by admin | Aug 4, 2021 | Software Testing, Blog |
We’re truly living in a fast-paced digital world. Because of this, it’s much easier to miss out on golden opportunities if your products don’t reach the right consumers at an opportune time. Because of this, businesses need to act immediately when they receive feedback from their customers. By staying on top of your engagements with users, you can create changes in your campaigns and come closer to leading the pack in a saturated digital marketplace.
Automation testing is indeed an integral part of the software release cycle, especially since businesses can achieve more by integrating Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment in the process. For this reason, working with a credible DevOps team and performance testing companies is a must if you want an agile-driven enterprise. With that being said, automation testing and DevOps work flawlessly to achieve this goal.
What is DevOps?
DevOps or Development and Operations cover a set of practices that limit software release cycles through continuous software delivery with excellent quality.
With DevOps, you get to create software enterprises that offer high-quality products and services that help accelerate your pace in the digital world and boost your ranking in the digital landscape.
How Can DevOps Speed Up Bug Fixes?
When you work with your consumers, you get to focus on integral parts of your product development that you won’t notice since you’re working on the backend. This is why consumer feedback is crucial since it plays a huge role in the betterment of your product.
But besides that, rolling out new product changes and updates frequently isn’t that easy. This is due to the complexities that may arise in updates that have been released on different devices, target geographies, and platforms. However, you can achieve a speedy rollout of updates by ensuring smooth product development, testing, and deployment strategy to eliminate bugs and glitches.
Seeing as manual testing isn’t enough to achieve these tasks, you need to cope with agile demands to help eliminate human errors and app bugs. With that being said, working with performance testing companies is crucial in developing a solid DevOps approach to fixing issues quickly.
Why Automation Testing and DevOps is a Winning Combination
There’s no doubt that integrating automation testing for web products can bring many benefits to your business. Especially now that you have a limited time to win the hearts of your consumers, you need to ensure that your product isn’t at their disposal.
Since you get to test your product at every stage, you get to boost your product’s performance and could help accelerate testing for the DevOps team, limiting the time it takes to revisit feedback and send it over to the development team.
With that being said, here’s why automation testing is crucial for DevOps:
- It provides consistent test results to help reap the benefits of an effective DevOps strategy;
- It improves your communications across different teams, eliminating reasons for delays;
- It helps produce faster test outcomes;
- Offers exceptional stability for product releases, which ultimately equates to great customer experience;
- Improves testing scalability and can focus on running different tests to help improve product quality.
The Bottom Line: Integrating Automation Testing and DevOps Strategies Can Help Improve Product Releases
Software enterprises are indeed walking on a thin rope, especially when you’re dealing with a fast-paced, ever-growing environment. With that, your software must be up to speed with these developments, and proper automation testing and DevOps strategies can help.
No matter the size of your company, it’s crucial that you consult with performance testing companies and experienced development teams to help provide you with test automation services that will be incorporated into your DevOps strategies.
Trust us — this will help boost your software capabilities and quality.
How Can Codoid Help You?
If you’re looking for performance testing companies, Codoid is here to help you.
We are an industry leader in QA, leading and guiding communities and clients with our passion for development and innovation. Our team of highly skilled engineers can help your team through software testing meetup groups, software quality assurance events, automation testing, and more.
Learn more about our services and how we can help you today!

by admin | Aug 6, 2021 | Software Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
Being good at any job requires continuous learning to become a habitual process of your professional life. Given the significance of DevOps in today’s day and age, it becomes mandatory for a software tester to have an understanding of it. So if you’re looking to find out what a software tester should know about DevOps, this blog is for you. Though there are several new terms revolving around DevOps like AIOps & TestOps, they are just the subsets of DevOps. Before jumping straight into the DevOps testing-related sections, you must first understand what DevOps is, the need for DevOps, and its principles. So let’s get started.
Definition of DevOps
“DevOps is about humans. DevOps is a set of practices and patterns that turn human capital into high-performance organizational capital” – John Willis. Another quote that clearly sums up everything about DevOps is from Gene Kim and it is as follows.
“DevOps is the emerging professional movement that advocates a collaborative working relationship between Development and IT Operations, resulting in the fast flow of planned work (i.e., high deploy rates), while simultaneously increasing the reliability, stability, resilience, and security of the production environment.” – Gene Kim.
The above statements strongly emphasize a collaborative working relationship between the Development and IT operations. The implication here is that Development and Operations shouldn’t be isolated at any cost.
Why do we need to merge Dev and Ops?
In the traditional software development approach, the development process would be commenced only if the requirements were captured fully. Post the completion of the development process, the software would be released to the QA team for quality check. One small mistake in the requirement phase will lead to massive reworks that could’ve been easily avoided.
Agile methodology advocates that one team should share the common goal instead of working on isolated goals. The reason is that it enables effective collaboration between businesses, developers, and testers to avoid miscommunication & misunderstanding. So the purpose here would be to keep everyone in the team on the same page so that they will be well aware of what needs to be delivered and how the delivery adds value to the customer.
But there is a catch when it comes to Agile as we are thinking only till the point where the code is deployed to production. Whereas, the remaining aspects like releasing the product in production machines, ensuring the product’s availability & stability are taken care of by the Operations team.
So let’s take a look at the kind of problems a team would face when the IT operations are isolated,
1. New Feature
Let’s say a new feature needs multiple configuration files for different environments. Then the dev team’s support is required until the feature is released to production without any errors. However, the dev team will say that their job is done as the code was staged and tested in pre-prod. It now becomes the Ops team’s responsibility to take care of the issue.
2. Patch Release
Another likely possibility is there might be a need for a patch release to fix a sudden or unexpected performance issue in the production environment. Since the Ops team is focused on the product’s stability, they will be keen to obtain proof that the patch will not impact the software’s stability. So they would raise a request to mimic the patch on lower environments. But in the meanwhile, end users will still be facing the performance issue until the proof is shown to the Ops team. It is a well-known fact that any performance issue that lasts for more than a day will most probably lead to financial losses for the business.
These are just 2 likely scenarios that could happen. There are many more issues that could arise when Dev and Ops are isolated. So we hope that you have understood the need to merge Dev and Ops together. In short, Agile teams develops and release the software frequently in lower environments. Since deploying in production is infrequent, their collaboration with Ops will not be effective to address key production issues.
When Dev + Ops = DevOps, new testing activities and tools will also be introduced.
DevOps Principles
We hope you’ve understood the need for DevOps by now. So let’s take a look at the principles based on which DevOps operate. After which we shall proceed to explore DevOps testing.
Eliminate Waste
Anything that increases the lead time without a reason is considered a waste. Waiting for additional information and developing features that are not required are perfect examples of this.
Build Quality In
Ensuring quality is not a job made only for the testers. Quality is everyone’s responsibility and should be built into the product and process from the very first step.
Create Knowledge
When software is released at frequent intervals, we will be able to get frequent feedback. So DevOps strongly encourages learning from feedback loops and improve the process.
Defer Commitment
If you have enough information about a task, proceed further without any delay. If not, postpone the decision until you get the vital information as revisiting any critical decision will lead to rework.
Deliver Fast
Continuous Integration allows you to push the local code changes into the master. It also lets us perform quality checks in testing environments. But when the development team pushes a bunch of new features and bug fixes into production on the day of release, it becomes very hard to manage the release. So the DevOps process encourages us to push smaller batches as we will be able to handle and rectify production issues quickly. As a result, your team will be able to deliver faster by pushing smaller batches at faster rates.
Respect People
A highly motivated team is essential for a product’s success. So when a process tries to blame the people for a failure, it is a clear sign that you are not in the right direction. DevOps lends itself to focus on the problem instead of the people during root cause analysis.
Optimise the whole
Let’s say you are writing automated tests. Your focus should be on the entire system and not just on the automated testing task. As a software testing company, our testers work by primarily focusing on the product and not on the testing tasks alone.
What is DevOps Testing?
As soon as Ops is brought into the picture, the team has to carry out additional testing activities & techniques. So in this section, you will learn the various testing techniques which are required in the DevOps process.
In DevOps, it is very common for you to see frequent delivery of any feature in small batches. The reason behind it is that if developers hand over a whole lot of changes for QA feedback, the testers will only be able to respond with their feedback in a day or two. Meanwhile, the developers would have to shift their focus towards developing other features.
So if any feedback is making a developer revisit the code that they had committed two or three days ago, then the developer has to pause the current work and recollect the committed code to make the changes as per the feedback. Since this process would significantly impact the productivity, the deployment is done frequently with small batches as it enables testers to provide quick feedback that makes it easy to revoke the release when it doesn’t go as expected.
A/B Testing
This type of testing involves presenting the same feature in two different ways to random end-users. Let’s say you are developing a signup form. You can submit two Signup forms with different field orders to different end-users. You can present the Signup Form A to one user group and the Signup Form B to another user group. Data-backed decisions are always good for your product. The reason why A/B testing is critical in DevOps is that it is instrumental in getting you quick feedback from end-users. It ultimately helps you to make better decisions.
Automated Acceptance Tests
In DevOps, every commit should trigger appropriate automated unit & acceptance tests. Automated regression testing frees people to perform exploratory testing. Though contractors are highly discouraged in DevOps, they are suitable to automate & manage acceptance tests. Codoid, as an automation testing company, has highly skilled automation testers, and our clients usually engage our test automation engineers to automate repetitive testing activities.
Canary Testing
Releasing a feature to a small group of users in production to get feedback before launching it to a large group is called Canary Testing. In the traditional development approach, the testing happens only in test environments. However, in DevOps, testing activities can happen before (Shift-Left) and after (Shift-Right) the release in production.
Exploratory Testing
Exploratory Testing is considered a problem-solving activity instead of a testing activity in DevOps. If automated regression tests are in place, testers can focus on Exploratory Testing to unearth new bugs, possible features and cover edge cases.
Chaos Engineering
Chaos Engineering is an experiment that can be used to check how your team is responding to a failure and verify if the system will be able to withstand the turbulent conditions in production. Chaos Engineering was introduced by Netflix in the year 2008.
Security Testing
Incorporate security tests early in the deployment pipeline to avoid late feedback.
CX Analytics
In classic performance testing, we would focus only on simulating traffic. However, we never try to concentrate on the client side’s performance and see how well the app is performing in low network bandwidth. As a software tester, you need to work closely with IT Ops teams to get various analytics reports such as Service Analytics, Log Analytics, Perf Analytics, and User Interaction Data. When you analyze the production monitoring data, you can understand how the new features are being used by the end-users and improve the continuous testing process.
Conclusion
So to sum things up, you have to be a continuous learner who focuses on methods to improve the product and deliver value. It is also crucial for everyone on the team to use the right tools and follow the DevOps culture. DevOps emphasizes automating the processes as much as possible. So to incorporate automated tests in the pipeline, you would need to know how to develop robust automated test suites to avoid false positives & negatives. If your scripts are useless, there is no way to achieve continuous testing as you would be continuously fixing the scripts instead. We hope that this has been an equally informative and enjoyable read. In the upcoming blog articles, we will be covering the various DevOps testing-related tools that one must know.

by admin | May 26, 2021 | Software Testing, Blog |
Open-source testing tools aid developers in determining functionality, regression, capacity, automation, and many other aspects of a mobile or desktop application. A software tool is open-source if its source code is available for free and if users can modify its original design.
Many open-source testing tools are available online—Robotil, Selenium, and JMeter are examples of open source testing tools, and they test different aspects of software use. QA and software testing services also use open-source tools; here are some reasons why open-source products could be a better option than a licensed tool.
Open-Source Tools Are Often More Stable
The most significant reason why you should choose open source tools is that they typically have large developer communities backing them, fueling innovation. With more developers or organizations using a tool, the more stable and mature it is. Selenium, a test automation tool for trying out actions in the browser, is one of the world’s most active open-source projects.
Selenium’s GitHub page shows hundreds of contributors and releases. In fact, Codoid has VisGrid, a GUI for Selenium Grid enabling a developer to create hubs and nodes for testing on a user interface instead of Command Prompt. Codoid released VisGrid in 2016, and it has since undergone 14 updates—the current version, VisGrid-1.14, integrates with Selenium 3.5.3.
Open-Source Tools Have No Vendor Lock-In
A common problem among companies that use proprietary databases, platforms, or software is vendor lock-in. When businesses choose a vendor with a lock-in period on their software, they cannot quickly move to an alternative without incurring much business disruption or expenses. Using open-source software is a workaround—since open source tools do not belong to only one vendor, companies do not have to deal with lock-in periods when using them.
Open-Source Tools Are Highly Customizable
If you want to use a single platform for many years, you need to ensure it will evolve with your needs. Companies would always need unique features that tools do not provide out of the box, so your QA tool should allow you to build a solution or adopt one from other developers.
It is why software testing companies use open-source tools. These software provide various extensions, plugins, custom commands, and other ways of modifying programs and applications to suit their clients’ needs. For example, Codoid has WelDree, a beginner-friendly, UI-based Cucumber feature executor. Some plugins or extensions are available on vendors’ websites or places like GitHub, while you can download others on forums and blogs.
Open-Source Tools Are Versatile
Software testing teams need to be fluent in various programming languages and know how to operate different platforms. The testing tools they use should be versatile and cover mobile apps, web apps, native apps, or hybrids. Open source tools are viable across platforms and languages, and they enable the versatility that software quality testers need. These tools have widespread adoption across organizations of all types and sizes.
Conclusion
Open source tools drive innovation and have plenty of support from developer communities. They are built on open standards, so you can customize open-source tools extensively. If you have needs unique to your company, using an open-source tool to build a custom solution is a great way of addressing these. Partnering with a performance testing company should ensure that your application works smoothly and efficiently.
Codoid is an industry-leading software testing company. We provide robust test automation solutions across cloud, mobile, and web environments, using Selenium, Appium, White Framework, Protractor, JMeter, and more. Contact us today for more information!

by admin | May 25, 2021 | Software Testing, Blog |
Test cases are documentations that consists of line-by-line instructions that define how testing has to be done. Test cases are very crucial when it comes to testing, as it acts as a well-defined guide for the testing team to validate if the application is free from bugs. Another important aspect is that test cases help to verify if the application meets the client’s requirements. So if a test case is written on the go without any planning or effort, it will result in huge losses, as a mistake here would act like a domino effect that impacts all the upcoming stages of testing. As one of the best software testing companies in the market, we have seen great results when effective test cases were implemented. So in this blog article, we will be focusing on how you can effectively write test cases.
What are the Headers that should be present in a Test Case?
Before we discuss on How to Write Effective Test Cases, let’s cover the basic aspects that every test case must have.
Name of the Project:
Whenever we write any test case, we should make sure to mention the name of the project to avoid any unnecessary confusion.
Module Name:
The software will usually be broken down into different modules so that they can be tested separately. So it is important to give each module a unique name so that different methods of testing can be assigned and implemented without any errors.
Reference Document:
A software requirements specification (SRS) or the Customer Requirement Specification (CRS) must be specified so that the testing team can test the application based on it.
Created By:
Every written piece of content would have an author and so make sure to mention the name of the person or the team that has created the test cases. Though it is not mandatory to include the designation of the person, it is recommended that you do so.
Test Case Created Date:
It goes without saying that when all the above information is vital, the date would be important as well. So make sure to specify the date that the test team should start testing, as it helps set a deadline.
Test Case ID:
Each and every Test Case should have a unique individual ID. It is like how each student has their own and unique identification number. It will help locate the test case if you want to reuse it or be helpful for any future references.
Test Scenario:
It acts as a descriptive guide that helps us understand each step. It also highlights the objective of the action that we are going to perform in the Test case.
Test Script (or) Steps:
Every step that should be carried out has to be mentioned under the Test Steps header. It is like explaining each step in an in-depth manner so that the testing test doesn’t miss out on any step resulting in deviations from the client requirement.
Test Data:
Mentioning what input should be given in each step is equally important while testing the application. It helps to keep the testing process on track without any missteps.
Expected Result:
The primary objective of any test is to verify if the expected or desired result is achieved at the end. The client requirement can be firmly established by properly defining the expected result to make the application error-free. Let’s take a look at an example to get a better understanding.
Example: If the user turns ON the fan switch, the Fan should rotate in an anticlockwise direction.
The expected result here is that the fan should rotate in the anticlockwise direction when it is switched on.
Actual Result:
But we cannot expect the result to be as expected in every scenario. That is why we have to make a note of the actual results we obtain while executing the test.
Example: In the same scenario as discussed above, it doesn’t mean that everything is working fine if the fan rotates. It must be verified according to the expectation and see if the fan rotates in the anticlockwise direction. If the fan rotates in the clockwise direction, we should make sure to make a record of it.
Status (or) Comment:
Once we have the expected result and the actual result, we will be able to come to a conclusion and decide if the application passed the test or not. Apart from updating the status, we can also add remarks about the result such as special scenarios and so on. We can also compare this to a student’s report sheet which denotes if the student has passed or failed and would have remarks based on the result as well.
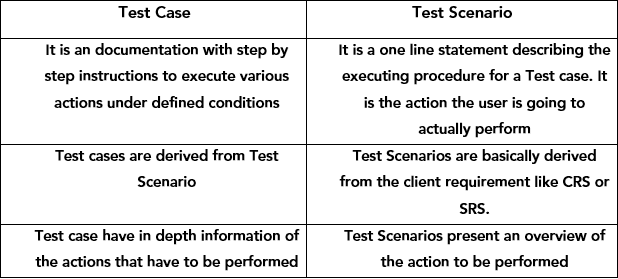
What is the Difference Between Test Case and Test Scenario?
This could be a common question that arises in many minds when this topic is discussed. So we have created a tabular column to establish the key differences between a test case and a test scenario.
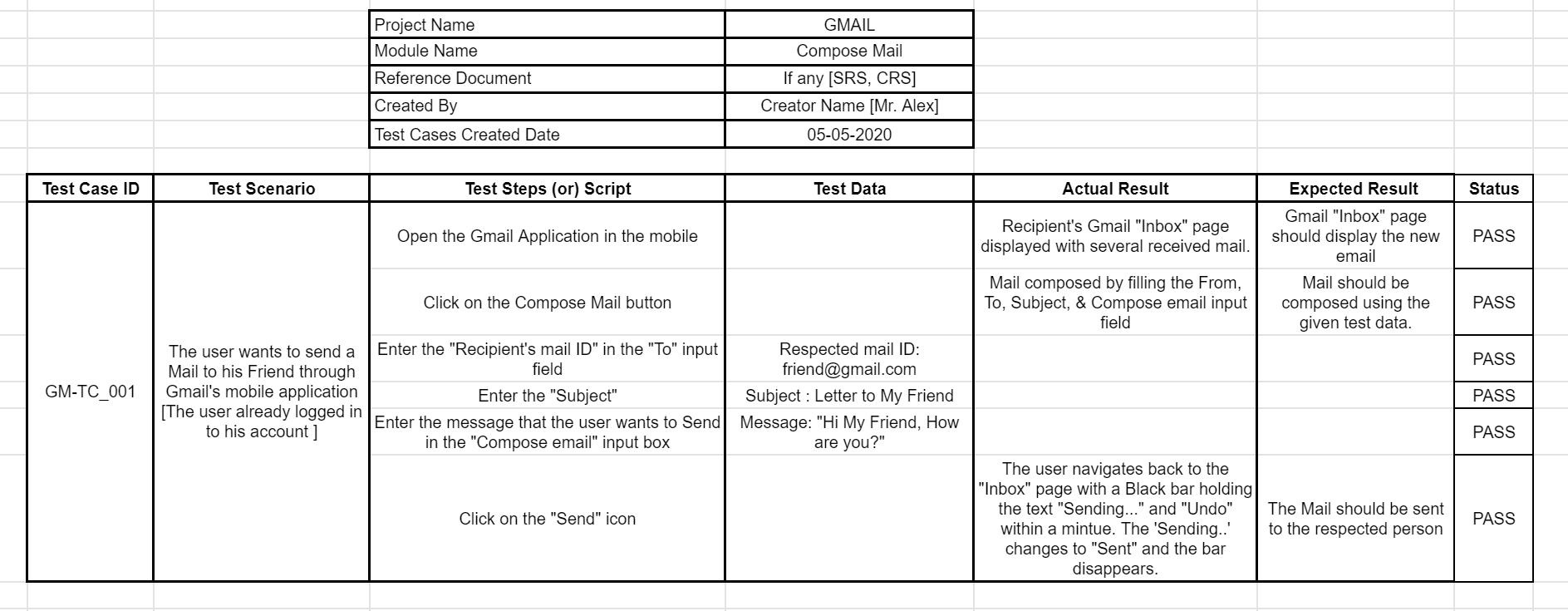
Sample Test Case:-
Now that we have gotten the basics out of the way, let’s dive into a full-fledged example and understand how to write effective test cases.
Test Scenario: A user has to send an email to someone else using their Gmail mobile application.
What are all the different types of Test Cases available?
Generally, test cases are classified into two main types,
i. Positive Test cases
ii. Negative Test cases
Positive Test cases:-
The Positive test cases do not differ much from the usual test cases, and so they are also known as formal test cases. A positive test case is used to very if the correct output is obtained when given the correct input.
Example:
Let’s say a user wants to transfer money through any UPI app, then he/she should find the correct recipient using their UPI ID or mobile number, enter the respected amount that they wish to transfer, and also enter the right UPI pin to complete the transaction. A positive test case would have the tester do the same actions by giving the correct input and seeing if everything works smoothly without any mishaps.
Negative Test cases:-
Negative Test cases are opposite to Positive test cases, as testers will provide an intentional negative or false input to make sure that the output is also negative. If we consider the same example we saw for positive test cases, the tester would try entering an incorrect UPI pin and see if the transaction fails. This is to make sure that only the authorized user will be able to operate the application, thereby increasing the security of the app. These tests are also called informal tests as they are not needed in every scenario, but they are pivotal in making sure that the application is secure.
Types of Positive Test Cases:-
Apart from the rare scenarios where negative test cases are used, positive test cases would be the more widely used preference. The Positive test cases can be further classified further based on the type of the project and the testing methods. But we will not be focusing on every type of test case as the other types are just subcategories of these 5 main types.
1. Functional Test cases
2. Integration Test cases
3. System Test Cases
4. Smoke Test cases
5. Regression Test Cases
Functional Test Cases:-
These test cases are written to check whether a particular functionality of the application is working properly or not.
Example:
If we take the same email sending example, then the test case that verifies if the send functionality is working correctly would be an apt example.
Integration Test Cases:-
These test cases are written to ensure that there is accurate data flow and database change across two combined modules or features.
Example:
The UPI money transaction example would fit well here too. During the transaction, the user enters the amount and enters the pin to complete the transaction. Once the transaction has been completed, the user will get a message about the deduction from their bank account as a result of the database change that has happened.
In this example, there is both data flow and database change between the two different modules.
System Test Cases:-
Earlier types saw us writing test cases only for a particular functionality or to see if the two modules work properly. But whenever the Testing environment is similar to the production environment, then the system test cases can be written to verify if the application is working correctly from its launch till the time it is closed. That is why this type of testing is also called end-to-end testing.
Example:
Here also we can take the same money transaction test case, but we have to test it starting right from the launch of the application to the successful transaction, and even until we receive the amount deduction message and have the transaction history updated in the user’s bank account.
Smoke Test Cases:-
Smoke tests that are also known as initial testing are very important in software testing as it acts like a preliminary test that every application should pass before extensive testing begins Smoke test cases should be written in a way that they check the critical functionalities of the software. We can then verify if the software is stable enough for further testing.
Example:
If we go back to the UPI payment app, then the testing team would have to test the application launch, account creation, and bank account addition before heading on to the transaction feature itself.
Regression Test Cases:-
Whenever the application gets any updates like UI updates, or new feature updates, the regression test cases come into play as they will be written based on the changes.
Example:
Let’s take an application most of us use on a daily basis, WhatsApp. Previously their testing team could have written test cases where the expected result could have been a list of emojis and the gif option being displayed when a user clicks on the Emoji option in the input text box.
But in one update, WhatsApp had introduced the stickers option. Since the new stickers would appear alongside the emojis and the gif option, the new test case would have been updated accordingly.
Guidelines on how to write effective test cases:
We have covered all the basic requisites that a test case must have and also the different types of test cases. This doesn’t necessarily mean that we can start writing perfect test cases right off the bat. So we will be covering a few important guidelines you should keep in your mind to write effective test cases.
1. CRS & SRS
The Testing team should be able to read and understand the Client requirements. But how is that made possible?
The client requirements for a project can be called a CRS or a Contract in simple terms. In this CRS document, the client will mention all their expectations about the software, such as how the software should perform and so on. This CRS document will be handled by the Business Analyst-(BA) of the company, and they will convert the CRS document into an SRS [System Requirement Specification] document.
The created SRS document has the functionality for each and every module and co-modules. Once the Business Analyst converts the CRS document into an SRS document they will provide the copy of the SRS document to the Testing and Development Teams. So the Testing team can read and understand the client requirement from the SRS.
2. Smoke Tests
Whenever we start writing the test cases, we should ensure to add smoke test cases to verify if the main functionality of the application is working.
3. Easy to Read
Writing easy-to-read test cases have advantages of their own. We can call it a success if a person who doesn’t have any technical knowledge can read the test cases and understand them clearly to work with the test cases.
4. Risk Evaluation
Writing extensive test cases that are not necessary should be avoided as it is a waste of resources. So proper risk evaluation has to be done prior to writing test cases so that the testing team can focus on the main requirement and core functionalities.
5. Format
The test cases always should start with either the application or the URL being launched, and it should end with the logging out option or closure of the application.
6. Avoid Assumptions
The Expected Result should be clearly captured for each and every test step, and all the features of the software (or) application should be tested without making any assumptions.
7. Dynamic values
Each and every step should not consist of multiple actions based on a single dynamic value. The dynamically changing values should not be hardcoded while writing the Test Cases. We have listed a few examples of such dynamic values.
Example:
Date, Time, Account Balance, Dynamically changing Game Slates, Reference Numbers, Points (or) Scores, etc.,
8. Dynamic Test Cases
But what should be done if we have to write a test case for a dynamically changing value? We can make use of common terms.
Example:
Let’s assume there is an online shopping site that is running a promotional campaign called ‘Happy New Year’ that provides its customers with a 20% off on their purchase. The dynamic value here is the campaign as it keeps changing in both name and value. So instead of writing a test case with the name of the one particular offer, it is better to use generic terms like ‘Promotional Campaign’
9. No Abbreviations
The Test cases should not be consist of any abbreviation (or) short forms. If in case the usage of an abbreviation is unavoidable, make sure to explain or define what it is in the test case. If not such open-ended information can lead to unnecessary mix-ups.
10. Optimal Distribution of Tests
A component level of verification should always happen only when you are writing functional test cases. You have to make sure that the same is not carried over when writing Integration and System Testing Test Cases. The Test Case document should cover all the types of the Test cases like Functional, Integration, System, and also Smoke Testing Test Cases.
How the test case helps the Testing team:
- Test case helps reduce the time and other resources required for testing.
- It helps to avoid test repetitions for the same feature of the application.
- It plays a major role in reducing the support maintenance cost of the software
- Even if we have to add a new member to the team during the course of the project, the new member will still be able to keep up with the team by reading the test cases.
- It helps to obtain maximum coverage of the application and fulfill the customer requirements
- The test cases help to ensure the quality of the software
- Test cases help us to think thoroughly and approach the process from as many angles as possible.
How to write effective test cases using the software?
The testing community has been writing test cases manually from the very beginning. But if you are looking for any software that reduces the time spent on writing test cases. You could take a look at the below test management systems,
Conclusion:
We hope you have enjoyed reading this blog. As a leading software testing service provider, we have always reaped the benefits of writing effective cases. But there is just no defined way to write test cases, as they are written in different formats depending on the project, the requirements, and the team involved. But we must always keep one point in our minds when we are thinking of how to write effective test cases, and that is to think from the point of view of the Client, Developer, End-User, and Tester. Then only we will be able to write quality test cases that will help us achieve 100% coverage.

by admin | May 18, 2021 | Software Testing, Blog |
Many companies run with Development and Operations teams working separately, which can cause problems in the long run. That is what DevOps plan can address: a collaborative approach that brings these two teams together. It streamlines and automates the software delivery lifecycle and aims to build better and more responsive software.
Contrary to popular belief, DevOps involves more than just a change in processes or tools. It is a cultural shift that removes barriers between teams to respond more efficiently to changing business requirements. As a result, it helps optimize workflow, deliver high-quality applications, and achieve other business goals.
Most organizations prefer continuous testing, but some are struggling to have a solid foundation for test automation. To address this, here are the methods to develop a DevOps testing strategy:
1. Scale test automation
Building a successful DevOps testing strategy requires scale test automation on the web and mobile. To scale web testing, use DIY, containerized computing, and cloud. For scaling mobile testing, opt for DIY, crowdsourcing, and cloud testing labs. Other options for scaling web and mobile testing are doing codeless and using open source frameworks.
2. Use supporting frameworks
Another method to create a DevOps testing strategy is to use supporting frameworks. To do this, provide assertion functions, a testing structure, mocks, spies, stubs, and a browser or browser-like environment with control of UI testing, scenario execution, and more.
Don’t forget to generate code coverage reports and display and watch test results. You also need to rely on a secure and up-to-date robust lab that can scale, is always available for all testing types, and can support all advanced automation capabilities.
3. Maintain a stable test automation suite
Since your product code is ever-changing, testing must also keep up with these changes. A stable test automation suite is crucial to ensure that automation continuously adds value. It has to be constantly maintained, audited, and refactored whenever required.
4. Use headless browsers
Headless browsers are developer-friendly tools that affect your testing strategy for web apps. Using them delivers a more stable build. Best of all, they are free, which can help you save money in the long run.
To use headless browsers, setting up Selenium Grid is not required. You just plug Google Puppeteer into your environment to do accessibility testing, performance auditing, and unit testing in JavaScript. This tactic helps scale test automation.
5. Use advanced reporting and analysis
Every testing activity requires a test report. Ensure to use a robust reporting platform and create detailed and actionable reports to help developers determine the root cause of issues and address them quickly.
6. Involve the full team in testing
When doing test automation at scale, involve the entire team. Assign business testers for exploratory and structured manual testing. On the other hand, software developers will create code-based test automation scripts and unit and build acceptance tests.
Conclusion
The secret to frequent, high-quality software delivery and becoming more competitive in the industry is DevOps testing. Since testing’s success highly relies on how you incorporate DevOps culture into your company, consider following the suggestions listed above. Also, seek automation testing services like ours as they play a major role in DevOps testing strategy.
If you need assistance from the best QA company, turn to us for help. At Codoid, we take pride in being an industry leader in QA. We offer analytics testing services, performance testing services, mobile application testing services, and more. Contact us to learn more about how we can help you!

by admin | Apr 27, 2021 | Software Testing, Blog |
Are you someone who wants to run their test cases on multiple browsers or machines? Then this BrowserStack Tutorial is a must-read for you as without it, you could be spending a lot of time, money, and effort to set up the multiple browsers or machines needed to perform the offline tests using real devices. As a premier Automation Testing Company in the market, we have opted for a cloud testing platform like BrowserStack that provides real cloud devices that consist of different platforms, browsers, and devices. BrowserStack is a cloud-based web and mobile testing platform using which is predominantly used by testers to perform Cross-browser testing of various web and native mobile applications across different platforms, different browsers, and different devices.
So it has been established that using the cloud is the optimal choice. But why BrowserStack in particular when there are other cloud testing platforms are available could be a question looming in your mind. You will find the answer to that question in detail in this BrowserStack Tutorial. We have mentioned all the wonders you could do using BrowserStack and explained how to do it as well.
Why BrowserStack?
BrowserStack can be used to avoid the complexity of switching between the operating systems, browsers, and its different versions. When it comes to mobile application testing, we can avoid the hassle of having to buy all the mobile devices that are available today to perform the testing. BrowserStack is very flexible and scalable, making it possible to test anywhere and anytime. We can use BrowserStack as a remote lab, and we can even use it as Real Desktop Browsers or Mobile Browsers. There is no setup required for using Browser Stack. We can use it directly on any independent machine by using the Browser Stack URL and its login credentials. Yes, it is that simple.
There are 4 main features of BrowserStack that we will be exploring in this blog and they are namely, Live, Automate, App Live, and App Automate. Let’s get the ball rolling by exploring the ‘Live’ feature.
BrowserStack Tutorial for Live/Manual Testing Feature
The Live option will help you perform manual testing in a list of real cloud device platforms like Android, iOS, Windows Phone, Windows, and Mac. Once you select any platform, it will show a list of browsers like Chrome, Mozilla, IE, UC Browser, and Safari with different versions. Once you have selected the browser of your choice, it will create a session and open a browser. You can simply enter the URL of the site and kick start your manual testing the same way you would do on a real device.
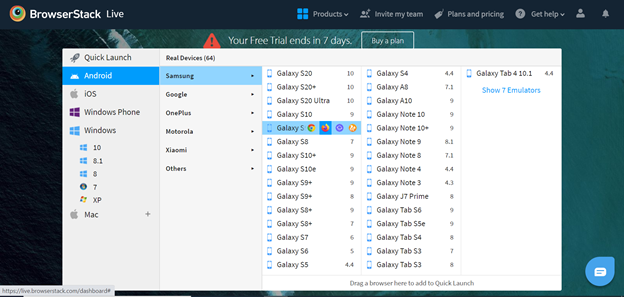
Key Features in Live:
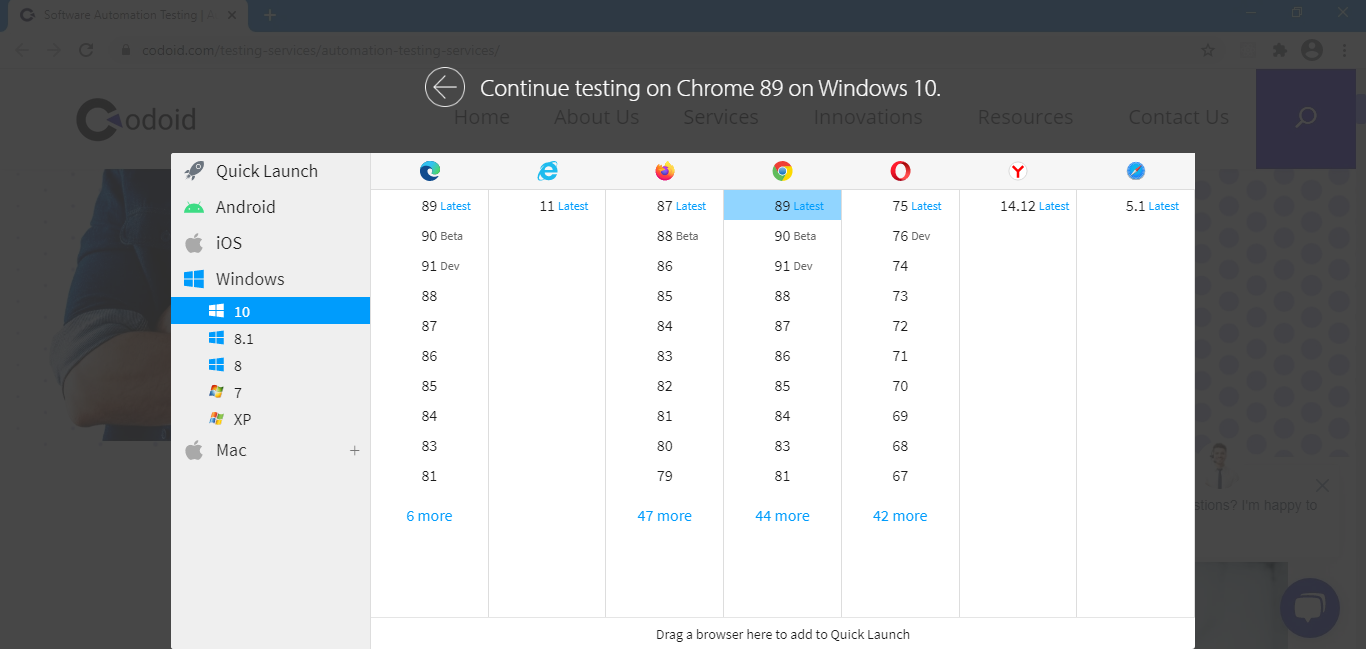
1. Switch Browser:
If you want to check the compatibility of the testing site in another browser, it is not necessary to close the current browser to switch to the other one. You can simply choose the ‘Switch Browser’ option, and it will display the device platform and browser list from which you can select the device and browser.
2. Resolution:
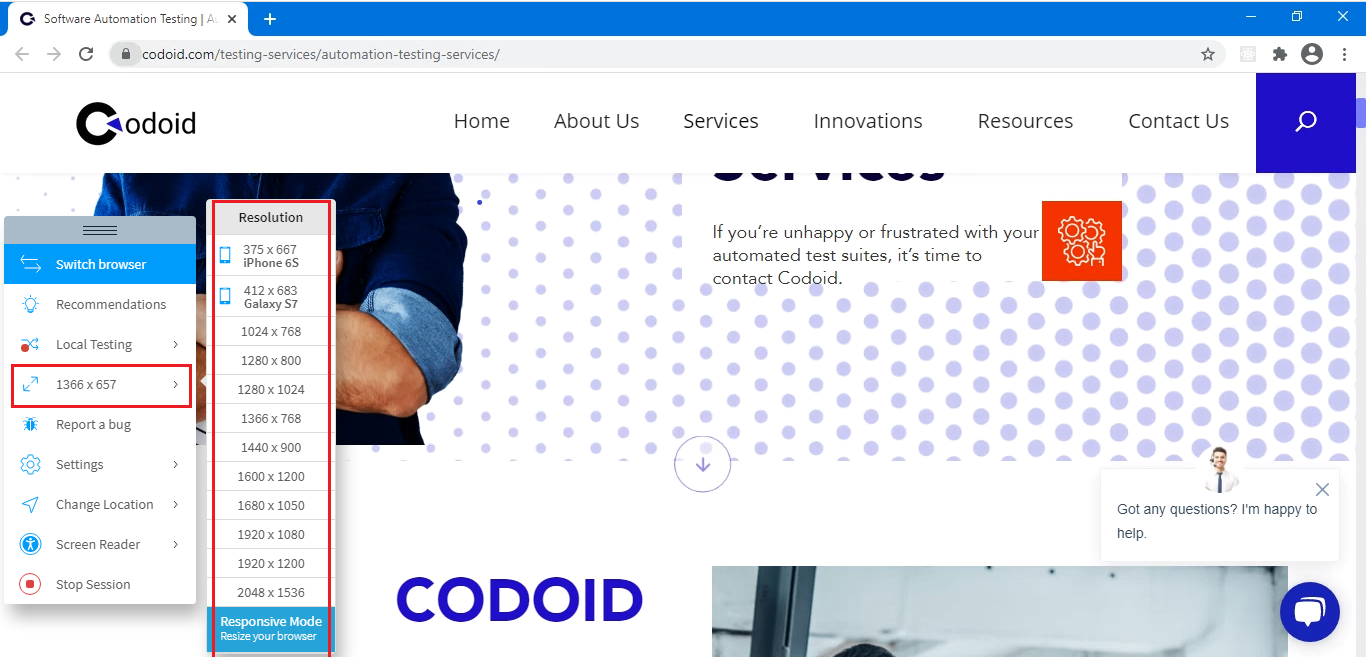
If you need to test your site in different screen resolutions, then you can make use of the ‘Resolution’ option. Once the ‘Resolution’ option is selected, a list of the available resolutions will appear, and you can select the required resolution to carry on with your testing as per your needs.
3. Reporting a Bug using BrowserStack:
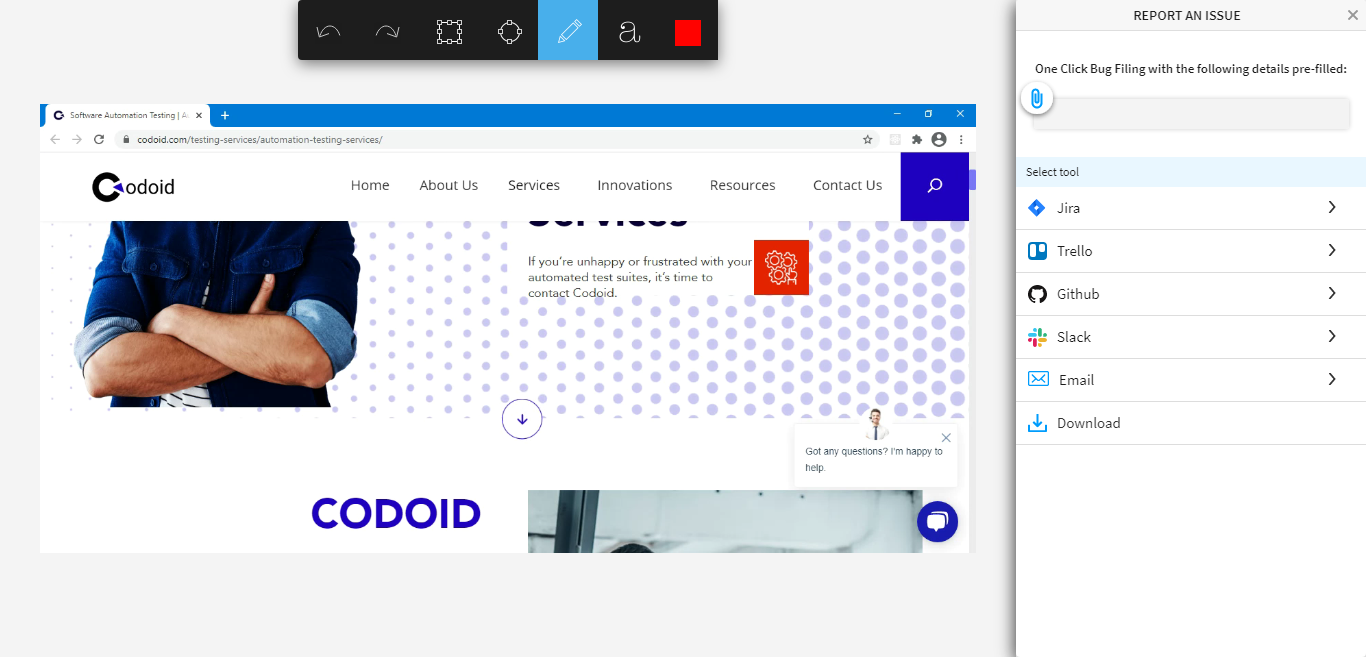
The primary objective of testing across so many platforms and devices is to identify and report the bugs that are present so that the end-user doesn’t face any difficulty. Once you have found a bug, you can report it by clicking on the Report a Bug option. After you click on this option, you will see an option box to highlight the issue on the page. You can highlight the issue by using different options like rectangle, circle, pencil, etc.
In addition to that, you can even select the mode to report a bug. There are so many tools like Jira, Trello, GitHub, and Slack through which you could report the bugs. You can even share it by email or download the issue page if needed.
4. Local Testing:
BrowserStack enables users to run tests on their internal development environments, on their localhost, or even behind a corporate firewall. This feature is called ‘Local Testing’.
Local Testing establishes a secure connection between the user’s machine and the BrowserStack cloud. Once Local Testing is set up, all the URLs will work straight out of the box, including the HTTPS URLs and also the ones behind a proxy or firewall.
BrowserStack local testing can be enabled for both ‘Live’ and ‘Automate’.
5. Local Testing Live
Download the BrowserStack local application from the local testing option and install it on your machine. Start the application, and you’ll see the BrowserStack local icon in the system tray area.
This enables Local Testing. Start a Live session and look for a green indicator on the Local Testing icon in the toolbar dock. You can launch the Live dashboard right from the app by just clicking on the BrowserStack Local app and navigating to Launch > Live.
To resolve all requests to local URLs via your machine, click on the Local Testing icon and check the ‘Resolve all URLs through my network’ option.
6. Local Testing Automate
We wanted to leave no stone unturned in this BrowserStack Tutorial and so we have listed the numerous Frameworks and languages that are supported in BrowserStack in the image below.

We can enable and disable local testing automatically using the code snippet in our test scripts. In this example, we have used Java language, and so it displays the Java BrowserStack local dependency. We need to add this dependency in pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>com.browserstack</groupId>
<artifactId>browserstack-local-java</artifactId>
<version>1.0.3</version>
</dependency>
This code snippet starts and stops BrowserStack local while running our test scripts.
import com.browserstack.local.Local;
# creates an instance of Local
Local bsLocal = new Local();
# replace <browserstack-accesskey> with your key. You can also set an environment variable - "BROWSERSTACK_ACCESS_KEY".
HashMap<String, String> bsLocalArgs = new HashMap<String, String>();
bsLocalArgs.put("key", "<browserstack-accesskey>");
# starts the Local instance with the required arguments
bsLocal.start(bsLocalArgs);
# check if BrowserStack local instance is running
System.out.println(bsLocal.isRunning());
#stop the Local instance
bsLocal.stop();
Steps involved in enabling BrowserStack local automate via command line:
1. Download the appropriate binary for your system:
- OS X (10.7 and above)
- Linux 32-bit
- Linux 64-bit
- Windows (XP and above)
2. Unzip the binary to a folder/directory on your machine.
3. Open your command-line interface and navigate to the folder containing the Local binary.
4. Run the binary using the following command:
BrowserStackLocal.exe --key sdfsdfsdfsgfggffsgdfg
After establishing the Local Testing connection, set the browserstack.local capability to true by adding the following snippet to your script:
caps.setCapability("browserstack.local", "true");
BrowserStack Tutorial for using the Automate Feature:
With the help of the ‘Automate’ feature we can use BrowserStack’s real cloud devices to automate our test scripts. The same languages and frameworks that were supported in Local Testing Automate will also be supported for Automate. So we can choose any language and framework from the list that we saw earlier. In this BrowserStack Tutorial, we will be using java to explain the BrowserStack Automate feature.
a) Selecting the OS and device/browser combination
You can easily select the OS and Device/Browser combination you’d like to test on, using the drop-down menus as shown below.
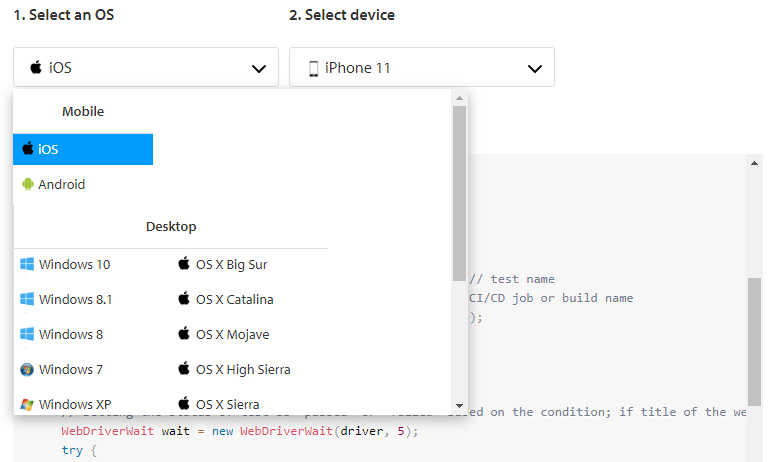
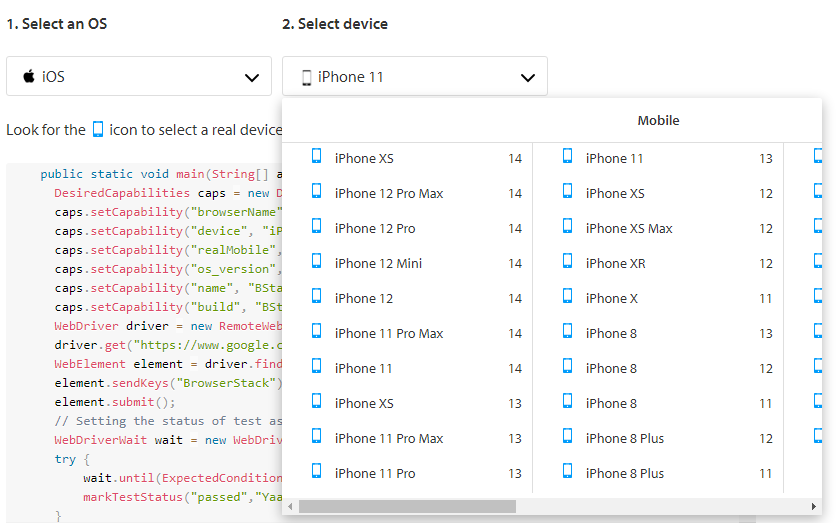
For the above-selected combination, the BrowserStack sample code will be automatically generated. Now we can set up the sample code in the framework to run our test scripts in BrowserStack. Write the variables for the user name and access key. Pass the user name and password in BrowserStack URL. Set the desired capabilities to see the logs. We are setting the desired capabilities to tell the web driver, to choose the mentioned operating system, browser, and browser version. Create the object for the web driver and get the URL to open the website.
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.Platform;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.DesiredCapabilities;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.RemoteWebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.JavascriptExecutor;
import java.net.URL;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.ExpectedConditions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.WebDriverWait;
public class JavaSample {
public static final String AUTOMATE_USERNAME = "<USERNAME>";
public static final String AUTOMATE_ACCESS_KEY = "<ACCESSKEY>";
public static final String URL = "https://" + AUTOMATE_USERNAME + ":" + AUTOMATE_ACCESS_KEY + "@hub-cloud.browserstack.com/wd/hub";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DesiredCapabilities caps = new DesiredCapabilities();
caps.setCapability("browserName", "iPhone");
caps.setCapability("device", "iPhone 11");
caps.setCapability("realMobile", "true");
caps.setCapability("os_version", "14.0");
caps.setCapability("name", "BStack-[Java] Sample Test"); // test name
caps.setCapability("build", "BStack Build Number 1"); // CI/CD job or build name
WebDriver driver = new RemoteWebDriver(new URL(URL), caps);
driver.get("https://www.google.com");
WebElement element = driver.findElement(By.name("q"));
element.sendKeys("BrowserStack");
element.submit();
// Setting the status of test as 'passed' or 'failed' based on the condition; if title of the web page contains 'BrowserStack'
WebDriverWait wait = new WebDriverWait(driver, 5);
try {
wait.until(ExpectedConditions.titleContains("BrowserStack"));
markTestStatus("passed","Yaay title contains 'BrowserStack'!",driver);
}
catch(Exception e) {
markTestStatus("failed","Naay title does not contain 'BrowserStack'!",driver);
}
System.out.println(driver.getTitle());
driver.quit();
}
// This method accepts the status, reason and WebDriver instance and marks the test on BrowserStack
public static void markTestStatus(String status, String reason, WebDriver driver) {
JavascriptExecutor jse = (JavascriptExecutor)driver;
jse.executeScript("browserstack_executor: {\"action\": \"setSessionStatus\", \"arguments\": {\"status\": \""+status+"\", \"reason\": \""+reason+"\"}}");
}
}
b) Execution process:
- Once the script starts its execution, it will trigger the BrowserStack to run the script.
- Every script execution will be maintained as a session with a unique session ID.
- Under ‘All projects’, the scripts that are running and the ones that have been executed will be displayed.
- Once the Script has started execution, all the logs will start getting recorded.
- We can see a live video about what’s happening during the execution in BrowserStack.
- Once the execution has been completed successfully, the Status will be changed from ‘Running’ to ‘Completed’. It will be denoted using a Green color dot.
- If the execution has failed because of any error, then the Status will be ‘Errors’.
- If the session had timed out, then the Status will be mentioned as “Timeout”, and the status will be denoted using a Yellow color dot.
Observe the automate tab. We can see the test name on the left side of the tab, where BrowserStack enables us to debug the code with the help of Text Logs, Visual Logs, and Video of the session
- Text Logs: They provide all the Information with the details of actions and timing.
- Visual Logs: They provide the details with screenshots.
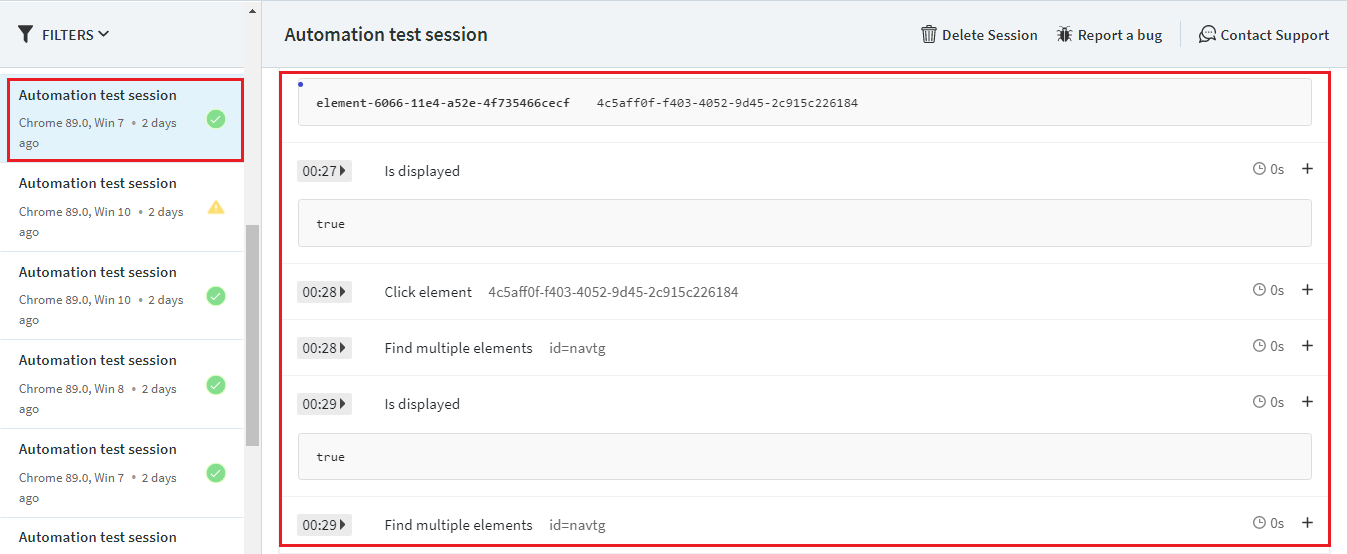
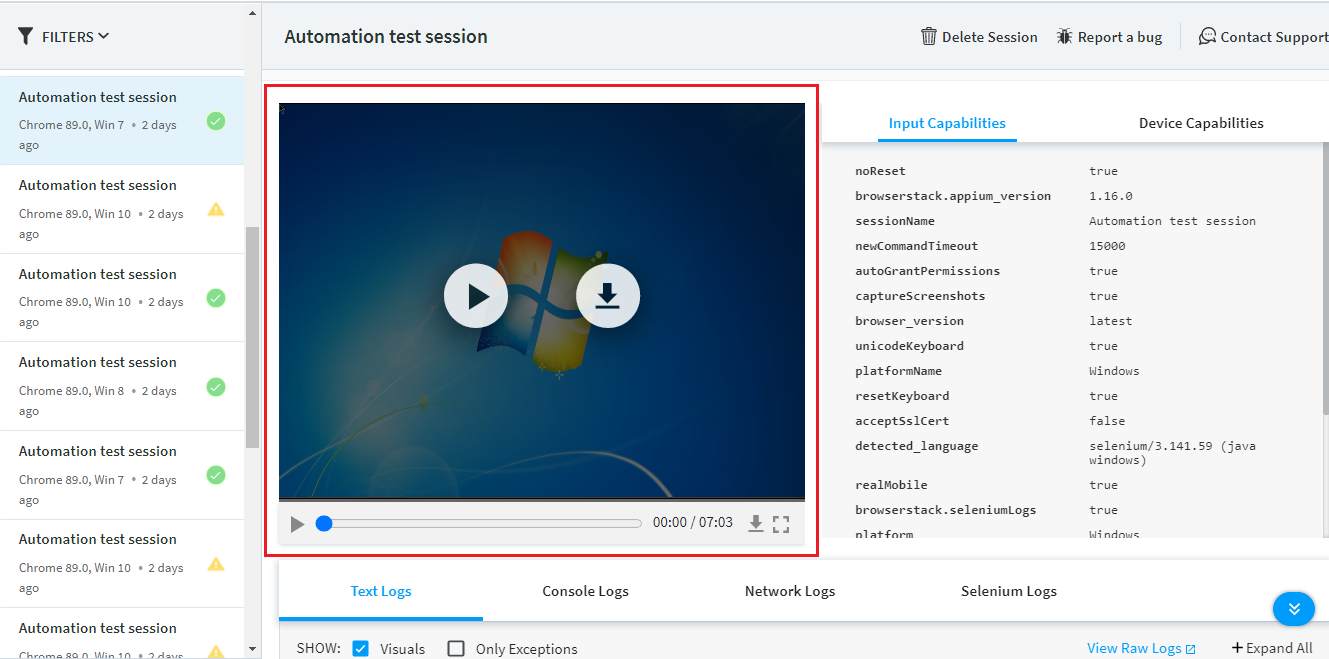
- Video: It records all the actions done through the automated script. It helps to identify the exact root cause of any error during execution.
It also has the option to play or download the video, using which we can watch the video in the dashboard or download it and use it to debug the error.
c) Run Tests in Parallel
On BrowserStack, we can run multiple Selenium WebDriver tests at the same time across various browser, device, and OS combinations. This is called Parallel Testing. Parallel Testing gives us the same benefits as running a multi-threaded application. We wanted to make sure that our BrowserStack Tutorial does more than just introduce you to the tool. We wanted everyone reading this blog to make use of BrowserStack’s full potential.
With Parallel Testing, we can run the same test on different browser/device combinations i.e. cross-browser testing, or run different tests on the same or different browser/device combinations as explained above. Parallel Testing will help us drastically reduce the run time of our test suite, resulting in faster build times and faster releases.
We can start testing in parallel using any of the popular test frameworks, and some of the popular frameworks are mentioned below:
- TestNG
- Gauge
- JBehave
- JUnit
- Selenide
- Serenity
Here, we are going to use the TestNG framework to explain Parallel Testing in detail.
To run the tests on multiple browsers in parallel with TestNG on BrowserStack Automate, follow the below steps:
1. Clone the testng-browserstack repo on GitHub (if not already done):
2. git clone https://github.com/browserstack/testng-browserstack.git
3. cd testng-browserstack
4. Install the dependencies using the following command:
5. mvn compile
6. Update parallel.conf.json files within the testng-browserstack/src/test/resources/conf directory with your BrowserStack credentials as shown below:
parallel.conf.json
{
"server": "hub-cloud.browserstack.com",
"user": "USERNAME",
"key": "ACCESSKEY",
"capabilities": {
"build": "testng-browserstack",
"name": "Bstack-[TestNG] Parallel Test",
"browserstack.debug": true
},
"environments": {
"chrome": {
"browser": "chrome"
},
"firefox": {
"browser": "firefox"
},
"safari": {
"os": "OS X",
"browser": "safari"
},
"ie": {
"browser": "internet explorer"
}
}
}
7. You can now run your tests in parallel on BrowserStack using the following command
d) How to Run tests in parallel without a framework
We have also demonstrated how to run tests in parallel without a framework using a sample script that shows a multi-threaded Java program in this BrowserStack Tutorial. Before we head on to the script, let’s take a look at its salient points.
- The same script is run across 3 different browser/device combinations viz. iPhone 12 Pro, Samsung Galaxy S20, and Safari on Big Sur.
- The capabilities are being populated in a HashTable, and that is being passed on to the test function.
- The test function has been written as a separate method, and it takes care of the starting of the test for each of the browsers after iterating on the HashTable that is passed on to it.
- Multi-threading has been implemented by defining multiple classes, all of which implement the Runnable Java class.
- The main class contains the main() method, and all the 3 threads are invoked from the main class
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.JavascriptExecutor;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.DesiredCapabilities;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.RemoteWebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.ExpectedConditions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.WebDriverWait;
class TestClass1 implements Runnable {
public void run() {
Hashtable<String, String> capsHashtable = new Hashtable<String, String>();
capsHashtable.put("device", "iPhone 12 Pro");
capsHashtable.put("real_mobile", "true");
capsHashtable.put("os_version", "14");
capsHashtable.put("build", "BStack-[Java] Sample Build");
capsHashtable.put("name", "Thread 1");
mainTestClass r1 = new mainTestClass();
r1.executeTest(capsHashtable);
}
}
class TestClass2 implements Runnable {
public void run() {
Hashtable<String, String> capsHashtable = new Hashtable<String, String>();
capsHashtable.put("device", "Samsung Galaxy S20");
capsHashtable.put("real_mobile", "true");
capsHashtable.put("os_version", "11.0");
capsHashtable.put("build", "BStack-[Java] Sample Build");
capsHashtable.put("name", "Thread 2");
mainTestClass r1 = new mainTestClass();
r1.executeTest(capsHashtable);
}
}
class TestClass3 implements Runnable {
public void run() {
Hashtable<String, String> capsHashtable = new Hashtable<String, String>();
capsHashtable.put("browser", "safari");
capsHashtable.put("browser_version", "14");
capsHashtable.put("os", "OS X");
capsHashtable.put("os_version", "Big Sur");
capsHashtable.put("build", "BStack-[Java] Sample Build");
capsHashtable.put("name", "Thread 3");
mainTestClass r1 = new mainTestClass();
r1.executeTest(capsHashtable);
}
}
public class mainTestClass {
public static final String USERNAME = "USERNAME";
public static final String AUTOMATE_KEY = "ACCESSKEY";
public static final String URL = "https://" + USERNAME + ":" + AUTOMATE_KEY + "@hub-cloud.browserstack.com/wd/hub";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Thread object1 = new Thread(new TestClass1());
object1.start();
Thread object2 = new Thread(new TestClass2());
object2.start();
Thread object3 = new Thread(new TestClass3());
object3.start();
}
public void executeTest(Hashtable<String, String> capsHashtable) {
String key;
DesiredCapabilities caps = new DesiredCapabilities();
// Iterate over the hashtable and set the capabilities
Set<String> keys = capsHashtable.keySet();
Iterator<String> itr = keys.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
key = itr.next();
caps.setCapability(key, capsHashtable.get(key));
}
WebDriver driver;
try {
driver = new RemoteWebDriver(new URL(URL), caps);
JavascriptExecutor jse = (JavascriptExecutor)driver;
// Searching for 'BrowserStack' on google.com
driver.get("https://www.google.com");
WebElement element = driver.findElement(By.name("q"));
element.sendKeys("BrowserStack");
element.submit();
// Setting the status of test as 'passed' or 'failed' based on the condition; if title of the web page contains 'BrowserStack'
WebDriverWait wait = new WebDriverWait(driver, 5);
try {
wait.until(ExpectedConditions.titleContains("BrowserStack"));
jse.executeScript("browserstack_executor: {\"action\": \"setSessionStatus\", \"arguments\": {\"status\": \"passed\", \"reason\": \"Title matched!\"}}");
}
catch(Exception e) {
jse.executeScript("browserstack_executor: {\"action\": \"setSessionStatus\", \"arguments\": {\"status\":\"failed\", \"reason\": \"Title not matched\"}}");
}
System.out.println(driver.getTitle());
driver.quit();
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
BrowserStack Tutorial for using the APP LIVE Feature
So the last feature that we will be seeing in this BrowserStack Tutorial is the App Live function that helps us to do native app testing in a list of real cloud devices. To use the native app in the BrowserStack devices, we can use the Upload or URL option.
a) Uploading/Testing the App
Click on the upload app button, and a system dialog window will open.
Go to the app folder, choose the App which you want to test, and the app will be loaded successfully. We will be able to see the app under the uploaded apps section.
This is not the only way to get this done, and you can upload the app in other ways as well. For example, you can click on ‘View all sources’ and select any type of source through which you are going to upload the app.
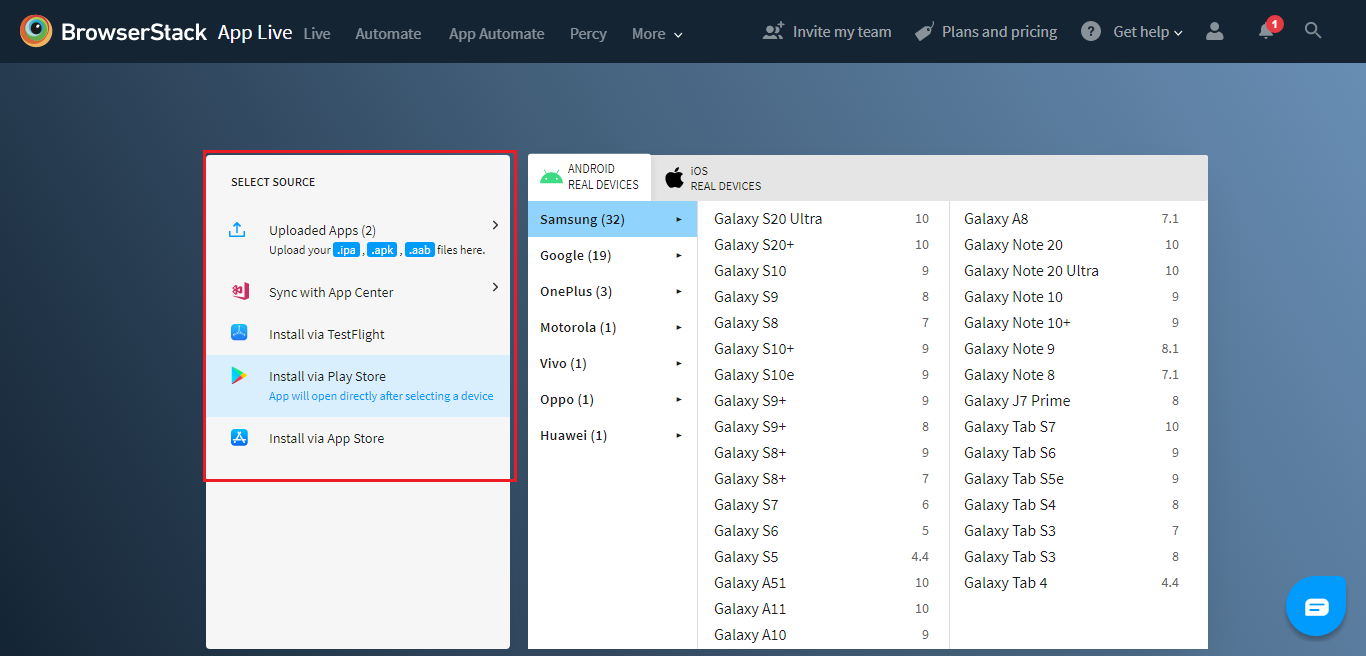
After Uploading the App, select any device from the list of real Android or iOS devices. The device of your choice will be selected, and the app will be installed in it. Now you are all set to perform testing like how you would do using a real device.
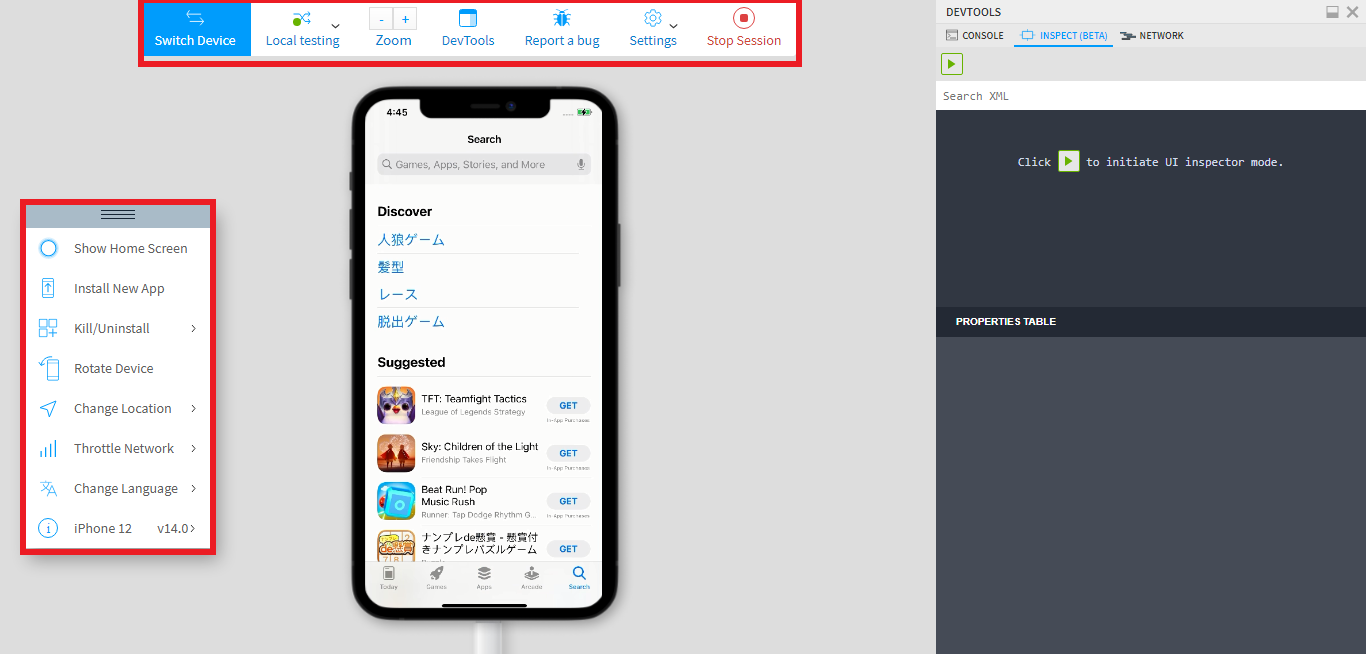
b) Key Functions of App Live
1) Switch Device Function
Just like how you can shift from one browser to another, you can migrate from one device to another to perform your testing as well. Click on the ‘Switch device’ option, if you wish to switch the device at any given time. Once you are done with testing in a particular device, click on the Stop session option and it will navigate you to the dashboard page. Click on settings to choose the session time out and monitor size.
We can report the bug by clicking on the Report a bug option, just like how we discussed in the above Live Testing Section. Now let’s take a look at the web tool kit menu, which has some more options to operate the device feasibly and test the application.
Click on the ‘Rotate Device’ option to rotate the device horizontally or vertically. You can click on the ‘Install App’ option to install the new application. If you want to just close the app and not the device, then click on the ‘Kill app’ option. Click on ‘Change language’ to change the language for testing. If you are looking to check the complete device information, click on the ‘Device info’ icon.
2) Deleting the App
Click on the delete icon, and you will see the checkbox at each app. Select the checkbox, and click on the delete link and it is also important to keep in mind that it will delete the uploaded app automatically after the completion of 60 days from the date of upload.
BrowserStack Tutorial for using APP AUTOMATE Feature
BrowserStack App Automate enables you to test native and hybrid mobile applications using a testing framework.
Here, we are going to use Appium to explain about App Automate. It’s easy to run your Appium tests written in Java on real Android and iOS devices on BrowserStack. This guide will help you get started with your first test.
1. Setup
- You will need a BrowserStack username and access key
2. Upload your app
Upload your Android app (.apk or .aab file) or iOS app (.ipa file) to BrowserStack servers using our REST API. Here is an example cURL request to upload the app :
curl -u "USERNAME:ACESSKEY" \
-X POST "https://api-cloud.browserstack.com/app-automate/upload" \
-F file=@/path/to/app/file/Application-debug.apk
A sample response for the above request is shown below:
{
"app_url":"bs://j3c874f21852ba57957a3fdc33f47514288c4ba4"
}
3. Setup and run your test
- Specify the application under test using the app capability. Use the app_url value returned at the time of app upload (Step 2) to set this capability.
- Specify the real Android or iOS device you want to test on, using the device capability.
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.List;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import io.appium.java_client.MobileBy;
import io.appium.java_client.android.AndroidDriver;
import io.appium.java_client.android.AndroidElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.ExpectedConditions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.WebDriverWait;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.DesiredCapabilities;
public class BrowserStackAndroid {
public static String userName = "USERNAME";
public static String accessKey = "ACCESSKEY";
public static void main(String args[]) throws MalformedURLException, InterruptedException {
DesiredCapabilities caps = new DesiredCapabilities();
caps.setCapability("device", "Samsung Galaxy S8 Plus");
caps.setCapability("os_version", "7.0");
caps.setCapability("project", "My First Project");
caps.setCapability("build", "My First Build");
caps.setCapability("name", "Bstack-[Java] Sample Test");
caps.setCapability("app", "<app_url>");
AndroidDriver<AndroidElement> driver = new AndroidDriver<AndroidElement>(new URL("https://"+userName+":"+accessKey+"@hub-cloud.browserstack.com/wd/hub"), caps);
AndroidElement searchElement = (AndroidElement) new WebDriverWait(driver, 30).until(
ExpectedConditions.elementToBeClickable(MobileBy.AccessibilityId("Search Wikipedia")));
searchElement.click();
AndroidElement insertTextElement = (AndroidElement) new WebDriverWait(driver, 30).until(
ExpectedConditions.elementToBeClickable(MobileBy.id("org.wikipedia.alpha:id/search_src_text")));
insertTextElement.sendKeys("BrowserStack");
Thread.sleep(5000);
List<AndroidElement> allProductsName = driver.findElementsByClassName("android.widget.TextView");
assert(allProductsName.size() > 0);
// The driver.quit statement is required, otherwise the test continues to execute, leading to a timeout.
driver.quit();
}
}
4. Viewing test results
You can access the results of your test sessions on the App Automate dashboard as well as using our REST API. You can drill down into the details of a specific test session to view its execution details and debugging information such as video recording, network logs, and device logs.
Conclusion
We hope this BrowserStack Tutorial has been a good read for you, and that it was worth your time. Stating that BrowserStack is a highly resourceful tool is an understatement, as it has been instrumental in helping us provide the best Automation Testing Services. BrowserStack is one tool you should add to your arsenal as the benefits it brings to the table are of high value. Though there are alternatives available for this very same purpose, as a leading QA company, we at Codoid have always used BrowserStack for all our projects and that is why we have written this BrowserStack Tutorial as well. They are the pioneers in their domain, making them the best choice if you don’t want to take a chance with your testing just like us.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the BrowserStack tool?
BrowserStack is a cloud-based testing tool where developers and testers can test their websites and mobile applications across browsers, operating systems, and real-time mobile devices.
-
Is BrowserStack a testing tool?
Yes, BrowserStack is a testing platform that enables easy testing of mobile applications and websites across Browsers and devices.
-
Is BrowserStack free to use?
Though it is not free to use, BrowserStack does have a free trial account that includes 30 minutes of live testing, 100 minutes of automated testing, 100 screenshots plus responsive, 30 minutes of app live testing, and 100 minutes of app automated testing.
-
Why is BrowserStack used?
It is challenging to test an application in real-time across a variety of browsers and mobile combinations, operating systems, and version ranges. By using BrowserStack, you may eliminate the hassle of switching between operating systems, browsers, and versions. It also allows users to test the latest version of mobile/tablet devices without purchasing it.
-
Who uses BrowserStack?
Both developers and testers use BrowserStack to do cross-browser testing for website applications and various mobile applications.