens of test cases in seconds.
- Coverage: Identify edge cases human testers might miss.
- Adaptability: Update test cases automatically as requirements change.
- Productivity: Free QA teams from repetitive tasks, letting them focus on strategy.
For example, imagine your team is testing a new login feature. A human tester might write cases for valid credentials, invalid credentials, and password reset. An AI tool, however, could also generate tests for edge cases like special characters in usernames, expired accounts, or multiple failed attempts.
Free AI Test Case Generators: LLMs (ChatGPT, Gemini, Grok)
For teams just exploring AI, free LLMs provide an easy entry point. By prompting tools like ChatGPT or Gemini with natural language, you can quickly generate basic test cases.
Pros:
- Zero cost (basic/free tiers available).
- Easy to use with simple text prompts.
- Flexible – can generate test cases, data, and scripts.
Cons:
- Internet required (data sent to cloud servers).
- Generic responses not always tailored to your application.
- Compliance risks for sensitive projects.
- Limited integrations with test management tools.
Example use case:
QA engineer asks ChatGPT: “Generate test cases for a mobile login screen with email and password fields.” Within seconds, it outputs structured cases covering valid/invalid inputs, edge cases, and usability checks.
While helpful for brainstorming or quick drafts, LLMs lack the robustness enterprises demand.
Paid AI Test Case Generators: Specialized Enterprise Tools
Moving beyond free LLMs, a range of enterprise-grade AI test case generator tools provide deeper capabilities, such as integration with CI/CD pipelines, visual testing, and self-healing automation. These platforms are typically designed for medium-to-large QA teams that need robust, scalable, and enterprise-compliant solutions.
Popular tools include:
TestRigor
- Strength: Create tests in plain English.
- How it works: Testers write steps in natural language, and TestRigor translates them into executable automated tests.
- Best for: Manual testers moving into automation without heavy coding skills.
- Limitations: Cloud-dependent and less effective for offline or highly secure environments. Subscription pricing adds up over time.
Applitools
- Strength: Visual AI for detecting UI bugs and visual regressions.
- How it works: Uses Visual AI to capture screenshots during test execution and compare them with baselines.
- Best for: Teams focused on ensuring consistent UI/UX across devices and browsers.
- Limitations: Strong for visual validation but not a full-fledged test case generator. Requires integration with other tools for complete test coverage.
Mabl
- Strength: Auto-healing tests and intelligent analytics.
- How it works: Records user interactions, generates automated flows, and uses AI to adapt tests when applications change.
- Best for: Agile teams with continuous deployment pipelines.
- Limitations: Heavily cloud-reliant and comes with steep subscription fees that may not suit smaller teams.
PractiTest
- Strength: Centralized QA management with AI assistance.
- How it works: Provides an end-to-end platform that integrates requirements, tests, and issues while using AI to suggest and optimize test cases.
- Best for: Enterprises needing audit trails, traceability, and advanced reporting.
- Limitations: Requires significant onboarding and configuration. May feel complex for teams looking for quick setup.
Testim.io (by Tricentis)
- Strength: AI-powered functional test automation.
- How it works: Allows record-and-playback test creation enhanced with AI for stability and reduced flakiness.
- Best for: Enterprises needing scalable test automation at speed.
- Limitations: Subscription-based, and tests often rely on cloud execution, raising compliance concerns.
Problems with LLMs and Paid AI Test Case Generators
While both free LLM-based tools and paid enterprise platforms are powerful, they come with significant challenges that limit their effectiveness for many QA teams:
1. Data Privacy & Compliance Risks
- LLMs like ChatGPT, Gemini, or Grok process data in the cloud, raising security and compliance concerns.
- Paid tools such as Mabl or Testim.io often require sensitive test cases to be stored on external servers, making them unsuitable for industries like banking, healthcare, or defense.
2. Internet Dependency
- Most AI-powered tools require a constant internet connection to access cloud services. This makes them impractical for offline environments, remote labs, or secure test facilities.
3. Cost and Subscription Overheads
- Free LLMs are limited in scope, while enterprise-grade solutions often involve recurring, high subscription fees. These costs accumulate over time and may not provide proportional ROI.
4. Limited Customization
- Cloud-based AI often provides generic responses. Paid tools may include customization, but they typically learn slowly or are limited to predefined templates. They rarely adapt as effectively to unique projects.
5. Integration & Maintenance Challenges
- While marketed as plug-and-play, many paid AI tools require configuration, steep learning curves, and continuous management. Self-healing features are helpful but can fail when systems change drastically.
6. Narrow Focus
- Some tools excel only in specific domains, like visual testing (Applitools), but lack broader test case generation abilities. This forces teams to combine multiple tools, increasing complexity.
These challenges set the stage for why Codoid’s Tester Companion is a breakthrough: it eliminates internet dependency, protects data, and reduces recurring costs while offering smarter test generation features.
How Tester Companion Generates Test Cases Smarter
Unlike most AI tools that require manual prompts or cloud access, Codoid’s Tester Companion introduces a more human-friendly and powerful way to generate test cases:
1. From BRDs (Business Requirement Documents)
Simply upload your BRD, and Tester Companion parses the content to create structured test cases automatically. No need to manually extract user flows or scenarios.
Example: Imagine receiving a 20-page BRD from a banking client. Instead of spending days writing cases, Tester Companion instantly generates a full suite of test cases for review and execution.
2. From Application Screenshots
Tester Companion analyzes screenshots of your application (like a login page or checkout flow) and auto-generates test cases for visible elements such as forms, buttons, and error messages.
Example: Upload a screenshot of your app’s signup form, and Tester Companion will create tests for valid/invalid inputs, missing field validation, and UI responsiveness.
3. AI + Human Collaboration
Unlike rigid AI-only systems, Tester Companion is designed to work with testers, not replace them. The tool generates cases, but QA engineers can easily edit, refine, and extend them to match project-specific needs.
4. Scalable Across Domains
Whether it’s banking, healthcare, e-commerce, or defense, Tester Companion adapts to different industries by working offline and complying with strict data requirements.
Learn more about its unique capabilities here: Codoid Tester Companion.
Why You Should Try Tester Companion First
Before investing time, effort, and budget into complex paid tools or relying on generic cloud-based LLMs, give Tester Companion a try. It offers the core benefits of AI-driven test generation while solving the biggest challenges of security, compliance, and recurring costs. Many QA teams discover that once they experience the simplicity and power of generating test cases directly from BRDs and screenshots, they don’t want to go back.
Comparison Snapshot: Test Companion vs. Popular Tools
| S. No |
Feature |
Test Companion (Offline) |
ChatGPT (LLM) |
TestRigor |
Applitools |
Mabl |
| 1 |
Internet Required |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| 2 |
Data Privacy |
Local, secure |
Cloud-processed |
Cloud |
Cloud |
Cloud |
| 3 |
Generates from BRD |
Yes |
No |
Limited |
No |
No |
| 4 |
Generates from Screenshot |
Yes |
No |
No |
Limited |
No |
| 5 |
Cost |
One-time license |
Free / Paid |
Subscription |
Subscription |
Subscription |
| 6 |
Speed |
Instant |
API delays |
Moderate |
Cloud delays |
Cloud delays |
| 7 |
Customization |
Learns from local projects |
Generic |
Plain-English scripting |
Visual AI focus |
Self-healing AI |
| 8 |
Compliance |
GDPR/HIPAA-ready |
Risky |
Limited |
(Enterprise plans) |
Limited |
Conclusion
The evolution of AI test case generators has reshaped the way QA teams approach test design. Free LLMs like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Grok are good for quick brainstorming, while enterprise-grade tools such as TestRigor, Applitools, and Mabl bring advanced features to large organizations. Yet, both categories come with challenges – from privacy risks and subscription costs to internet dependency and limited customization.
This is where Codoid’s Tester Companion rises above the rest. By working completely offline, supporting test generation directly from BRDs and application screenshots, and eliminating recurring subscription costs, it offers a unique blend of security, affordability, and practicality. It is purpose-built for industries where compliance and confidentiality matter, while still delivering the speed and intelligence QA teams need.
In short, if you want an AI test case generator that is secure, fast, cost-effective, and enterprise-ready, Tester Companion is the clear choice.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is a test case generator using AI?
A test case generator using AI is a tool that leverages artificial intelligence, natural language processing, and automation algorithms to automatically create test cases from inputs like requirements documents, Jira tickets, or application screenshots.
-
What are the benefits of using a test case generator using AI?
It accelerates test creation, increases coverage, reduces repetitive work, and identifies edge cases that manual testers may miss. It also helps QA teams integrate testing more efficiently into CI/CD pipelines.
-
Can free tools like ChatGPT work as a test case generator using AI?
Yes, free LLMs like ChatGPT can generate test cases quickly using natural language prompts. However, they are cloud-based, may raise privacy concerns, and are not enterprise-ready.
-
What are the limitations of paid AI test case generators?
Paid tools such as TestRigor, Applitools, and Mabl provide advanced features but come with high subscription costs, internet dependency, and compliance risks since data is processed in the cloud.
-
Why is Codoid’s Tester Companion the best test case generator using AI?
Unlike cloud-based tools, Tester Companion works fully offline, ensuring complete data privacy. It also generates test cases directly from BRDs and screenshots, offers one-time licensing (no recurring fees), and complies with GDPR/HIPAA standards.
-
How do I choose the right AI test case generator for my team?
If you want quick drafts or experiments, start with free LLMs. For visual testing, tools like Applitools are helpful. But for secure, cost-effective, and offline AI test case generation, Codoid Tester Companion is the smarter choice.

by Rajesh K | Aug 19, 2025 | Security Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) have become the lifeblood of digital transformation. From mobile banking apps to enterprise SaaS platforms, APIs power the seamless flow of data between applications, services, and devices. However, with this power comes an equally significant risk: security vulnerabilities. A single exposed API can lead to massive data leaks, unauthorized access, and even complete system compromise. This is where API security testing steps in as a crucial practice. And while advanced security testing often requires specialized penetration testing tools, many teams underestimate the power of a tool they’re already familiar with, Postman. Known primarily as a functional testing and API development tool, Postman can also serve as an effective solution for basic API security testing. With its ability to manipulate requests, inject custom headers, and automate scripts, Postman provides development and QA teams with a practical way to catch vulnerabilities early in the lifecycle.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore:
- Why API security testing is essential
- The difference between general security testing and API-specific testing
- Common API vulnerabilities
- How to use Postman for API security testing
- Step-by-step examples of common tests (with mandatory screenshots/visuals)
- Best practices for integrating security testing into your workflow
- Compliance and regulatory considerations
By the end of this blog, you’ll understand how Postman can fit into your security toolkit, helping you protect sensitive data, ensure compliance, and build customer trust.
Key Highlights
- Postman as a Security Tool: Learn how Postman, beyond functional testing, can perform basic API security checks.
- Common Vulnerabilities: Explore API risks such as broken authentication, parameter tampering, and HTTP method misuse.
- Step-by-Step Testing Guide: Practical instructions for running security tests in Postman.
- Compliance Benefits: How Postman testing supports laws like the Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA).
- Best Practices: Tips for integrating API security testing into CI/CD pipelines.
- Comparison Insights: Postman vs. specialized penetration testing tools.
- FAQs Section: Answers to top search queries around Postman API security testing.
Why API Security Testing Matters
The adoption of APIs has skyrocketed across industries. Unfortunately, APIs are now also the primary attack vector for hackers. According to OWASP, the OWASP API Security Top 10 highlights the most common vulnerabilities exploited today, including:
- Broken Authentication – Weak authentication mechanisms allow attackers to impersonate users.
- Excessive Data Exposure – APIs returning more data than necessary, enabling attackers to intercept sensitive information.
- Injection Attacks – Malicious input is inserted into requests that trick the server into executing harmful commands.
- Broken Object Level Authorization (BOLA) – Attackers are manipulating object IDs to access unauthorized data.
Real-life breaches underscore the importance of proactive API security testing. For example, the Twitter API breach exposed millions of users’ contact information simply due to a failure in properly validating API requests. Incidents like these demonstrate that API security is not just a technical necessity; it’s a business-critical priority.
Postman for API Security Testing
While Postman was originally designed for API development and functional validation, it has powerful features that make it suitable for basic security testing, especially during development. Postman allows testers and developers to:
- Modify Requests Easily: Change headers, tokens, and payloads on the fly.
- Test Authentication Flows: Simulate both valid and invalid tokens.
- Automate Tests: Use Postman collections and scripts for repeated checks.
- Visualize Responses: Quickly see how APIs behave with manipulated requests.
This makes Postman an ideal tool for catching vulnerabilities early, before APIs reach production.
Common Security Tests in Postman (with Examples)
1. Missing Authentication
Objective: Ensure restricted endpoints reject unauthenticated requests.
How to Test in Postman:
- Select a protected endpoint (e.g., /user/profile).
- Remove the Authorization header/token.
- Send the request.
Expected: API should return 401 Unauthorized or 403 Forbidden.
Risk if Fails: Anyone could access sensitive data without logging in.
2. Broken Authentication
Objective: Check if the API validates tokens correctly.
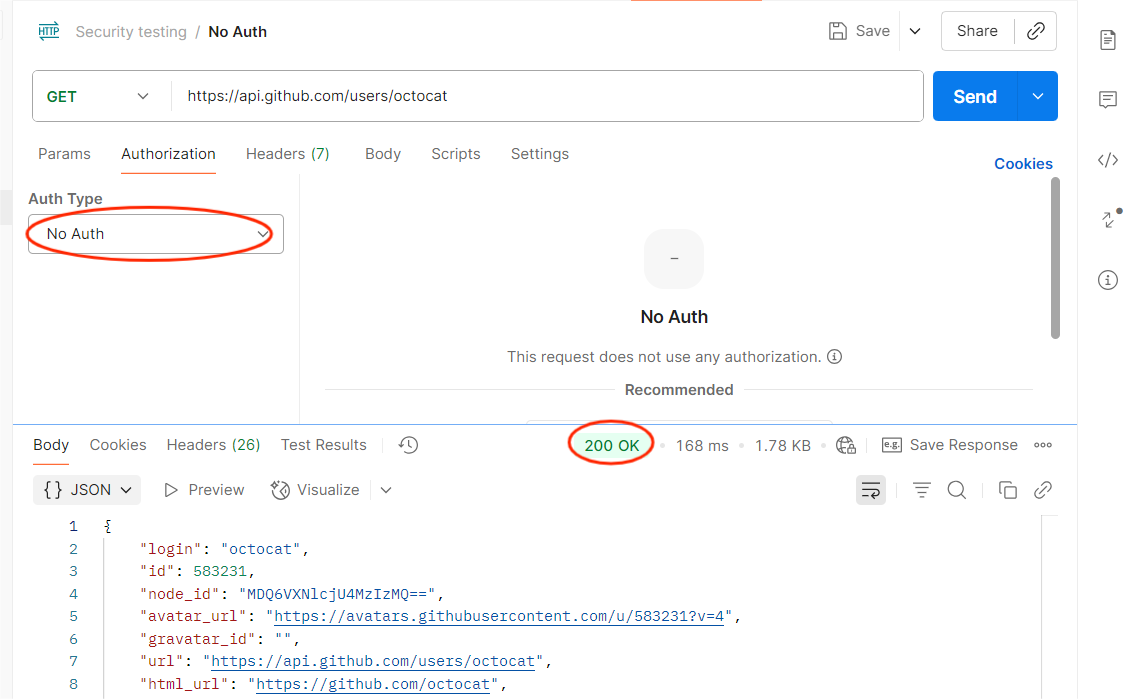
How to Test in Postman:
- Replace a valid token with an expired or random token.
- Send the request.
Expected: API should deny access with 401 or 403.
Risk if Fails: Attackers could use stolen or fake tokens to impersonate users.
3. Parameter Tampering
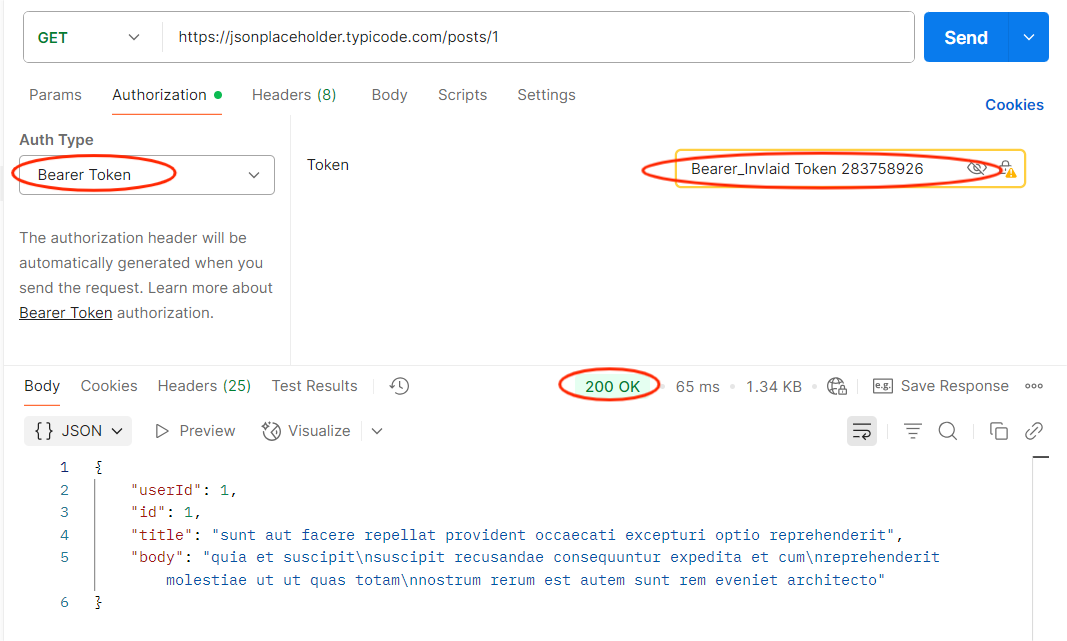
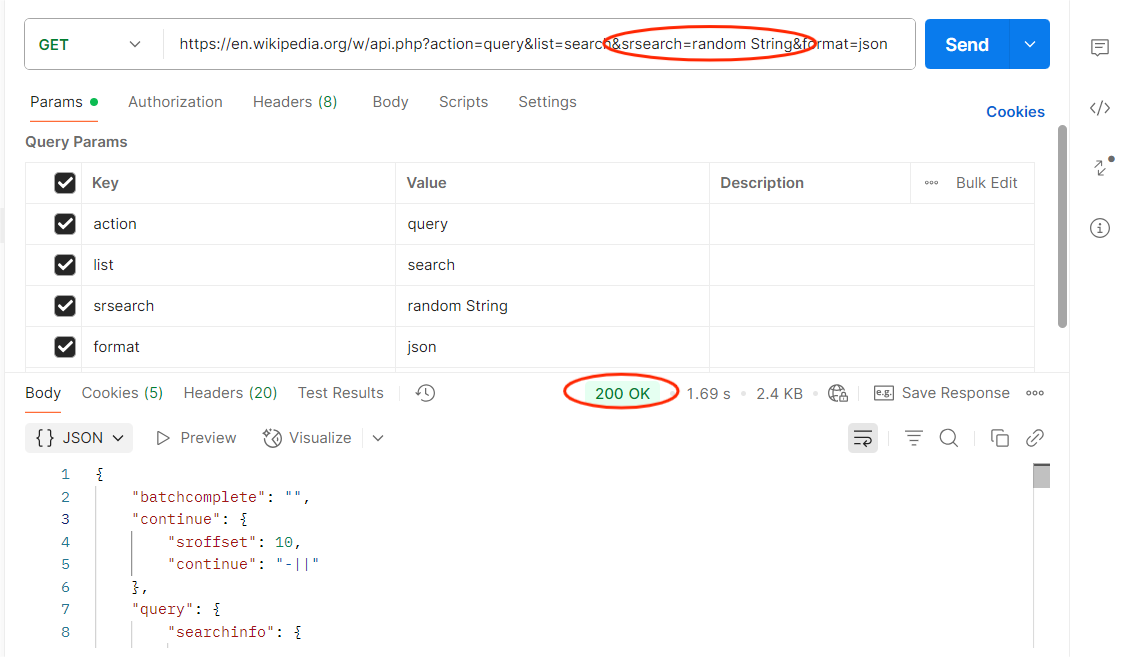
Objective: Ensure unauthorized data access is blocked.
How to Test in Postman:
- Identify sensitive parameters (user_id, order_id).
- Change them to values you shouldn’t have access to.
- Send the request.
Expected: API should reject unauthorized parameter changes.
Risk if Fails: Attackers could access or modify other users’ data.
4. HTTP Method Misuse
Objective: Verify that APIs only allow intended methods.
How to Test in Postman:
- Take an endpoint (e.g., /user/profile).
- Change method from GET to DELETE.
- Send the request.
Expected: API should return 405 Method Not Allowed.
Risk if Fails: Attackers could perform unintended actions.
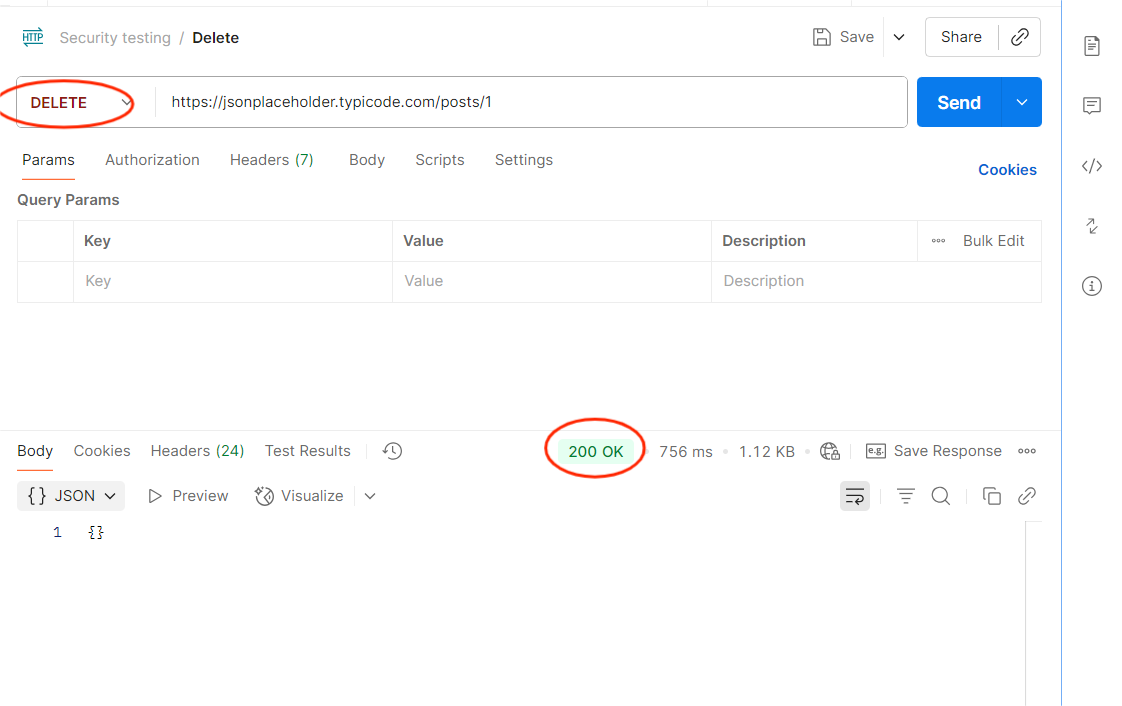
Step-by-Step Guide to Conducting API Security Testing in Postman
- Preparation: Identify all API endpoints (documented and undocumented).
- Discovery: Use Postman collections to organize and catalog APIs.
- Testing: Apply common vulnerability tests (authentication, authorization, input validation).
- Automation: Set up test scripts for repeated validation in CI/CD.
- Remediation: Document vulnerabilities and share with development teams.
- Re-Validation: Fix and re-test before production deployment.
Best Practices for Secure API Testing with Postman
- Integrate with CI/CD: Automate basic checks in your pipeline.
- Use Environment Variables: Manage tokens and URLs securely.
- Adopt OWASP API Security Top 10: Align your Postman tests with industry best practices.
- Combine Manual + Automated Testing: Use Postman for basic checks, and penetration testing tools for deeper analysis.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
In regions like India, compliance with laws such as the Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA) is mandatory. Failing to secure APIs that handle personal data can result in heavy penalties. Postman testing helps organizations demonstrate due diligence in securing APIs, complementing more advanced security tools.
Comparison Table: Postman vs. Advanced Security Tools
| S. No |
Feature |
Postman (Basic Testing) |
Specialized Tools (Advanced Testing) |
| 1 |
Ease of Use |
High – user-friendly GUI |
Moderate – requires expertise |
| 2 |
Authentication Testing |
Yes |
Yes |
| 3 |
Parameter Tampering Detection |
Yes |
Yes |
| 4 |
Injection Attack Simulation |
Limited |
Extensive |
| 5 |
Business Logic Testing |
Limited |
Strong (manual pen testing) |
| 6 |
Automation in CI/CD |
Yes |
Yes |
| 7 |
Cost |
Free (basic) |
High (license + expertise) |
Conclusion
API security testing is no longer optional. As APIs become central to digital experiences, ensuring their security is a business-critical responsibility. Postman, while not a full-fledged penetration testing tool, provides an accessible and practical starting point for teams to test APIs for common vulnerabilities. By using Postman for missing authentication, broken authentication, parameter tampering, and HTTP method misuse, you can catch security gaps early and avoid costly breaches. Combined with compliance benefits and ease of integration into CI/CD, Postman helps you shift security left into the development cycle.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Can Postman replace penetration testing tools?
No. Postman is excellent for basic security checks, but cannot fully replace penetration testing tools that identify complex vulnerabilities.
-
Is Postman suitable for enterprise-grade security?
It’s suitable for early-stage validation but should be complemented with advanced testing in enterprises.
-
Can Postman tests be automated?
Yes. Collections and Newman (Postman’s CLI tool) allow you to run automated tests in CI/CD pipelines.
-
What vulnerabilities can Postman NOT detect?
Postman struggles with advanced exploits like Race Conditions, Mass Assignment, and Chained Attacks. These require expert analysis.
-
How often should API security tests be performed?
Continuously, integrate into your development workflow, not just before production.

by Rajesh K | Aug 13, 2025 | Artificial Intelligence, Blog, Latest Post |
Picture this: you’re making breakfast, scrolling through your phone, and an idea pops into your head. What if there was an app that helped people pick recipes based on what’s in their fridge, automatically replied to client emails while you were still in bed, or turned your voice notes into neat to-do lists without you lifting a finger? In the past, that idea would probably live and die as a daydream unless you could code or had the budget to hire a developer. Fast forward to today, thanks to Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4, LLaMA, and Mistral, building an AI-powered app is no longer reserved for professional programmers. You can describe what you want in plain English, and the AI can help you design, code, debug, and even improve your app idea. The tools are powerful, the learning curve is gentler than ever, and many of the best resources are free. In this guide, I’m going to walk you through how to create an app using AI from scratch, even if you’ve never written a line of code. We’ll explore what “creating an app using AI” really means, why LLMs are perfect for beginners, a step-by-step beginner roadmap, real examples you can try, the pros and cons of paid tools versus DIY with LLMs, and common mistakes to avoid. And yes, we’ll keep it human, encouraging, and practical.
1. What Does “Creating an App Using AI” Actually Mean?
Let’s clear up a common misconception right away: when we say “AI app,” we don’t mean you’re building the next Iron Man J.A.R.V.I.S. (although… wouldn’t that be fun?).
An AI-powered app is simply an application where artificial intelligence handles one or more key tasks that would normally require human thought.
That could be:
- Understanding natural language – like a chatbot that can answer your questions in plain English.
- Generating content – like an app that writes social media captions for you.
- Making recommendations – like Netflix suggesting shows you might like.
- Analyzing images – like Google Lens recognizing landmarks or objects.
- Predicting outcomes – like an app that forecasts the best time to post on Instagram.
In this guide, we’ll focus on LLM-powered apps that specialize in working with text, conversation, and language understanding.
Think of it this way: the LLM is the brain that interprets what users want and comes up with responses. Your app is the body; it gives users an easy way to interact with that brain.
2. Why LLMs Are Perfect for Beginners
Large Language Models are the closest thing we have to a patient, all-knowing coding mentor.
Here’s why they’re game-changing for newcomers:
- They understand plain English (and more)
You can literally type:
“Write me a Python script that takes text from a user and translates it into Spanish.”
…and you’ll get functional code in seconds.
- They teach while they work
You can ask:
“Why did you use this function instead of another?”
and the LLM will explain its reasoning in beginner-friendly language.
- They help you debug
Copy-paste an error message, and it can suggest fixes immediately.
- They work 24/7, for free or cheap
No scheduling meetings, no hourly billing, just instant help whenever you’re ready to build.
Essentially, an LLM turns coding from a lonely, frustrating process into a guided collaboration.
3. Your Beginner-Friendly Roadmap to Building an AI App
Step 1 – Start with a Simple Idea
Every great app starts with one question: “What problem am I solving?”
Keep it small for your first project. A focused idea will be easier to build and test.
Examples of beginner-friendly ideas:
- A writing tone changer: turns formal text into casual text, or vice versa.
- A study companion: explains concepts in simpler terms.
- A daily journal AI: summarizes your day’s notes into key points.
Write your idea in one sentence. That becomes your project’s compass.
Step 2 – Pick Your AI Partner (LLM)
You’ll need an AI model to handle the “thinking” part of your app. Some beginner-friendly options:
- OpenAI GPT (Free ChatGPT) – Very easy to start with.
- Hugging Face Inference API – Free models like Mistral and BLOOM.
- Ollama – Run models locally without an internet connection.
- Google Colab – Run open models in the cloud for free.
For your first project, Hugging Face is a great pick; it’s free, and you can experiment with many models without setup headaches.
Step 3 – Pick Your Framework (Your App’s “Stage”)
This is where your app lives and how people will use it:
- Web app – Streamlit (Python, beginner-friendly, looks professional).
- Mobile app – React Native (JavaScript, cross-platform).
- Desktop app – Electron.js (JavaScript, works on Mac/Windows/Linux).
For a first-timer, Streamlit is the sweet spot, simple enough for beginners but powerful enough to make your app feel real.
Step 4 – Map Out the User Flow
Before coding, visualize the journey:
- User Input – What will they type, click, or upload?
- AI Processing – What will the AI do with that input?
- Output – How will the app show results?
Draw it on paper, use Figma (free), or even a sticky note. Clarity now saves confusion later.
Step 5 – Connect the AI to the App
This is the magic step where your interface talks to the AI.
The basic loop is:
User sends input → App sends it to the AI → AI responds → App displays the result.
If this sounds intimidating, remember LLMs can generate the exact code for your chosen framework and model.
Step 6 – Start with Core Features, Then Add Extras
Begin with your main function (e.g., “answer questions” or “summarize text”). Once that works reliably, you can add:
- A tone selector (“formal,” “casual,” “friendly”).
- A history feature to review past AI responses.
- An export button to save results.
Step 7 – Test Like Your Users Will Use It
You’re not just looking for “Does it work?”, you want “Is it useful?”
- Ask friends or colleagues to try it.
- Check if AI responses are accurate, quick, and clear.
- Try unusual inputs to see if the app handles them gracefully.
Step 8 – Share It with the World (Free Hosting Options)
You can deploy without paying a cent:
- Streamlit Cloud – Ideal for Streamlit apps.
- Hugging Face Spaces – For both Python and JS apps.
- GitHub Pages – For static sites like React apps.
Step 9 – Keep Improving
Once your app is live, gather feedback and make small updates regularly. Swap in better models, refine prompts, and polish the UI.
4. Paid Tools vs. DIY with LLMs – What’s Best for You?
There’s no universal “right choice,” just what fits your situation.
| S. No |
Paid AI App Builder (e.g., Glide, Builder.ai) |
DIY with LLMs |
| 1 |
Very beginner-friendly |
Some learning curve |
| 2 |
Hours to days |
Days to weeks |
| 3 |
Limited to platform tools |
Full flexibility |
| 4 |
Subscription or per-app fee |
Mostly free (API limits apply) |
| 5 |
Low – abstracted away |
High – you gain skills |
| 6 |
Platform-controlled |
100% yours |
If you want speed and simplicity, a paid builder works. If you value control, learning, and long-term savings, DIY with LLMs is more rewarding.
5. Real-World AI App Ideas You Can Build with LLMs
Here are five beginner-friendly projects you could make this month:
- AI Email Reply Assistant – Reads incoming emails and drafts replies in different tones.
- AI Recipe Maker – Suggests recipes based on ingredients you have.
- AI Flashcard Generator – Turns study notes into Q&A flashcards.
- AI Blog Outline Builder – Creates structured outlines from a topic keyword.
- AI Daily Planner – Turns your freeform notes into a schedule.
6. Tips for a Smooth First Build
- Pick one core feature and make it great.
- Save your best prompts, you’ll reuse them.
- Expect small hiccups; it’s normal.
- Test early, not just at the end.
7. Common Mistakes Beginners Make
- Trying to add too much at once.
- Forgetting about user privacy when storing AI responses.
- Not testing on multiple devices.
- Skipping error handling, your app should still respond gracefully if the AI API fails.
8. Free Learning Resources
Conclusion – Your AI App is Closer Than You Think
The idea of creating an app can feel intimidating until you realize you have an AI co-pilot ready to help at every step. Start with a simple idea. Use an LLM to guide you. Build, test, improve. In a weekend, you could have a working prototype. In a month, a polished tool you’re proud to share. The hardest part isn’t learning the tools, it’s deciding to start.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is an AI-powered app?
An AI-powered app is an application that uses artificial intelligence to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence. Examples include chatbots, recommendation engines, text generators, and image recognition tools.
-
Can I create an AI app without coding?
Yes. With large language models (LLMs) and no-code tools like Streamlit or Hugging Face Spaces, beginners can create functional AI apps without advanced programming skills.
-
Which AI models are best for beginners?
Popular beginner-friendly models include OpenAI’s GPT series, Meta’s LLaMA, and Mistral. Hugging Face offers free access to many of these models via its Inference API.
-
What free tools can I use to build my first AI app?
Free options include Streamlit for building web apps, Hugging Face Spaces for hosting, and Ollama for running local AI models. These tools integrate easily with LLM APIs.
-
How long does it take to create an AI app?
If you use free tools and an existing LLM, you can build a basic app in a few hours to a couple of days. More complex apps with custom features may take longer.
-
What’s the difference between free and paid AI app builders?
Free tools give you flexibility and ownership but require more setup. Paid builders like Glide or Builder.ai offer speed and ease of use but may limit customization and involve subscription fees.