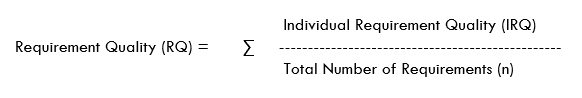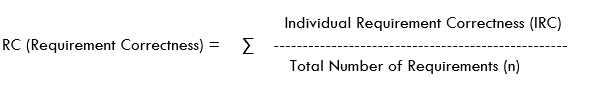by admin | Mar 24, 2020 | Software Testing, Fixed, Blog |
In this blog it is assumed that we know the importance of testing thus, for now, it’s time to understand what are all the different software testing types that are available and when to use what. A proper test plan must have documentation and the timelines of each type of testing alongside the description. The three major classifications based on the mode of execution are:
White/clear box testing
White box testing talks about the testing conducted at a technical and very low level. This testing is to validate the structure, design, and implementation of the system. Writing the unit tests, integration tests also designing scripts at the system level is part of this classification.
This type of testing is done by understanding the source code. The objective of this testing is to validate all part of the source code like decision branch, loop and statement are verified.
Unit testing which is done by developer is a part of White box testing.
Black box testing
This is solely the functional validation done by the manual functional testing. These tests are designed by understanding the requirement then execute them manually then verify the results. The test coverage techniques used in this process are to ensure the test coverage is high with not taking overhead of documenting too many repetitive tests.
The testers who do this type of testing will not conduct code review / assess the code coverage/statements etc. They don’t have any understanding of what code is written. But they are executed and functionally validated to ensure that Application does what is expected out of it.
Grey box testing
This is a blended mix of both white box as well as the black box testing. In this, we try to cover both the strategies. A tester who does this Grey box testing has partial knowledge of code. Predominantly they execute a function written with different functions input and assess the quality of function.
The black box testing can further be divided into three major types
Functional testing
In this testing type, our focus is to validate the functionality by understanding the requirement. This is a simulation of a user test. The intention of this test is to determine whether the product built-in right fashion.
This functional testing is further classified into a few types they are
Smoke testing
This is a build verification test, once the development gives build its essential to execute the most common scenarios that are needed to confirm the given revision of build is a good candidate for further testing.
Sanity testing
Sanity test is a prioritized test, if at all the timelines given and the amount of testing to be done are unparalleled then we pick the edge cases and the most priority test cases to deem the sanity of a build. Ideally speaking this is a subset of regression testing.
Adhoc testing
This is a functional test without any concrete plan, based on the experience we have developed on the application front we execute the scenarios.
Non-functional testing
In this testing alongside validating the functionality we mainly focus on testing the performance of an application by subjecting that to a specific load as determined. It’s not just limited to the performance we validate so many other characteristics of applications. The types of Non-Functional testing done are
Performance testing
It helps to assess the stability of software under a certain workload
Volume testing
It helps to test the software with a huge volume of data and assess the response of the Software to huge volume.
Load testing
When a huge load of data is given to a program, how it handles the load. Huge Spike is given in a short span of time and understands how it handles.
Security testing
When some vulnerability is injected into the system under test, how it handles such condition. It is to validate if it is able to recover from such vulnerability. It is predominantly used to test the application whether it is free from any threat or risk.
Localization testing
When we declare an application has multi-lingual support, we need to perform Localization testing to ensure whether the application is able to display pages/content in the current local language. Here all the links and contents are validated to ensure that content is designed to specific to that local language.
Compatibility testing
When we publish software, we declare on what all different hardware, Operating system, network, browsers, devices, etc it will support. This will be a part of the release notes. We need to ensure sunder such conditions this software supports without any issue. Testing done to validate on different hardware, Operating system, devices, etc are called compatibility testing.
Endurance testing / Soak Testing
A specific load is given to the Application for a prolonged period of time to assess system performance/behavior.
Regression testing
Regression testing is conducted to ensure, the code fixes have not caused any new breakage of the application in some other place. In this test instead of running the failed case alone, we run all the test cases that were passed before to confirm the presence or absence of defects. Regression testing helps us to find the stability of the applications as we pass by the timelines.
This test should be run with an agreed frequency to ensure that the addition of new functionality, integration of any other new component and any bug fixes have not affected any other existing system functionalities.
Levels of software testing
In the process of the software development life cycle, we have corresponding testing phase involved. The ideology is to conduct testing at different levels to ensure the functionality and we don’t deviate from the process. When we discuss the levels of testing, we don’t specifically limit the scope to the testing phase, rather we discuss the kind of testing done at every phase of SDLC and here it could be the fact that many teams intervention might be observed. Following are the different levels of testing that we conduct in SDLC process.
Unit testing
This is the first low-level test that’s conducted by the developer. In this testing, we test only the particular component for its working condition also the developer has to ensure the proper statement, decision and path coverage was done with reference to the requirement built. If unit tests are failed developer has to look into the problem and fix them immediately as no further testing can be unless this is completed successfully.
Integration testing
This is the next phase of unit testing, in this level of testing we focus on the integration that is established between the modules and check whether the services give proper requests and responses. This is done by both testing team development team. Integration tests, in general, are kind of API tests as the whole system not ready yet. We have two more subcategories of these tests based on the unavailability of a specific master or slave module.
Top down approach
This approach is adopted when any slave or listener component in the application is not available for testing but we need to conduct testing to meet the deadline. In this case whatever the module that’s not available yet would get replaced by a stub. The stub is a simulating system, which acts as the regular component that we should have got ideally in place.
Bottom down approach
It’s the reciprocal process of the above-mentioned one. If at all the master component or service is not ready to test and we have to test the other components then the master component would get replaced by a dummy driver system. Although the driver is not a real system we will give the power to drive the other components as per the need.
System testing
This testing is done once the whole system is made available, the focus of the test is to validate within the system. All possible scenarios and customer use cases must be thoroughly tested. This is the most prioritized official test as we learn a lot of bugs and also this is the level where we see the system turns out to be a reliable one.
System integration testing
This level of testing is conducted when the complete end to end connectivity of the application with all possible external downstream/ upstream systems was connected. This is the real time test where the test replicates the usage of the customer flow once the application gets launched.
User acceptance testing
Use acceptance test is conducted by the customer or product owner. This is the final verification test that’s performed before the application goes live. This test builds confidence in the business as to whether or not the reliability criteria that’s set was met and application is good to be launched. This is again classified into two sorts based on the environment where it’s conducted. The rationale behind doing this test at two sites is to isolate any external parameters that are actually intervening in the results we observe. This will rather help to pin down certain problems and root cause the problems.
Alpha testing
This test is done at the actual test team sites to understand the results. All observations are made a note to compare against with other types of the UAT testing.
Beta testing
This test is done at the customer sight, after the execution the results are compared to understand and conclude
1. If the same problems have occurred.
2. The problems observed at one’s sight are due to the improper or slow infrastructure and not of the application.
Conclusion:
The above listed are types of testing that are used predominantly used in most of the Organization. There are some special testing conducted for specific needs like to test Gaming Application, different techniques, and testing types will be used. But this blog extensively covers the testing type which is for testing the most common type of Applications which covers 80% of the Organization requirement. Thanks for reading this blog.

by admin | Apr 10, 2020 | Software Testing, Fixed, Blog |
Functional Testing is a type of software testing which is performed to validate the basic functionality of the Software Application against functional requirements. Software is developed based on business requirement and Functional Testing helps and assures that Software developed is as per the business requirements.
Functional testing comes under black-box testing as functional tester does not bother about how the code is written or conducts code review to validate the code, instead, he executes the software and provide inputs based on business and functional requirement and validates against his expected result to certify the Application.
Functional Testing can be carried out for any software irrespective of Web Application, desktop application, web service or a stored procedure. Be it any type of Technology, the objective is to validate the functionality of the system under test is as per the business / functional requirement.
Why Functional Testing:
Why Functional Testing leads to a question of why testing?
Testing is done to ensure that the application works as expected. When an application is delivered without testing, then there is no assurance/guarantee that the application will function as expected. More than 60% of testing efforts go to Functional Testing effort. Remaining efforts would be a part of Non-Functional Testing like Performance, usability, security, etc.
Without Functional Testing we cannot conclude software does the operation as expected and hence Functional Testing is as important as software being developed by the development team.
Aspects of Functional Testing
Below are the key aspects of Functional Testing:
1. Testing based on Functional Requirement
2. Testing based on Business Process
Testing based on Functional Requirement
This Testing is based on the nature of the application functionality. Whenever a build is provided based on User stories / Functional Specification / Business Requirement document, we carry out various types of testing to prove it function as expected.
Before delivering the Application to Functional Testing team, developers do testing and it is called Unit Testing. Once developers complete the Unit Testing Application build is delivered to the testing team for Functional Testing.
Before we conduct a thorough Functional Testing we perform Smoke and Sanity Testing to ensure that build is stable and can be carried out for further testing. When a build is failed in smoke and sanity, that means the build has a serious flaw and developer has to further work on it.
Once Smoke and Sanity Testing is passed, Integration, System Testing and System Integration Testing is performed to certify the Application under test.
Testing based on the Business process:
When we say Business process from Functional Testing point of view, it is the End to End flow of business-critical functionality. Example) if an Application deals with Payment processing, then the business process would be testing the Payment setup until payment initiation until successful / exception criteria.
We could define a critical end to end business process considering positive and negative flow and testing these critical business areas. From this aspect, we could also perform risk-based testing based on the testing timeline and the number of business process areas.
Entry and Exit criteria of Functional Testing
Below are the key Entry criteria for Functional Testing:
Requirements must be fully frozen with clearly defined expected outcome (Requirements could come in the form of Business Requirement / Functional Specification document or User Stories)
Development should be completed
Build must be unit tested and completely signed off by the development team
Test Strategy and Test plan should be completed and should be signed off by stakeholders
Test data should be available for execution
Below are the key Exit criteria for Functional Testing:
Test cases should be prepared with complete coverage on requirements
Test cases should be reviewed and signed off by the Business team
Test cases must be executed and Severeity1 and 2 defects should be closed by Testing team
Functional Testing Strategies:
Before performing functional testing, below pointers/strategy would help to manage the test effectively:
Validate if the requirements are clear
1. To test effectively requirements should be clear with the clearly defined input and output criteria’s
2. If the requirements are not clear, enter into series of discussion with Business team, development team and project stakeholders beforehand and take steps to crystallize the requirement.
3. Even after series of discussion, if requirements are not clear come up with the In-scope and out of scope and keep requirements whichever are not clear in out of scope.
4. Raise a project-level risk and get into agreement with project stakeholders.
Assess and come up with proper Functional Plan
1. Based on the requirement clarity and project scope come up with Functional Test plan covering the scope of testing, type of testing to be conducted, Test schedule, resource requirement, risk management procedure, etc
2. Once the Functional Test plan is prepared, get it signed off from project stakeholders
Identify the Test Schedule and Execution Timeline
1. Based on the project plan, identify time allotted for Testing phase
2. Calculate the execution timeline
3. Come up with Risk-based Testing approach for better functional coverage
4. If the timeline is less, execute P1, P2 Test cases and get into agreement with Stakeholders
Resource fulfillment and Automation assessment
1. Based on the project schedule and Test schedule, assess and do feasibility of Automation and validate the benefits expected out of automation
2. Identify the right resource requirement if automation can be implemented
Proper Defect Management
1. Assign proper defect Manager / Coordinator for conducting defect triage calls
2. Escalate for Sev1 and Sev2 priority fixing with development counterparts
3. Extend timelines or come up with alternate plans based on Environment/delay in defect fixes
4. Assign to testers based on defect fix by the development team
5. Review of defect retesting and closure
Proper Test Completion Report
1. When Functional Testing is completed, Test Completion report has to be prepared
2. While preparing Completion report, ensure in-scope and out of scope is declared properly
3. Update inference from Functional Testing and any defects are open/deferred update it properly in the closure report
4. Update what went well, what not went well with a reason along with improvement areas as well to be updated
Key Metrics that we report on Functional Testing
Functional Testing metrics can be classified based on the Test Phases:
Test Design Metrics:
Total Test Coverage
Automation Coverage
Test Design productivity (Manual and Automation)
Test Execution Metrics:
Test Execution productivity (Manual and Automation)
Test Execution Coverage
Error Discovery Rate
Test cases Passed / Failed / Blocked / Deferred
Defect Metrics:
Defect Leakage
Defect Removal Efficiency
Defect Density
Defect Fix Rate
Key Business Outcome
Present the Functional Testing Outcome post every release during retrospection/release closure discussion.
Invite key stakeholders and provide an update to key parties on overall Functional Testing outcome and benefits through Functional Testing activity. Since the QA team is much closer to the Business team in-terms of business requirements understanding, present how much of defects have been raised with criticality and how many defects converted to release / functional enhancement will be the key thing to be discussed. This will be an interesting story to Business team.

by admin | Apr 5, 2020 | Software Testing, Fixed, Blog |
Welcome to Codoid blogs once again, in this blog we are going to see about software testing metrics. Below are the topics we will cover in this blog.
What is a Metric
Why Metric is required
Types of Metrics in Testing
Testing Metrics in Detail
What is a Metric
As per standard definition, A Metric is a quantifiable measure to track the progress of certain areas which we want to constantly monitor and report.
Metric is used to predict something which we wanted to measure and we can set a benchmark for it so that we can compare it with a certain interval of time. Example) Speed which we travel can be a metric and we can keep a benchmark as 48 kmph. We can constantly measure every day or every week and we can compare against our benchmark.
Why Metric is required:
1. Metric will help us to give us a prediction on how are we performing.
2. It gives us direction on how we perform release after release to ensure we are constantly improving. If there is a decline in performance, we can take corrective steps to improve that particular factor
3. It helps us to uncover potential risks in our project.
(Example, We are targeting to go live on a date assuming 10 days of Test Execution with 20 TC / Day productivity, Let’s assume for consecutive 5 days productivity is only 10 TC / Day, this could eventually delay our execution by 5 more days and will delay the release. It is a potential risk to the project. On tracking this execution productivity on a day to day basis during execution timeline, will tap the project in our control, we could take action on 2nd day itself and keep the project on track.)
4. Improves the Test Coverage and Automation coverage.
5. It helps in continuous process improvement, once we become mature in a way of tracking, we could add a few more metrics and helps in coming up with continuous improvement in our project delivery.
6. It helps to plan for release in a better way. As with each and every release, if we track metrics, we could use predictions and with the lessons learned from previous releases, we can come up with better planning.
7. It overall improves the Cost, Quality and Time in delivering the project.
Types of Metrics in Testing
Based on the STLC phases, we can define metrics for each phase of Testing. Let us see them in detail in this section.
STLC Phases are:
Requirement Analysis
Test Planning
Test Design
Test Execution
Test Closure
And for each of these phases we have multiple metrics to track.
Testing Metrics in Detail
Requirement Analysis
Requirement Quality:
Requirement Quality defines the correctness/accuracy of the requirement.
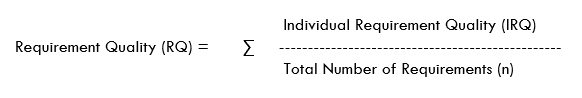
IRQ – is the quality of Individual requirements which signifies whether the requirement is valid (value 1) or invalid (value 0). It can be measured in percentage as well.
Correctness of Requirement:
This metrics helps us to determine if the requirement is correct/valid/is not a duplicate.
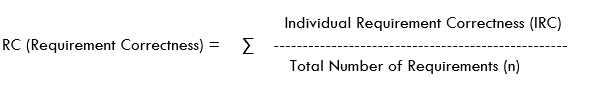
IRC will be 1, if it is a valid requirement, else it will be 0
Requirement Creep:
This metric helps to understand how much percentage of requirements added post requirement gathering phase.

Test Planning
Metrics in Test Planning is used to arrive at how effective testing is carried out. We track and tap the control of the project by taking various measurements during Test Design and Test Execution activities. Below are the few measurement criteria that help in the effective Test Planning
Resource Requirement Vs Fulfilment
Effort burnt VS Progress
Cost Spent Vs Work Done
Cost Spent Vs Requirement Coverage
Overhead Cost
Team productivity
Test Design
Test design is the most important phase in Software Testing. There are a lot of metrics that can be generated in Test Design phase and will be useful to management for tracking purpose.
Some of the Metrics with formula are given below:
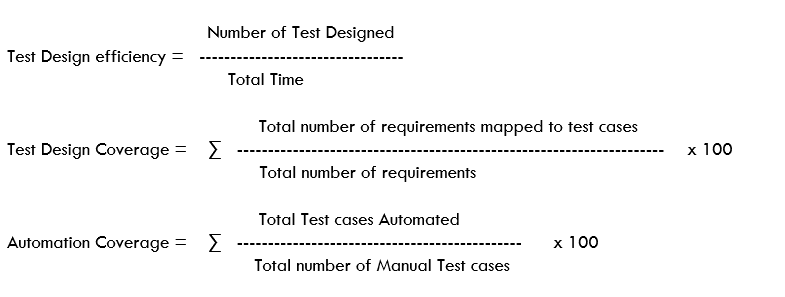
Test Execution
Below are few standard metrics used in Test Execution phase:
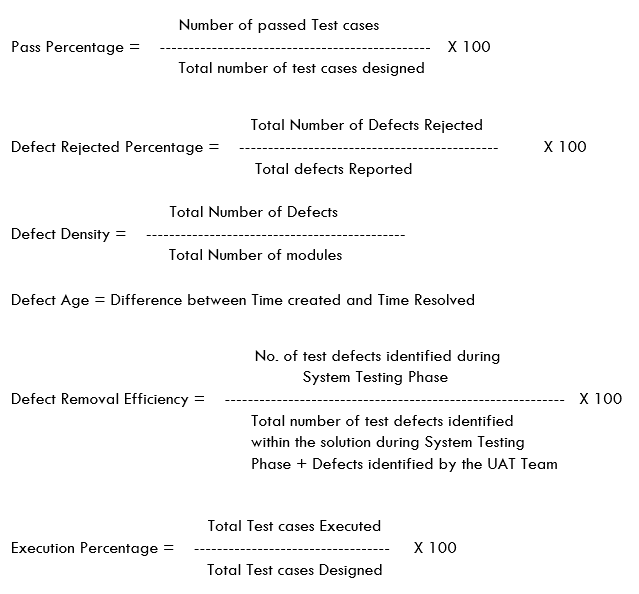

Test Closure:
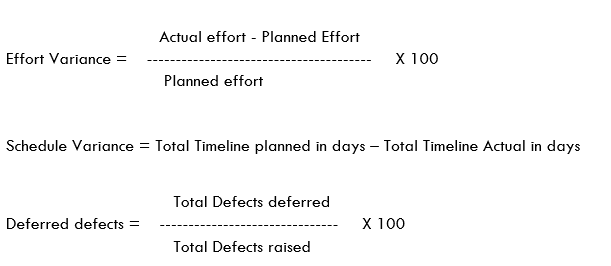
Defects by priority and severity will be tracked as a part of Test closure report
Conclusion:
Testing Metrics are helping us to track our progress and improve our delivery quality in a better way. There are so many metrics available to track the progress and Test Management tools nowadays are better equipped with various features to track these metrics and it also has various customization mechanism to track custom metrics rather than following standard metrics, we should first finalize KPI and Metrics for our measuring the performance and utilize these tools features to satisfy our requirement.

by admin | Feb 1, 2020 | Software Testing, Fixed, Blog |
This blog was written with the purpose of being a complete guide to usability testing. Usability testing ensures that the interface of your app is built to fit the end-user expectations and incorporates easy usage, learnability of the system, and user experience satisfaction. It has many dimensions where usability tests translate your app’s experience into a successful validation process.
So when do you need to conduct usability testing?
The earlier a defect is found, the better in the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) it will be cheaper to fix. Since usability test results affect the design of the product, it should start at the same level as the software (to undergo changes) throughout the SDLC process. Continuous and rigorous testing will yield maximum results. As an internal process, designers and developers on the project perform the testing to analyze the system for design and code to be modified as per the changes detected in the usability testing phase.
Here are some methods of usability testing:
Usability tests validate if the software is how a user would like it to be and whether it is a comfortable and holistic experience for the user.
- During the design phase – Draw your app/website design and evaluate its workability.
- In the build phase – Randomly test to determine the app’s usability factors.
- Hire real-time users to use your app/website and report results.
- Check statistics based on the input wireframes.
- Employ a QA services company that specializes in the usability testing field
Standard types of usability tests:
Guerilla usability testing Set up your tests where there is a lot of traffic, which allows you to ask passers-by for feedback of your app/website to evaluate user experience.
Unmoderated usability testing Uses third-party software to recruit ideal sample users for your test to interact with your app/website in their natural environment while recording their task completion to give you objective feedback.
Moderated usability testing Interacts with sample users in person or via video call to elaborate on their comments or help users understand tasks and keep them on track.
Now let’s discuss the 9 phases of usability testing,
Phase 1: Decide which part of your application/website you’ll test.Do you have particular concerns with your interaction or workflow? Want to know what your users will do on your product page? List your app/website’s pros and cons and create a concrete hypothesis for your testing.
Phase 2: Pick your test tasks. Your sample user’s task should be similar to your end-users goals with your app/website when they interact with it, for example, while transacting a purchase.
Phase 3: Set a level for success. Decide what you want to test and how you plan to check it and then accordingly set criteria to determine success levels for each task. Establishing a measurement for success/failure helps determine if your app/website’s user experience is intuitively designed.
Phase 4: Write scripts and plan tests. The purpose of the tests should be added to the beginning of your script and must include what you’ll be recording during the testing phase of your app/website. Gather knowledge of your sample user while they perform the tasks to make your test consistent and unbiased.
Phase 5: Assign roles. While testing usability ensures that your moderator is neutral while guiding sample users through the tasks mentioned in the script. During the testing, ensure notes are taken, which will later help extract insights to prove your hypothesis.
Phase 6: Identify your sample users. Recruitment of a sample user base and keep it small during every testing phase to ensure it resembles your actual user base as closely as possible.
Phase 7: Conduct the tests. During the testing, check if your sample users can complete tasks one at a time without assistance because the results from the testing can diagnose the pros and cons of your design.
Phase 8: Analyze results. The results obtained after testing will help you discover problem patterns so you can assess the severity of each usability issue. While examining the data, please pay attention to user performance and their feelings about your app/website.
Phase 9: Review and report findings. Insights from your results will help layout the next steps to improve your app/website’s design. Correct enhancements can be done before the next round of testing.
In Conclusion:
Usability testing is, therefore, vital as it is a great technique to help your UX designers in your development team by giving them the necessary insight on how their users interact with the final app/website. Always employ one of the top QA companies to carry out your Usability Testing to make sure you can apply appropriate techniques to improve the quality and design of your app/website and that the end product is user-centered. Codoid is considered an industry expert on usability, and we would be happy to help you out with your next launch.

by admin | Jan 27, 2020 | Software Testing, Fixed, Blog |
Test Case Management in Jira eases Software quality assurance activities during sprint. Nowadays, we almost have all the required project management functions in Jira. If you are managing test cases outside Jira, it will be a cumbersome task to share test results to your team. Even if you share the results in Excel format in attachment section in a Jira ticket, it will not provide the following flexibility – aligning test executions in test cycles for selected release and tracking software testing metrics for each sprint.
- If you are updating a test step status in local excel sheet, your team cannot view the test result as and when it is needed.
- Managing test cases and test executions in a separate tool. Consider, you are using a test case management tool which does not have Jira integration, then it will be a tough time for your team to link and communicate the defects in Jira.
- Creating and organizing test plans. If Jira is used for project management, then publishing the test plan in Jira project should be the right choice. Once the test manager creates the plan, it needs to be shared to the entire team.
There are many modern Jira plugins available for test case management in Jira. Let’s review them one by one.
Zephyr it is a well known plugin for test case management in Jira. You can create test cases, test cycles, and track QA metrics using Zephyr. If you have automation test scripts, then you can update test cases status in Zephyr by calling its endpoints. We, as a software testing company, use Zephyr for multiple testing projects.
Xray You can manage all your Tests as Jira issues using Xray. If you want to write Gherkin Scenarios in Jira, then you can specify and integrate with test automation frameworks.
synapseRT This is a suitable plugin for waterfall model or an independent testing project. You can trace all the way from requirements to bugs. Also, manage requirement versioning & baselining and organize Test Cases in a Tree Format with the help of Test Suites.
Test Management The Test Management plugin is another tool supported by Jira. It has similar components to those of synapseRT and Zephyr, and facilitates test case creation and managing test cases using the different test suites.
TM4J TM4J is a QA & Test Management app for Jira. You can manage your test assets in single repository for quick access and reduced redundancy and reuse test cases across your projects, releases and sprints for regression.
TestFLO The most flexible test management plugin for Jira. Requirements testing, test case management and test reporting directly in Jira.
Test Collab You can quickly manage test cases from Test Collab, assign test executions, maintain Many-to-Many relationship Jira using Test Collab.
QMetry QMetry Test Management for Jira – the best test management app in Jira helps make Jira a full ALM solution covering from requirements management, project management to test management.
TestRail The top selling and modern test management tool to efficiently run your QA & testing efforts. Used by teams at companies such as Atlassian, Apple, Microsoft & Amazon, TestRail is a great choice for teams of all sizes. To use this plugin, you need TestRail account.
PractiTest It is a free for PractiTest users. You can report bugs directly to Jira from PractiTest with reproduction steps.
As a software testing services company, writing quality test cases and managing them effectively is vital role to provide high-quality QA services. Organizing & managing test cases in Jira enables better collaboration among testers and developers. Contact Us for your software testing needs.

by admin | Feb 5, 2020 | Software Testing, Fixed, Blog |
2020 has just begun, but there are already plenty of advancements in the world of testing, some of these trends that will dominate are Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Internet of Things (IoT) to name a few. QA services provided by specialized QA companies and their teams are more adept at helping you implement these latest trends into your software testing process. There were many prominent trends in 2019 in the software testing landscape as the automation testing industry is dynamic, and our team has made some predictions on where things are headed this year
Machine Learning
Almost 2/5th of all companies are looking to implement ML projects, and industry experts believe that this number is likely to skyrocket in the coming years . But despite the assuring prospects of ML application, the concept is still in its nascent stage in software testing. So there are multiple challenges present for it to move on to the next level. There is an increasing demand for ML, and QA teams know that it is time for them to acquire skill sets like data science, statistics, and maths. These skills will complement core domain skills in automation testing and software development engineering testing
AI
Testers adopt a combination of AI skills and traditional skills, and this has lead to new job profiles like AI Quality Assurance (QA) analyst and data scientist. Nowadays, automation tool developers, focus on practical building tools and companies reassess options based on their budget to make the best use of information gained from AI. Such tools need to meet cost-efficiency and technical aspect requirements of the business, like read production logs, respond to production activities, and generate test scenarios.
DevOps
Test automation in agile teams is now more established because nearly 50% of IT companies are automating half their testing, and the adoption rate is only going to ascend this year. Companies adopt Agile and DevOps practices to increase the quality and speed of software development in test automation processes. Test automation performs repeated tasks, to detect bugs quicker, and render perpetual feedback loops, ensuring test coverage. Companies thus save a significant cut on costs, time, and personnel when they integrate automation testing in their QA process.
Data Mining
QA teams must combine automated and manual testing to achieve the best software quality. Developers must continually update themselves by learning about new tools and upgrading the system accordingly. Extensive data can be easily deciphered, and AI and ML will help you make better decisions by enhancing your market strategies through precise data validations. Such enormous data is anticipated to increase at an exponential rate since industries are shifting towards a data-oriented world, and the need for testing big data applications is on the rise.
IoT
The number of IoT devices around the world is estimated to reach 20.5 billion by the end of this year, and so it is evident that it must undergo testing. It will check security assurance, data integrity evaluation, ease of use, device compatibility, scalability, etc. IoT testing engineers have a lot of work, especially in monitoring communication protocols and operating systems. QA teams are expected to enhance their knowledge and skills to conduct successful usability,security, and performance IoT testing.
Cybersecurity
The digital revolution comes with plenty of security threats, and we must recognize the importance of security testing for our software, systems, applications, and network. Software teams have to ensure products are resilient to threats and take cybersecurity seriously so that risk compliances are covered. Security testing helps secure money and data transactions and also protects your end-users.
In conclusion
The seven listed trends will give you a sneak peek into the current prevailing software testing trends of 2020. As one of the best QA companies out there, we believe that the digital transformation is continually evolving; testing engineers, and software product enterprises alike. We should, therefore, stay abreast of the latest changes and innovations and inform quality assurance teams to take these trends into account while building their strategies, so that you can climb the ladder of success.