by Rajesh K | Jul 3, 2025 | Performance Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
Delivering high-performance applications is not just a competitive advantage it’s a necessity. Whether you’re launching a web app, scaling an API, or ensuring microservices perform under load, performance testing is critical to delivering reliable user experiences and maintaining operational stability. To meet these demands, teams rely on powerful performance testing tools to simulate traffic, identify bottlenecks, and validate system behavior under stress. Among the most popular open-source tools are JMeter vs Gatling vs k6 each offering unique strengths tailored to different team needs and testing strategies. This blog provides a detailed comparison of JMeter, Gatling, and k6, highlighting their capabilities, performance, usability, and suitability across varied environments. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of which tool aligns best with your testing requirements and development workflow.
Overview of the Tools
Apache JMeter
Apache JMeter, developed by the Apache Software Foundation, is a widely adopted open-source tool for performance and load testing. Initially designed for testing web applications, it has evolved into a comprehensive solution capable of testing a broad range of protocols.
Key features of JMeter include a graphical user interface (GUI) for building test plans, support for multiple protocols like HTTP, JDBC, JMS, FTP, LDAP, and SOAP, an extensive plugin library for enhanced functionality, test script recording via browser proxy, and support for various result formats and real-time monitoring.
JMeter is well-suited for QA teams and testers requiring a robust, GUI-driven testing tool with broad protocol support, particularly in enterprise or legacy environments.
Gatling
Gatling is an open-source performance testing tool designed with a strong focus on scalability and developer usability. Built on Scala and Akka, it employs a non-blocking, asynchronous architecture to efficiently simulate high loads with minimal system resources.
Key features of Gatling include code-based scenario creation using a concise Scala DSL, a high-performance execution model optimized for concurrency, detailed and visually rich HTML reports, native support for HTTP and WebSocket protocols, and seamless integration with CI/CD pipelines and automation tools.
Gatling is best suited for development teams testing modern web applications or APIs that require high throughput and maintainable, code-based test definitions.
k6
k6 is a modern, open-source performance testing tool developed with a focus on automation, developer experience, and cloud-native environments. Written in Go with test scripting in JavaScript, it aligns well with contemporary DevOps practices.
k6 features test scripting in JavaScript (ES6 syntax) for flexibility and ease of use, lightweight CLI execution designed for automation and CI/CD pipelines, native support for HTTP, WebSocket, gRPC, and GraphQL protocols, compatibility with Docker, Kubernetes, and modern observability tools, and integrations with Prometheus, Grafana, InfluxDB, and other monitoring platforms.
k6 is an optimal choice for DevOps and engineering teams seeking a scriptable, scalable, and automation-friendly tool for testing modern microservices and APIs.
Getting Started with JMeter, Gatling, and k6: Installation
Apache JMeter
Prerequisites: Java 8 or higher (JDK recommended)
To begin using JMeter, ensure that Java is installed on your machine. You can verify this by running java -version in the command line. If Java is not installed, download and install the Java Development Kit (JDK).
Download JMeter:
Visit the official Apache JMeter site at https://jmeter.apache.org/download_jmeter.cgi. Choose the binary version appropriate for your OS and download the .zip or .tgz file. Once downloaded, extract the archive to a convenient directory such as C:\jmeter or /opt/jmeter.
Run and Verify JMeter Installation:
Navigate to the bin directory inside your JMeter folder and run the jmeter.bat (on Windows) or jmeter script (on Unix/Linux) to launch the GUI. Once the GUI appears, your installation is successful.
To confirm the installation, create a simple test plan with an HTTP request and run it. Check the results using the View Results Tree listener.
Gatling
Prerequisites: Java 8+ and familiarity with Scala
Ensure Java is installed, then verify Scala compatibility, as Gatling scripts are written in Scala. Developers familiar with IntelliJ IDEA or Eclipse can integrate Gatling into their IDE for enhanced script development.
Download Gatling:
Visit https://gatling.io/products and download the open-source bundle in .zip or .tar.gz format. Extract it and move it to your desired directory.
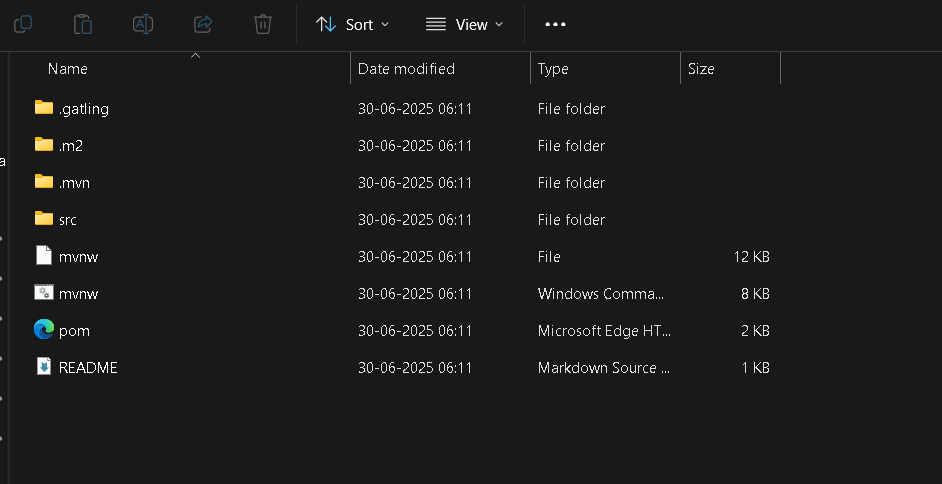
Explore the Directory Structure:
- src/test/scala: Place your simulation scripts here, following proper package structures.
- src/test/resources: Store feeders, body templates, and config files.
- pom.xml: Maven build configuration.
- target: Output folder for test results and reports.
Run Gatling Tests:
Open a terminal in the root directory and execute bin/gatling.sh (or .bat for Windows). Choose your simulation script and view real-time console stats. Reports are automatically generated in HTML and saved under the target folder.
k6
Prerequisites: Command line experience and optionally Docker/Kubernetes familiarity
k6 is built for command-line use, so familiarity with terminal commands is beneficial.
Install k6:
Follow instructions from https://grafana.com/docs/k6/latest/set-up/install-k6/ based on your OS. For macOS, use brew install k6; for Windows, use choco install k6; and for Linux, follow the appropriate package manager instructions.
Verify Installation:
Run k6 version in your terminal to confirm successful setup. You should see the installed version of k6 printed.
Create and Run a Test:
Write your test script in a .js file using JavaScript ES6 syntax. For example, create a file named test.js:
import http from 'k6/http';
import { sleep } from 'k6';
export default function () {
http.get('https://test-api.k6.io');
sleep(1);
}
Execute it using k6 run test.js. Results will appear directly in the terminal, and metrics can be pushed to external monitoring systems if integrated.
k6 also supports running distributed tests using xk6-distributed or using the commercial k6 Cloud service for large-scale scenarios.
1. Tool Overview
| S. No |
Feature |
JMeter |
Gatling |
k6 |
| 1 |
Language |
Java-based; GUI and XML config |
Scala-based DSL scripting |
JavaScript (ES6) scripting |
| 2 |
GUI Availability |
Full-featured desktop GUI |
Only a recorder GUI |
No GUI (CLI + dashboards) |
| 3 |
Scripting Style |
XML, Groovy, Beanshell |
Programmatic DSL (Scala) |
JavaScript with modular scripts |
| 4 |
Protocol Support |
Extensive (HTTP, FTP, etc.) |
HTTP, HTTPS, WebSockets |
HTTP, HTTPS, WebSockets |
| 5 |
Load Generation |
Local and distributed |
Local and distributed |
Local, distributed, cloud-native |
| 6 |
Licensing |
Apache 2.0 |
Apache 2.0 |
AGPL-3.0 (OSS + paid SaaS) |
2. Ease of Use & Learning Curve
| S. No |
Feature |
JMeter |
Gatling |
k6 |
| 1 |
Learning Curve |
Moderate – intuitive GUI |
Steep – requires Scala |
Easy to moderate – JavaScript |
| 2 |
Test Creation |
GUI-based, verbose XML |
Code-first, reusable scripts |
Script-first, modular JS |
| 3 |
Best For |
QA engineers, testers |
Automation engineers |
Developers, SREs, DevOps teams |
3. Performance & Scalability
| S. No |
Feature |
JMeter |
Gatling |
k6 |
| 1 |
Resource Efficiency |
High usage under load |
Lightweight, optimized |
Extremely efficient |
| 2 |
Concurrency |
Good with distributed mode |
Handles large users well |
Massive concurrency design |
| 3 |
Scalability |
Distributed setup |
Infrastructure-scalable |
Cloud-native scalability |
4. Reporting & Visualization
| S. No |
Feature |
JMeter |
Gatling |
k6 |
| 1 |
Built-in Reports |
Basic HTML + plugins |
Rich HTML reports |
CLI summary + Grafana/InfluxDB |
| 2 |
Real-time Metrics |
Plugin-dependent |
Built-in stats during execution |
Strong via CLI + external tools |
| 3 |
Third-party |
Grafana, InfluxDB, Prometheus |
Basic integration options |
Deep integration: Grafana, Prometheus |
5. Customization & DevOps Integration
| S. No |
Feature |
JMeter |
Gatling |
k6 |
| 1 |
Scripting Flexibility |
Groovy, Beanshell, JS extensions |
Full Scala and DSL |
Modular, reusable JS scripts |
| 2 |
CI/CD Integration |
Jenkins, GitLab (plugin-based) |
Maven, SBT, Jenkins |
GitHub Actions, Jenkins, GitLab (native) |
| 3 |
DevOps Readiness |
Plugin-heavy, manual setup |
Code-first, CI/CD pipeline-ready |
Automation-friendly, container-native |
6. Pros and Cons
| S. No |
Tool |
Pros |
Cons |
| 1 |
JMeter |
GUI-based, protocol-rich, mature ecosystem |
High resource use, XML complexity, not dev-friendly |
| 2 |
Gatling |
Clean code, powerful reports, efficient |
Requires Scala, limited protocol support |
| 3 |
k6 |
Lightweight, scriptable, cloud-native |
No GUI, AGPL license, SaaS for advanced features |
7. Best Use Cases
| S. No |
Tool |
Ideal For |
Not Ideal For |
| 1 |
JMeter |
QA teams needing protocol diversity and GUI |
Developer-centric, code-only teams |
| 2 |
Gatling |
Teams requiring maintainable scripts and rich reports |
Non-coders, GUI-dependent testers |
| 3 |
k6 |
CI/CD, cloud-native, API/microservices testing |
Users needing GUI or broader protocol |
JMeter vs. Gatling: Performance and Usability
Gatling, with its asynchronous architecture and rich reports, is a high-performance option ideal for developers. JMeter, though easier for beginners with its GUI, consumes more resources and is harder to scale. While Gatling requires Scala knowledge, it outperforms JMeter in execution efficiency and report detail, making it a preferred tool for code-centric teams.
JMeter vs. k6: Cloud-Native and Modern Features
k6 is built for cloud-native workflows and CI/CD integration using JavaScript, making it modern and developer-friendly. While JMeter supports a broader range of protocols, it lacks k6’s automation focus and observability integration. Teams invested in modern stacks and microservices will benefit more from k6, whereas JMeter is a strong choice for protocol-heavy enterprise setups.
Gatling and k6: A Comparative Analysis
Gatling offers reliable performance testing via a Scala-based DSL, focusing on single test types like load testing. k6, however, allows developers to configure metrics and test methods flexibly from the command line. Its xk6-browser module further enables frontend testing, giving k6 a broader scope than Gatling’s backend-focused design.
Comparative Overview: JMeter, Gatling, and k6
JMeter, with its long-standing community, broad protocol support, and GUI, is ideal for traditional enterprises. Gatling appeals to developers preferring maintainable, code-driven tests and detailed reports. k6 stands out in cloud-native setups, prioritizing automation, scalability, and observability. While JMeter lowers the entry barrier, Gatling and k6 deliver higher flexibility and efficiency for modern testing environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Which tool is best for beginners?
JMeter is best for beginners due to its user-friendly GUI and wide community support, although its XML scripting can become complex for large tests.
-
Is k6 suitable for DevOps and CI/CD workflows?
Yes, k6 is built for automation and cloud-native environments. It integrates easily with CI/CD pipelines and observability tools like Grafana and Prometheus.
-
Can Gatling be used without knowledge of Scala?
While Gatling is powerful, it requires familiarity with Scala for writing test scripts, making it better suited for developer teams comfortable with code.
-
Which tool supports the most protocols?
JMeter supports the widest range of protocols including HTTP, FTP, JDBC, JMS, and SOAP, making it suitable for enterprise-level testing needs.
-
How does scalability compare across the tools?
k6 offers the best scalability for cloud-native tests. Gatling is lightweight and handles concurrency well, while JMeter supports distributed testing but is resource-intensive.
-
Are there built-in reporting features in these tools?
Gatling offers rich HTML reports out of the box. k6 provides CLI summaries and integrates with dashboards. JMeter includes basic reports and relies on plugins for advanced metrics
-
Which performance testing tool should I choose?
Choose JMeter for protocol-heavy enterprise apps, Gatling for code-driven and high-throughput tests, and k6 for modern, scriptable, and scalable performance testing.
by Rajesh K | Jun 1, 2025 | Artificial Intelligence, Blog, Latest Post |
Automated UI testing has long been a critical part of software development, helping ensure reliability and consistency across web applications. However, traditional automation tools like Selenium, Playwright, and Cypress often require extensive scripting knowledge, complex framework setups, and time-consuming maintenance. Enter Operator GPT, an intelligent AI agent that radically simplifies UI testing by allowing testers to write tests in plain English. Built on top of large language models like GPT-4, it can understand natural language instructions, perform UI interactions, validate outcomes, and even adapt tests when the UI changes. In this blog, we’ll explore how Operator GPT works, how it compares to traditional testing methods, when to use it, and how it integrates with modern QA stacks. We’ll also explore platforms adopting this technology and provide real-world examples to showcase its power.
What is Operator GPT?
Operator GPT is a conversational AI testing agent that performs UI automation tasks by interpreting natural language instructions. Rather than writing scripts in JavaScript, Python, or Java, testers communicate with Operator GPT using plain language. The system parses the instruction, identifies relevant UI elements, performs interactions, and returns test results with screenshots and logs.
Key Capabilities of Operator GPT:
- Natural language-driven testing
- Self-healing test flows using AI vision and DOM inference
- No-code or low-code test creation
- Works across browsers and devices
- Integrates with CI/CD pipelines and tools like Slack, TestRail, and JIRA
Traditional UI Testing vs Operator GPT
| S. No |
Feature |
Traditional Automation Tools (Selenium, Playwright) |
Operator GPT |
| 1 |
Language |
Code (Java, JS, Python) |
Natural Language |
| 2 |
Setup |
Heavy framework, locator setup |
Minimal, cloud-based |
| 3 |
Maintenance |
High (selectors break easily) |
Self-healing |
| 4 |
Skill Requirement |
High coding knowledge |
Low, great for manual testers |
| 5 |
Test Creation Time |
Slow |
Fast & AI-assisted |
| 6 |
Visual Recognition |
Limited |
Built-in AI/vision mapping |
How Operator GPT Works for UI Testing
- Input Instructions: You give Operator GPT a prompt like:
“Test the login functionality by entering valid credentials and verifying the dashboard.”
- Web/App Interaction: It opens a browser, navigates to the target app, locates elements, interacts (like typing or clicking), and performs validation.
- Result Logging: Operator GPT provides logs, screenshots, and test statuses.
- Feedback Loop: You can refine instructions conversationally:
“Now check what happens if password is left blank.”
Example: Login Flow Test with Operator GPT
Let’s walk through a real-world example using Reflect.run or a similar GPT-powered testing tool.
Test Scenario:
Goal: Test the login functionality of a demo site
URL: https://practicetestautomation.com/practice-test-login/
Credentials:
- Username: student
- Password: Password123
Natural Language Test Prompt:
- Go to https://practicetestautomation.com/practice-test-login/.
- Enter username as “student”.
- Enter password as “Password123”.
- Clicks the login button
- Click the login button.
Verify that the page navigates to a welcome screen with the text “Logged In Successfully”.
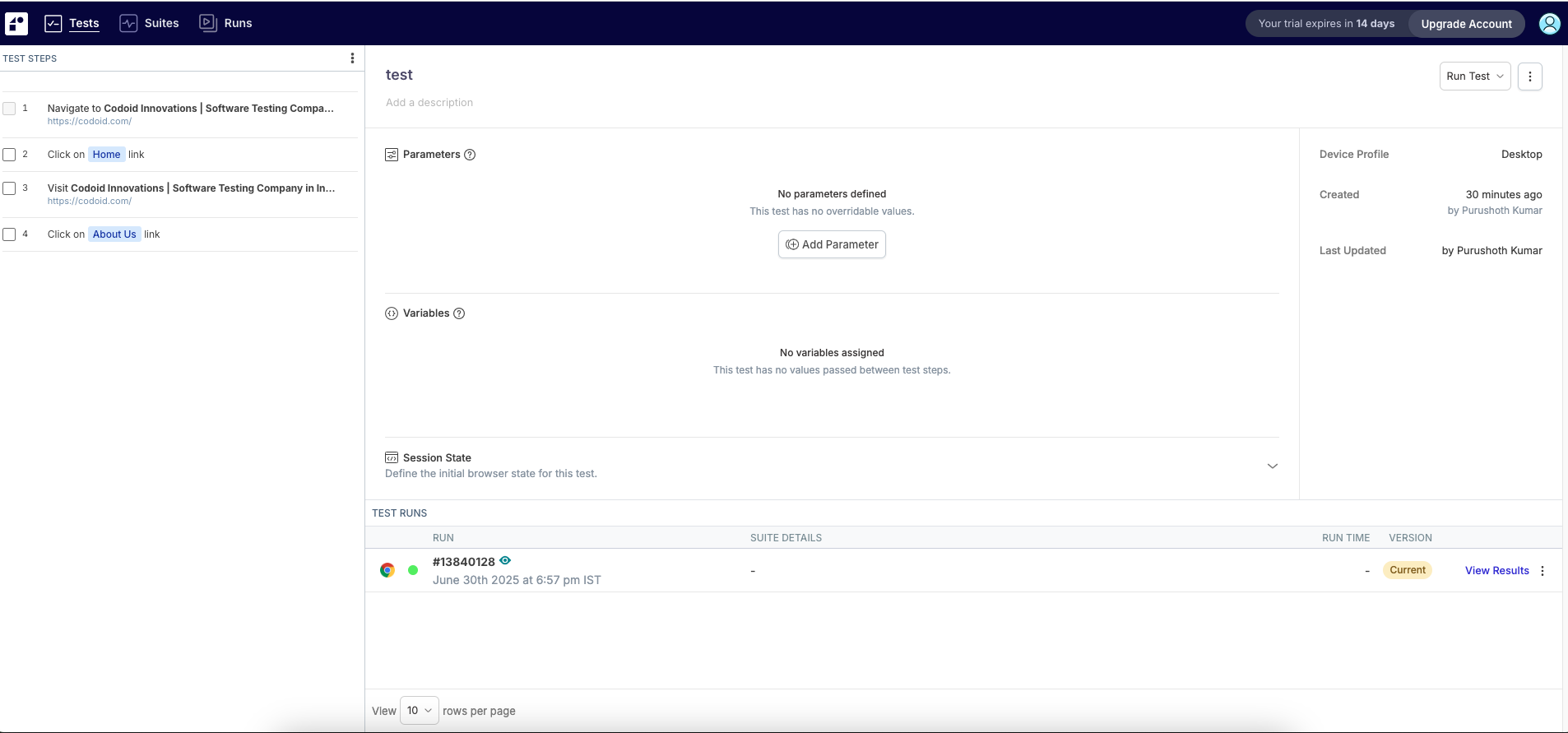
{
"status": "PASS",
"stepResults": [
"Navigated to login page",
"Entered username: student",
"Entered password: *****",
"Clicked login",
"Found text: Logged In Successfully"
],
"screenshot": "screenshot-logged-in.png"
}
This test was created and executed in under a minute, without writing a single line of code.
Key Benefits of Operator GPT
The real strength of Operator GPT lies in its ability to simplify, accelerate, and scale UI testing.
1. Reduced Time to Test
Natural language eliminates the need to write boilerplate code or configure complex test runners.
2. Democratized Automation
Manual testers, product managers, and designers can all participate in test creation.
3. Self-Healing Capability
Unlike static locators in Selenium, Operator GPT uses vision AI and adaptive learning to handle UI changes.
4. Enhanced Feedback Loops
Faster test execution means earlier bug detection in the development cycle, supporting true continuous testing.
Popular Platforms Supporting GPT-Based UI Testing
- Reflect.run – Offers no-code, natural language-based UI testing in the browser
- Testim by Tricentis – Uses AI Copilot to accelerate test creation
- AgentHub – Enables test workflows powered by GPT agents
- Cogniflow – Combines AI with automation for natural instruction execution
- QA-GPT (Open Source) – A developer-friendly project using LLMs for test generation
These tools are ideal for fast-paced teams that need to test frequently without a steep technical barrier.
When to Use Operator GPT (And When Not To)
Ideal Use Cases:
- Smoke and regression tests
- Agile sprints with rapid UI changes
- Early prototyping environments
- Teams with limited engineering resources
Limitations:
- Not built for load or performance testing
- May struggle with advanced DOM scenarios like Shadow DOM
- Best paired with visual consistency for accurate element detection
Integrating Operator GPT into Your Workflow
Operator GPT is not a standalone tool; it’s designed to integrate seamlessly into your ecosystem.
You can:
- Trigger tests via CLI or REST APIs in CI/CD pipelines
- Export results to TestRail, Xray, or JIRA
- Monitor results directly in Slack with chatbot integrations
- Use version control for prompt-driven test cases
This makes it easy to blend natural-language testing into agile and DevOps workflows without disruption.
Limitations to Consider
- It relies on UI stability; drastic layout changes can reduce accuracy.
- Complex dynamic behaviors (like real-time graphs) may require manual checks.
- Self-healing doesn’t always substitute for code-based assertions.
That said, combining Operator GPT with traditional test suites offers the best of both worlds.
The Future of Testing:
Operator GPT is not just another automation tool; it represents a shift in how we think about testing. Instead of focusing on how something is tested (scripts, locators, frameworks), Operator GPT focuses on what needs to be validated from a user or business perspective. As GPT models grow more contextual, they’ll understand product requirements, user stories, and even past defect patterns, making intent-based automation not just viable but preferable.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is Operator GPT?
Operator GPT is a GPT-powered AI agent for automating UI testing using natural language instead of code.
-
Who can use Operator GPT?
It’s designed for QA engineers, product managers, designers, and anyone else involved in software testing no coding skills required.
-
Does it replace Selenium or Playwright?
Not entirely. Operator GPT complements these tools by enabling faster prototyping and natural language-driven testing for common flows.
-
Is it suitable for enterprise testing?
Yes. It integrates with CI/CD tools, reporting dashboards, and test management platforms, making it enterprise-ready.
-
How do I get started?
Choose a platform (e.g., Reflect.run), connect your app, type your first test, and watch it run live.

by Rajesh K | Jun 26, 2025 | Accessibility Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
Ensuring accessibility is not just a compliance requirement but a responsibility. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 1 in 6 people globally live with some form of disability. These users often rely on assistive technologies like screen readers, keyboard navigation, and transcripts to access digital content. Unfortunately, many websites and applications fall short due to basic accessibility oversights. Accessibility testing plays a crucial role in identifying and addressing these issues early. Addressing common accessibility issues not only helps you meet standards like WCAG, ADA, and Section 508, but also improves overall user experience and SEO. A more inclusive web means broader reach, higher engagement, and ultimately, greater impact. Through this article, we explore common accessibility issues found in real-world projects. These are not theoretical examples; they’re based on actual bugs discovered during rigorous testing. Let’s dive into the practical breakdown of accessibility concerns grouped by content type.
1. Heading Structure Issues
Proper heading structures help users using screen readers understand the content hierarchy and navigate pages efficiently.
Bug 1: Heading Not Marked as a Heading
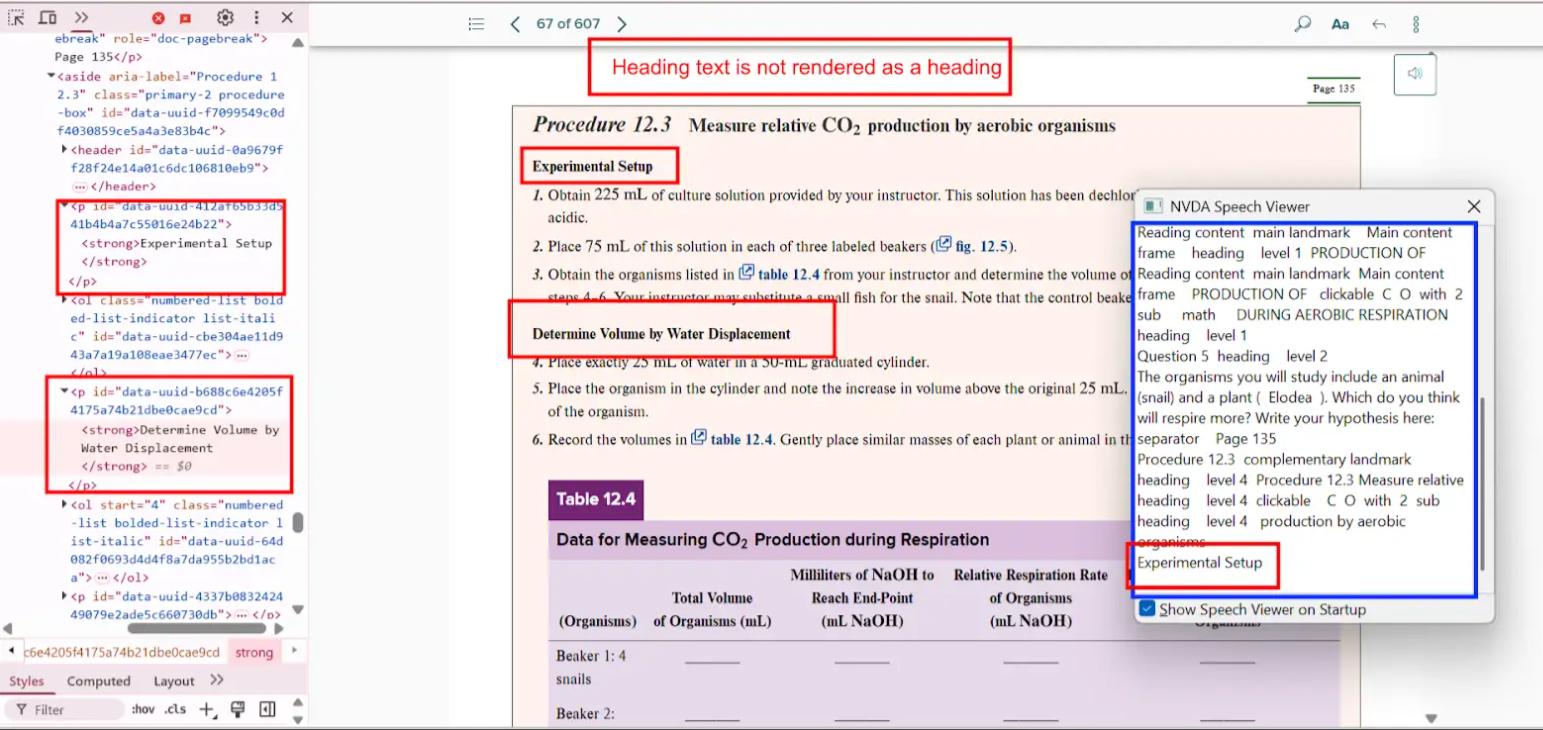
- Actual: The heading “Project Scope Statement” is rendered as plain text without any heading tag.
- Expected: Apply appropriate semantic HTML like
<h1>, <h2>, etc., to define heading levels.
- Impact: Users relying on screen readers may miss the section altogether or fail to grasp its significance.
- Tip: Always structure headings in a logical hierarchy, starting with
<h1>.
Bug 2: Incorrect Heading Level Used
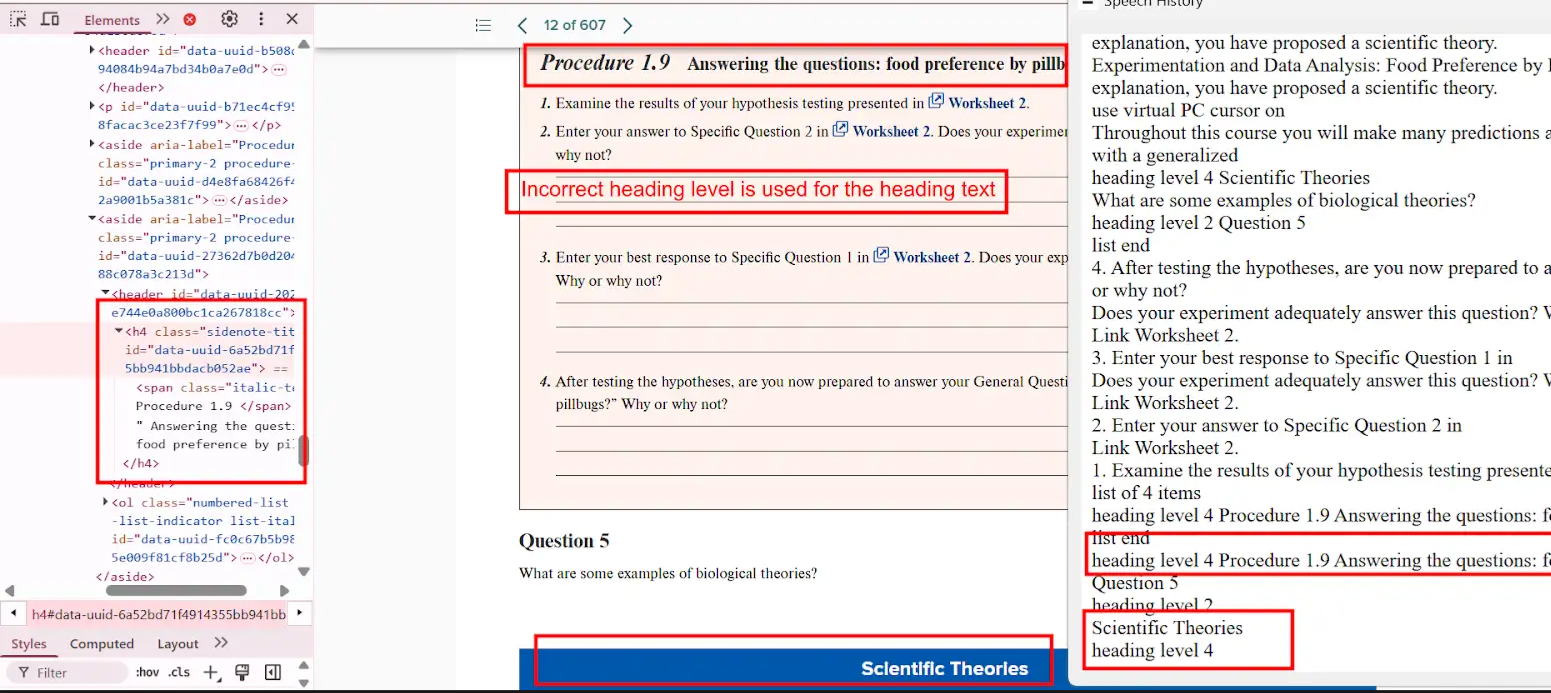
- Actual: “Scientific Theories” is read as
<h4>, although it should be a sub-section of an <h4> heading.
- Expected: Adjust the tag to
<h5> or correct parent heading level.
- Impact: Breaks logical flow for assistive technologies, causing confusion.
- Tip: Use accessibility tools like the WAVE tool to audit heading levels.
Bug 3: Missing <h1> Tag
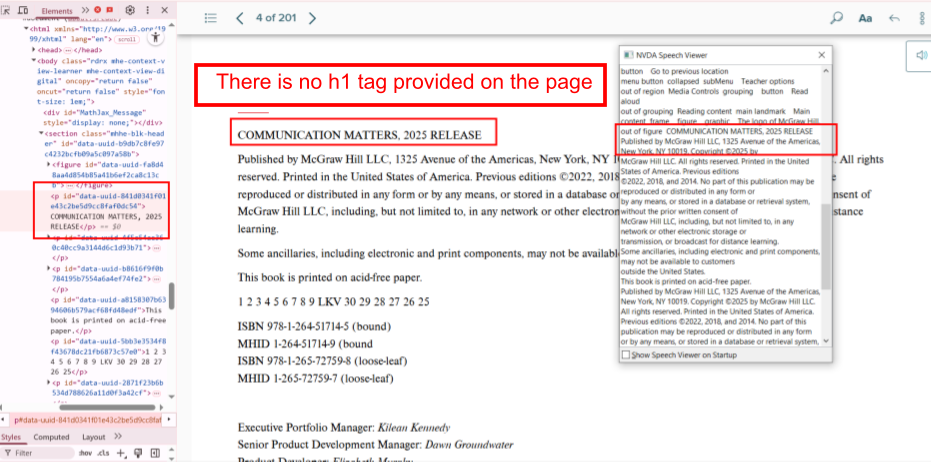
- Actual: The page lacks an
<h1> tag, which defines the main topic.
- Expected: Include an
<h1> tag at the top of every page.
- Impact: Reduces both accessibility and SEO.
- Tip:
<h1> should be unique per page and describe the page content.
2. Image Accessibility Issues
Images need to be accessible for users who cannot see them, especially when images convey important information.
Bug 4: Missing Alt Text for Informative Image
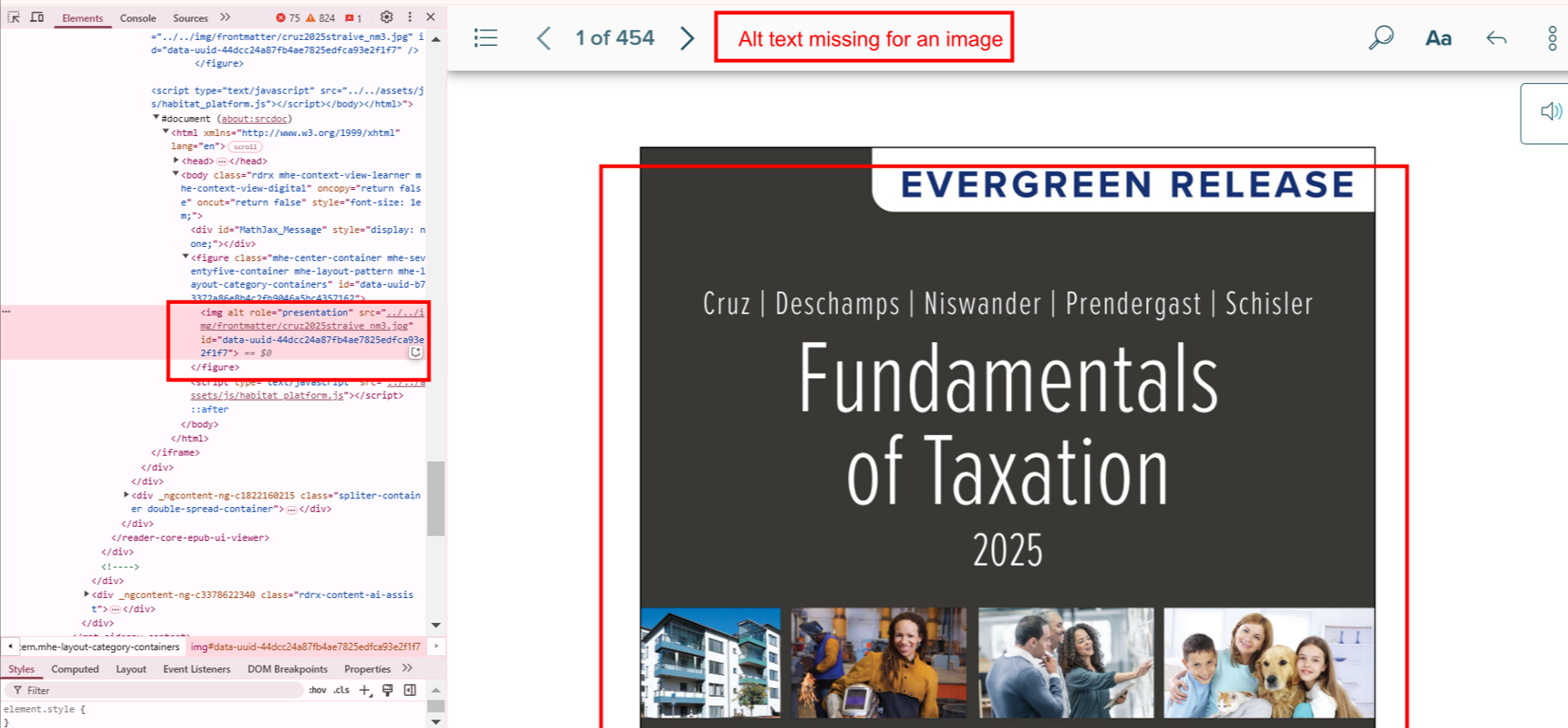
- Actual: Alt attribute is missing for an image containing instructional content.
- Expected: Provide a short, meaningful alt text.
- Impact: Screen reader users miss essential information.
- Tip: Avoid using “image of” or “picture of” in alt text; go straight to the point.
Bug 5: Missing Long Description for Complex Image
- Actual: A complex diagram has no detailed description.
- Expected: Include a
longdesc or use ARIA attributes for complex visuals.
- Impact: Users miss relationships, patterns, or data described.
- Tip: Consider linking to a textual version nearby
3. List Markup Issues
List semantics are crucial for conveying grouped or ordered content meaningfully.
Bug 7: Missing List Tags

- Actual: A series of points is rendered as plain text.
- Expected: Use
<ul> or <ol> with <li> for each item.
- Impact: Screen readers treat it as one long paragraph.
- Tip: Use semantic HTML, not CSS-based visual formatting alone.
Bug 8: Incorrect List Type
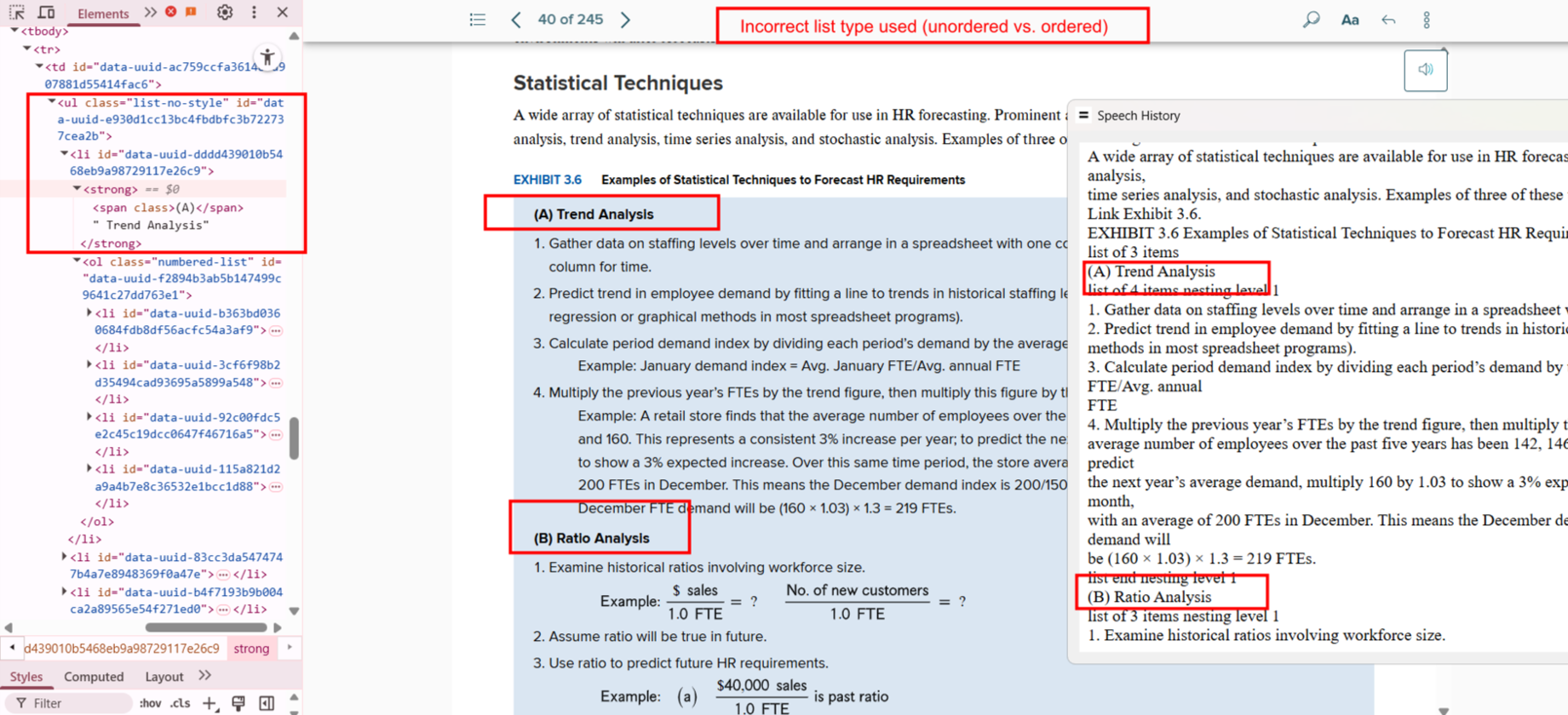
- Actual: An ordered list is coded as
<ul>.
- Expected: Replace
<ul> with <ol> where sequence matters.
- Impact: Users can’t tell that order is significant.
- Tip: Use
<ol> for steps, sequences, or rankings.
Bug 9: Single-Item List
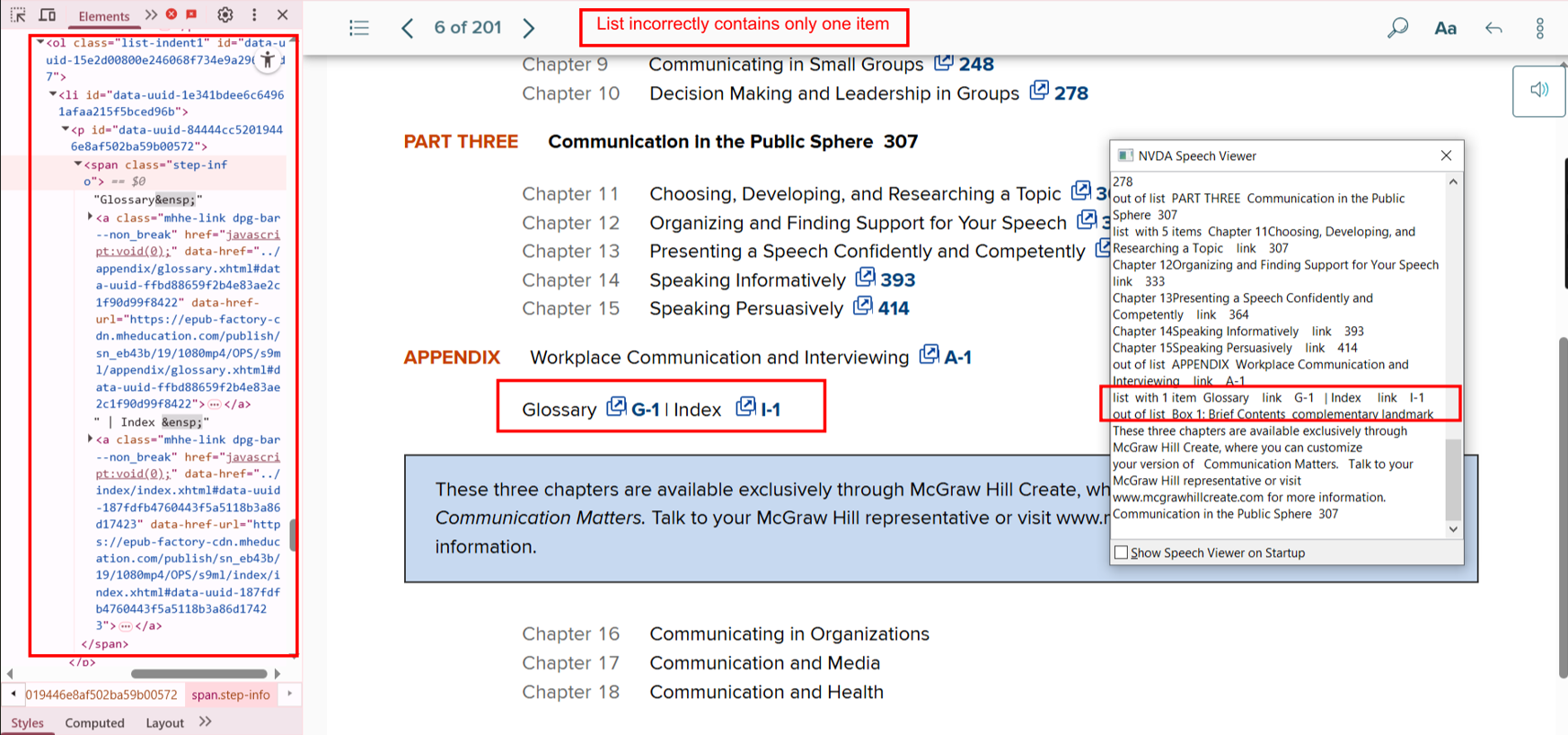
- Actual: A list with only one
<li>.
- Expected: Remove the list tag or combine with other content.
- Impact: Adds unnecessary navigation complexity.
- Tip: Avoid lists unless grouping multiple elements.
Bug 10: Fragmented List Structure
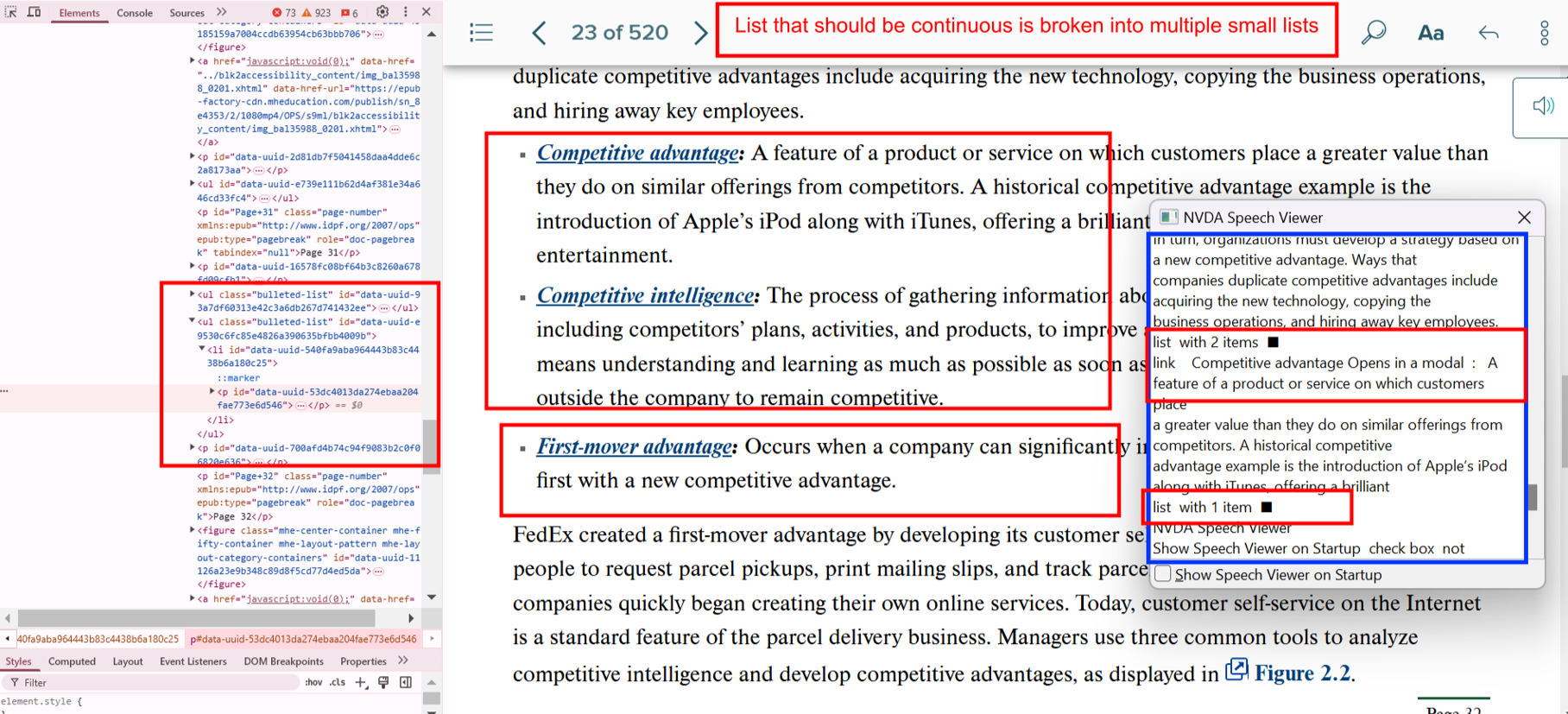
- Actual: Related list items split across separate lists.
- Expected: Combine all relevant items into a single list.
- Impact: Misrepresents logical groupings.
- Tip: Use list nesting if needed to maintain hierarchy.
4. Table Accessibility Issues
Tables must be well-structured to be meaningful when read aloud by screen readers.
Bug 11: Missing Table Headers
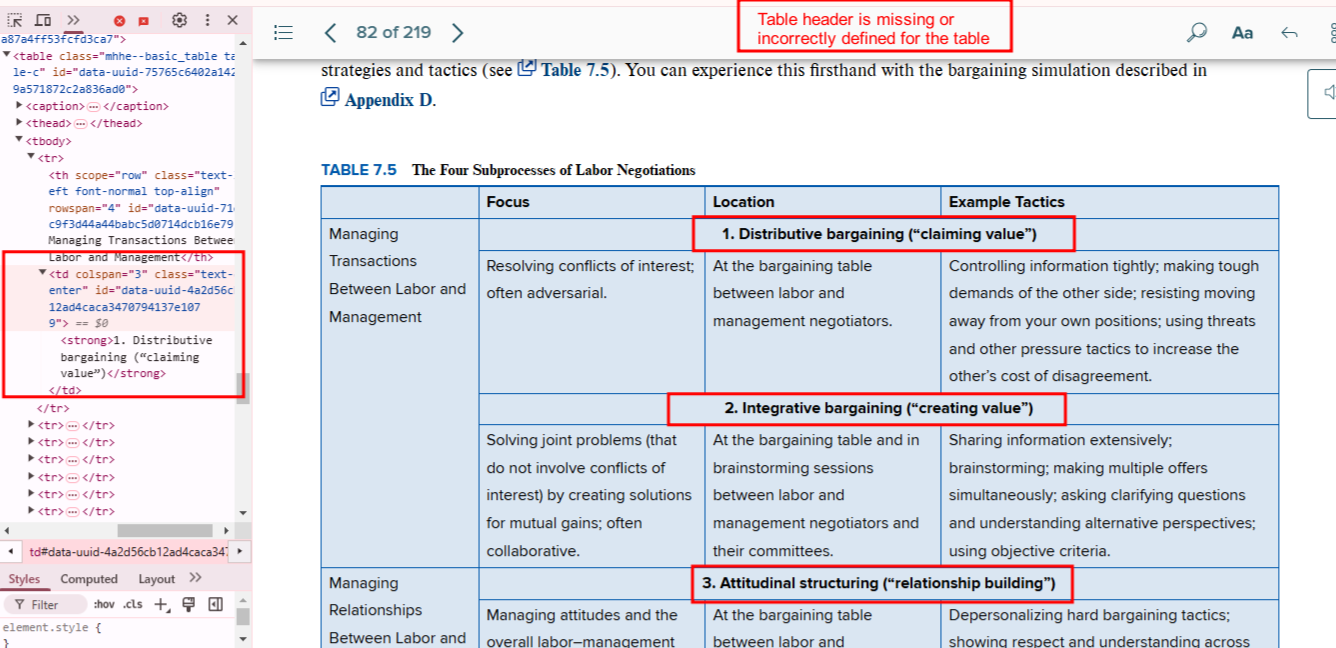
- Actual: Data cells lack
<th> elements.
- Expected: Use
<th> for headers, with appropriate scope attributes.
- Impact: Users can’t understand what the data represents.
- Tip: Define row and column headers clearly.
Bug 12: Misleading Table Structure
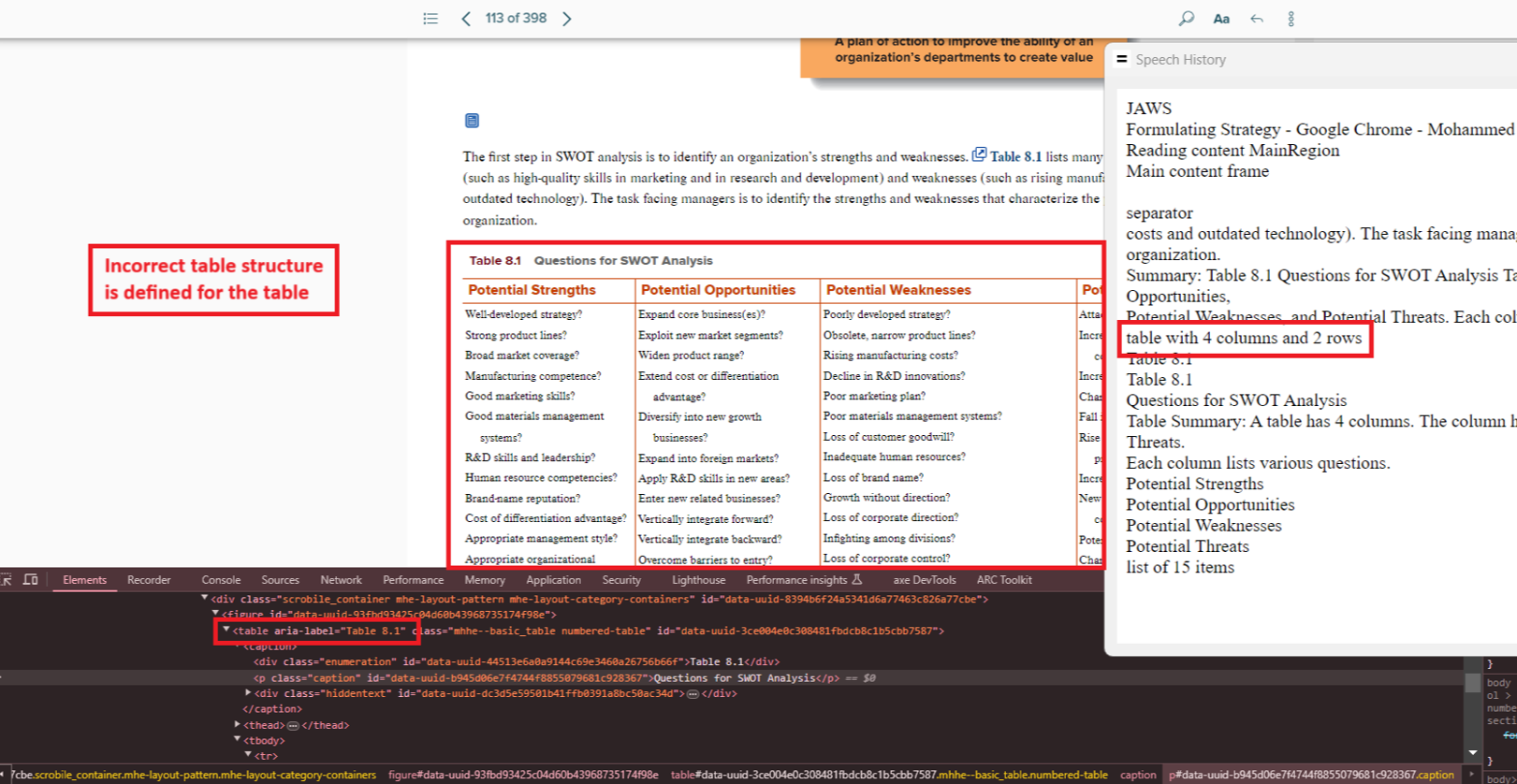
- Actual: Table structure inaccurately reflects 2 rows instead of 16.
- Expected: Ensure correct markup for rows and columns.
- Impact: Critical data may be skipped.
- Tip: Validate with screen readers or accessibility checkers.
Bug 13: Inadequate Table Summary
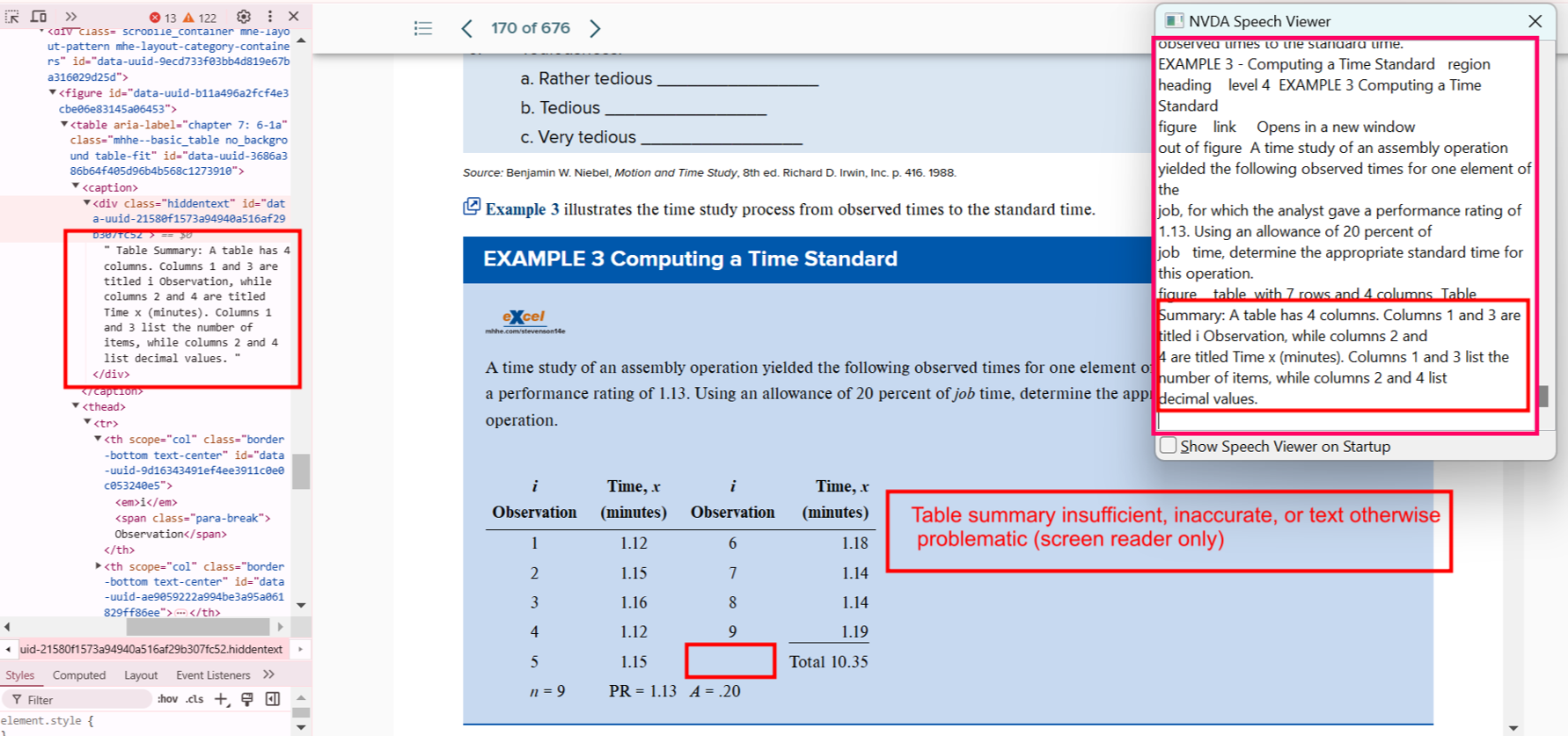
- Actual: Blank cells aren’t explained.
- Expected: Describe cell usage and purpose.
- Impact: Leaves users guessing.
- Tip: Use ARIA attributes or visible descriptions.
Bug 14: List Data Formatted as Table
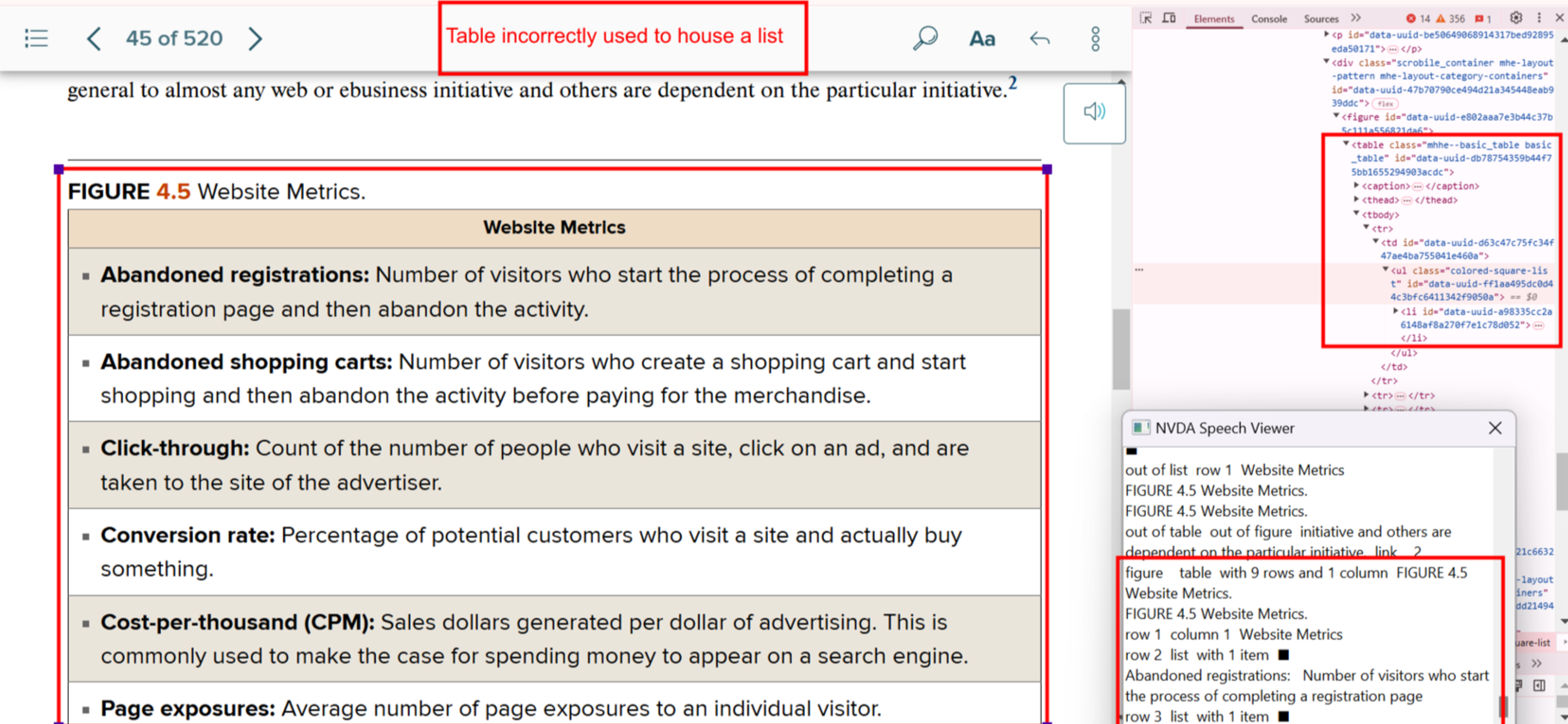
- Actual: Single-category list shown in table format.
- Expected: Reformat into semantic list.
- Impact: Adds unnecessary table complexity.
- Tip: Choose the simplest semantic structure.
Bug 15: Layout Table Misuse
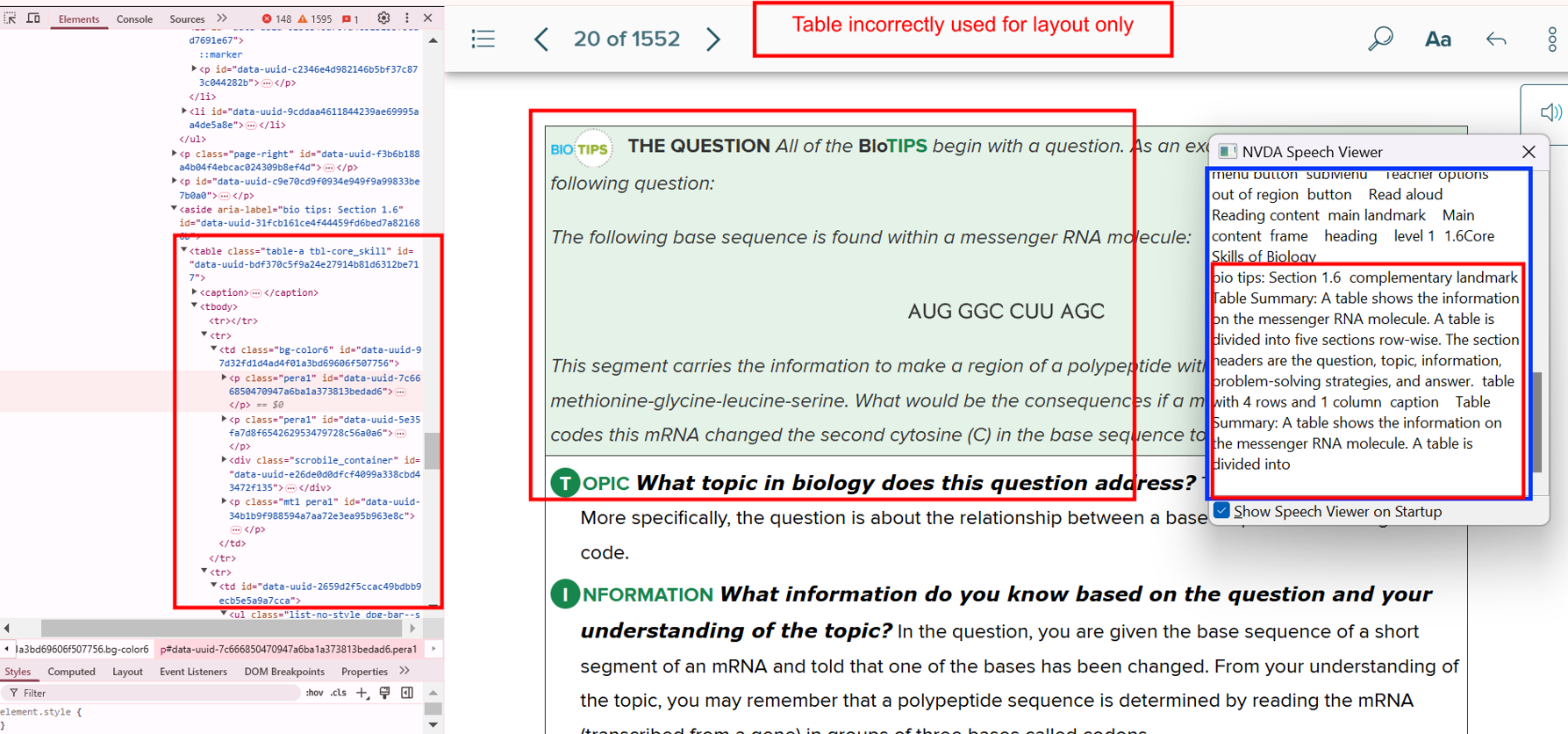
- Actual: Used tables for page layout.
- Expected: Use
<div>, <p>, or CSS for layout.
- Impact: Screen readers misinterpret structure.
- Tip: Reserve
<table> strictly for data.
Bug 16: Missing Table Summary
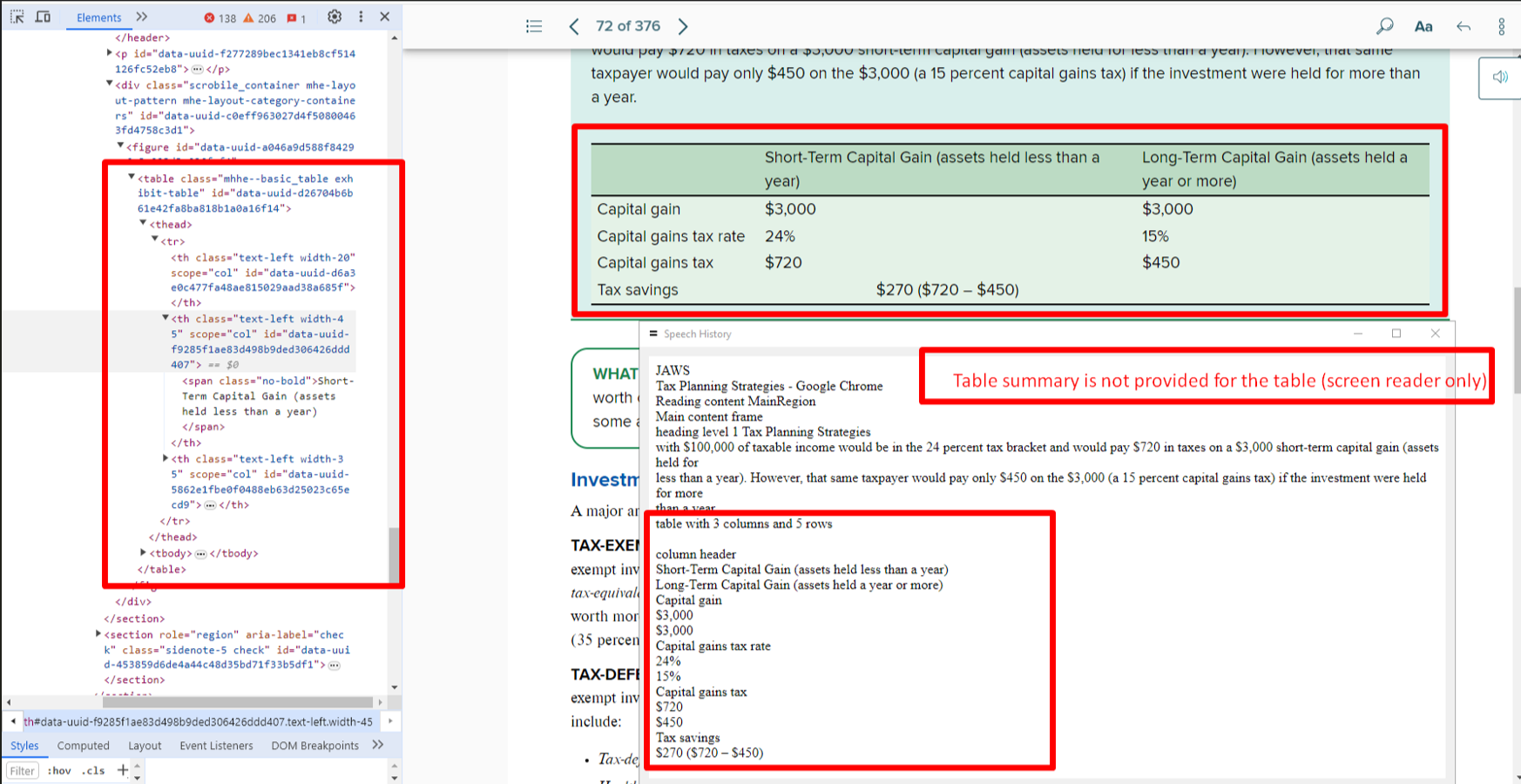
- Actual: No summary for complex data.
- Expected: Add a concise summary using
summary or aria-describedby.
- Impact: Users cannot grasp table context.
- Tip: Keep summaries short and descriptive.
Bug 17: Table Caption Missing
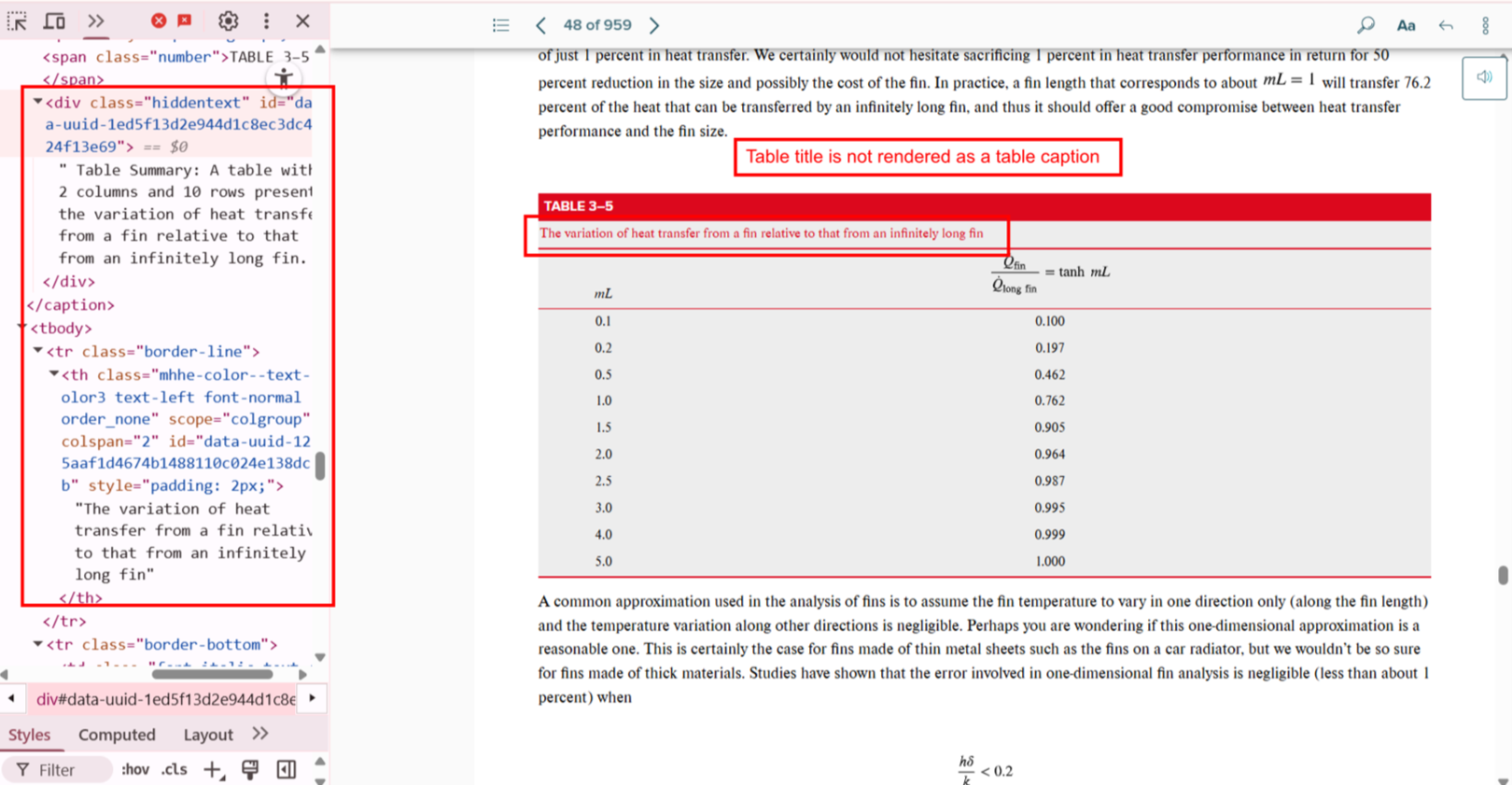
- Actual: Title outside of
<table> tags.
- Expected: Use
<caption> within <table>.
- Impact: Screen readers do not associate title with table.
- Tip: Use
<figure> and <figcaption> for more descriptive context.
5. Link Issues
Properly labeled and functional links are vital for intuitive navigation.
Bug 18: Inactive URL
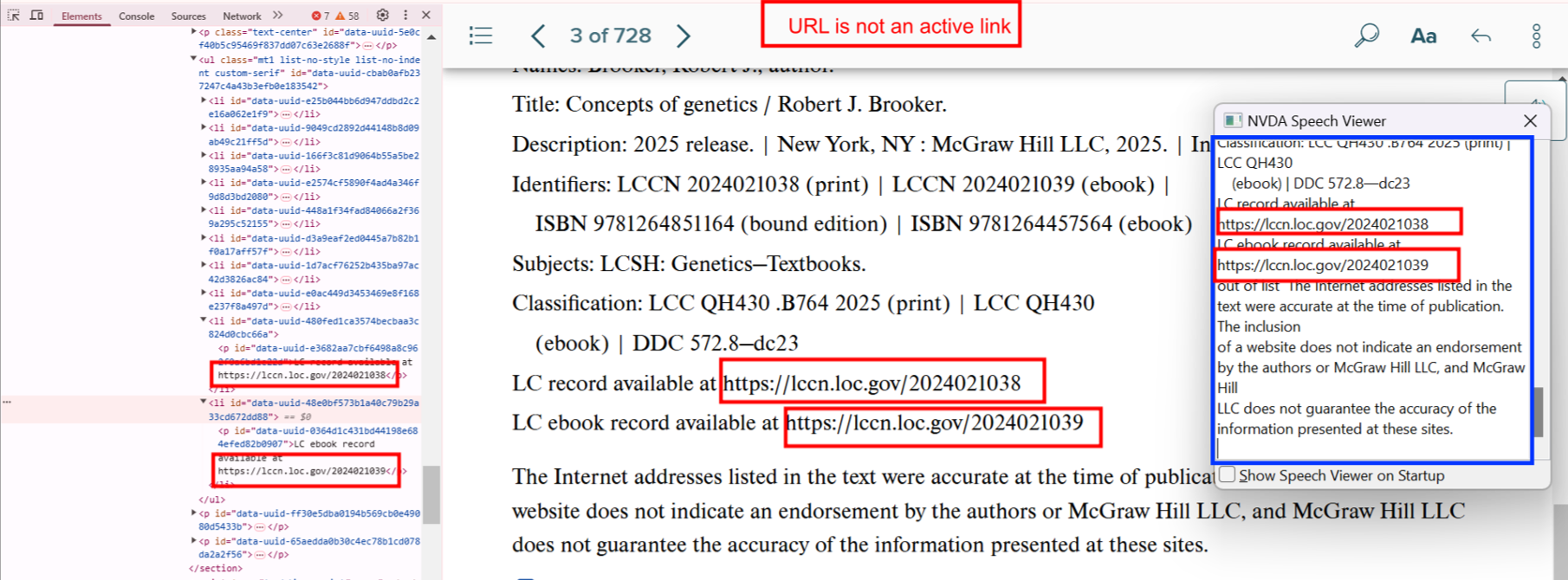
- Actual: URL presented as plain text.
- Expected: Use anchor tag
<a href="">.
- Impact: Users can’t access the link.
- Tip: Always validate links manually during testing.
Bug 19: Broken or Misleading Links
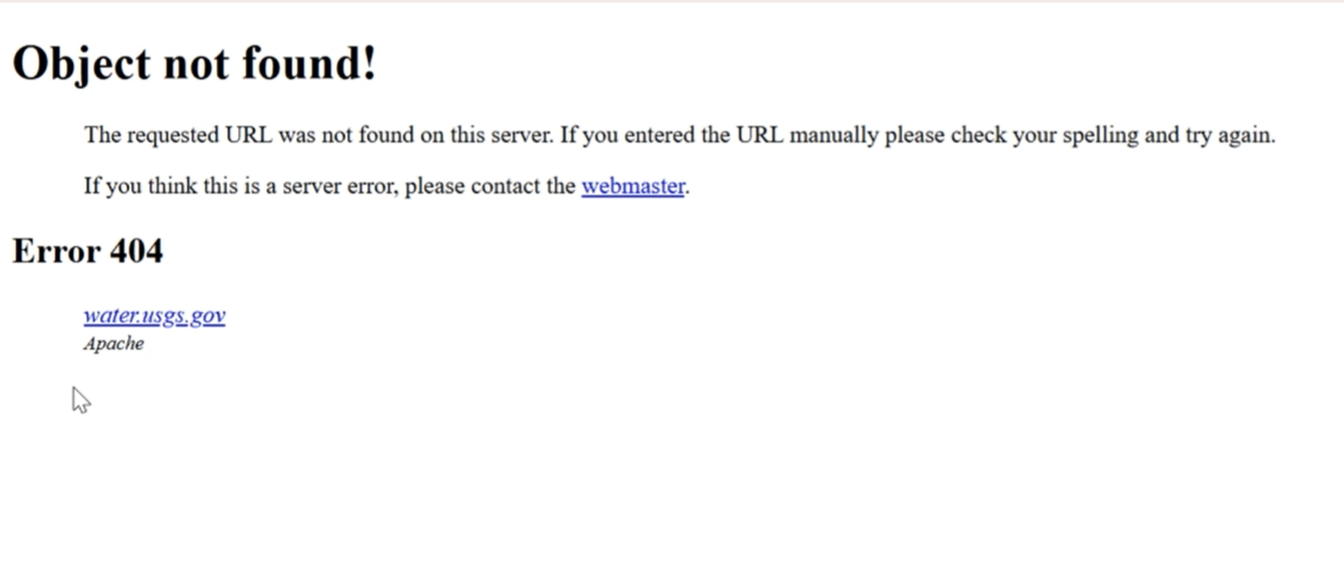
- Actual: Links go to 404 or wrong destination.
- Expected: Link to accurate, live pages.
- Impact: Users lose trust and face navigation issues.
- Tip: Set up automated link checkers.
6. Video Accessibility Issues
Accessible videos ensure inclusion for users with hearing or visual impairments.
Bug 20: Missing Transcript
- Actual: No transcript provided for the video.
- Expected: Include transcript button or inline text.
- Impact: Hearing-impaired users miss information.
- Tip: Provide transcripts alongside or beneath video.
Bug 21: No Audio Description
- Actual: Important visuals not described.
- Expected: Include described audio track or written version.
- Impact: Visually impaired users lose context.
- Tip: Use tools like YouDescribe for enhanced narration.
7. Color Contrast Issues (CCA)
Contrast ensures readability for users with low vision or color blindness.
Bug 22: Poor Contrast for Text
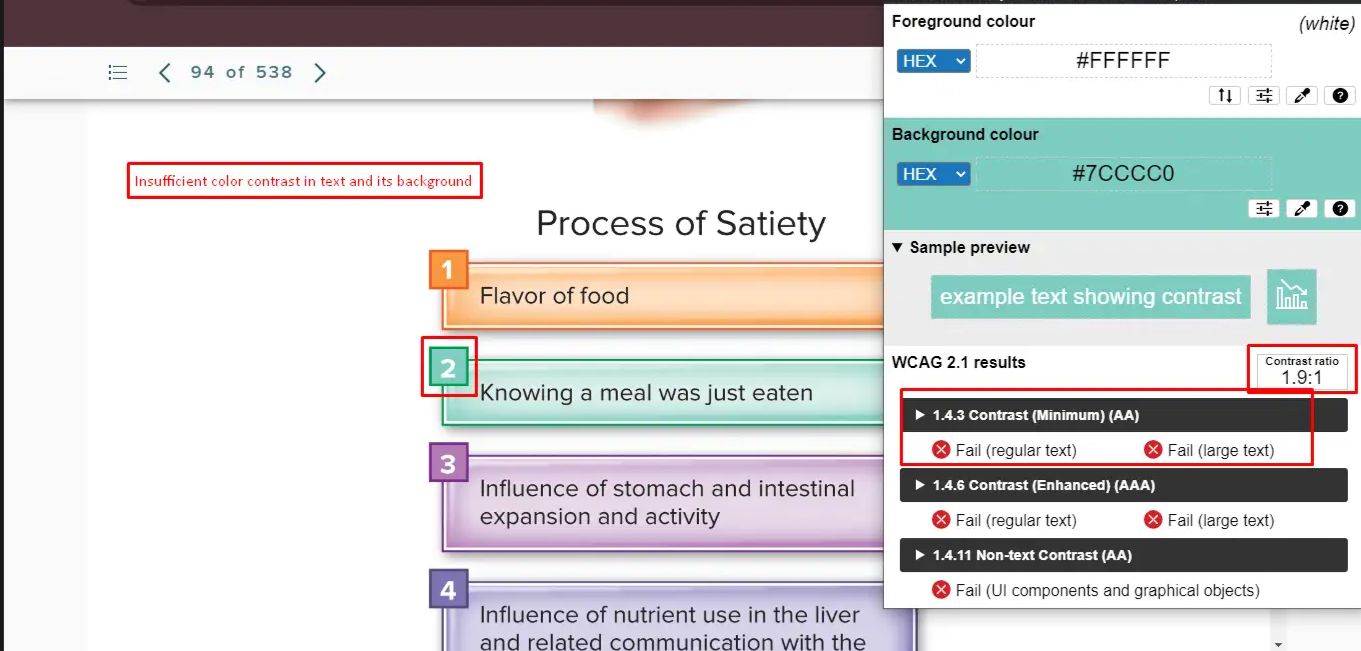
- Actual: Ratio is 1.9:1 instead of the required 4.5:1.
- Expected: Maintain minimum contrast for normal text.
- Impact: Text becomes unreadable.
- Tip: Use tools like Contrast Checker to verify.
Bug 23: Low Contrast in Charts
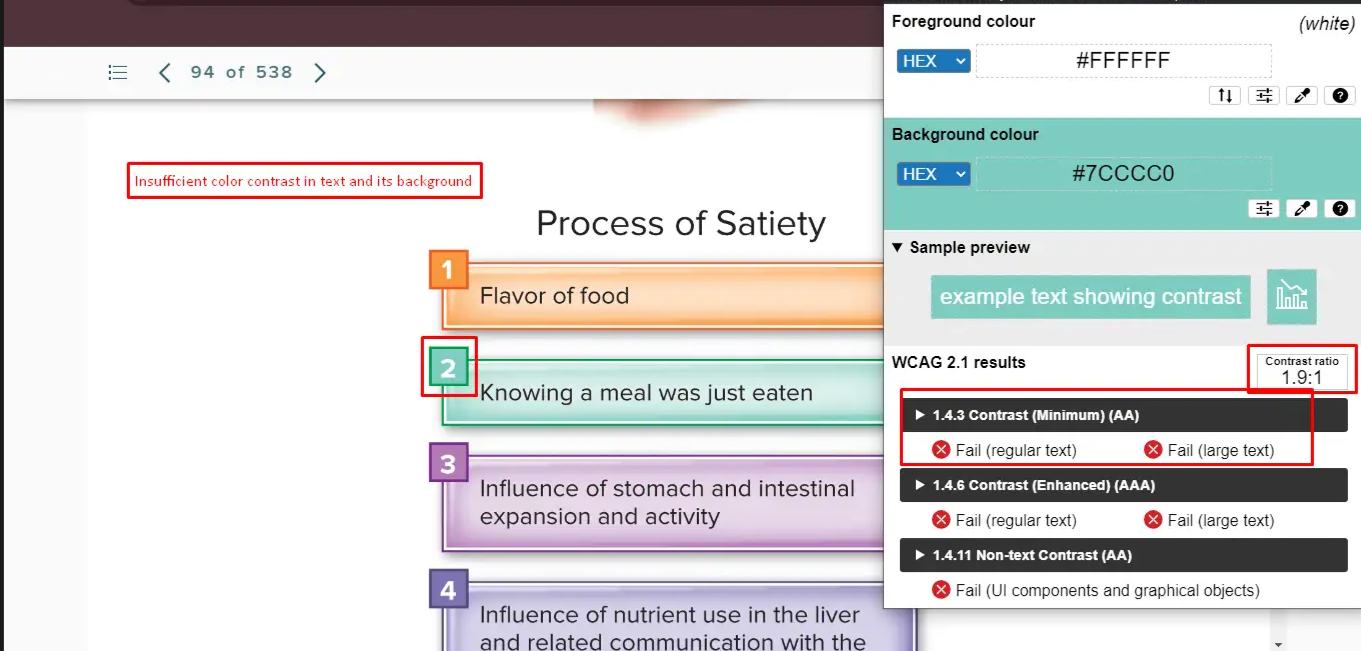
- Actual: Graph fails the 3:1 non-text contrast rule.
- Expected: Ensure clarity in visuals using patterns or textures.
- Impact: Data becomes inaccessible.
- Tip: Avoid using color alone to differentiate data points.
Bug 24: Color Alone Used to Convey Info

- Actual: No labels, only color cues.
- Expected: Add text labels or icons.
- Impact: Colorblind users are excluded.
- Tip: Pair color with shape or label.
8. Scroll Bar Issues
Horizontal scroll bars can break the user experience, especially on mobile.
Bug 25: Horizontal Scroll at 100% Zoom
- Actual: Page scrolls sideways unnecessarily.
- Expected: Content should be fully viewable without horizontal scroll.
- Impact: Frustrating on small screens or for users with mobility impairments.
- Tip: Use responsive design techniques and test at various zoom levels.
Conclusion
Accessibility is not a one-time fix but a continuous journey. By proactively identifying and resolving these common accessibility issues, you can enhance the usability and inclusiveness of your digital products. Remember, designing for accessibility not only benefits users with disabilities but also improves the experience for everyone. Incorporating accessibility into your development and testing workflow ensures legal compliance, better SEO, and greater user satisfaction. Start today by auditing your website or application and addressing the bugs outlined above.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What are common accessibility issues in websites?
They include missing alt texts, improper heading levels, broken links, insufficient color contrast, and missing video transcripts.
-
Why is accessibility important in web development?
It ensures inclusivity for users with disabilities, improves SEO, and helps meet legal standards like WCAG and ADA.
-
How do I test for accessibility issues?
You can use tools like axe, WAVE, Lighthouse, and screen readers along with manual QA testing.
-
What is color contrast ratio?
It measures the difference in luminance between foreground text and its background. A higher ratio improves readability.
-
Are accessibility fixes expensive?
Not fixing them is more expensive. Early-stage remediation is cost-effective and avoids legal complications.

by Rajesh K | Jun 24, 2025 | Performance Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
Modern web and mobile applications live or die by their speed, stability, and scalability. Users expect sub-second responses, executives demand uptime, and DevOps pipelines crank out new builds faster than ever. In that high-pressure environment, performance testing is no longer optional; it is the safety net that keeps releases from crashing and brands from burning. Apache JMeter, a 100 % open-source tool, has earned its place as a favorite for API, web, database, and micro-service tests because it is lightweight, scriptable, and CI/CD-friendly. This JMeter Tutorial walks you through installing JMeter, creating your first Test Plan, running realistic load scenarios, and producing client-ready HTML reports, all without skipping a single topic from the original draft. Whether you are a QA engineer exploring non-functional testing for the first time or a seasoned SRE looking to tighten your feedback loop, the next 15 minutes will equip you to design, execute, and analyze reliable performance tests.
What is Performance Testing?
To begin with, performance testing is a form of non-functional testing used to determine how a system performs in terms of responsiveness and stability under a particular workload. It is critical to verify the speed, scalability, and reliability of an application. Unlike functional testing, which validates what the software does, performance testing focuses on how the system behaves.
Goals of Performance Testing
The main objectives include:
- Validating response times to ensure user satisfaction.
- Confirming that the system remains stable under expected and peak loads.
- Identifying bottlenecks such as database locks, memory leaks, or CPU spikes, that can degrade performance.
Types of Performance Testing
Moving forward, it’s important to understand that performance testing is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Various types exist to address specific concerns:
- Load Testing: Measures system behavior under expected user loads.
- Stress Testing: Pushes the system beyond its operational capacity to identify breaking points.
- Spike Testing: Assesses system response to sudden increases in load.
- Endurance Testing: Evaluates system stability over extended periods.
- Scalability Testing: Determines the system’s ability to scale up with increasing load.
- Volume Testing: Tests the system’s capacity to handle large volumes of data.
Each type helps uncover different aspects of system performance and provides insights to make informed improvements.
Popular Tools for Performance Testing
There are several performance testing tools available in the market, each offering unique features. Among them, the following are some of the most widely used:
- Apache JMeter: Open-source, supports multiple protocols, and is highly extensible.
- LoadRunner: A commercial tool offering comprehensive support for various protocols.
- Gatling: A developer-friendly tool using Scala-based DSL.
- k6: A modern load testing tool built for automation and CI/CD pipelines.
- Locust: An event-based Python tool great for scripting custom scenarios.
Why Choose Apache JMeter?
Compared to others, Apache JMeter stands out due to its versatility and community support. It is completely free and supports a wide range of protocols, including HTTP, FTP, JDBC, and more. Moreover, with both GUI and CLI support, JMeter is ideal for designing and automating performance tests. It also integrates seamlessly with CI/CD tools like Jenkins and offers a rich plugin ecosystem for extended functionality.
Installing JMeter
Getting started with Apache JMeter is straightforward:
- First, install Java (JDK 8 or above) on your system.
- Next, download JMeter from the official website: https://jmeter.apache.org.
- Unzip the downloaded archive.
- Finally, run jmeter.bat for Windows or jmeter.sh for Linux/macOS to launch the GUI.
Once launched, you’ll be greeted by the JMeter GUI, where you can start creating your test plans.
What is a Test Plan?
A Test Plan in JMeter is the blueprint of your testing process. Essentially, it defines the sequence of steps to execute your performance test. The Test Plan includes elements such as Thread Groups, Samplers, Listeners, and Config Elements. Therefore, it acts as the container for all test-related settings and components.
Adding a Thread Group in JMeter
Thread Groups are the starting point of any Test Plan. They simulate user requests to the server.
How to Add a Thread Group:
- To begin, right-click on the Test Plan.
- Navigate to Add → Threads (Users) → Thread Group.
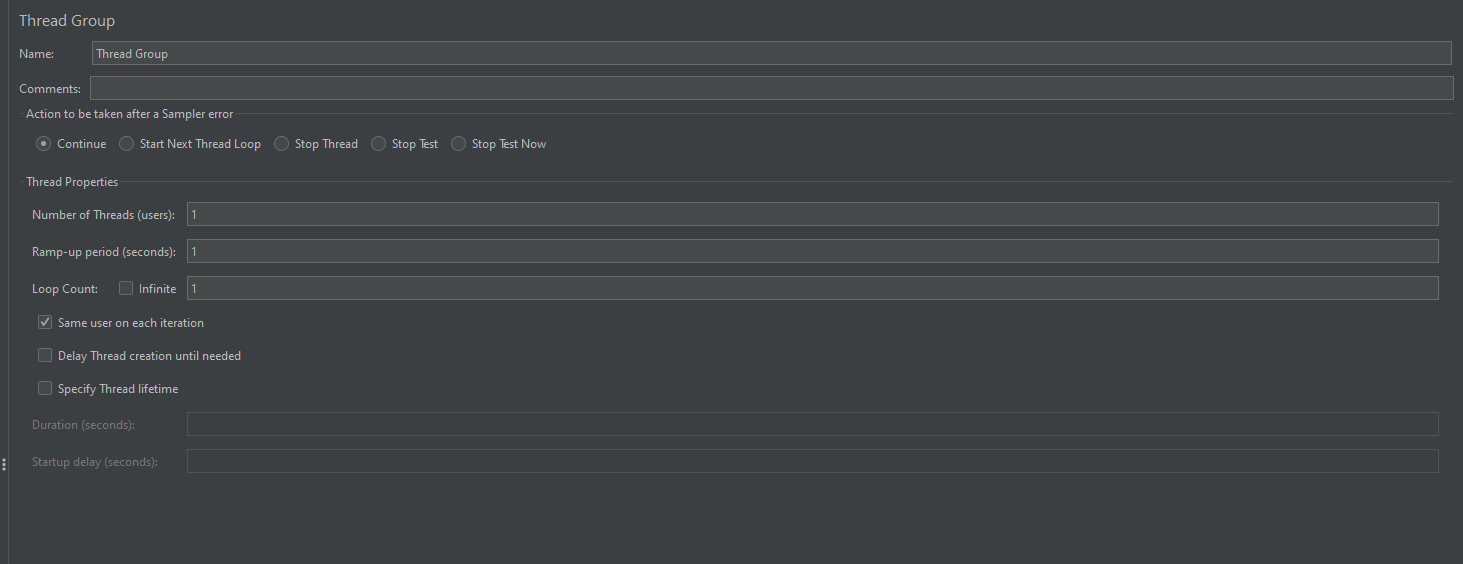
Thread Group Parameters:
- Number of Threads (Users): Represents the number of virtual users.
- Ramp-Up Period (in seconds): Time taken to start all users.
- Loop Count: Number of times the test should be repeated.
Setting appropriate values for these parameters ensures a realistic simulation of user load.
How to Add an HTTP Request Sampler
Once the Thread Group is added, you can simulate web requests using HTTP Request Samplers.
Steps:
- Right-click on the Thread Group.
- Choose Add → Sampler → HTTP Request.
Configure the following parameters:
- Protocol: Use “http” or “https”.
- Server Name or IP: The domain or IP address of the server. (Ex: Testing.com)
- Path: The API endpoint or resource path. (api/users)
- Method: HTTP method like GET or POST.
This sampler allows you to test how your server or API handles web requests.
Running Sample HTTP Requests in JMeter (Using ReqRes.in)
To better illustrate, let’s use https://reqres.in, a free mock API.
Example POST request settings:
- Protocol: https
- Server Name: reqres. in
- Method: POST
- Path: /api/users
In the Body Data tab, insert:
{
"name": "morpheus",
"job": "leader"
}
This setup helps simulate a user creation API request.
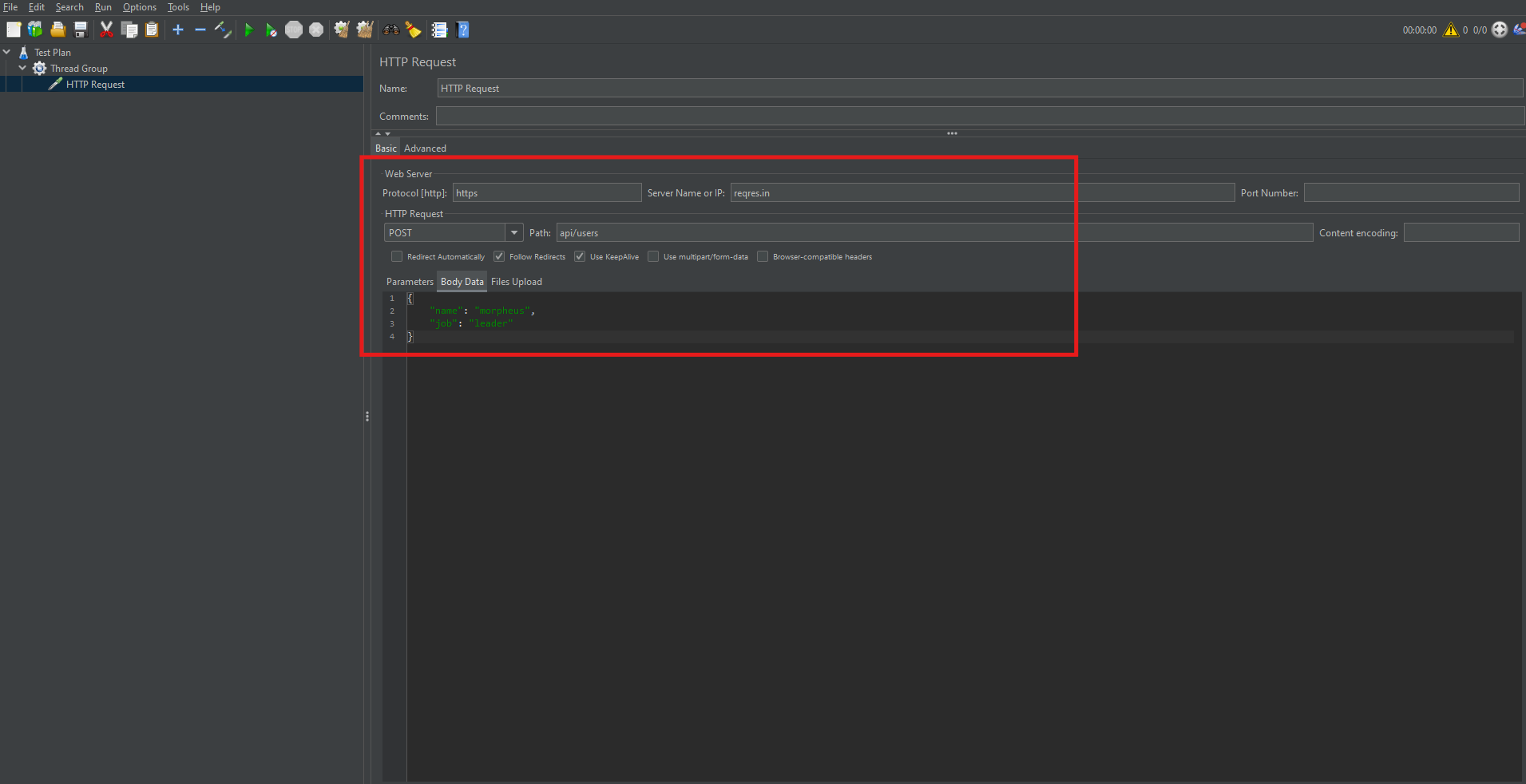
Adding Authorization with HTTP Header Manager
In many cases, you may need to send authenticated requests.
- Obtain your API key or token.
- Right-click on the HTTP Request Sampler.
- Choose Add → Config Element → HTTP Header Manager.
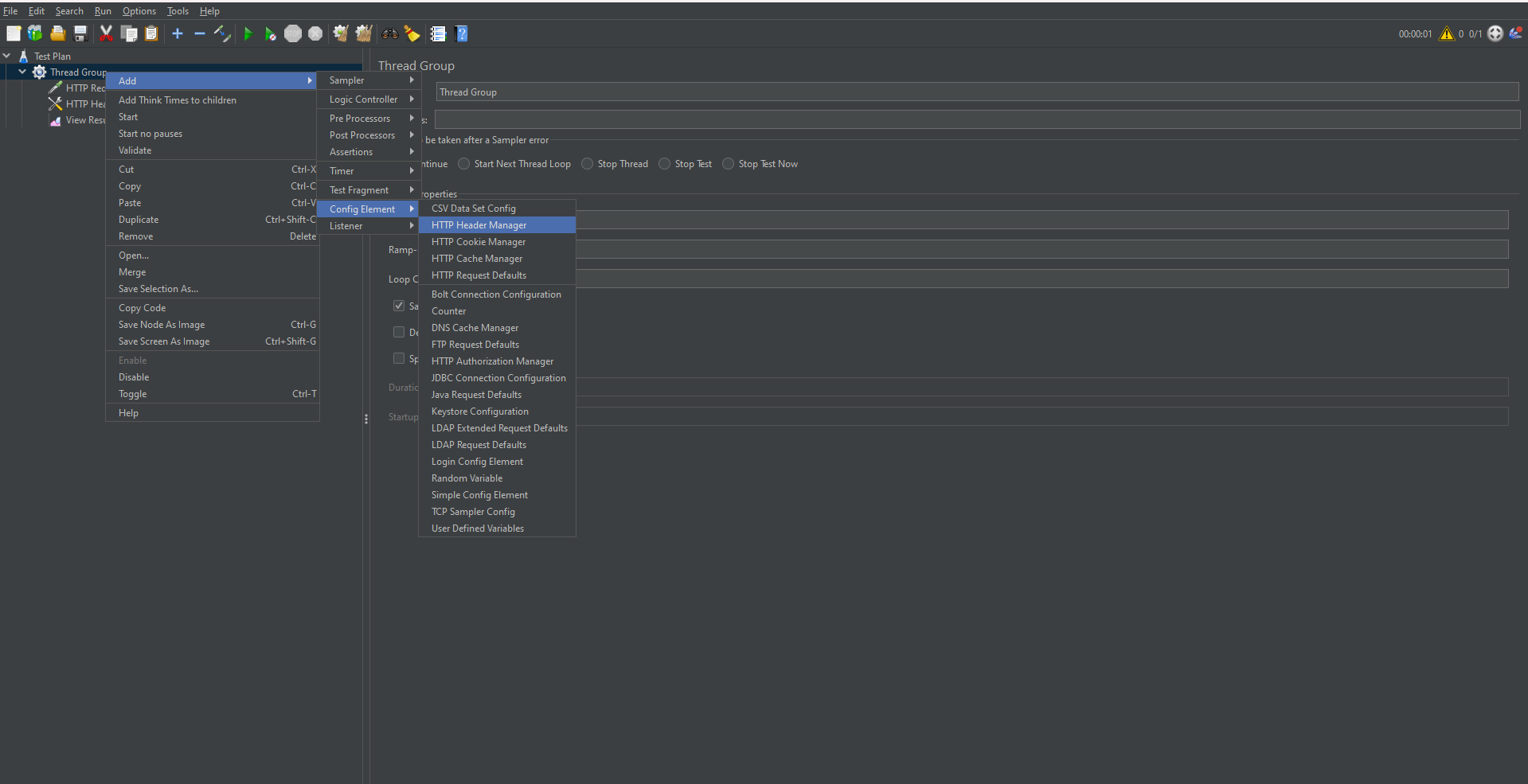
- Add the header:
- Name: x-api-key
- Value: your API token
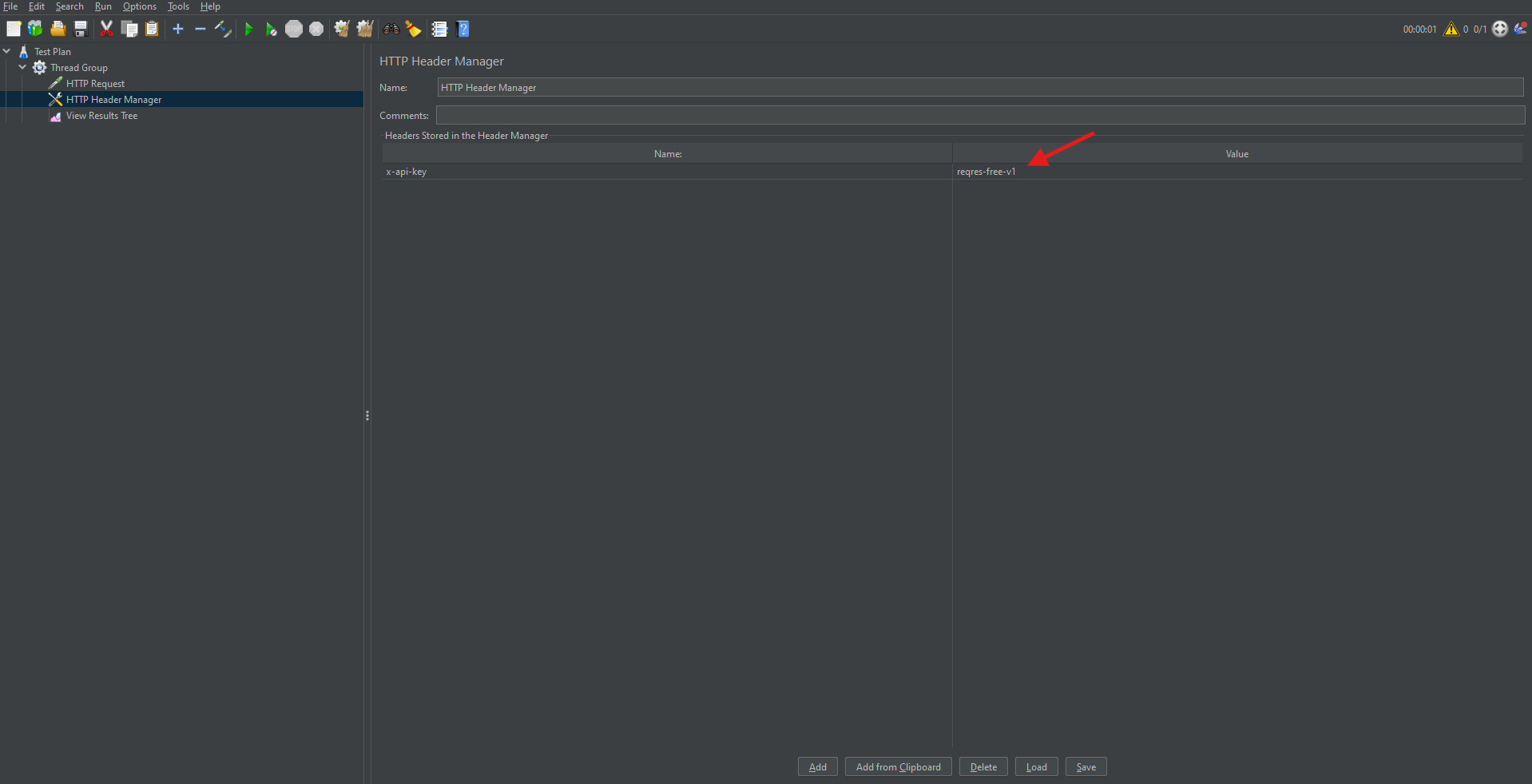
This allows JMeter to attach necessary authorization headers to requests.
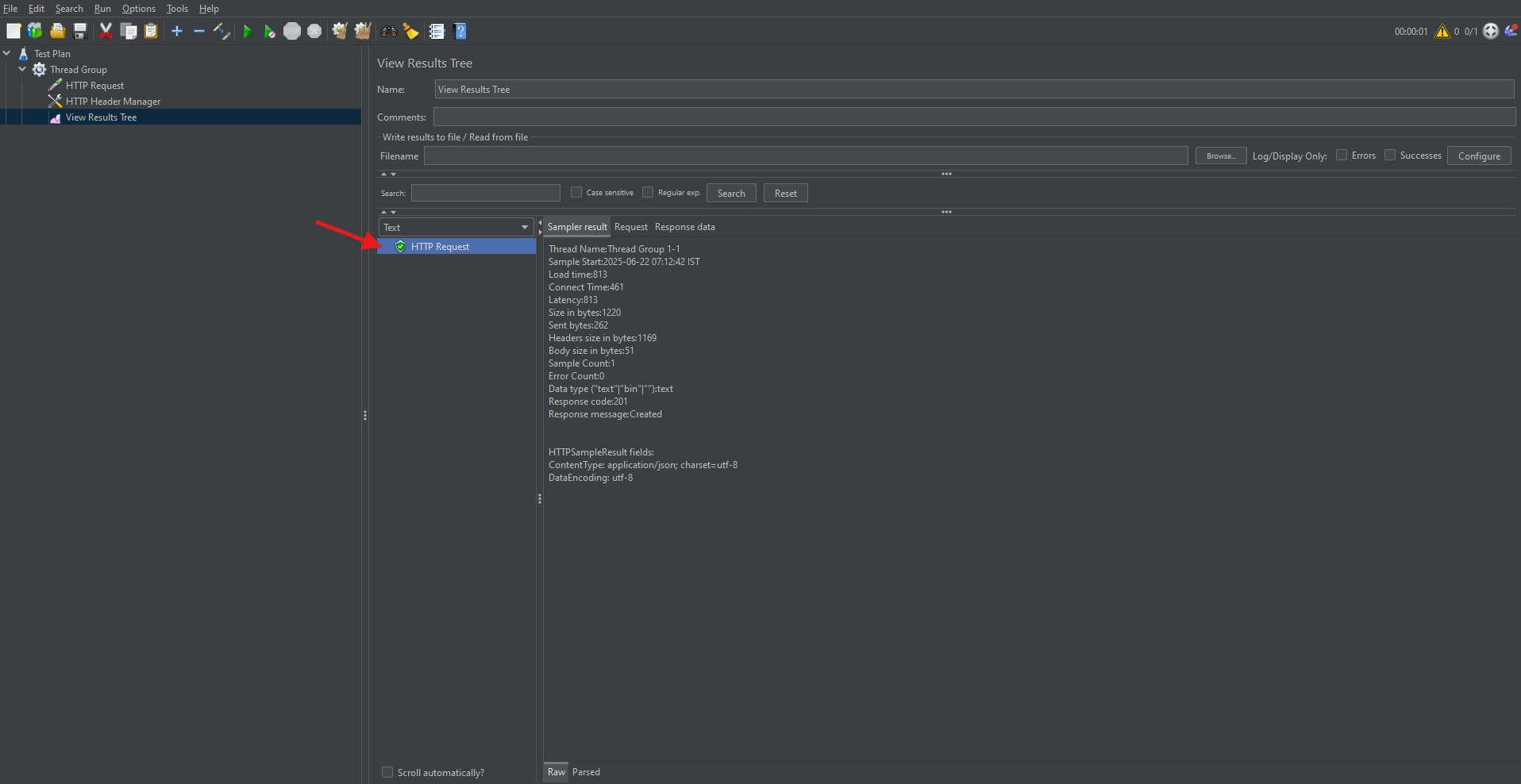
Adding Listeners to Monitor and Analyze Results
Listeners are components that gather, display, and save the results of a performance test. They play a critical role in interpreting outcomes.
Common Listeners:
- View Results Tree: Displays request and response data.
- Summary Report: Shows key metrics such as average response time, throughput, and error rate.
- Graph Results: Plots response times visually over time.
How to Add a Listener:
- Right-click on the Thread Group.
- Choose Add → Listener → Select the desired listener.
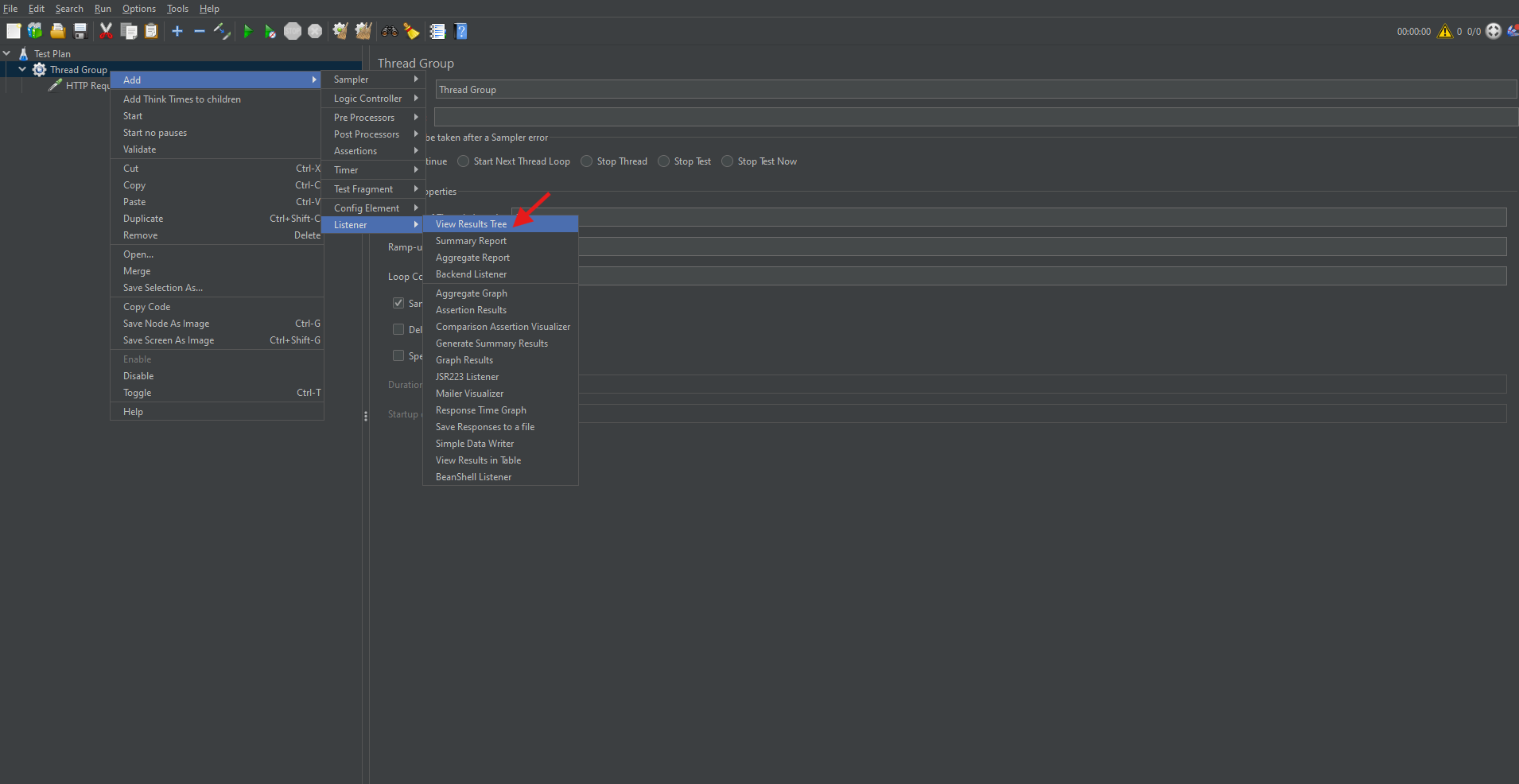
Listeners are essential for interpreting test performance.
Running the Test Plan
Once your Test Plan is configured, it’s time to execute it:
- Click the green Run button.
- Save the Test Plan when prompted.
- Observe real-time test execution in the selected Listeners.
- Stop the test using the Stop button (■) when done.
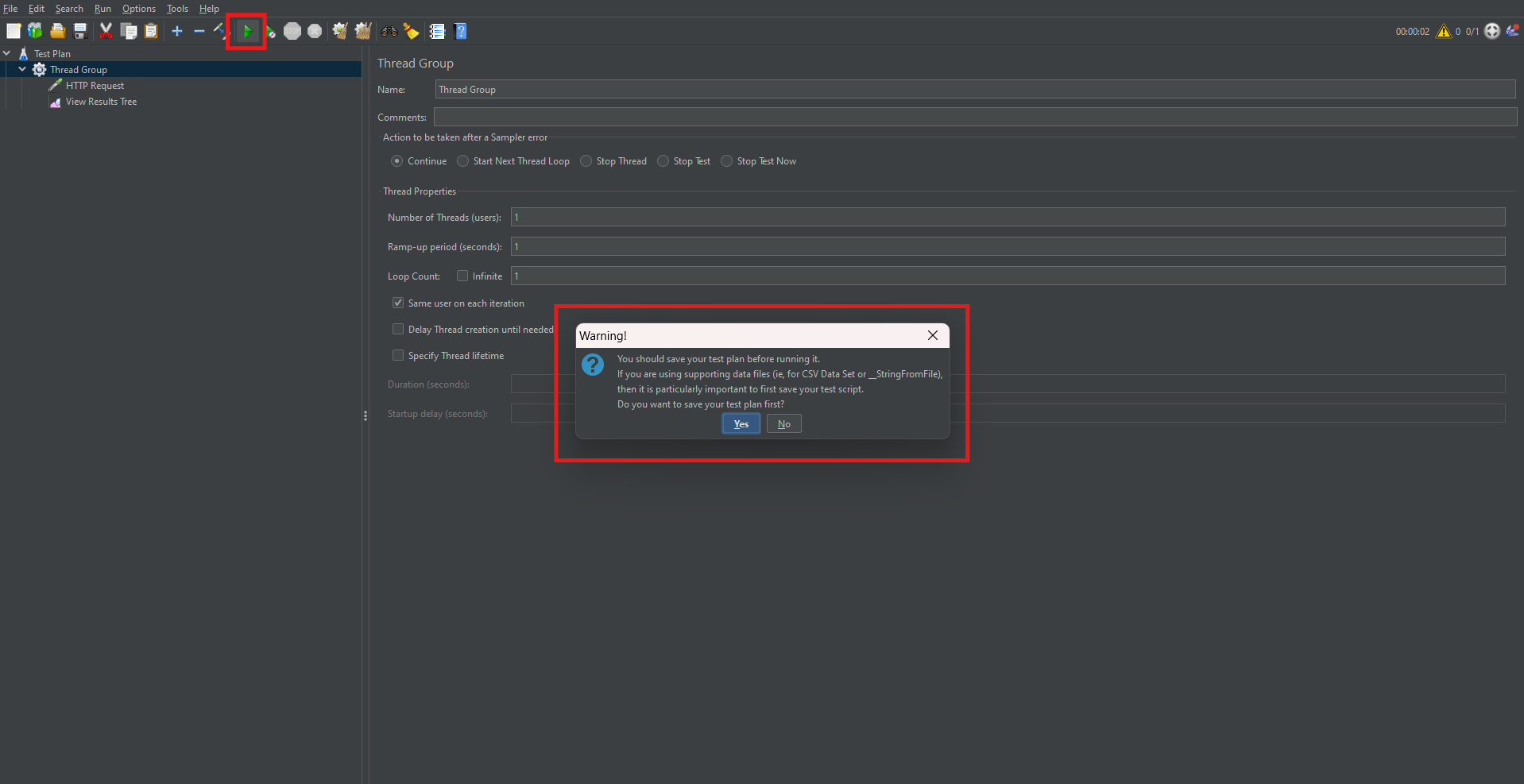
This execution simulates the defined user behavior and captures performance metrics.
Simulating Multiple Users
To thoroughly assess scalability, increase the load by adjusting the “Number of Threads (Users)” in the Thread Group.
For example:
- 10 users simulate 10 simultaneous requests.
- 100 users will increase the load proportionally.
This enables realistic stress testing of the system under high concurrency.
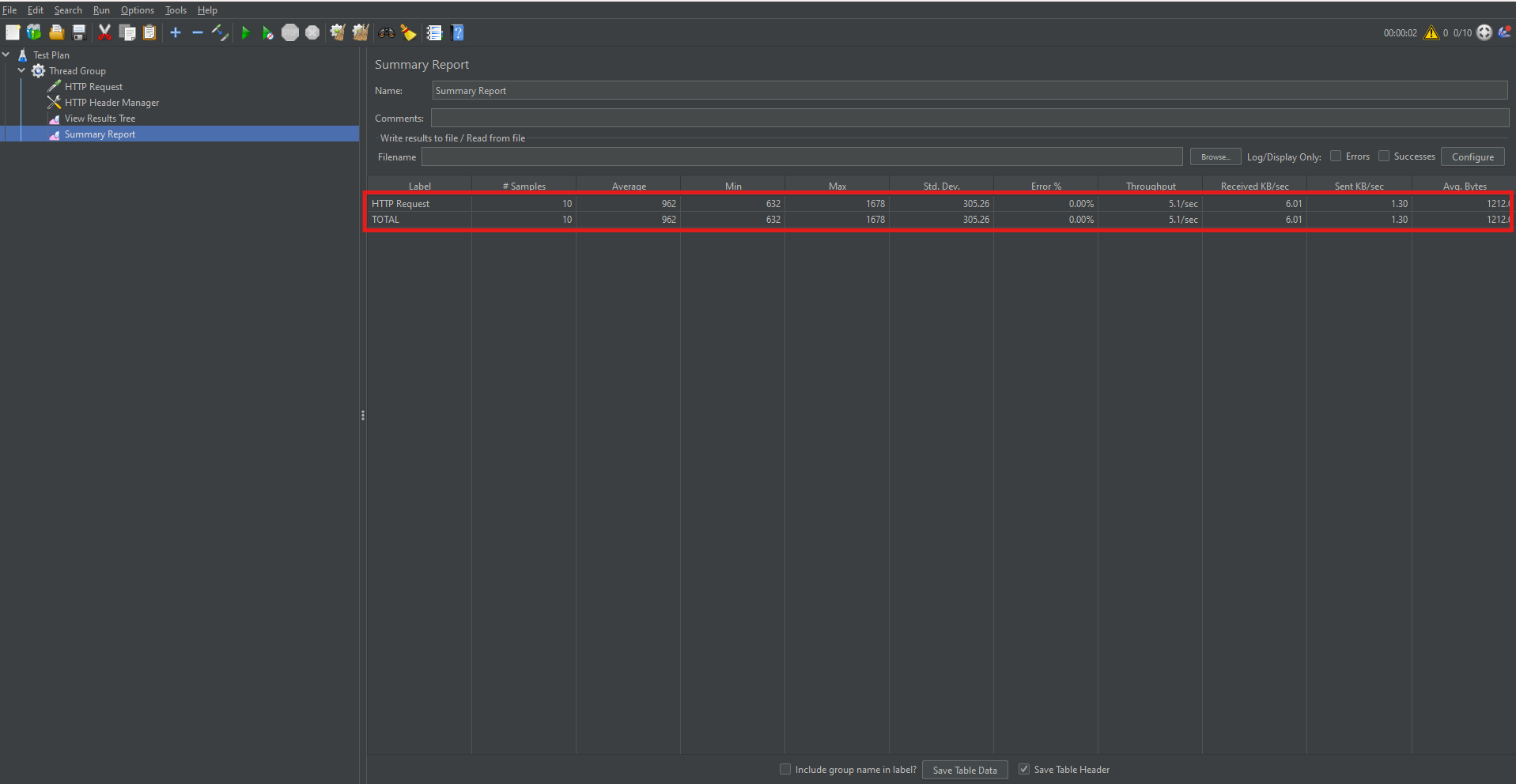
Analyzing Test Results with Summary Report
The Summary Report provides crucial insights like average response time, throughput, and error percentages. Therefore, it’s essential to understand what each metric indicates.
Key Metrics:
- Average: Mean response time of all requests.
- Throughput: Number of requests handled per second.
- Error% : Percentage of failed requests.
Reviewing these metrics helps determine if performance criteria are met.
Generating an HTML Report in GUI Mode
To create a client-ready report, follow these steps:
Step 1: Save Results to CSV
- In the Summary or Aggregate Report listener, specify a file name like results.csv.
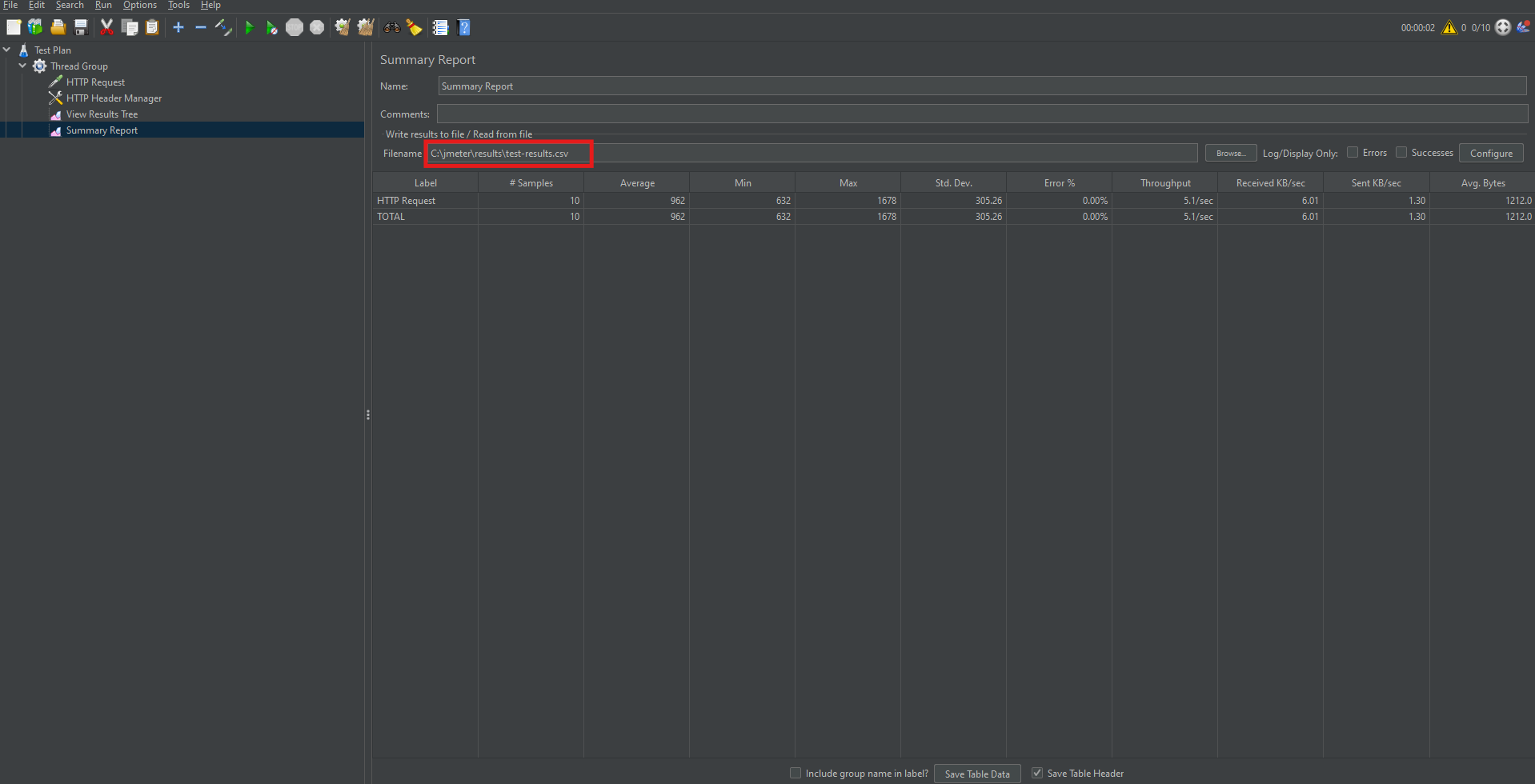
Step 2: Create Output Directory
- For example, use path: D:\JMeter_HTML_Report
Step 3: Generate Report
- Go to Tools → Generate HTML Report.
- Provide:
- Results file path.
- user.properties file path.
- Output directory.
- Click “Generate Report”.
Step 2: Create Output Directory
Step 4: View the Report
- Open index.html in the output folder using a web browser.
The HTML report includes graphical and tabular views of the test results, which makes it ideal for presentations and documentation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Apache JMeter provides a flexible and powerful environment for performance testing of web applications and APIs. With its support for multiple protocols, ability to simulate high loads, and extensible architecture, JMeter is a go-to choice for QA professionals and developers alike.
This end-to-end JMeter tutorial walked you through:
- Installing and configuring JMeter.
- Creating test plans and adding HTTP requests.
- Simulating load and analyzing test results.
- Generating client-facing HTML reports.
By incorporating JMeter into your testing strategy, you ensure that your applications meet performance benchmarks, scale efficiently, and provide a smooth user experience under all conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Can JMeter test both web applications and APIs?
Yes, JMeter can test both web applications and REST/SOAP APIs. It supports HTTP, HTTPS, JDBC, FTP, JMS, and many other protocols, making it suitable for a wide range of testing scenarios.
-
Is JMeter suitable for beginners?
Absolutely. JMeter provides a graphical user interface (GUI) that allows beginners to create test plans without coding. However, advanced users can take advantage of scripting, CLI execution, and plugins for more control.
-
How many users can JMeter simulate?
JMeter can simulate thousands of users, depending on the system’s hardware and how efficiently the test is designed. For high-volume testing, it's common to distribute the load across multiple machines using JMeter's remote testing feature.
-
What is a Thread Group in JMeter?
A Thread Group defines the number of virtual users (threads), the ramp-up period (time to start those users), and the loop count (number of test iterations). It’s the core component for simulating user load.
-
Can I integrate JMeter with Jenkins or other CI tools?
Yes, JMeter supports non-GUI (command-line) execution, making it easy to integrate with Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or other CI/CD tools for automated performance testing in your deployment pipelines.
-
How do I pass dynamic data into JMeter requests?
You can use the CSV Data Set Config element to feed dynamic data like usernames, passwords, or product IDs into your test, enabling more realistic scenarios.
-
Can I test secured APIs with authentication tokens in JMeter?
Yes, you can use the HTTP Header Manager to add tokens or API keys to your request headers, enabling authentication with secured APIs.

by Rajesh K | Jun 20, 2025 | Automation Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) has become integral to automation testing in .NET projects, and SpecFlow has long been a go-to framework for writing Gherkin scenarios in C#. However, SpecFlow’s development has slowed in recent years, and it has lagged in support for the latest .NET versions. Enter Reqnroll, a modern BDD framework that picks up where SpecFlow left off. Reqnroll is essentially a fork of SpecFlow’s open-source core, rebranded and revitalized to ensure continued support and innovation. This means teams currently using SpecFlow can transition to Reqnroll with minimal friction while gaining access to new features and active maintenance. The SpecFlow to Reqnroll migration path is straightforward, making it an attractive option for teams aiming to future-proof their automation testing efforts.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk QA engineers, test leads, automation testers, and software developers through migrating from SpecFlow to Reqnroll, step by step. You’ll learn why the shift is happening, who should consider migrating, and exactly how to carry out the migration without disrupting your existing BDD tests. By the end, you’ll understand the key differences between SpecFlow and Reqnroll, how to update your projects, and how to leverage Reqnroll’s improvements. We’ll also provide real-world examples, a comparison table of benefits, and answers to frequently asked questions about SpecFlow to Reqnroll. Let’s ensure your BDD tests stay future-proof and rock n’ roll with Reqnroll!
Why Migrate from SpecFlow to Reqnroll?
If you’ve been relying on SpecFlow for BDD, you might be wondering why a migration to Reqnroll is worthwhile. Here are the main reasons teams are making the switch from SpecFlow to Reqnroll:
- Active Support and Updates: SpecFlow’s support and updates have dwindled, especially for newer .NET releases. Reqnroll, on the other hand, is actively maintained by the community and its original creator, ensuring compatibility with the latest .NET 6, 7, 8, and beyond. For example, SpecFlow lacked official .NET 8 support, which prompted the fork to Reqnroll to fill that gap. With Reqnroll, you benefit from prompt bug fixes and feature enhancements backed by an engaged developer community.
- Enhanced Features: Reqnroll extends SpecFlow’s capabilities with advanced tools for test management and reporting. Out of the box, Reqnroll supports generating detailed test execution reports and linking tests to requirements for better traceability. Teams can organize and manage test cases more efficiently within Reqnroll, enabling full end-to-end visibility of BDD scenarios. These enhancements go beyond what SpecFlow offered by default, making your testing suite more robust and informative.
- Seamless Integration: Reqnroll is designed to work smoothly with modern development tools and CI/CD pipelines. It integrates with popular CI servers (Jenkins, Azure DevOps, GitHub Actions, etc.) and works with IDEs like Visual Studio and VS Code without hiccups. There’s even a Reqnroll Visual Studio Extension that supports both SpecFlow and Reqnroll projects side by side, easing the transition for developers. In short, Reqnroll slots into your existing development workflow just as easily as SpecFlow did if not more so.
- High Compatibility: Since Reqnroll’s codebase is directly forked from SpecFlow, it maintains a high level of backward compatibility with SpecFlow projects. Everything that worked in SpecFlow will work in Reqnroll in almost the same way, with only some namespaces and package names changed. This means you won’t have to rewrite your feature files or step definitions from scratch – migration is mostly a find-and-replace job (as we’ll see later). The learning curve is minimal because Reqnroll follows the same BDD principles and Gherkin syntax you’re already used to.
- Community-Driven and Open Source: Reqnroll is a community-driven open-source project, free to use for everyone. It was created to “reboot” SpecFlow’s open-source spirit and keep BDD accessible. The project invites contributions and has options for companies to sponsor or subscribe for support, but the framework itself remains free. By migrating, you join a growing community investing in the tool’s future. You also eliminate reliance on SpecFlow’s trademarked, closed-source extensions – Reqnroll has already ported or is rebuilding those essential extras (more on that in the comparison table below).
In summary, migrating to Reqnroll lets you continue your BDD practices with a tool that’s up-to-date, feature-rich, and backed by an active community. Next, let’s look at how to plan your migration approach.
Planning Your SpecFlow to Reqnroll Migration
Before migrating, choose between two main approaches:
1. Quick Switch with Compatibility Package:
Use the Reqnroll.SpecFlowCompatibility NuGet package for a minimal-change migration. It lets you continue using the TechTalk.SpecFlow namespace while running tests on Reqnroll. This option is ideal for large projects aiming to minimize disruption—just swap out NuGet packages and make small tweaks. You can refactor to Reqnroll-specific namespaces later.
2. Full Migration with Namespace Changes:
This involves fully replacing SpecFlow references with Reqnroll ones (e.g., update using TechTalk.SpecFlow to using Reqnroll). Though it touches more files, it’s mostly a search-and-replace task. You’ll remove SpecFlow packages, add Reqnroll packages, and update class names. This cleaner, long-term solution avoids reliance on compatibility layers.
Which path to choose?
For a quick fix or large codebases, the compatibility package is fast and easy. But for long-term maintainability, a full migration is recommended. Either way, back up your project and use a separate branch to test changes safely.
Now, let’s dive into the step-by-step migration process.
SpecFlow to Reqnroll Migration Steps
Moving from SpecFlow to Reqnroll involves a series of straightforward changes to your project’s packages, namespaces, and configuration. Follow these steps to transition your BDD tests:
Step 1: Update NuGet Packages (Replace SpecFlow with Reqnroll)
The first step is to swap out SpecFlow’s NuGet packages for Reqnroll’s packages. Open your test project’s package manager (or .csproj file) and make the following changes:
- Remove SpecFlow Packages: Uninstall or remove any NuGet references that start with SpecFlow. This includes the main SpecFlow package and test runner-specific packages like SpecFlow.NUnit, SpecFlow.MsTest, or SpecFlow.xUnit. Also, remove any CucumberExpressions.SpecFlow.* packages, as Reqnroll has built-in support for Cucumber Expressions.
- Add Reqnroll Packages: Add the corresponding Reqnroll package for your test runner: for example, Reqnroll.NUnit, Reqnroll.MsTest, or Reqnroll.xUnit (matching whichever test framework your project uses). These packages provide Reqnroll’s integration with NUnit, MSTest, or xUnit, just like SpecFlow had. If you opted for the compatibility approach, also add Reqnroll.SpecFlowCompatibility, which ensures your existing SpecFlow code continues to work without immediate refactoring.
After updating the package references, your project file will list Reqnroll packages instead of SpecFlow. For instance, a .csproj snippet for an MSTest-based BDD project might look like this after the change:
<ItemGroup>
<!-- Test framework dependencies -->
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.NET.Test.Sdk" Version="17.X.X" />
<PackageReference Include="MSTest.TestAdapter" Version="3.X.X" />
<PackageReference Include="MSTest.TestFramework" Version="3.X.X" />
<!-- Reqnroll packages (replaced SpecFlow packages) -->
<PackageReference Include="Reqnroll.MsTest" Version="2.0.0" />
<PackageReference Include="Reqnroll.SpecFlowCompatibility" Version="2.0.0" />
<PackageReference Include="Reqnroll.SpecFlowCompatibility.Actions.Selenium" Version="2.0.0" />
</ItemGroup>
Once these package changes are made, restore the NuGet packages and build the project. In many cases, this is the only change needed to get your tests running on Reqnroll. However, if you did the full migration path (not using the compatibility package), you’ll have some namespace adjustments to handle next.
Step 2: Replace Namespaces and References in Code
With the new Reqnroll packages in place, the next step is updating your code files to reference Reqnroll’s namespaces and any renamed classes. This is primarily needed if you opted for a full migration. If you installed the Reqnroll.SpecFlowCompatibility package, you can skip this step for now, as that package allows you to continue using the TechTalk.SpecFlow namespace temporarily.
For a full migration, perform a global find-and-replace in your solution:
- Namespaces: Replace all occurrences of TechTalk.SpecFlow with Reqnroll. This applies to using directives at the top of your files and any fully qualified references in code. Make sure to match case and whole words so you don’t accidentally alter feature file text or other content. Most of your step definition classes will have using TechTalk.SpecFlow; this should become using Reqnroll; (or in some cases using Reqnroll.Attributes;) to import the [Binding] attribute and other needed types in the Reqnroll library.
- Class and Interface Names: Some SpecFlow-specific classes or interfaces have been renamed in Reqnroll. For example, ISpecFlowOutputHelper (used for writing to test output) is now IReqnrollOutputHelper. Similarly, any class names that contained “SpecFlow” have been adjusted to “Reqnroll”. Use find-and-replace for those as well (e.g., search for ISpecFlow and SpecFlowOutput, etc., and replace with the new names). In many projects, the output helper interface is the main one to change. If you encounter compile errors about missing SpecFlow types, check if the type has a Reqnroll equivalent name and update accordingly.
- Attributes: The [Binding] attribute and step definition attributes ([Given], [When], [Then]) remain the same in usage. Just ensure your using statement covers the namespace where they exist in Reqnroll (the base Reqnroll namespace contains these, so using Reqnroll is usually enough). The attribute annotations in your code do not need to be renamed, for example, [Given(“some step”)] is still [Given(“some step”)]. The only difference is that behind the scenes, those attributes are now coming from Reqnroll’s library instead of SpecFlow’s.
After these replacements, build the project again. If the build succeeds, great – your code is now referencing Reqnroll everywhere. If there are errors, they typically fall into two categories:
Missing Namespace or Type Errors:
If you see errors like a reference to TechTalk.SpecFlow still lingering or a missing class, double-check that you replaced all references. You might find an edge case, such as a custom hook or attribute that needed an additional using Reqnroll.Something statement. For instance, if you had a custom value retriever or dependency injection usage with SpecFlow’s BoDi container, note that BoDi now lives under Reqnroll.BoDi, you might add using Reqnroll.BoDi; in those files.
SpecFlow v3 to v4 Breaking Changes:
Reqnroll is based on the SpecFlow v4 codebase. If you migrated from SpecFlow v3 (or earlier), some breaking changes from SpecFlow v3→v4 could surface (though this is rare and usually minor). One example is Cucumber Expressions support. Reqnroll supports the more readable Cucumber Expressions for step definitions in addition to regex. Most existing regex patterns still work, but a few corner cases might need adjustment (e.g., Reqnroll might interpret a step pattern as a Cucumber Expression when you meant it as a regex). If you get errors like “This Cucumber Expression has a problem”, you can fix them by slightly tweaking the regex (for example, adding ^…$ anchors to force regex mode or altering escape characters) as described in the Reqnroll docs. These cases are uncommon but worth noting.
In general, a clean build at this stage means all your code is now pointing to Reqnroll. Your Gherkin feature files remain the same – steps, scenarios, and feature definitions don’t need changing (except perhaps to take advantage of new syntax, which is optional). For example, you might later decide to use Cucumber style parameters ({string}, {int}, etc.) in your step definitions to replace complex regex, but this is not required for migration it’s just a nice enhancement supported by Reqnroll.
Example: Imagine a SpecFlow step definition class for a login feature. Before migration, it may have looked like:
// Before (SpecFlow)
using TechTalk.SpecFlow;
[Binding]
public class LoginSteps
{
[Given(@"the user is on the login page")]
public void GivenTheUserIsOnTheLoginPage() {
// ... (implementation)
}
}
After migration to Reqnroll, with namespaces replaced, it becomes:
// After (Reqnroll)
using Reqnroll;
[Binding]
public class LoginSteps
{
[Given("the user is on the login page")]
public void GivenTheUserIsOnTheLoginPage() {
// ... (implementation)
}
}
As shown above, the changes are minimal – the using now references Reqnroll and the rest of the code remains functionally the same. We removed the @ in the given regex because in Reqnroll you could choose to use a simpler Cucumber expression (here the quotes indicate a string), but even if we kept the regex it would still work. This demonstrates how familiar your code will look after migration.
Step 3: Adjust Configuration Settings
SpecFlow projects often have configuration settings in either a specflow.json file or an older App.config/specFlow section. Reqnroll introduces a new JSON config file named reqnroll.json for settings, but importantly, it is designed to be backwards compatible with SpecFlow’s config formats. Depending on what you were using, handle the configuration as follows:
- If you used specflow.json: Simply rename the file to reqnroll.json. The content format inside doesn’t need to change much, because Reqnroll accepts the same configuration keys. However, to be thorough, you can update two key names that changed:
- stepAssemblies is now called bindingAssemblies in Reqnroll (this is the setting that lists additional assemblies containing bindings).
- If you had bindingCulture settings, note that in Reqnroll those fall under a language section now (e.g., language: { binding: “en-US” }).
- These old names are still recognized by Reqnroll for compatibility, so your tests will run even if you don’t change them immediately. But updating them in the JSON is recommended for clarity. Also, consider adding the official JSON schema reference to the top of reqnroll.json (as shown in Reqnroll docs) for IntelliSense support.
If you used an App.config (XML) for SpecFlow: Reqnroll’s compatibility package can read most of the old App.config settings without changes, except one line. In the of App.config, the SpecFlow section handler needs to point to Reqnroll’s handler. You should replace the SpecFlow configuration handler line with the Reqnroll one, for example:
<configSections>
<!-- Old: <section name="specFlow" type="TechTalk.SpecFlow.Configuration.ConfigurationSectionHandler, TechTalk.SpecFlow" /> -->
<section name="specFlow" type="Reqnroll.SpecFlowCompatibility.ReqnrollPlugin.ConfigurationSectionHandler, Reqnroll.SpecFlowCompatibility.ReqnrollPlugin" />
</configSections>
- The above change is only needed if you still rely on App.config for settings. Going forward, you might migrate these settings into a reqnroll.json for consistency, since JSON is the modern approach. But the compatibility package ensures that even if you leave most of your App.config entries as-is, Reqnroll will pick them up just fine (after that one section handler tweak).
- Default configuration: If you had no custom SpecFlow settings, then Reqnroll will work with default settings out of the box. Reqnroll will even honor a specflow.json left in place (thanks to compatibility), so renaming to reqnroll.json is optional but encouraged for clarity.
After updating the config, double-check that your reqnroll.json (if present) is included in the project (Build Action = Content if needed) so it gets copied and recognized at runtime. Configuration differences are minor, so this step is usually quick.
Step 4: Run and Verify Your Tests
Now it’s the moment of truth, running your BDD tests on Reqnroll. Execute your test suite as you normally would (e.g., via dotnet test on the command line, or through Visual Studio’s Test Explorer). Ideally, tests that were green in SpecFlow should remain green under Reqnroll without any changes to the test logic. Reqnroll was designed to preserve SpecFlow’s behavior, so any failing tests likely indicate a small oversight in migration rather than a fundamental incompatibility.
If all tests pass, congratulations, you’ve successfully migrated to Reqnroll! You should see in the test output or logs that Reqnroll is executing the tests now (for example, test names might be prefixed differently, or the console output shows Reqnroll’s version). It’s a good idea to run tests both locally and in your CI pipeline to ensure everything works in both environments.
Troubleshooting: In case some tests fail or are behaving oddly, consider these common post-migration tips:
- Check for Missed Replacements: A failing step definition could mean the binding wasn’t picked up. Perhaps a using TechTalk.SpecFlow remained in a file, or a step attribute regex now conflicts with Cucumber expression syntax as mentioned earlier. Fixing those is usually straightforward by completing the find/replace or adjusting the regex.
- Cucumber Expression Pitfalls: If a scenario fails with an error about no matching step definition, yet the step exists, it might be due to an edge-case interpretation of your regex as a Cucumber Expression. Adding ^ and $ around the pattern in the attribute tells Reqnroll to treat it strictly as regex. Alternatively, adopt the cucumber expression format in the attribute. For example, a SpecFlow step like [When(@”the user enters (.*) and (.*)”)] could be rewritten as [When(“the user enters {string} and {string}”)] to leverage Reqnroll’s native parameter matching. Both approaches resolve ambiguity.
- MSTest Scenario Outlines: If you use MSTest as your test runner, be aware that Reqnroll generates scenario outlines as individual data-driven test cases by default (using MSTest’s data row capability). In some setups, this can cause the test explorer to show scenario outline scenarios as “skipped” if not configured properly. The fix is to adjust a setting to revert to SpecFlow’s older behavior: set allowRowTests to false for Reqnroll’s MSTest generator (this can be done in reqnroll.json under the generator settings). This issue and solution are documented in Reqnroll’s migration guide. If using NUnit or xUnit, scenario outlines should behave as before by default.
- Living Documentation: SpecFlow’s LivingDoc (HTML living documentation generator) is not directly available in Reqnroll yet, since the SpecFlow+ LivingDoc tool was closed-source. If your team relies on living documentation, note that the Reqnroll community is working on an open-source alternative. In the meantime, you can use the SpecFlow+ LivingDoc CLI as a workaround with Reqnroll’s output, per the discussion in the Reqnroll project. This doesn’t affect test execution, but it’s something to be aware of post-migration for your reporting process.
Overall, if you encounter issues, refer to the official Reqnroll documentation’s troubleshooting and “Breaking Changes since SpecFlow v3” sections, they cover scenarios like the above in detail. Most migrations report little to no friction in this verification step.
Step 5: Leverage Reqnroll’s Enhanced Features (Post-Migration)
Migrating to Reqnroll isn’t just a lateral move, it’s an opportunity to level up your BDD practice with new capabilities. Now that your tests are running on Reqnroll, consider taking advantage of these improvements:
- Advanced Test Reporting: Reqnroll can produce rich test reports, including HTML reports that detail each scenario’s outcome, execution time, and more. For example, you can integrate a reporting library or use Reqnroll’s API to generate an HTML report after your test run. This provides stakeholders with a clear view of test results beyond the console output. Visual idea: an image of a sample Reqnroll test report showing a summary of scenarios passed/failed.
- Requirements Traceability: You can link your scenarios to requirements or user stories using tags. For instance, tagging a scenario with @Requirement:REQ-101 can associate it with a requirement ID in your management tool. Reqnroll doesn’t require a separate plugin for this; it’s part of the framework’s ethos (even the name “Reqnroll” hints at starting BDD from requirements). By leveraging this, you ensure every requirement has tests, and you can easily gather which scenarios cover which requirements. This is a great way to maintain traceability in agile projects.
- Data-Driven Testing Enhancements: While SpecFlow supported scenario outlines, Reqnroll’s native support for Cucumber Expressions can make parameterized steps more readable. You can use placeholders like {int}, {string}, {float} in step definitions, which improves clarity. For example, instead of a cryptic regex, [Then(“the order is [successfully ]processed”)] cleanly indicates an optional word successfully in the step. These small syntax improvements can make your test specifications more approachable to non-developers.
- Integration and Extensibility: Reqnroll has ported all major integration plugins that SpecFlow had. You can continue using dependency injection containers (Autofac, Microsoft DI, etc.) via Reqnroll.Autofac and others. The Visual Studio and Rider IDE integration is also in place, so you still get features like navigating from steps to definitions, etc. As Reqnroll evolves, expect even more integrations. Keep an eye on the official docs for new plugins (e.g., for report generation or other tools). The fact that Reqnroll is community-driven means that if you have a need, you can even write a plugin or extension for it.
- Parallel Execution and Async Support: Under the hood, Reqnroll generates task-based async code for your test execution, rather than the synchronous code SpecFlow used. This modernization can improve how tests run in parallel (especially in xUnit, which handles async tests differently) and positions the framework for better performance in the future. As a user, you don’t necessarily have to change anything to benefit from this, but it’s good to know that Reqnroll is using modern .NET async patterns which could yield speed improvements for I/O-bound test steps and such.
By exploring these features, you’ll get more value from your migration. Reqnroll is not just a stop-gap for SpecFlow; it’s an upgrade. Encourage your team to gradually incorporate these capabilities, for example, generate a periodic test report for the team, or start tagging scenarios with requirement IDs.
With the migration steps completed and new features in your toolkit, you’re all set on Reqnroll. Next, let’s compare SpecFlow and Reqnroll side-by-side and highlight what’s changed or improved.
SpecFlow vs Reqnroll – Key Differences and Benefits
To summarize the changes, here’s a comparison of SpecFlow and Reqnroll across important aspects:
| S. No |
Aspect |
SpecFlow (Before) |
Reqnroll (After) |
| 1 |
Origin & Support |
Open-source BDD framework for .NET, but support/updates have slowed in recent years. |
Fork of SpecFlow maintained by the community; actively updated and .NET 8+ compatible. |
| 2 |
Package Names |
NuGet packages named SpecFlow.* (e.g., SpecFlow.NUnit, SpecFlow.MsTest). |
Packages renamed to Reqnroll.* (e.g., Reqnroll.NUnit, Reqnroll.MsTest). Drop-in replacements are available on NuGet. |
| 3 |
Namespaces in Code |
Use TechTalk.SpecFlow namespace in step definitions and hooks. |
Use Reqnroll namespace (or compatibility package to keep the old namespace). Classes like TechTalk.SpecFlow.ScenarioContext becomes Reqnroll.ScenarioContext. |
| 4 |
BDD Syntax Support |
Gherkin syntax with Regex for step parameters (SpecFlow v3 lacked Cucumber Expressions). |
Gherkin syntax is fully supported; Cucumber Expressions can be used for step definitions, making steps more readable (regex is still supported too). |
| 5 |
Execution Model |
Step definitions are executed synchronously. |
Step definitions execute with task-based async under the hood, aligning with modern .NET async patterns (helps in parallel test execution scenarios). |
| 6 |
Feature Parity |
Most BDD features (hooks, scenario outlines, context sharing) are available. |
All SpecFlow features ported; plus improvements in integration (e.g., VS Code plugin, updated VS extension). Scenario outline handling is slightly different for MSTest (can be configured to match SpecFlow behavior). |
| 7 |
Plugins & Integrations |
Rich ecosystem, but some tools like LivingDoc were proprietary (SpecFlow+). |
Nearly all plugins have been ported to open source: e.g., ExternalData, Autofac DI, etc. SpecFlow+ Actions (Selenium, REST, etc.) available via Reqnroll.SpecFlowCompatibility packages. LivingDoc to be rebuilt (currently not included due to closed-source) |
| 8 |
Data Tables |
Used Table class for Gherkin tables. |
Table class still exists, with an alias DataTable introduced for consistency with Gherkin terminology. Either can be used. |
| 9 |
Community & License |
SpecFlow was free (open-source core) but backed by a company (Tricentis) with some paid add-ons. |
Reqnroll is 100% open source and free, with community support. Companies can opt into support subscriptions, but the framework itself has no license fees. |
| 10 |
Future Development |
Largely stagnant; official support for new .NET versions uncertain. |
Rapid development and community-driven roadmap. Already added .NET 8 support and planning new features (e.g., improved living documentation). Reqnroll versioning starts fresh (v1, v2, etc.) for clarity. |
As shown above, Reqnroll retains all the core capabilities of SpecFlow – so you’re not losing anything in the move – and it brings multiple benefits: active maintenance, new syntax options, performance alignments with async, and freedom from proprietary add-ons. In everyday use, you might barely notice a difference except when you upgrade to a new version of .NET or need a new plugin and find that Reqnroll already has you covered.
Conclusion: Embrace the Future of .NET BDD with Reqnroll
Migrating from SpecFlow to Reqnroll enables you to continue your BDD practices with confidence, knowing your framework is up-to-date and here to stay. The migration is straightforward, and the improvements are immediately tangible from smoother integration in modern toolchains to added features that enhance testing productivity. By following this step-by-step guide, you can smoothly transition your existing SpecFlow tests to Reqnroll and future-proof your test automation.
Now is the perfect time to make the switch and enjoy the robust capabilities Reqnroll offers. Don’t let your BDD framework become a legacy anchor; instead, embrace Reqnroll and keep rolling forward with behavior-driven development in your .NET projects.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Do I need to rewrite my feature files?
No. Reqnroll processes your existing .feature files exactly as SpecFlow did.
-
How long does migration take?
Many teams finish within an hour. The largest effort is updating NuGet references and performing a global namespace replace.
-
What about SpecFlow’s LivingDoc?
Reqnroll is developing an open-source alternative. In the meantime, continue using your existing reporting solution or adopt Reqnroll’s HTML reports.
-
Does Reqnroll work with Selenium, Playwright, or REST testing plugins?
Yes. Install the equivalent Reqnroll compatibility package for each SpecFlow.Actions plugin you previously used.
-
Is Reqnroll really free?
Yes. The core framework and all official extensions are open source. Optional paid support subscriptions are available but not required.

by Rajesh K | Jun 18, 2025 | Software Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
If software projects still followed a “code everything first, test at the end” model, modern teams would be drowning in last-minute bugs, missed launch dates, and emergency hot-fixes. Customers have little patience for broken features, and competitors ship improvements weekly sometimes daily. To keep pace, engineering leaders have embraced Shift Left Testing: moving software testing activities as far left on the project timeline as possible and running them continuously. Rooted in shift left testing principles, the idea is simple but powerful: find and fix defects while they are cheap and easy to fix, not after they have spread across the codebase or reached production. Studies show that a bug caught during development can cost up to thirty times less to remedy than the same bug discovered in production. Fixing it sooner also prevents domino-effect rework that can derail sprint commitments.
Shift Left isn’t only about cost; it changes culture. Developers and QA engineers collaborate from day one, agree on acceptance criteria, and build automated tests alongside the code. Testing stops being a painful gate at the end instead, it becomes a routine quality pulse that guides design choices and safeguards continuous delivery. Done well, Shift Left delivers three wins at once: higher product quality, faster release cycles, and lower overall cost. This guide explains how it works, which tests must run earliest, and how you can roll out a Shift Left strategy that sticks.
What Is Shift Left Testing?
Shift Left Testing means planning, designing, and executing tests earlier in the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) instead of waiting until coding is “finished.” The typical waterfall flow places requirements on the far left and testing on the far right. By “shifting left,” you embed testing tasks unit tests, integration checks, static analysis, security scans within each development stage.
Core principles include:
- Early Involvement – Include testing considerations in the initial requirements and design phases. Testers should collaborate with product owners and developers when user stories and features are being defined. By doing this, teams can spot ambiguity or potential problem areas up front and design better solutions. When developers write code, they already know the test cases and quality criteria it needs to satisfy.
- Continuous Testing – Make testing a continuous activity at every stage of development, not just a one-time phase . Every code change or build should trigger tests from unit tests to integration and even exploratory tests so that immediate feedback is available. This continuous feedback loop ensures any new bug is caught quickly, long before it can affect later stages . (For more on continuous testing in practice, read our Continuous Testing in DevOps guide (internal link).)
- Extensive Automation – Embrace automation to execute tests rapidly and repeatedly. Automated tests (unit, API, regression suites, etc.) can run in parallel with development, providing instant alerts if something breaks . Automation is crucial for Shift Left because it supports the high frequency of tests (especially in a CI/CD pipeline) without slowing down the team. It also frees up human testers to focus on complex scenarios and exploratory testing.
- Collaboration and Shared Ownership – Break down silos between developers, QA, and operations. Everyone is responsible for quality. Developers are encouraged to write and run unit tests and integration tests, while testers might get involved in reviewing code or designing test cases during development. This overlap fosters a “whole team” approach to quality where issues can be discussed and resolved collaboratively in real time . In Agile terms, think of it as turning QA into Quality Engineering (QE) – quality is built into the product with active contribution from all roles, rather than tested in at the end.
The outcome? Defects are prevented or caught right after they appear, long before they cause schedule slips or reach customers.
Shift Left vs. Traditional Testing (Comparison Table)
One of the best ways to understand the impact of Shift Left Testing is to compare it with a traditional testing approach. In conventional (waterfall-style) development, testing happens late often after all development is complete. In a Shift Left approach, testing happens early and throughout development. The biggest differences lie in when testing occurs, who is involved, and why it’s done. The table below summarizes the key differences between Traditional Testing and Shift Left Testing:
| S. No |
Aspect |
Traditional Testing (Test Late) |
Shift Left Testing (Test Early & Often) |
| 1 |
When Testing Occurs |
Primarily at the end of the SDLC (after development is finished). |
Throughout the SDLC, starting from requirements/design stages . Early tests (unit, integration) run in each iteration. |
| 2 |
Approach to Quality |
Reactive find and fix bugs right before release. Quality checks are a final gate. |
Proactive prevent and catch defects early. Quality is built-in from the beginning as part of design and coding. |
| 3 |
Team Involvement |
QA testers are mostly involved at the end. Little developer involvement in testing; silos between dev and test teams. |
Whole-team involvement. Developers, QA, and even Ops collaborate on testing from day one . Developers write tests, testers partake in requirements and design discussions. |
| 4 |
Tools & Automation |
Often relies on manual testing and separate QA environments towards project end. Automation may be minimal or late. |
Heavy use of test automation and CI/CD pipeline integration for continuous tests. Testing tools are in place from the start (unit testing frameworks, CI build checks, etc.). |
| 5 |
Defect Detection |
Bugs are found late, potentially after they’ve impacted large portions of code. Late defects often cause project delays and expensive fixes. |
Bugs are caught early, in small code units or components . This minimizes the impact and cost of defects, preventing late-stage surprises. |
| 6 |
Cost & Time Impact |
Higher cost of fixes (defects discovered at end might require major rework) and longer time to market . A bug found just before release can derail schedules. |
Lower cost of fixes (issues are resolved when easier/cheaper to fix ) and faster delivery. Few last-minute issues means ontime releases with less firefighting. |
As shown above, traditional testing defers quality checks to the “extreme right” of the timeline, whereas shift-left testing pushes them to the “left” (early stages) . In a traditional model, if testers find a critical bug at the end, the software must loop back to developers, causing delays and cost overruns . Shift Left flips this scenario: by testing early, issues are discovered when they’re smaller and easier to fix, so development can continue smoothly. In fact, it’s often said that “the difference lies in when the testing happens and why” shift-left aims to prevent issues early, whereas late testing often ends up just documenting issues after the fact.
To illustrate, consider how each approach handles a new feature. In a traditional process, developers might build the entire feature over weeks, then hand it to QA. QA finds bugs that send the feature back for rework, leading to surprise delays. In a shift-left approach, QA and dev work together from the start testers help define acceptance criteria, developers write unit tests as they code, and small increments are tested immediately. The feature is validated continuously, so by the time it’s “done,” there are no major surprises. This leads to fewer late-stage defects and a more predictable timeline. As a result, teams that shift left can deliver features faster without sacrificing quality, while traditional approaches often struggle with long test fix cycles toward the end of projects.
Benefits of Shifting Left: Why Test Early?
Adopting Shift Left Testing principles brings a host of tangible benefits to software teams and businesses. By catching issues sooner and baking quality into the process, organizations can achieve faster delivery, lower costs, and better products. Here are some key benefits of shifting left:
- Early Defect Detection & Prevention: The primary benefit is finding bugs earlier in the development process, which makes them much easier and cheaper to fix . Developers can address issues in their code before it integrates with larger systems, preventing small bugs from snowballing into major problems. Early testing essentially prevents defects from ever reaching production. As a result, teams avoid the nightmare of discovering critical issues right before a release or (worse) in front of customers. One study notes that fixing a bug during development could cost 30x less than fixing it in production so early bug detection has a huge ROI.
- Lower Costs & Less Rework: Because defects are caught when they’re simpler to resolve, the cost of quality issues drops dramatically. There’s less need for expensive, last-minute project rework or emergency patches. For example, if a security vulnerability in a payment app is only discovered after release, the company must spend significant time and money on hotfixes, customer support, and possibly downtime losses expenses that would have been far lower if the issue was caught earlier. By shifting left, teams fix bugs when they’re introduced (often in a single module or during a build) rather than refactoring broad swaths of completed work. This reduces the risk of project overruns and protects the budget. (One report even estimates network outage costs at $5,600 per minute reinforcing how critical early issue prevention can be.)
- Faster Time-to-Market: Shifting left can accelerate development cycles and delivery of features. It’s simple: when you start testing earlier, you uncover and address obstacles sooner, which means fewer delays later. Teams that integrate continuous testing report significantly shorter intervals between releases. Instead of a long test-fix period at the end, issues are resolved on the fly. This leads to a smoother, more parallel workflow where development and testing happen concurrently. Ultimately, features get to market faster because there’s no waiting on a big testing phase or extensive bugfix cycle at the end. As the saying goes, “the sooner you start, the sooner you finish” early bug fixing means you don’t pay for those bugs with added time before release . Many organizations have found that shifting left helped them ship updates quickly and frequently without compromising quality.
- Higher Software Quality: When testing is ingrained throughout development, the end product’s quality naturally improves. Shift Left Testing principles brings rigorous and frequent quality checks at every stage, leading to more stable and polished software . Issues are not only fixed earlier but also often found before code is merged, resulting in cleaner architecture and codebase. This proactive approach yields fewer defects escaping to production and a stronger code foundation. Frequent testing also improves test coverage more of the code and use cases get tested than in a last- minute rush. The outcome is a high-quality application with minimal patches and hotfixes needed down the line , which means users encounter far fewer bugs. In short, shift-left principles help deliver a product that meets requirements and user expectations from day one.
- Improved Team Collaboration & Efficiency: Shift Left fosters a culture of collaboration that can make teams more efficient and effective. Developers and testers working together from the start means better communication, shared understanding, and faster feedback loops . Instead of throwing work “over the wall,” everyone stays on the same page regarding quality goals. This can boost developer morale and ownership as well – developers get quick feedback on their code and can be confident in making changes, knowing that continuous tests have their back . Testers, on the other hand, become proactive contributors rather than last-minute gatekeepers, often gaining more technical skills (like scripting or using automation tools) in the process. Overall, the team spends less time in blame or scramble mode and more time steadily improving the product. The shared responsibility for quality means issues are addressed by the right people at the right time, with less back-and-forth.
- Customer Satisfaction & Stakeholder Confidence: By enabling on-time delivery of a reliable, high-quality product, Shift Left Testing principles ultimately leads to happier customers and stakeholders . When releases go out with fewer bugs (especially critical ones), user experience improves and trust in the product grows. Additionally, being able to hit delivery timelines (because you’re not derailed by late defects) boosts the confidence of project managers and executives. They can plan releases more predictably and meet market commitments. In a B2B context, demonstrating a robust testing process that catches issues early can be a selling point clients have confidence that the software will be stable. All of this translates to better business outcomes, whether it’s higher customer retention, fewer support calls, or a stronger reputation for quality.
How to Implement Shift Left Testing (Best Practices)
Shifting your testing approach leftward requires more than just a mandate, it involves process changes, cultural shifts, and tooling upgrades. Here are some best practices and practical steps to implement Shift Left Testing principles in your team:
1.Foster a Collaborative “Quality Culture”:
Begin by breaking the mindset that testing is solely QA’s job. Encourage developers, testers, and product owners to work together on quality from the outset. Include testers in early-stage activities for example, have QA representatives attend requirements gathering and design meetings. This ensures potential test scenarios and pitfalls are considered early . Likewise, encourage developers to participate in test planning or review test cases. The goal is to create a culture where everyone feels responsible for the product’s quality. When communication flows freely between dev and QA, bugs are caught and addressed faster. (Remember: shifting left isn’t a tool or a single step – it’s a team mindset shift.)
2.Start Testing from Day One (Plan for Early Testing):
Don’t wait until code is complete to think about testing. As soon as requirements are defined, start formulating a test plan and test cases. For each new feature or user story, ask “How will we test this?” up front. Adopting practices like Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) or writing acceptance criteria for each story can help bake testing into the planning. Developers can also practice Test-Driven Development (TDD) writing unit tests for a function before writing the function itself. TDD ensures that coding is guided by testing goals and that every unit of code has associated tests from the very beginning. By planning and writing tests early, you create a safety net that catches regressions as development progresses.
3.Integrate Testing into CI/CD Pipelines:
A technical backbone of Shift Left Testing is a robust Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) setup with automated tests. Make sure your team has a CI system (like Jenkins, GitLab CI, etc.) where every code commit triggers a build and run of your test suite. Start with automated unit tests developers should write and maintain unit tests for their code and have them run on each commit. Then include integration tests, API tests, and other automated checks as appropriate for your application. The idea is that by the time code reaches later stages (staging or pre-production), it has already passed a gauntlet of tests from earlier stages. Integrating static code analysis tools for security and code quality into CI is also advisable (this performs a kind of “automated code review” every time code is pushed). A well- implemented CI pipeline will provide immediate feedback if a developer introduces a bug, the pipeline fails within minutes, and they can fix it before moving on. This keeps defects from accumulating. Essentially, continuous testing through CI/CD is what enables shift-left at scale: it’s how you test “early and often” in practice.
4.Leverage Test Automation & Tools:
Manual testing alone can’t keep up with the speed of modern development, especially when shifting left. Invest in good test automation tools and frameworks that fit your tech stack (e.g., JUnit or PyTest for unit tests, Selenium or Cypress for UI tests, Postman or RestAssured for API tests, etc.). Automation is crucial for running repetitive tests quickly. Aim to automate not just functional tests, but also regression tests and smoke tests that can run whenever new code is integrated. Automated tests ensure consistency and speed they’ll catch if a new code change breaks an existing feature within minutes, which is vital for early detection. Additionally, consider tools for test data management (so you have fresh, relevant test data for early testing) and environment virtualization (like using Docker containers or service virtualization to simulate parts of the system that aren’t built yet, allowing testing in isolation). The more you can automate and simulate, the earlier in the pipeline you can run meaningful tests. Tip: Start small by automating the highest value tests (e.g. critical user flows or core units) and expand coverage iteratively.
5.Implement Fast Feedback Loops:
The effectiveness of Shift Left depends on getting feedback to the right people quickly. Ensure that when tests fail or issues are found, the team knows right away. This could be as simple as configuring CI to send alerts on test failures or having dashboards that track test results in real time. It’s also a good practice to conduct regular code reviews and peer testing for instance, developers can review each other’s code for potential issues (a form of shifting quality checks left into the coding stage itself) and even write unit tests for each other’s modules. Consider scheduling short “bug bash” sessions early in development sprints where the team collectively tests new features in a development environment to flush out issues. The idea is to create tight feedback loops: find issues, fix, and learn from them quickly. This might also involve refining requirements when testers or developers identify unclear or conflicting requirements early on. Some teams incorporate shift-left principles by adopting tools that provide instant code feedback (like linters or static analyzers in the IDE, which highlight potential bugs or security vulnerabilities as code is written).
6.Train and Empower Team Members:
Shifting left may require new skills or knowledge, especially for teams used to siloed roles. Provide training for developers on writing good automated tests and using testing frameworks. Similarly, train QA engineers on the development process and basic coding so they can participate more deeply (for example, writing simple automated tests or scripts). Encourage a cross-functional skill development: testers who can read code and developers who understand testing theory will collaborate much more effectively. It can also help to designate “quality champions” or mentors on the team to support others in following shift-left practices. Remember that implementing shift-left is an iterative journey – start with pilot projects or specific areas where early testing could show immediate improvements, then share those wins to get buy-in from the rest of the organization.
By following these steps, teams can gradually move toward a full shift-left testing approach. It’s often helpful to measure your progress track metrics like defect rates in production vs. in development, time taken to resolve bugs, or the percentage of test coverage at different stages. Many organizations see improvements in all these metrics as they implement shift-left practices. Moreover, industry experts advise that key enablers for shift-left success are a supportive culture and proper tooling. Integrating security checks (shift-left security) alongside testing is another emerging best practice – this means running security scans and threat modeling early as well, to catch vulnerabilities when they’re easiest to fix.
In summary, implementing Shift Left Testing principles is about people, process, and tools. Get your team on board with the philosophy of early testing, adjust your development workflow to embed testing steps from the beginning, and use automation to support the increased testing frequency. With these in place, you’ll significantly reduce the pain of late-stage bug fixes and pave the way for continuous delivery of high- quality software.
Key Testing Types in a Shift-Left Strategy
| Hierarchy Level |
Testing Type |
Why It Belongs Early |
Mandatory? |
| Level 1 |
Unit Tests
Static Code Analysis / Linting |
Validate each function or class as code is written.
Spot style issues, security flaws, and code smells instantly. |
Yes – baseline |
| Level 2 |
Component / Integration Tests
API Contract Tests |
Ensure modules interact correctly and contracts hold.
Verify request/response formats as services evolve. |
Highly recommended |
| Level 3 |
Security Scans (Dependencies, Secrets)
Performance Micro-Benchmarks |
Catch CVEs and leaked credentials before merge.
Flag major regressions in critical code paths early. |
Recommended |
| Level 4 |
UI Smoke Tests |
Lightweight checks that core screens render and flows work. |
Optional in early stages |
Practical tip:
- Run Level 1 on every commit.
- Gate merges with Level 2.
- Schedule Level 3 nightly.
- Add Level 4 where rapid UI feedback is valuable.
Benefits of Shifting Left
- Early Defect Detection – Bugs surface minutes after code is written, not weeks later.
- Lower Fix Cost – Simple, localized changes beat large-scale rework.
- Faster Delivery – No giant “test/fix” crunch at the end; sprints finish on time.
- Higher Quality – Continuous checks raise overall stability and user trust.
- Better Team Morale – Developers and testers collaborate, avoiding blame games.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction – Fewer production incidents keep users happy.
Real-World Example
A fintech team built a new payment feature. Under their old process, QA found a critical security flaw two days before launch, delaying release by a week and costing thousands in fixes. After adopting Shift Left testing principles:
- QA joined requirement workshops and identified risky input scenarios.
- Developers wrote unit and API tests plus static-analysis checks from day one.
- CI ran these tests on each commit; a vulnerability scan flagged an unsafe dependency immediately.
- The issue was fixed the same afternoon—long before staging.
Result: The feature shipped on schedule with zero security incidents post-release, saving the company money and reputation.
Shift Left in Agile and DevOps
- Agile: Testing fits inside each sprint; the definition of “done” requires passing automated checks.
- DevOps: Continuous integration pipelines fail fast if any unit or integration test breaks.
- DevSecOps: Security scanning shifts left alongside functional tests, enabling early threat mitigation.
These methodologies rely on Shift Left to sustain rapid, reliable delivery.
Conclusion
Shift Left Testing is more than a trend; it’s a strategic approach to building quality from the start. By testing early in the software development life cycle (SDLC), teams catch issues sooner, reduce rework, and accelerate delivery. Rooted in shift left testing principles, it fosters a proactive quality culture, minimizes late-stage surprises, and supports faster, more reliable releases. Whether you’re using Agile, DevOps, or CI/CD, adopting shift-left principles empowers your team to deliver better software more quickly. It may require change, but the long-term gains in efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction are well worth it.
Test early, fix faster, and release with confidence.
.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What does “shift left” mean in testing?
It means moving testing tasks from late stages to early stages of development so defects are found quickly.
-
Why is shift-left important for Agile and DevOps teams?
Short sprints and continuous delivery need rapid feedback; early automated tests keep quality high without slowing releases.
-
Which tests are absolutely mandatory when shifting left?
Unit tests and static code analysis they form the first safety net for every code change.
-
Does shift-left remove the need for final-stage testing?
No. You still run end-to-end or user-acceptance checks, but far fewer surprises remain because most bugs were prevented early.