by admin | Sep 19, 2019 | Performance Testing, Fixed, Blog |
Soak Testing is part of performance testing and is a kind of software testing for Systems under Load (SUL). This testing is carried out to determine and verify that the software is able to withstand high volumes over an extended period. Soak testing can uncover issues such as memory allocation, log file handles, database resource utilization, and others. A performance testing company uses soak testing to measure the stability of the system over an extended period and as part of load testing services.
A soak test is expected to execute more transactions in the entire day – those that would be typical on a busy day – to determine any issues with performance that could crop up due to a large number of transactions. This kind of test is also referred to as a stability test. Software testing experts recommend soak testing since the analysis from it forms a critical part of app development.

It is important for businesses to understand that soak testing can only be carried out by an expert company proficient in the realm of software testing. This is so since soak testing uses a whole lot of data, and only experts would be able to remove any incidental issues without wasting time and other precious resources. Such a company would be able to swiftly diagnose and rectify any performance issues, before they become bottlenecks using the most contemporary techniques, tools, and methodology.
Characteristics of Soak Testing Soak Testing is also called Endurance Testing – as the name suggests, it helps to determine whether the software being tested can ‘endure’ continuous high loads and estimate the reaction parameters of the system. There are several occasions when a business would experience peak usage over a longer duration, of their software and unless the system is able to endure such loads, it would crash and result in mayhem. For example: a popular e-commerce site declared massive discounts of a range of items over a period of 3 days. However, within a few hours the site crashed leaving the company embarrassed and the consumers extremely irate and feeling cheated. Such incidents bring a bad reputation to a company and in some cases can turn litigious.
A soak test should have the following ‘qualities’:
- The duration of the peak soak test would be regularly controlled by the available time
- The app should continue functioning without any issues even in a broader timeframe
- It must cover the testing parameters as determined by the business and testing partner
Every system has a typical support window time period. The time between such ‘windows’ helps to determine soak test coverage. A soak test is indispensable to identify a memory leak, depletion of system resources, and lessening of resources with a database management system.
In Conclusion:
Given the importance and sensitivities involved in a perfect software/system, it is necessary for specialists to conduct soak testing. Companies may not be equipped to understand and determine their soak testing requirements, and need to partner with a leading software testing company. Connect with us today to help determine your soak testing requirements, and know more about the wide range of services we offer.

by admin | Sep 28, 2019 | Performance Testing, Fixed, Blog |
Continuous performance testing gives your development teams a fighting chance against hard-to-diagnose performance and load-handling bugs, as well as quickly identifying major functional bugs. One of the key tenets of continuous integration is to reduce the time between a change being made and the discovery of defects within that change. “Fail fast” is the mantra we often use to communicate this tenet. This approach provides us with the benefit of allowing our development teams to quickly pinpoint the source of an issue compared to the old method of waiting weeks or months between a development phase and a test phase.
For this approach to work, however, development and QA teams have to be able to run a consistent suite of automated tests regularly, and these tests must have sufficient coverage to ensure a high likelihood of catching the most critical bugs. If a test suite is too limited in scope, then it misses many important issues; a test suite that takes too long to run will increase the time between the introduction of a defect and the tester raising the issue. This is why we introduce and continue to drive automated testing in our agile environments.

We have observed a recurring set of three major factors that, when present, significantly increase the effectiveness of our tests in a continuous integration environment:
- Flexibility: Our tests must be able to be executed on demand at any time.
- Coverage: Our test coverage must be maximized with respect to the time available.
- Effectiveness: We must be able to catch the hard-to-pinpoint defects immediately.
When the concept of continuous integration and continuous testing was introduced to me some years ago, the discussion centered primarily on the unit and functional testing. Our teams implemented unit tests into their code, and the test team wrote a small set of automated functional tests that could be run on demand. Performance tests, however, were still largely relegated to the back of the room until the project was nearly completed. We thought it necessary to wait until functional testing was almost over in order to get the level of quality “high enough” so that performance testing would run without (functional) issues.
Flexibility: Performance Tests Are Automated
Performance tests are, by their very nature, almost always automated. They have to be because it is very difficult to drive large levels of load or volume using manual testing methods. Pressing the “submit” button on your mouse ten thousand times in succession is far more difficult and far less repeatable than submitting the same transaction via an automated test. Because of this high degree of automation inherent in performance tests, they can be executed any time as needed, including off days and weekends. This flexibility allows our teams to run tests overnight on changes that are made late in the day before the testers and developers arrive the next morning.
Coverage: Performance Tests Quickly Cover Broad Areas of Functionality
Performance tests generally provide “good enough” coverage of major functions without going too deep into the functionality. They cover a broad swath of commonly used functions within a quick turnaround time. If a functional bug exists in a major feature, it very often gets caught in the net of a performance test. Your performance tester is likely to be one of the first to begin screaming about a major bug in a functional feature. This is not to say that continuous performance testing can or should take the place of automated functional testing, but performance tests do, inherently, add a strong measure of functional validation.
You ought to be cautious not to allow your performance tests to become the de facto functional tests, as doing so can cause the team to lose focus on finding performance issues. When used together, however, functional and performance tests become effective partners in finding those bugs that otherwise bring your testing to a grinding halt.
Effectiveness: Performance Tests Catch Hard-to-Pinpoint Defects Immediately
Another important lesson we have learned managing performance test teams is that it’s rare for a performance issue to be caused by a code change that was made to intentionally impact performance. In other words, the majority of performance-related bugs occur in otherwise innocuous code. Quite often, we find that a defective change has a very minor performance impact when the lines of code are executed once, but when executed thousands or millions of times, they have a major cumulative slowing effect.
Consider the otherwise harmless line of code that, when changed, creates a performance delay of, say, only ten milliseconds per iteration. Now assume that the code iterates through that loop ten times per transaction. That ten-millisecond delay per loop is now compounded into a hundred-millisecond delay per transaction. If we multiply that one-tenth of a second delay by hundreds or even thousands of transactions per second, this tiny performance delay is now causing a major decrease in the number of transactions our system can process per second.
The key here is that functional changes are generally prescriptive. By this, I mean that a functional code change makes the system behave differently by design and by intention. Performance changes, however, especially negative performance changes, are less likely to be prescriptive and more likely to be an unintentional side effect of an otherwise well-intended change.

Identifying and eliminating these unintentional side effects and figuring out why a system is slowing down becomes increasingly difficult as more time passes between the introduction of the issue and when our tester catches it. If the next performance test doesn’t occur for weeks or even months later, performing root cause analysis on the issue can become next to impossible. Catching these types of performance issues quickly is key to giving your developers the best chance of pinpointing the source of the bug and fixing it. Developers and testers alike will be able to spend less time searching for the proverbial needle in the haystack and more time focusing on getting the product ready for a quality release.
Scaling Up Your Performance Testing
If you don’t do performance testing, start now! Even basic performance tests can provide major benefits when run in a continuous fashion. Start with a single transaction, parameterize the test to accept a list of test inputs/data, and scale that transaction up using a free tool such as JMeter or The Grinder. Add additional transactions one at a time until you’ve got a good sampling of the most important transactions in your system. Today’s performance test tools are much easier to use than previous generations, and most basic tools today support features that were once considered advanced, such as parameterization, assertions (validation of system responses), distributed load generation, and basic reporting.
If you do performance testing, but only occasionally or at the end of a project, select a subsection of those tests and run them every day. Or, if constraints dictate otherwise (such as test environment availability), run them as often as you possibly can, even if that means running them weekly or less often. The key here is to pick up the repetitions and reduce the amount of time between repetitions, failing as fast as possible. Remember, the word “continuous” doesn’t have to mean “constant.”
Report the results of your continuous performance tests in a way that makes them accessible to everyone who needs them. We recommend a dashboard that provides an at-a-glance overview of the current state of your performance tests with the ability to drill down into more detailed results.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting and fixing performance issues is difficult enough without having to wade through weeks or months of code changes to find the source of an issue. By closing the gap between the time a performance issue is introduced and the time we find it, we simplify the process of troubleshooting, eliminate a major source of frustration, and give our teams more time to work on the overall quality of our products. Because they contain a compelling mix of flexibility, coverage, and effectiveness, performance tests are very often powerful candidates for continuous testing.

by admin | Sep 2, 2019 | Performance Testing, Fixed, Blog |
A large number of organizations fall prey to performance problems with their system, websites, apps, and other online sites. This happens since they fail to have these tested under real world conditions, and also because they remain unaware of the performance testing errors that need to be prevented. A proficient and expert software testing partner would be able to conduct performance tests without the errors, thereby ensuring top quality software. Here are some of the common performance testing errors:

Ambiguity in Defining Goals
Load testing needs clear and quantifiable goals else the testing exercise is simply a guessing game. The goals should be based on the actual requirements of the business of the client. These could be performance under normal and heavy load conditions, response time per activity, or the volume of data the system is expected to manage, and other such goals.
Incomplete/Shoddy Planning
Performance considerations of software must be in the forefront even in the design stage – ignoring this is bound to cause problems later. In fact, organizations must ensure that performance testing assurance be part of the SLAs as part of the designing phase.
Delaying Performance Testing
Some organizations believe that conducting performance testing can wait to the end of the SLDC. This is false, and an expert performance testing company would advise the client on the benefits of running performance tests throughout the development lifecycle without delay. They would also be able to provide insights with regard to the kind of performance levels that the business can expect post conducting the entire set of tests.
Too Much Emphasis on Time
This error has to do with regard to using inadequate stop and think times – that is forgetting to add the reading and reaction time of users. A meticulous performance testing regime would emulate the actual interaction that users would have with the application. However, not simulating these actual scenarios would bring up unrealistic results, causing concern and panic. Avoiding this performance testing error would be critical to success.
Testing on Single Use Case
Inexperienced software testing teams would use a single test case setting when conducting performance testing. This would not only create problems but also skew results with regard to the kind of scenarios the application would encounter in real world situations. Expert performance testers would apply appropriate and easy to use tools that would enable a variety of statistical approaches that would bring up several kinds of variances. This in turn would offer a much more realistic indication of real world use cases.
Running Tests from a Single Location
Technical reasons or budget concerns sometimes makes software testing teams run performance testing services from within the firewall. This obviously will not be a true measure of the kind of performance the application would be able to provide in a real world scenario/or under load conditions.
Incomplete Analysis/Using Assumptions
The job of a tool while running a test is to collect data/KPIs (key performance indicators). It is necessary to allow the test run to be complete before trying to analyze the data. Using the data midway amounts to using assumptions since it would be impossible to identify trends. The errors presented at the end of the test cycle are what need to be analyzed thoroughly. While this is extremely critical, it is also one of the most challenging tasks faced by testers – using an experienced performance testing company will ensure process rigor.
Applying Small Amounts of Hardcoded Data
Some testers take the easy route by using a comparatively smaller set of hardcoded static data. This in no way can provide a realistic picture of the actual performance of a live application. An expert company undertaking performance testing services would generate inexpensive data to create huge amounts of realistic evidence. This would provide a better indication of the expected performance of the app/software product once it is in the market.
Lack of Test Run Documentation
Repeating tests and comparing results from each test is an essential part of load testing services. However, without adequate documentation for the multiple tests, the parameters applied, application versions, and the varying test settings – it would be a nightmare to track the changes and compare results. A proficient testing company would provide easy to use, efficient, and transparent documentation each time.
In Conclusion
There are already a number of things that could potentially lower the performance of your product, in addition to these errors. It would make business sense to partner with a top class performance testing company to ensure that these errors are avoided at the start. Efficient performance testing forms the basis of a high quality product – and most companies are unable to get it right despite their best intentions. Connect with our experts and leave all the worrying to us – top quality products guaranteed every time.

by admin | Aug 17, 2019 | Performance Testing, Fixed, Blog |
Load testing checks the ability of a software application to perform under anticipated user loads. The objective of load testing is to identify potential bottlenecks in an application before sending it ‘to market’. Further, load testing aims to check the availability of a system, its performance, capacity, and to validate its ability to deliver the service or functionality requested by the user/as intended. Any top performance testing company would ensure that testers also validate server response. This is performed by checking database execution time and verifying the response time of the application under low, normal, moderate, and heavy load conditions. The fact is experts know that load and functionality related problems usually happen, and hence every single step of performance validation is critical to success. Companies specializing in load and performance testing will validate server responses each time. This validation covers a vast gamut of activities, and some of these include validating – response code, basic structure of a page, main components, page completeness, important points of the activity currently being conducted, and a lot more.
Deliver Top Quality Products
A top performance testing company would ensure that accuracy of the server response each time. To achieve this, test engineers would ensure that load testing products provide efficient validation functionality. By devising test scenarios and validation parameters that guarantee the successful execution of services being tested, testers can ensure validation of the server response to some extent. Some test engineers may view this from a load testing perspective – for instance, identifying pages with responses that exceed certain specified duration. Engineers undertaking load testing services would need to investigate such discrepancies and provide immediate remediation.

Checking the Response Codes
Load testing service engineers could discover that unexpected data is going out as a user request-response. Response codes are essential to detect such anomalies in the server response. For instance, a properly functioning web server is expected to generate a response code of 200. However, testers of a performance testing company may detect responses such as 401, 404, and 503. These responses indicate a clear problem while validating the server response during load testing exercises. Further, the total time required to load an entire webpage is indicative of server response performance in certain testing scenarios.
Hardware Problems
Computer hardware performance is critical to load testing exercises. An engineer providing performance testing services must assess the performance of testing hardware before evaluating test results. The hardware (such as a web server or a server farm) hosting an application must perform optimally at all times. An intelligent approach to this would be to perform distributed load testing from multiple geographical locations. Additionally, modern testing tools and frameworks can help detect hardware problems that could distort the server response in test environments.
Validation Rules
Test engineers performing load testing services can deploy validation rules to assess the accuracy of server responses. Validation rules represent comparison criteria that testers can add to scenarios and these rules work by comparing server response data against expected values. A tester can create a specific validation rule if a server ‘responds’ with incorrect data. Typically, validation rules can be built around simple data types such as strings, long strings, numbers, Boolean values, and complex data such as objects or arrays. Such techniques represent benchmarks in the realm of server response validation during load testing.
In Conclusion
Server response has a direct impact on the experience of a software application or product by the end user. Therefore, this parameter must be tested from multiple perspectives to guarantee client satisfaction and user delight. Functional problems usually emerge during load and performance testing – not typically during load execution but during dry-runs of low load. Additionally, inconsistent response times, spikes, and others are certain ‘typical flawed load behaviors’. The premise of validating server responses during load and performance testing is to find unusual and unexpected flaws. Experts testers would excel in such testing exercises – connecting with us puts you in the driver’s seat.

by admin | Aug 8, 2019 | Performance Testing, Fixed, Blog |
Today, you will learn how to perform distributed load testing in Locust. If you are not familiar with Locust, then let’s refresh the basics and see how to perform distributed execution. Locust is an open source load testing tool and you can describe all your test in Python code.

Installation Locust is a Python library. It does not have any UI to write or configure your test. You can describe all your test in Python code.
Locust File CreationCreate a python file using the below code.
from locust import HttpLocust, TaskSet, task
class UserBehavior(TaskSet):
@task
def index(self):
self.client.get("/")
class WebsiteUser(HttpLocust):
task_set = UserBehavior
min_wait = 5000
max_wait = 9000
Note: If a file has HttpLocust class, then it will be considered as LocustFile. In the above code, we have two classes, one is TaskSet which is used to declare all your tests and the second one is HttpLocust which represents one user and it should have task_set attribute.
Executing Locust FileUse the below command to run your Locust file.
locust -f locust-examples/locustfile.py --host=http://google.com
Note: As per the above command, our LocustFile is placed inside a folder (i.e. locust-examples). Once you execute the above command, Locust web monitor will start and you can start load execution from web monitor
Locust Web MonitorYou can launch the web monitor using http://localhost:8089/.
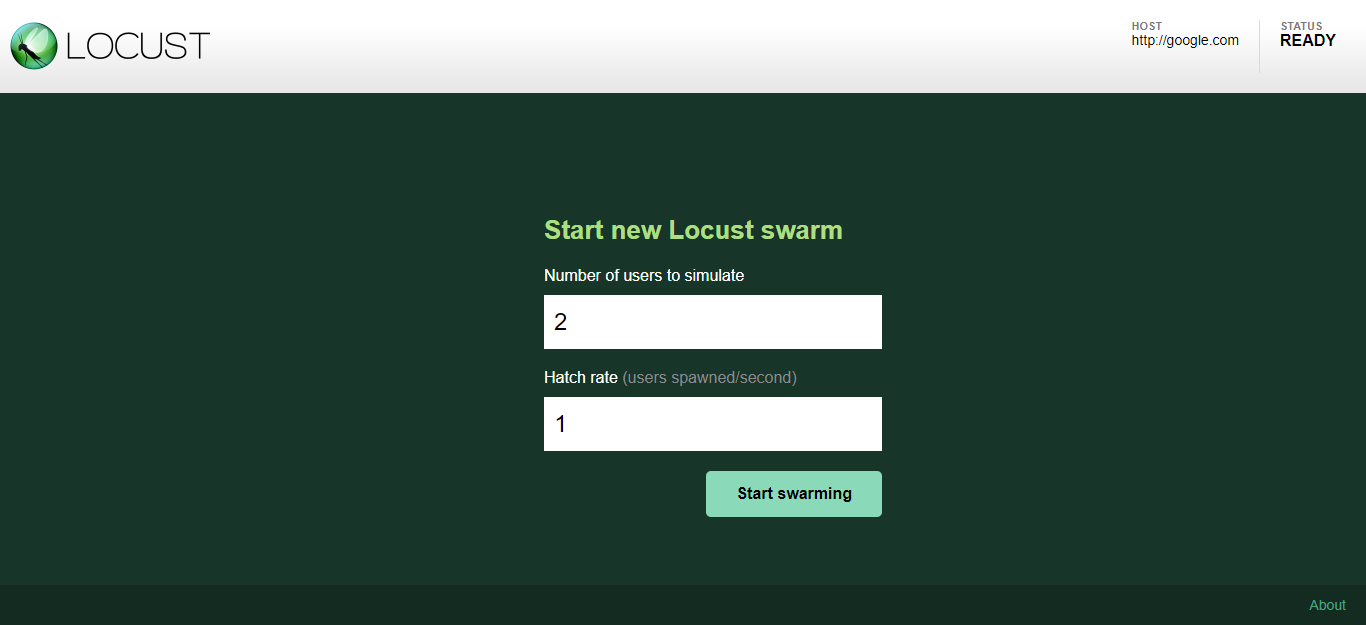
Now, click Start Swarming button after entering number of users and Hatch rate.
Distributed Execution
To start locust in master mode:
locust -f my_locustfile.py --master
And then on each slave (replace 192.168.0.14 with IP of the master machine):
locust -f my_locustfile.py --slave --master-host=192.168.0.14

by admin | Aug 8, 2019 | Performance Testing, Fixed, Blog |
Businesses and enterprises rely heavily on digital applications for critical functions and hence it is important to validate whether applications can withstand realistic workload scenarios. Application load testing helps test engineers determine the behavior of a system under normal (and anticipated) peak load conditions. Such exercises help to identify the maximum operating capacity of an application and detect any bottlenecks. In essence, load testing ensures a given function, program, or system can handle the assignments it is designed to execute.

Beyond Functional Testing
The functional testing of an application, while important, in no way degrades the centrality of application load testing – a performance testing company undertakes such testing to measure the performance of an application over time. Commercially available load testing tools help ensure applications can withstand normal amounts of user traffic and can navigate spikes and unusual conditions. Further, application load testing helps validate the fundamental features of a software product – measure the speed, accuracy, and stability of the software, identify discrepancies, resolve issues, and improve optimization and load capability.
Components of Load Testing
Commercial providers of load testing services can gather requirements, map relevant user journeys, establish a baseline, and automate and integrate the various units of a software product as part of application load testing activities. Such actions help providers of load testing services to gain a deeper understanding of the end-user experience, identify how users interact with an application, use monitoring data from any APM tools, run tests to establish a solid baseline for further testing, and prioritize load testing as a part of CI/CD processes, while integrating with automation tools already in use.
Cloud: Insurance for Performance
When load testing services adopt a firm stance on performance using cloud-based testing services would make the task more efficient. This choice of action reduces the costs of failure in application load testing campaigns. It helps to minimize risk related to performance requirements, increase customer satisfaction, detect performance bottlenecks, and improve the scalability of an application. Further, it boosts the deployment quality of any tested application, optimizes costs related to hardware and software, reduces the risks and costs associated with downtime, and provides tangible statistics to developers. Additionally, commercial cloud-based load testing services help start-ups to build a better and more scalable application.
Measure and Repeat
Measuring the performance of an application is an important aspect of performance testing. Measurements allow testing engineers to derive an understanding of choke points and bottlenecks within a software application. The use of application and server performance monitoring services empowers measurement activities and enables load testing campaigns to attain fruition. Additionally, measuring the internal working of an application and comparing these with load testing results helps implement tweaks to a modern software application. Finally, software testers need to repeat testing processes and refine them for better outcomes. It is important to continue writing tests, undertake functional and load tests, and execute measurements. These actions allow them to identify issues, make improvements, and release new iterations of an application – leading to a better, stronger and more scalable service for end-users.
In Conclusion
Load testing remains critical whether an application is a mobile, web or client/server design. Therefore, a performance testing company should plan for dedicated resources, who would be experts in development, execution, and keeping load testing up-to-date in line with customer standards and requirements. Customers have several choices in the market, and their expectation of a high quality application should guide performance testing companies in executing their services. Load testing ensures that the application delivers even under heavy user loads, traffic spikes, failover switches, and situations fraught with network speed variables. To work with the very best performance testing company – connect with our experts.


































