by Rajesh K | Jul 22, 2025 | Artificial Intelligence, Blog, Latest Post |
Artificial Intelligence is no longer a distant dream; it’s rapidly reshaping how we build, test, and release software. And just when we thought GPT-4o was groundbreaking, OpenAI is gearing up to launch its next leap: GPT-5. For software testers, QA engineers, and automation experts, this isn’t merely another version upgrade; it’s a complete transformation. GPT-5 is poised to become a pivotal asset in the QA toolbox, offering unmatched speed, accuracy, and automation for nearly every testing task. Expected to roll out by mid to late Summer 2025, GPT-5 brings with it advanced reasoning, broader context understanding, and fully multimodal capabilities. But more than the technical specifications, it’s the real-world implications for QA teams that make this evolution truly exciting.
In this blog, we’ll explore how GPT-5 will elevate testing practices, automate tedious tasks, improve testing accuracy, and ultimately reshape how QA teams operate in an AI-first world. Let’s dive in.
When Is GPT-5 Launching?
While OpenAI hasn’t confirmed a precise date, industry chatter and leaks point to a July or August 2025 launch. That gives forward-thinking QA teams a valuable window to prepare. More specifically, this is the perfect time to:
- Explore GPT-4o (the current multimodal model)
- Test AI-assisted tools for documentation, log analysis, or code review
- Identify current inefficiencies that GPT-5 might eliminate
Pro Tip: Start using GPT-4o today to experiment with AI-driven tasks like automated test case generation or log parsing. This will help your team acclimate to GPT’s capabilities and smooth the transition to GPT-5.
What Makes GPT-5 So Different?
GPT-5 isn’t just an upgraded chatbot. It’s expected to be a fully agentic, unified, multimodal system capable of understanding and executing complex, layered tasks. Let’s unpack what that mean and more importantly, what it means for software testing teams.
1. A Unified, Context-Aware Intelligence
Previous versions like GPT-3.5, GPT-4, and even GPT-4o came in different variants and capabilities. GPT-5, however, is expected to offer a single adaptive model that intelligently adjusts to user context.
Instead of juggling tools for generating test cases, analyzing logs, and reviewing code, testers can now use one model to handle it all.
For QA Teams: You can move fluidly between tasks like test case generation, regression suite review, and defect triaging without ever switching tools.
2. Massive Context Window: Up to 1 Million Tokens
One of GPT-5’s biggest leaps forward is its expanded context window. Where GPT-4 capped out at 128,000 tokens, GPT-5 could support up to 1 million tokens.
Imagine feeding an entire product’s source code, full regression suite, and two weeks’ worth of logs into one prompt and getting back an intelligent summary or action plan. That’s the kind of power GPT-5 unlocks.
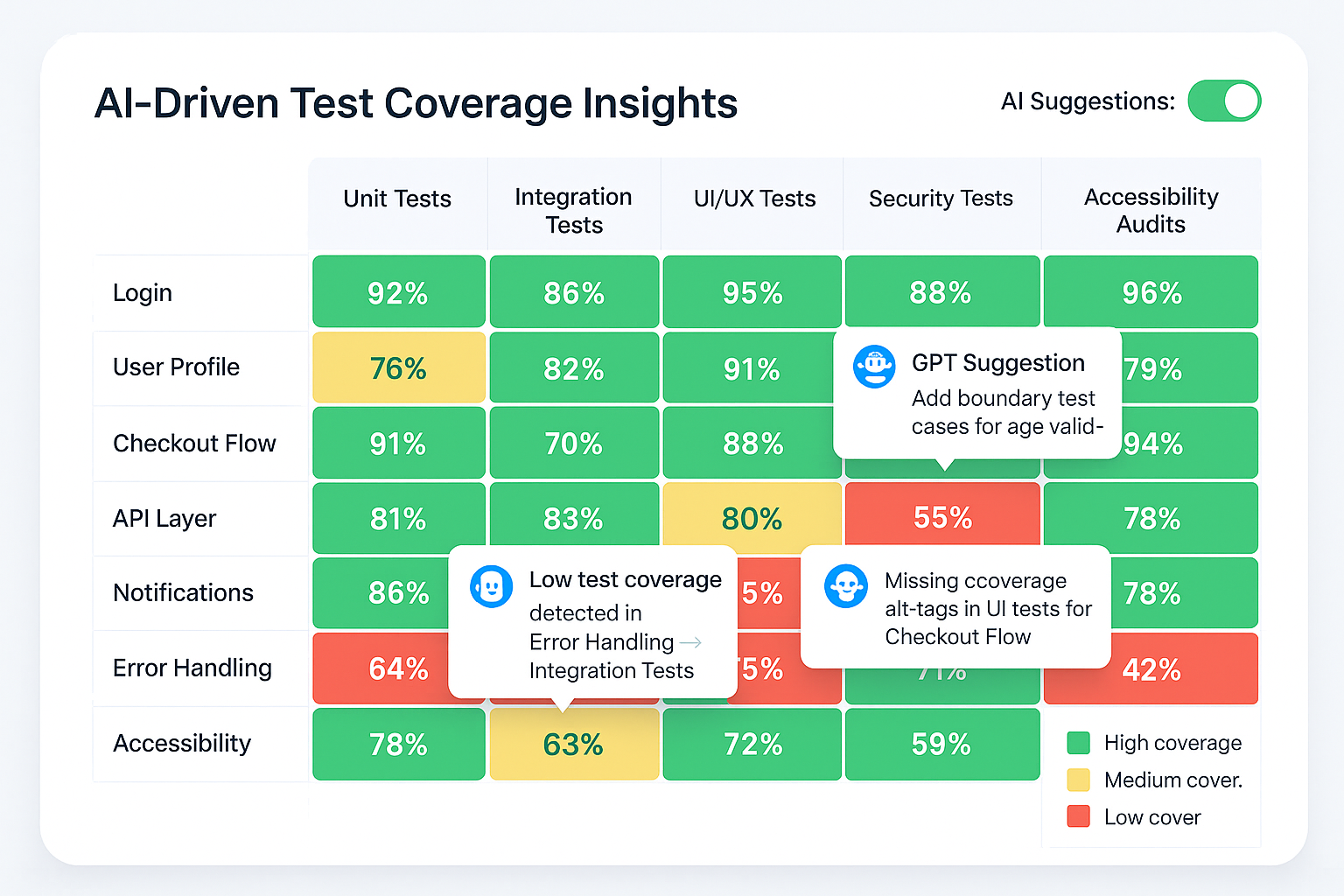
Example: Upload your full test plan, including test scripts, requirement documents, and bug reports, and GPT-5 can flag missing test coverage or suggest new edge cases in a single pass.
3. Truly Multimodal Understanding
GPT-5’s ability to handle text, images, voice, and possibly even video, makes it ideal for modern, agile testing environments.
- Upload UI screenshots and get instant feedback on layout bugs or accessibility issues.
- Speak commands during live testing sessions to fetch results or summarize logs.
- Analyze structured data like test case matrices or Swagger files directly.
Example: Upload a screenshot of your checkout page, and GPT-5 can identify misaligned elements, contrast errors, or missing alt tags, all essential for accessibility compliance.
4. Agentic Capabilities: From Instructions to Execution
GPT-5 will likely act as an autonomous AI agent, meaning it can carry out multi-step tasks independently. This is where the real productivity gains come into play.
Some examples of agentic behavior include:
- Triggering test runs in your CI/CD pipeline
- Fetching test results from TestRail or Zephyr
- Submitting bug reports directly into Jira
- Running scripts to simulate real user activity
Real-World Scenario: Say, “Run regression tests on the latest build, compare results to the previous run, and log any new failures.” GPT-5 could manage the entire workflow execution to reporting without further human input.
5. Improved Accuracy and Reduced Hallucination
GPT-5 is also being designed to minimize hallucinations those frustrating moments when AI confidently gives you incorrect information.
This upgrade is especially critical in software testing, where logical reasoning and factual accuracy are non-negotiable. You’ll be able to trust GPT-5 for things like:
- Accurately generating test cases from specs
- Reproducing bugs based on logs or user steps
- Suggesting bug fixes that are actually executable
QA Win: Reduced false positives, better bug reproduction, and a lot less manual rechecking of AI outputs.
How GPT-5 Will Reshape Your Testing Workflow
So, what does all this mean for your day-to-day as a tester or QA lead?
Here’s a breakdown of how GPT-5 can automate and enhance various parts of the software testing lifecycle:
| S. No |
Testing Area |
GPT-5 Impact |
| 1 |
Test Case Generation |
Generate edge, boundary, and negative cases from specs |
| 2 |
Code Review |
Spot logical bugs and performance bottlenecks |
| 3 |
Defect Triage |
Summarize bug logs and suggest fixes |
| 4 |
UI/UX Testing |
Identify layout issues via image analysis |
| 5 |
Accessibility Audits |
Check for WCAG violations and missing ARIA labels |
| 6 |
API Testing |
Simulate requests and validate responses |
| 7 |
Log Analysis |
Pinpoint root causes in massive logs |
| 8 |
CI/CD Integration |
Trigger tests and analyze coverage gaps |
Example: A tester uploads a user story for login functionality. GPT-5 instantly generates test cases, including failed login attempts, timeout scenarios, and JWT token expiry all aligned with business logic.
Preparing Your QA Team for the GPT-5 Era
1. Start with GPT-4o
Get hands-on with GPT-4o to understand its current capabilities. Use it to:
- Draft basic test cases
- Detect UI bugs in screenshots
- Extract key insights from logs
This practical experience lays the groundwork for smoother GPT-5 adoption.
2. Identify Where AI Can Help Most
Pinpoint tasks where your team loses time or consistency like:
- Manually writing regression test cases
- Debugging from 1,000-line logs
- Reviewing accessibility in every release
GPT-5 can take over these repetitive yet vital tasks, letting your team focus on strategic areas.
3. Plan Toolchain Integration
Evaluate how GPT-5 could plug into your existing stack. Think:
- TestRail or Zephyr for managing cases
- Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or CircleCI for automation
- Jira or YouTrack for defect management
Also, explore OpenAI’s API to build custom testing agents that fit your infrastructure.
4. Train Your Team in Prompt Engineering
GPT-5 will only be as good as the prompts you give it.
Bad Prompt:
“Test the signup form.”
Great Prompt:
“Write 10 boundary and 10 negative test cases for the signup form, covering email format, password strength, and age validation.”
Invest in prompt training sessions. It’s the key to unlocking GPT-5’s true power.
5. Track ROI and Optimize
Once integrated, measure performance improvements:
- How much faster are test cycles?
- How many defects are caught earlier?
- How much manual effort is saved?
Use this data to refine your testing strategy and justify further investment in AI-driven tools.
Looking Ahead: The Future Role of QA in an AI-First World
GPT-5 isn’t here to replace QA professionals; it’s here to augment them. Your role will evolve from test executor to AI orchestrator.
You’ll spend less time writing the same test scripts and more time:
- Strategizing for edge-case scenarios
- Guiding AI to cover risk-heavy areas
- Collaborating across Dev, Product, and Design for better releases
Insight: In the future, the best QA engineers won’t be the ones who write the most test cases but the ones who can teach AI to do it better.
Emerging Trends to Watch
- AI-Powered Test Prioritization: Use historical bug data and code diffs to run only the most impactful tests.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Let GPT-5 flag flaky tests or unstable environments as soon as they occur.
- Cross-Team Sync: Designers, developers, and QA teams can interact with GPT-5 in shared channels, closing the feedback loop faster than ever.
Final Thoughts: GPT-5 Will Redefine QA Excellence
The release of GPT-5 is more than just a new chapter it’s a rewriting of the rulebook for QA teams. Its powerful blend of multimodal understanding, intelligent orchestration, and reduced friction can make quality assurance more efficient, more strategic, and more collaborative. But success won’t come by default. To capitalize on GPT-5, QA teams need to start now by experimenting, learning, and embracing change.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Is GPT-5 better than GPT-4o for testers?
Yes. GPT-5 is expected to offer better reasoning, a larger context window, and full agentic capabilities tailored for technical tasks.
-
Can GPT-5 replace manual testing?
Not entirely. GPT-5 enhances manual testing by automating repetitive work, but exploratory and strategic testing still need human oversight.
-
What tools can GPT-5 integrate with?
GPT-5 can work with TestRail, Jira, Jenkins, GitHub Actions, Postman, and others via APIs or third-party plugins.
-
Is GPT-5 suitable for non-coders in QA?
Absolutely. With natural language inputs, non-coders can describe testing needs, and GPT-5 will generate test scripts, reports, or defect summaries.
-
How can my team start preparing?
Begin using GPT-4o, master prompt writing, and identify workflows that GPT-5 can streamline or automate.
by Rajesh K | Jul 18, 2025 | AI Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
Artificial Intelligence (AI) continues to revolutionize industries, driving unprecedented productivity and efficiency. One of its most transformative effects is on the field of automation testing, where AI tools are helping QA teams write test scripts, identify bugs, and optimize test coverage faster than ever. Among today’s standout AI tools are GitHub Copilot vs Microsoft Copilot. Though similarly named and under Microsoft’s ecosystem, these tools address entirely different needs. GitHub Copilot is like a co-pilot for developers, always ready to jump in with smart code suggestions and streamline your programming and test automation workflow. Meanwhile, Microsoft Copilot feels more like a business assistant that’s embedded right into your day-to-day apps, helping you navigate your workload with less effort and more impact.
So, how do you decide which one fits your needs? Let’s break it down together. In this blog, we’ll explore their differences, use cases, benefits, and limitations in a conversational, easy-to-digest format. Whether you’re a developer drowning in code or a business professional juggling meetings and emails, there’s a Copilot ready to help.
Understanding the Basics: What Powers GitHub and Microsoft Copilot?
Shared Foundations: OpenAI Models
Both GitHub Copilot and Microsoft Copilot are powered by OpenAI’s language models, but they’re trained and optimized differently:
| Copilot |
Underlying Model |
Hosted On |
| GitHub Copilot |
OpenAI Codex (based on GPT-3) |
GitHub servers |
| Microsoft Copilot |
GPT-4 (via Azure OpenAI) |
Microsoft Azure |
Deep Dive into GitHub Copilot
If you write code regularly, you’ve probably wished for an assistant who could handle the boring stuff like boilerplate code, test generation, or fixing those annoying syntax errors. That’s exactly what GitHub Copilot brings to the table.
Core Capabilities:
- Smart code completion as you type
- Entire function generation from a simple comment
- Generate test cases and documentation
- Translate comments or pseudo-code into working code
- Refactor messy or outdated code instantly
Supported Programming Languages:
GitHub Copilot supports a wide array of languages including:
Python, JavaScript, TypeScript, Java, Ruby, Go, PHP, C++, C#, Rust, and more
Why Developers Love It:
- It helps cut development time by suggesting full functions and reusable code snippets.
- Reduces errors early with syntax-aware suggestions.
- Encourages best practices by modeling suggestions on open-source code patterns.
Real-world Example:
Let’s say you’re building a REST API in Python. Type a comment like # create an endpoint for user login, and Copilot will instantly draft a function using Flask or FastAPI, including error handling and basic validation. That’s time saved and fewer bugs.
Comprehensive Look at Microsoft Copilot
Now, imagine you’re in back-to-back meetings, drowning in emails, and you’ve got a massive report to prepare. Microsoft Copilot jumps in like a helpful assistant, reading your emails, summarizing documents, or generating entire PowerPoint presentations—all while you focus on bigger decisions.
Core Capabilities:
- Rewrite and summarize documents or emails
- Draft email responses with tone customization
- Analyze spreadsheets and create charts using natural language
- Turn meeting transcripts into organized action items
- Build presentations from existing content or documents
Practical Use Cases:
- Word: Ask Copilot to summarize a 20-page legal document into five bullet points.
- Excel: Type “show sales trends by quarter” and it creates the charts and insights.
- Outlook: Auto-generate replies, follow-ups, or even catch tone issues.
- Teams: After a meeting, Copilot generates a summary and assigns tasks.
- PowerPoint: Turn a planning document into a visually appealing slide deck.
Why Professionals Rely on It:
- It eliminates repetitive manual tasks.
- Helps teams collaborate faster and better.
- Offers more clarity and focus by turning scattered data into actionable insights.
Security and Privacy Considerations
| Feature |
GitHub Copilot |
Microsoft Copilot |
| Data Residency |
Public code repositories |
Enterprise data residency within Azure |
| Data Retention |
Potential snippet retention |
Zero retention of business data |
| Compliance & Security |
Trust Center & Filtering options |
Microsoft 365 Compliance, DLP, permissions |
Pricing & Licensing Overview
| Copilot |
Pricing Model |
Ideal Audience |
| GitHub Copilot |
Free (students/open-source), $10-$19/user/month |
Developers, coding teams |
| Microsoft Copilot |
₹2,495 (~$30)/user/month + Microsoft 365 E3/E5 |
Business and enterprise users |
Why Were GitHub Copilot and Microsoft Copilot Created?
GitHub Copilot’s Purpose:
GitHub Copilot was born out of the need to simplify software development. Developers spend a significant portion of their time writing repetitive code, debugging, and referencing documentation. Copilot was designed to:
- Reduce the friction in the coding process
- Act as a real-time mentor for junior developers
- Increase code quality and development speed
- Encourage best practices through intelligent suggestions
Its goal? To let developers shift from mundane code generation to building more innovative and scalable software.
Microsoft Copilot’s Purpose:
Microsoft Copilot emerged as a response to the growing complexity of digital workflows. In enterprises, time is often consumed by writing reports, parsing emails, formatting spreadsheets, or preparing presentations. Microsoft Copilot was developed to:
- Minimize time spent on repetitive office tasks
- Maximize productivity across Microsoft 365 applications
- Turn information overload into actionable insights
- Help teams collaborate more effectively and consistently
It’s like having a productivity partner that understands your business tools and workflows inside out.
Which Copilot Is Right for You?
Choose GitHub Copilot if:
- You write or maintain code daily.
- You want an AI assistant to speed up coding and reduce bugs.
- Your team collaborates using GitHub or popular IDEs.
Choose Microsoft Copilot if:
- You spend most of your day in Word, Excel, Outlook, or Teams.
- You need help summarizing, analyzing, or drafting content quickly.
- You work in a regulated industry and need enterprise-grade security.
Conclusion
GitHub Copilot and Microsoft Copilot are both designed to make you more productive but in totally different ways. Developers get more done with GitHub Copilot by reducing coding overhead, while business professionals can focus on results, not grunt work, with Microsoft Copilot.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the difference between GitHub Copilot and Microsoft Copilot?
GitHub Copilot is designed for developers to assist with coding inside IDEs, while Microsoft Copilot supports productivity tasks in Microsoft 365 apps.
-
Can GitHub Copilot help junior developers?
Yes, it provides real-time coding suggestions, helping less experienced developers learn and follow best practices.
-
What applications does Microsoft Copilot integrate with?
Microsoft Copilot works with Word, Excel, Outlook, PowerPoint, and Teams to boost productivity and streamline workflows.
-
Is GitHub Copilot good for enterprise teams?
Absolutely. GitHub Copilot for Business includes centralized policy management and organization-wide deployment features.
-
Does Microsoft Copilot require an additional license?
Yes, it requires a Microsoft 365 E3/E5 license and a Copilot add-on subscription
-
Is GitHub Copilot free?
It’s free for verified students and open-source maintainers. Others can subscribe for $10/month (individuals) or $19/month (business).
-
Can Microsoft Copilot write code too?
It’s not built for coding, but it can help with simple scripting in Excel or Power Automate.
-
Is my data safe with Microsoft Copilot?
Absolutely. It uses Microsoft’s enterprise-grade compliance model and doesn’t retain your business data.
by Rajesh K | Jul 16, 2025 | Automation Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
In today’s high-velocity software development world, test automation has become the lifeblood of continuous integration and delivery. However, as testing needs grow more complex, automation tools must evolve to keep pace. One of the most promising innovations in this space is the Model Context Protocol (MCP), a powerful concept that decouples test logic from browser execution. While commercial implementations exist, open-source MCP servers are quietly making waves by offering scalable, customizable, and community-driven alternatives. This post dives deep into the world of open-source MCP servers, how they work, and why they might be the future of scalable test automation.
Understanding the Model Context Protocol (MCP)
To appreciate the potential of open-source MCP servers, we must first understand what MCP is and how it redefines browser automation. Developed by the Playwright team, MCP isn’t tied exclusively to Playwright, but rather, it represents a protocol that any automation engine could adopt.
So, what does MCP do exactly? In essence, MCP separates the test runner (logic) from the execution environment (browser). Instead of embedding automation logic directly into a browser context, MCP allows the test logic to live externally and communicate via a standardized protocol. This opens up a host of new architectural possibilities, especially for large-scale, distributed, or AI-driven test systems.
Why MCP is a Game-Changer
MCP isn’t just another buzzword; it addresses critical pain points in automation:
- Isolates test logic from browser runtime: This separation ensures better test reliability and maintainability.
- Facilitates execution in headless or distributed environments: Perfect for CI/CD pipelines.
- Ideal for AI-augmented or low-code automation: Enables smarter, more intuitive testing workflows.
- Supports multi-user test scenarios: Especially useful in enterprise-grade environments.
With these benefits, it’s no surprise that open-source implementations are gaining traction.
A Look at MCP Architecture
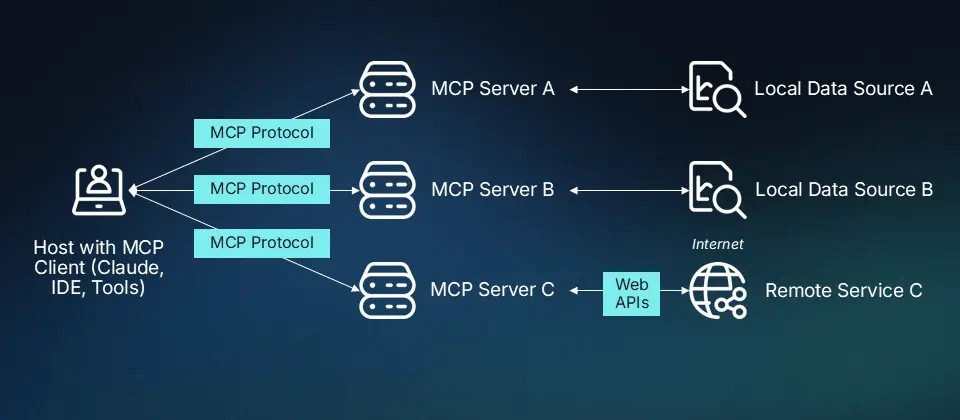
The MCP ecosystem consists of four core components:
- Model: A logical representation of a user or a test robot. Each model can operate independently and have its own logic.
- Context: A browser session that includes cookies, session storage, and isolation parameters. Think of it like a sandbox for each model.
- Client: Any tool or script that sends MCP-compatible requests. This could be anything from a custom CLI tool to IDEs like Cursor.
- Server: The engine that receives MCP requests and interacts with the browser, typically using Playwright.
This modular design is what makes MCP so flexible and scalable.
Leading Open Source MCP Servers
1. Playwright MCP Server (@playwright/mcp)
Maintained by: Microsoft / Playwright team
GitHub: @playwright/mcp
Stable Version: 0.0.18 (as of 2025)
License: MIT
Key Features:
- Native integration with Playwright automation protocols
- JSON-RPC over WebSocket for efficient communication
- Stateless operation supporting multiple contexts
- Compatible with tools like Cursor IDE and Playwright SDKs
Supported Modes:
- Headless/Headed execution
- Browser context pooling
- Multi-client distributed control
This is the gold standard for MCP implementation and a natural choice for teams already invested in Playwright.
2. Custom Python MCP Server (Community Maintained)
Built with: FastAPI + WebSockets
Use Case: Ideal for integrating with Python-based test frameworks like Pytest or Robot Framework
Availability: Various GitHub forks
Key Features:
- Lightweight JSON-RPC server
- Easy to customize and extend
- Docker-compatible for seamless deployment
For teams entrenched in the Python ecosystem, this implementation offers both simplicity and flexibility.
3. Headless MCP Containers
Use Case: Containerized MCP environments with pre-configured browsers
Technology: Typically built using Docker + @playwright/mcp
How it Works:
- Each container spins up a browser (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, WebKit)
- Exposes MCP endpoints for remote execution
Perfect for CI/CD pipelines and parallel testing jobs. This method is particularly effective for scaling test runs across distributed environments.
Real-World Applications of MCP
The adoption of MCP is already evident in several real-world tools and workflows:
- Cursor IDE: Allows real-time interaction with the MCP servers for Playwright tests
- GitHub Copilot for Tests: Uses MCP to analyze pages and auto-suggest test actions
- VSCode Extensions: Integrate with local MCP servers to support live test debugging
- CI Pipelines: Run MCP in headless mode to enable remote execution and test orchestration
These integrations illustrate the versatility and practicality of MCP in modern development workflows.
Ecosystem Support for MCP
| Sno |
Tool |
MCP Support |
| 1 |
Cursor IDE |
Full |
| 2 |
Playwright SDKs |
Partial/Native |
| 3 |
Puppeteer |
Not yet |
| 4 |
Selenium |
Not yet |
Clearly, MCP is becoming a key pillar in Playwright-centric ecosystems, with more tools expected to join in the future.
Final Thoughts: The Future is Open (Source)
Open-source MCP servers are more than just a technical novelty. They represent a shift towards a more modular, scalable, and community-driven approach to browser automation. As teams seek faster, smarter, and more reliable ways to test their applications, the flexibility of open-source MCP servers becomes an invaluable asset. Whether you’re a DevOps engineer automating CI pipelines, a QA lead integrating AI-driven test flows, or a developer looking to improve test isolation, MCP provides the architecture to support your ambitions. In embracing open-source MCP servers, we aren’t just adopting new tools; we’re aligning with a future where automation is more collaborative, maintainable, and scalable than ever before.
Interested in contributing or adopting an open-source MCP server? Start with the @playwright/mcp GitHub repo. Or, if you’re a Python enthusiast, explore the many community-led FastAPI implementations. The future of browser automation is here, and it’s open.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is an Open Source MCP Server?
An Open Source MCP (Model Context Protocol) Server is a backend service that separates test logic from browser execution, allowing for modular and scalable automation using community-maintained, customizable tools.
-
How does MCP improve test automation?
MCP improves automation by isolating the test logic from browser context, enabling parallel execution, better debugging, and support for headless or distributed systems.
-
Is MCP only compatible with Playwright?
No. Although developed by the Playwright team, MCP is a generic protocol. It can be adopted by other automation tools as well.
-
What are some popular Open Source MCP implementations?
The most notable implementations include Microsoft’s @playwright/mcp server, community-driven Python MCP servers using FastAPI, and Docker-based headless MCP containers.
-
Can I integrate MCP into my CI/CD pipeline?
Yes. MCP servers, especially containerized ones, are ideal for CI/CD workflows. They support headless execution and can be scaled across multiple jobs.
-
Is MCP suitable for low-code or AI-driven testing tools?
Absolutely. MCP’s modular nature makes it ideal for low-code interfaces, scriptable UIs, and AI-driven test generation tools.
-
Does Selenium or Puppeteer support MCP?
As of now, Selenium and Puppeteer do not natively support MCP. Full support is currently available with Playwright-based tools.
by Rajesh K | Jul 14, 2025 | Software Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
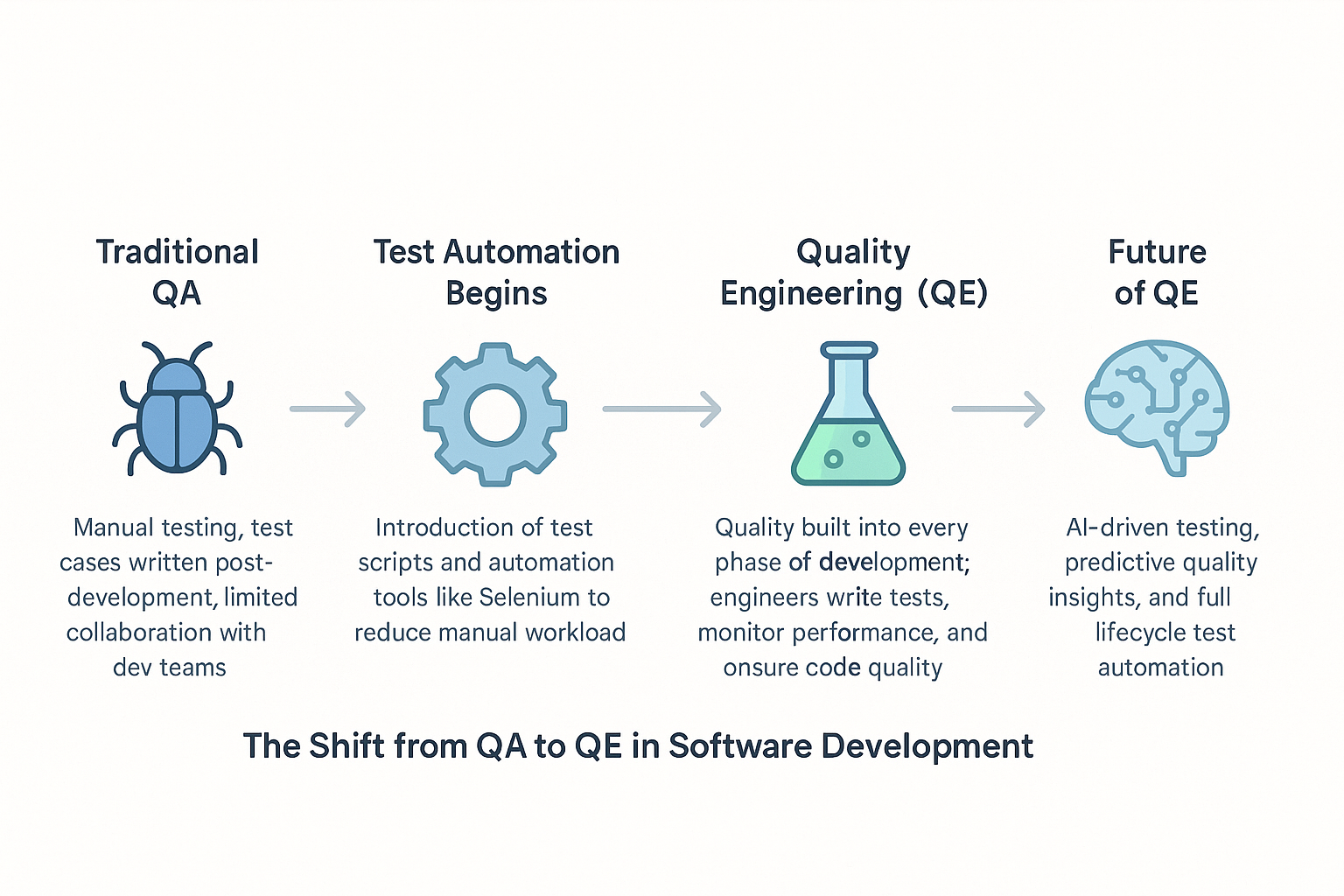
In the dynamic world of software development, the roles of Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Engineering (QE) have become increasingly significant. Although often used interchangeably, QA and QE represent two distinct philosophies and approaches to ensuring software quality. Understanding the difference between QA vs QE isn’t just a matter of semantics; it’s a strategic necessity that can impact product delivery timelines, customer satisfaction, and organizational agility. Quality Assurance has traditionally focused on maintaining standards and preventing defects through structured processes. In contrast, Quality Engineering emphasizes continuous improvement, leveraging automation, integration, and modern development methodologies to ensure quality is built into every stage of the development lifecycle.
As the demand for robust, reliable software grows, the pressure on development teams to produce high-quality products quickly has never been greater. This shift has led to the evolution from traditional QA to modern QE, prompting organizations to rethink how they define and implement quality.
This comprehensive guide will explore:
- Definitions and distinctions between QA and QE
- Historical evolution of both roles
- Key principles, tools, and methodologies
- How QA and QE impact the software development lifecycle
- Real-world applications and use cases
- Strategic advice for choosing and balancing both
Whether you’re a QA engineer looking to future-proof your skills or a tech lead deciding how to structure your quality teams, this post will provide the clarity and insights you need.
What is Quality Assurance (QA)?
Quality Assurance is a systematic approach to ensuring that software meets specified requirements and adheres to predefined quality standards. QA focuses on process-oriented activities that aim to prevent defects before they reach the end-user.
Key Objectives of QA:
- Detect and prevent defects early
- Ensure compliance with standards and regulations
- Improve the development process through audits and reviews
- Enhance customer satisfaction
Core Practices:
- Manual and automated test execution
- Risk-based testing
- Test case design and traceability
- Regression testing
Real-life Example: Imagine launching a healthcare application. QA processes ensure that critical features like patient data entry, billing, and compliance logging meet regulatory standards before deployment.
What is Quality Engineering (QE)?
Quality Engineering takes a broader and more proactive approach to software quality. It integrates quality checks throughout the software development lifecycle (SDLC), using automation, CI/CD pipelines, and collaboration across teams.
Key Objectives of QE:
- Embed quality throughout the SDLC
- Use automation to accelerate testing
- Foster continuous improvement and learning
- Improve time-to-market without compromising quality
Core Practices:
- Test automation and framework design
- Performance and security testing
- CI/CD integration
- Shift-left testing and DevOps collaboration
Example: In a fintech company, QE engineers automate tests for real-time transaction engines and integrate them into the CI pipeline. This ensures each code change is instantly verified for performance and security compliance.
A Historical Perspective: QA to QE
Origins of QA
QA finds its roots in manufacturing during the Industrial Revolution, where early pioneers like Frederick Winslow Taylor introduced methods to enhance production quality. It later evolved into statistical quality control and eventually into Total Quality Management (TQM).
Rise of QE
As software complexity increased, the need for more adaptive and continuous approaches led to the rise of QE. Emerging technologies like machine learning, cloud computing, and containerization demanded real-time testing and feedback mechanisms that QA alone couldn’t deliver.
Transitioning to QE allowed teams to scale testing, support agile methodologies, and automate redundant tasks.
QA vs QE: What Sets Them Apart?
| S. No |
Aspect |
Quality Assurance (QA) |
Quality Engineering (QE) |
| 1 |
Primary Focus |
Process consistency and defect prevention |
Continuous improvement and test automation |
| 2 |
Approach |
Reactive and checklist-driven |
Proactive and data-driven |
| 3 |
Testing Methodology |
Manual + limited automation |
Automated, integrated into CI/CD |
| 4 |
Tools |
ISO 9001, statistical tools |
Selenium, Jenkins, TestNG, Cypress |
| 5 |
Goal |
Ensure product meets requirements |
Optimize the entire development process |
| 6 |
Team Integration |
Separate from dev teams |
Embedded within cross-functional dev teams |
Methodologies and Tools
QA Techniques:
- Waterfall testing strategies
- Use of quality gates and defect logs
- Functional and non-functional testing
- Compliance and audit reviews
QE Techniques:
- Agile testing and TDD (Test-Driven Development)
- CI/CD pipelines with automated regression
- Integration with DevOps workflows
- Machine learning for predictive testing
How QA and QE Impact the SDLC
QA’s Contribution:
- Maintains documentation and traceability
- Ensures final product meets acceptance criteria
- Reduces production bugs through rigorous test cycles
QE’s Contribution:
- Reduces bottlenecks via automation
- Promotes faster delivery and frequent releases
- Improves developer-tester collaboration
Use Case: A SaaS startup that transitioned from traditional QA to QE saw a 35% drop in production defects and reduced release cycles from monthly to weekly.
Team Structures and Roles
QA Team Roles:
- QA Analyst: Designs and runs tests
- QA Lead: Manages QA strategy and reporting
- Manual Tester: Conducts exploratory testing
QE Team Roles:
- QE Engineer: Builds automation frameworks
- SDET (Software Development Engineer in Test): Writes code-level tests
- DevOps QA: Monitors quality metrics in CI/CD pipelines
Choosing Between QA and QE (Or Combining Both)
While QA ensures a strong foundation in risk prevention and compliance, QE is necessary for scalability, speed, and continuous improvement.
When to Choose QA:
- Regulatory-heavy industries (e.g., healthcare, aviation)
- Projects with fixed scopes and waterfall models
When to Embrace QE:
- Agile and DevOps teams
- High-release velocity environments
- Need for frequent regression testing
Ideal Approach: Combine QA and QE
- Use QA for strategic oversight and manual validations
- Use QE to drive test automation and CI/CD integration
Conclusion: QA vs QE Is Not a Battle It’s a Balance
As software development continues to evolve, so must our approach to quality. QA and QE serve complementary roles in the pursuit of reliable, scalable, and efficient software delivery. The key is not to choose one over the other, but to understand when and how to apply both effectively. Organizations that blend the disciplined structure of QA with the agility and innovation of QE are better positioned to meet modern quality demands. Whether you’re scaling your automation efforts or tightening your compliance protocols, integrating both QA and QE into your quality strategy is the path forward.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Is QE replacing QA in modern development teams?
No. QE is an evolution of QA, not a replacement. Both roles coexist to support different aspects of quality.
-
Can a QA professional transition to a QE role?
Absolutely. With training in automation, CI/CD, and agile methodologies, QA professionals can successfully move into QE roles.
-
Which role has more demand in the industry?
Currently, QE roles are growing faster due to the industry's shift toward DevOps and agile. However, QA remains essential in many sectors.
-
What skills are unique to QE?
Automation scripting, familiarity with tools like Selenium, Jenkins, and Docker, and understanding of DevOps pipelines.
-
How do I know if my organization needs QA, QE, or both?
Evaluate your current development speed, defect rates, and regulatory needs. If you're aiming for faster releases and fewer bugs, QE is essential. For process stability, keep QA.

by Rajesh K | Jul 11, 2025 | Software Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
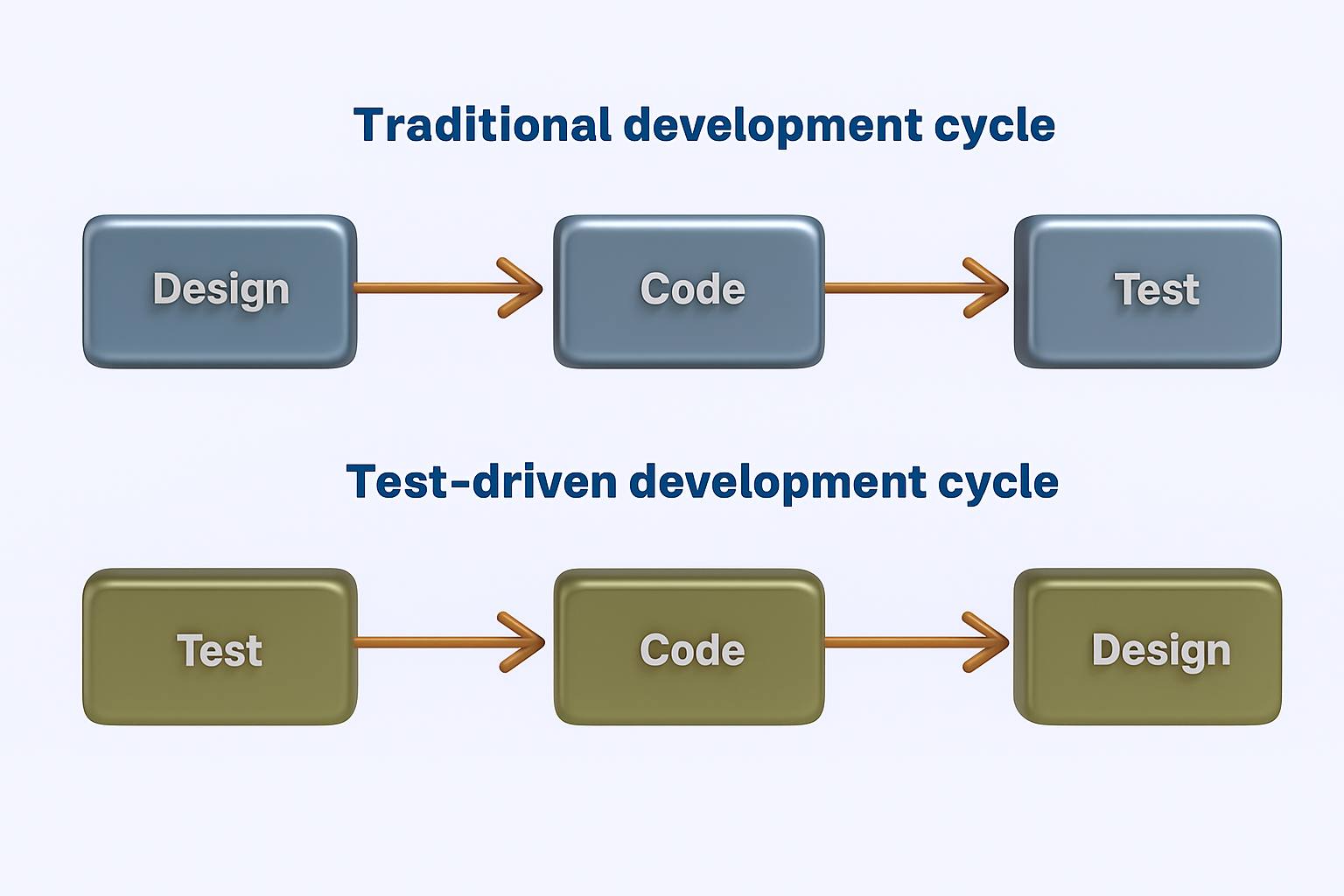
In the fast-paced world of software development, teams are expected to deliver high-quality products quickly, often under shifting requirements. Enter Test Driven Development in Agile, a software testing strategy that flips traditional coding on its head by writing tests before the actual code. This preemptive approach ensures that every new feature is verified from the start, resulting in fewer bugs, faster feedback loops, and more maintainable code. TDD is especially powerful within Agile frameworks, where iterative progress, continuous feedback, and adaptability are core principles. By integrating software testing into the early stages of development, teams stay aligned with business goals, stakeholders are kept in the loop, and the software evolves with greater confidence and less rework.
But adopting TDD is more than just writing tests; it’s about transforming your development culture. Whether you’re a QA lead, automation tester, or product owner, understanding how TDD complements Agile can help you deliver robust applications that meet customer needs and business goals.
What is Test Driven Development (TDD)?
Test Driven Development (TDD) is a development methodology where tests are written before the actual code. This ensures that each unit of functionality is driven by specific requirements, resulting in focused, minimal, and testable code.
Core Principles of TDD:
- Write a test first for a new feature.
- Run the test and watch it fail (Red).
- Write just enough code to pass the test (Green).
- Refactor the code to improve the design while keeping tests green.
This process, known as the Red-Green-Refactor cycle, is repeated for every new feature or function.
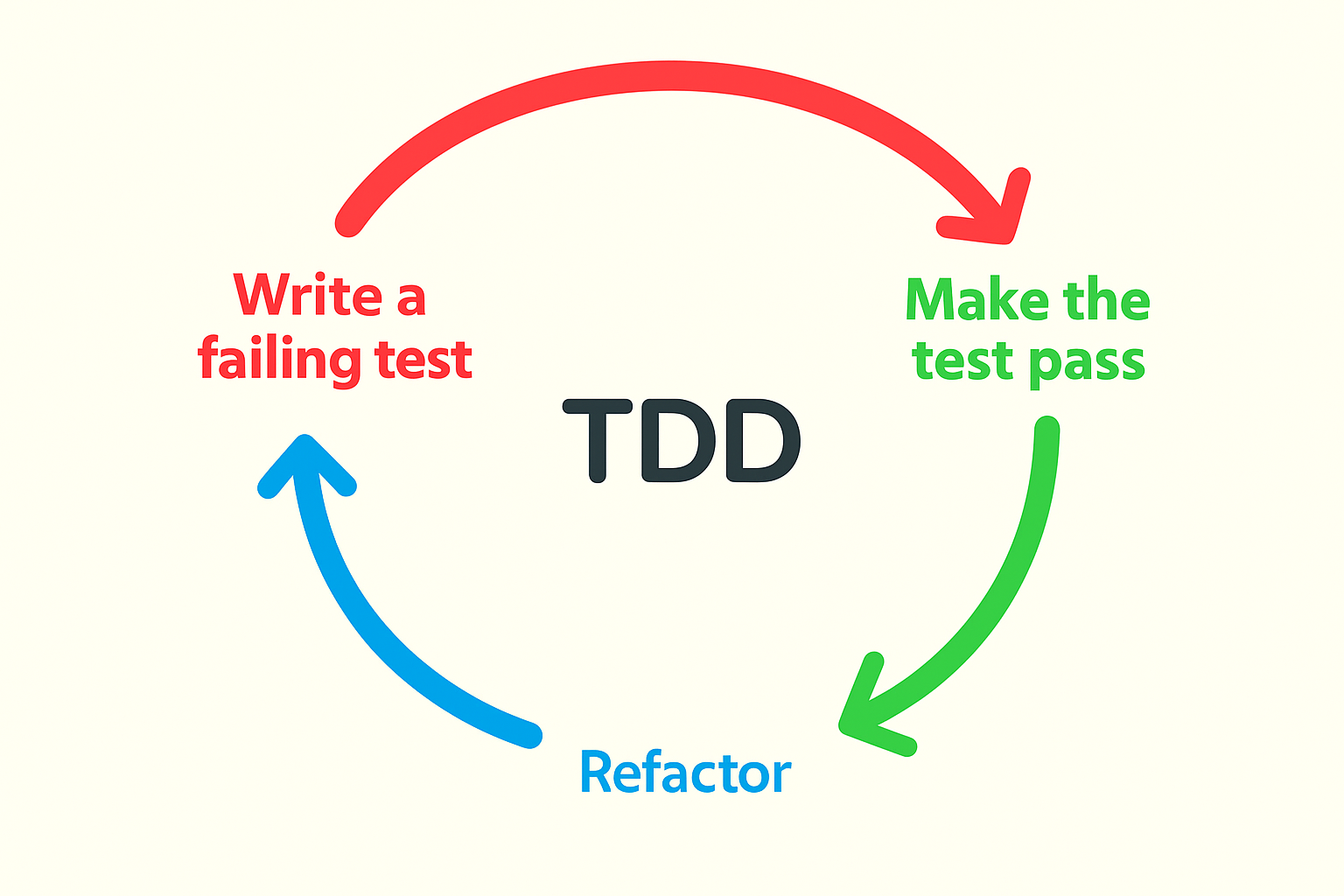
The Red-Green-Refactor Cycle Explained
Here’s a quick breakdown of how this loop works:
- Red: Write a unit test for a specific behavior. It should fail because the behavior doesn’t exist yet.
- Green: Write the minimum code necessary to make the test pass.
- Refactor: Clean up the code while keeping all tests passing.
This tight loop ensures fast feedback, minimizes overengineering, and leads to cleaner, more reliable code.
How TDD Integrates with Agile Methodologies
Agile promotes adaptability, transparency, and continuous delivery. TDD aligns perfectly with these values by embedding quality checks into each sprint and ensuring features are verified before they’re shipped.
TDD Enables Agile by:
- Ensuring code quality in short iterations
- Offering real-time validation of features
- Empowering cross-functional collaboration
- Supporting continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) pipelines
Example:
During a sprint, a development team writes tests based on the acceptance criteria of a user story. As they develop the functionality, the passing tests confirm adherence to requirements. If the criteria change mid-sprint, modifying tests keeps the team aligned with new priorities.
Key Benefits of TDD in Agile Teams
| S. No |
Benefit |
How It Helps Agile Teams |
| 1 |
Higher Code Quality |
Prevents bugs through test-first development |
| 2 |
Faster Feedback |
Reduces cycle time with instant test results |
| 3 |
Better Collaboration |
Shared understanding of feature requirements |
| 4 |
Safe Refactoring |
Enables confident changes to legacy code |
| 5 |
Improved Maintainability |
Modular, testable code evolves easily |
| 6 |
Supports Continuous Delivery |
Automated tests streamline deployment |
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
- Inadequate Test Coverage
Problem: Over-focus on unit tests might ignore system-level issues.
Solution: Complement TDD with integration and end-to-end tests.
- Initial Slowdown in Development
Problem: Writing tests first can feel slow early on.
Solution: ROI comes with time through reduced bugs and maintenance.
- Skill Gaps
Problem: Teams may lack test writing experience.
Solution: Invest in training and pair programming.
- Balancing Coverage and Speed
Focus on:
- High-risk areas
- Edge cases
- Critical user flows
Best Practices for Effective TDD in Agile
- Start Small: Begin with simple units before scaling to complex logic.
- Use the Inside-Out Approach: Write core logic tests before peripheral ones.
- Maintain Clean Test Code: Keep tests as clean and readable as production code.
- Document Test Intent: Comment on what the test verifies and why.
- Review and Refactor Tests: Don’t let test code rot over time.
Tools and Frameworks to Support TDD
| S. No |
Stack |
Frameworks |
CI/CD Tools |
| 1 |
Java |
JUnit, TestNG |
Jenkins, GitLab CI |
| 2 |
.NET |
NUnit, xUnit |
Azure DevOps, TeamCity |
| 3 |
JavaScript |
Jest, Mocha |
GitHub Actions, CircleCI |
| 4 |
Python |
PyTest, unittest |
Travis CI, Bitbucket Pipelines |
Advanced TDD Strategies for Scaling Teams
- Automate Everything: Integrate testing in CI pipelines for instant feedback.
- Mock External Systems: Use mocks or stubs for APIs and services to isolate units.
- Measure Test Coverage: Aim for 80–90%, but prioritize meaningful tests over metrics.
- Test Data Management: Use fixtures or factories to handle test data consistently.
Real-World Example: TDD in a Sprint Cycle
A product team receives a user story to add a “Forgot Password” feature.
Sprint Day 1:
QA and dev collaborate on writing tests for the expected behavior.
Tests include: email input validation, error messaging, and token generation.
Sprint Day 2–3:
Devs write just enough code to pass the tests.
Refactor and push code to CI. Tests pass.
Sprint Day 4:
Stakeholders demo the feature using a staging build with all tests green.
Outcome:
- No bugs.
- Code was released with confidence.
- Stakeholders trust the process and request more TDD adoption.
Conclusion
Test Driven Development in agile is not just a technical methodology; it’s a mindset shift that helps Agile teams deliver more reliable, maintainable, and scalable software. By placing testing at the forefront of development, TDD encourages precision, accountability, and collaboration across roles. It supports the core Agile values of responsiveness and continuous improvement, enabling teams to produce functional code with confidence. Whether you’re starting small or scaling enterprise-wide, implementing TDD can lead to significant improvements in your software quality, team efficiency, and stakeholder satisfaction. Start embedding TDD in your Agile workflow today to future-proof your development process.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the biggest advantage of TDD in Agile?
The biggest advantage is early bug detection and confidence in code changes, which aligns with Agile’s goal of fast, reliable delivery.
-
How much time should be spent on writing TDD tests?
Typically, 20–30% of development time should be reserved for writing and maintaining tests.
-
Is TDD suitable for large and complex applications?
Yes, especially when combined with integration and end-to-end testing. It helps manage complexity and enables safer refactoring.
-
Can TDD slow down initial development?
It might initially, but over time, it leads to faster and more stable releases.
-
What skills do developers need for TDD?
Strong knowledge of testing frameworks, good design practices, and experience with version control and CI/CD tools.

by Rajesh K | Jul 10, 2025 | Automation Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
Automation testing has revolutionized software quality assurance by streamlining repetitive tasks and accelerating development cycles. However, manually creating test scripts remains a tedious, error-prone, and time-consuming process. This is where Playwright Codegen comes in a built-in feature of Microsoft’s powerful Playwright automation testing framework that simplifies test creation by automatically generating scripts based on your browser interactions. In this in-depth tutorial, we’ll dive into how Playwright Codegen can enhance your automation testing workflow, saving you valuable time and effort. Whether you’re just starting with test automation or you’re an experienced QA engineer aiming to improve efficiency, you’ll learn step-by-step how to harness Playwright Codegen effectively. We’ll also cover its key advantages, possible limitations, and provide hands-on examples to demonstrate best practices.
What is Playwright Codegen?
Playwright Codegen acts like a macro recorder specifically tailored for web testing. It captures your interactions within a browser session and converts them directly into usable test scripts in JavaScript, TypeScript, Python, or C#. This powerful feature allows you to:
- Rapidly bootstrap new test scripts
- Easily learn Playwright syntax and locator strategies
- Automatically generate robust selectors
- Minimize manual coding efforts
Ideal Use Cases for Playwright Codegen
- Initial setup of automated test suites
- Smoke testing critical user flows
- Quickly identifying locators and interactions for complex web apps
- Learning and training new team members
Prerequisites for Using Playwright Codegen
Before getting started, ensure you have:
- Node.js (version 14 or later)
- Playwright installed:
- Automatically via:
npm init playwright@latest
- Or manually:
npm install -D @playwright/test
npx playwright install
Step-by-Step Guide to Using Playwright Codegen
Step 1: Launch Codegen
Run the following command in your terminal, replacing <URL> with the web address you want to test:
npx playwright codegen <URL>
Example:
npx playwright codegen https://codoid.com
This launches a browser, records your interactions, and generates corresponding code.
Step 2: Select Your Output Language (Optional)
You can specify your preferred programming language:
npx playwright codegen --target=python https://example.com
npx playwright codegen --target=typescript https://example.com
Step 3: Save and Execute Your Script
- Copy the generated code.
- Paste it into a test file (e.g., test.spec.ts).
- Execute your test:
Sample Cleaned-Up Test
import { test, expect } from '@playwright/test';
test('login flow', async ({ page }) => {
await page.goto('https://example.com/login');
await page.fill('#username', 'myUser');
await page.fill('#password', 'securePass123');
await page.click('button[type="submit"]');
await expect(page).toHaveURL('https://example.com/dashboard');
});
Commonly Used Codegen Flags
| S. No |
Flag |
Description |
| 1 |
–target=<lang> |
Output language (js, ts, Python, C#) |
| 2 |
–output=filename |
Save the generated code directly to a file |
| 3 |
–save-storage=auth.json |
Save login session state for authenticated tests |
| 4 |
–device=<device> |
Emulate devices (e.g., \”iPhone 13\”) |
Example:
npx playwright codegen --target=ts --output=login.spec.ts https://example.com
Handling Authentication
Playwright Codegen can save and reuse authentication states:
npx playwright codegen --save-storage=auth.json https://yourapp.com/login
Reuse saved login sessions in your tests:
test.use({ storageState: 'auth.json' });
Tips for Writing Effective Playwright Tests
- Regularly clean up generated scripts to remove unnecessary actions.
- Always add meaningful assertions (expect()) to verify functionality.
- Refactor code to follow the Page Object Model (POM) for better scalability.
- Regularly review and maintain your test scripts for maximum reliability.
Advantages of Using Playwright Codegen
- Time Efficiency: Rapidly generates test scaffolds.
- Beginner-Friendly: Eases the learning of syntax and locators.
- Reliable Selectors: Uses modern, stable selectors.
- Language Versatility: Supports JavaScript, TypeScript, Python, and C#.
- Prototyping: Ideal for MVP or smoke tests.
- Authentication Handling: Easily reuse authenticated sessions.
- Mobile Emulation: Supports device emulation for mobile testing.
Conclusion
Playwright Codegen is an excellent starting point to accelerate your test automation journey. It simplifies initial test script creation, making automation more accessible for beginners and efficient for seasoned testers. For long-term success, ensure that generated tests are regularly refactored, validated, and structured into reusable and maintainable components. Ready to master test automation with Playwright Codegen? Download our free automation testing checklist to ensure you’re following best practices from day one!
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is Playwright Codegen used for?
Playwright Codegen is used to automatically generate test scripts by recording browser interactions. It's a quick way to bootstrap tests and learn Playwright's syntax and selector strategies.
-
Can I use Playwright Codegen for all types of testing?
While it's ideal for prototyping, smoke testing, and learning purposes, it's recommended to refine the generated code for long-term maintainability and comprehensive testing scenarios.
-
Which programming languages does Codegen support?
Codegen supports JavaScript, TypeScript, Python, and C#, allowing flexibility based on your tech stack.
-
How do I handle authentication in Codegen?
You can use the --save-storage flag to save authentication states, which can later be reused in tests using the storageState property.
-
Can I emulate mobile devices using Codegen?
Yes, use the --device flag to emulate devices like \"iPhone 13\" for mobile-specific test scenarios.
-
Is Codegen suitable for CI/CD pipelines?
Codegen itself is more of a development aid. For CI/CD, it's best to use the cleaned and optimized scripts generated via Codegen.
-
How can I save the generated code to a file?
Use the --output flag to directly save the generated code to a file during the Codegen session.