by admin | May 8, 2020 | Software Testing, Fixed, Blog |
CSV stores data in tabular format. Importing CSV files can be achieved at much faster, rate with less memory consumption. In this blog article, we have listed a few Python CSV File Read Examples for your better understanding and reference. We, as a QA company, use large CSV files to verify data quality between source and target. In order to automate data quality checks, we use Python libraries to import CSV files programmatically.
Built-in CSV Library
Python has built-in CSV library. You can read & write a CSV file. You needn’t install additional packages to use this module.
import csv
with open('test_data.csv', 'r') as file:
reader = csv.reader(file)
for row in reader:
print(row)
Read CSV using Pandas
Pandas is a powerful data analysis Python library. Let’s say for instance if you wish to import large CSV files on one go for Pandas. We, as an automation testing company have used Pandas library for our ETL & Data Analytics projects at various occasions and found it noteworthy.
import pandas as pd
test_data = pd.read_csv("test_data.csv")
#Reading First Value from name column
print(test_data["name"][0])
Convert XLSX to CSV
If you want to convert XLSX to CSV in Python programming, you can try out xlsx2csv library. It converts large XLSX file to CSV.
CleverCSV
CleverCSV detects the dialect of a file automatically , additionally it has command line implementation, if you would like to check the file outside Python environment.
# importing this way makes it easy to port existing code to CleverCSV!
import clevercsv as csv
with open("data.csv", "r", newline="") as fp:
# you can use verbose=True to see what CleverCSV does:
dialect = csv.Sniffer().sniff(fid.read(), verbose=False)
fp.seek(0)
reader = csv.reader(fp, dialect)
rows = list(reader)
In Conclusion
When you use Python libraries, you can craft your test automation scripts quickly and concisely instead of writing lengthy snippets. The above listed libraries will be helpful when you handle CSV files. We, as a software testing company, use various Python packages for ETL & Data Analytics testing projects. There are several other Python CSV File Read packages available in the market, However, they are not active in development. We hope you enjoyed this blog article and found it worthwhile.

by admin | Aug 3, 2020 | Software Testing, Fixed, Blog |
Any web-app or app intent to provide a truly universal experience, must be seamlessly functional on whatever device/ OS/ browser combinations their customer prefers. Having access to the latest hardware, operating systems, and platforms allows the testing process to be more streamlined, less expensive, and more innovative. In order to meet this objective, device availability becomes imperative and organisations spend several hundreds to thousands of dollars in procuring and maintaining these physical devices which are used for testing. This necessitates the need for a cloud-based device testing environment such as AWS Device Farm.
There are many cloud based solutions such as SauceLabs, BrowserStack, Perfecto mobile etc. AWS is another cloud testing platform which allows testing of apps over real android and iOS devices. AWS Device farm is a cloud-based application testing environment that enables remote testing of websites and mobile apps on a significant number of real mobile devices and an extensive range of desktop browsers, without the hassles of managing of building any testing infrastructure. It offers access to both modern and legacy versions of devices from multiple manufacturers.
AWS device farm has three pricing options for mobile app testing.
Pay as you go There won’t be any charge for the first 1000 minutes and you will be charged $0.17per device per minute.
Unlimited test & access This is a slot based plan. You can buy a slot for $250/per month. Let’s say you buy an Android slot. Now, you can access any real Android device using the slot for unlimited hours. If you want to run in parallel, you need to buy more slots. I.e. one slot, you can access one device at a time.
Private devices In this option, you can choose devices of specific hardware and software configurations that you wish to run your tests, those devices will be reserved for you till you unsubscribe from the plan. This plan starts from $200 per month.
An interesting feature is the possibility to connect remotely to a specific device model via a remote screen and install our app. As of today, AWS device farm has 162 device combinations. You can access devices which are eligible for remote access. If you want a real device for manual testing, then open Device Farm Page and start a session. You can hold a session for a maximum of 150 minutes.
You may ask a question: Why should I go for private devices as I already have a slot for manual testing. What difference does it make? Private devices are dedicated to you. In other options, the devices which you access on remote sessions are actually used by someone a while ago. However, the private devices will be allocated dedicatedly for your account. No other users can access it.
Appium is a widely used tool for automating your mobile application, you can run Appium scripts using TestNG, Junit, Node.JS, Python and Ruby. Many cloud device services allow you to upload test scripts, however in AWS device farm, you have to upload a test package to execute on multiple devices simultaneously. Uploading the script has upside and downside. Upside – we don’t need a highly configured machine to run the test scripts. Downside – sometimes it is hard to figure out scripting issues.
Usually, on some cloud testing provider such as SauceLabs, the test code will run on your computer while instructing cloud devices to do something, but in Device Farm you need to package all your tests to be run on the cloud. When executing tests, ADF uses an approach which we call as server-side execution. This means that the test code runs entirely on their infrastructure. The alternative to this is what providers like Browserstack or Saucelabs use where the test code runs on the user’s machine, called client-side execution, and interacts with the cloud service via a web service.
In general, client-side execution is easier to implement; if you already know how to execute tests locally, the configuration changes you need to make are minimal. Amazon Device Farm approach is a bit trickier as it requires a few extra steps, namely packaging and uploading everything necessary to run your tests to their servers.
Automated tests can be scheduled in Jenkins to perform continuous testing using the Amazon Device Farm for each new build of the application. There is an Amazon Device farm plugin available for Jenkins. Here are the steps on how to configure your AWS account with Jenkins.
Steps to use this plugin:
1. Log into your Jenkins web UI.
2. Click on the job you wish to edit.
3. On the left-hand side of the screen, click “Configure”.
4. Scroll down to the “Post-build Actions” header.
5. Click “Add post-build action” and select “Run Tests on AWS Device Farm”.
6. Select the project you would like to use.
7. Select the device pool you would like to use.
8. Select if you’d like to have the test artifacts (such as the logs and screenshots) archived locally.
9. In “Application”, fill in the path to your compiled application for testing native or hybrid app. Check “It is a web application.” for testing web app.
10. Choose the test framework, provide the path to your test package location and other relevant details.
11. Configure device state parameters like radio details, extra data and device locations.
12. Configure the maximum execution timeout. The default execution timeout is 60 minutes.
13. Set the execution configuration parameters: video recording and app performance monitoring.
14. Click “Save”.
If you don’t want to use Jenkins UI and are looking for a code based plugin, then you can try aws-device-farm-gradle-plugin. Using this plugin, you can configure your application file and test files in the Gradle build system.
AWS allows third-party security auditors to assess the security and compliance of AWS Device Farm. AWS device farm has data retention policies. The data entered or saved in the device will be wiped out once the session is closed. However, Uploaded applications & test packages, logs, and video recordings will be retained certain days.
Almost most of the devices are public and shared ones, you cannot hold the devices for more than 150 minutes per session for both manual and automation testing. There is no information about the access limit for private devices.
If you have robust automated test scripts and you have performed multiple dry runs locally, then AWS device farm is a suitable platform for your cloud devices testing. However, don’t forget to use the 1000 minutes free trial before you go for any plans. We, as a software testing company, use different cloud testing platforms to test mobile applications on real devices. We would recommend choosing the platforms based on your testing needs. Before choosing a cloud testing tool, check how quickly the new devices are added and whether the remote access provides the selected device without any delay.
One of the best advantages of AWS device farm is uploading the test package once and getting the result for multiple devices. Whereas in other cloud testing platforms, you need to execute the same test package using your machine. With device farm we get detailed logs, performance graphs and screenshots are generated during each run to provide general and device-specific feedback. The service offers a lot of flexibility by allowing the state and configuration of each device to be altered in order to reproduce very specific test scenarios. Ensure the test cases selection for automation test execution is done via build file arguments. So that you can use a single build file with the same test package.
We hope you have enjoyed reading this blog article and found it insightful.

by admin | Jun 22, 2020 | Software Testing, Fixed, Blog |
Over the last decade there has been an increasing shift towards the software life cycle process from waterfall to Agile, and now it is moving towards DevOps continuous integration and deployment. Each one has its own set of practices that stresses the importance of collaboration and communication among software developers and other IT professionals.
DevOps promotes frequent interaction between IT department and business users, and tries to regularly build and deliver software that meets business users’ changing requirement needs. Keeping that in mind, there has to be links to requirements, and the test management tools should have some operability with test automation and defect management, since many organizations are shifting from manual approaches such as the use of excel sheets and Word documents to organize their testing process.
As a tester, we should make sure the test management tool should encompass the below day to day activities:
Creating and maintaining the test artefacts (requirements, test cases, etc) specific to each release/cycle.
Establishing traceability and coverage between the test assets.
Test execution support – Test suite creation, test execution status capture, etc.
Metric collection/Report-graph generation for analysis.
Bug tracking/defect management.
Integrate with VCS and CI/CD tools.
While considering test tool selection, one should understand their needs before examining each tool. One should keep their needs simple and avoid an over-engineered solution that will be expensive and more difficult to deploy. The only object is here is to ensure that the product should reap real benefit over the long haul. Let’s see what benchmark the test management tool should satisfy in this blog.
No man is an island, and the testing process is no exception, we must know the fact that any test management tool can’t serve its intended purpose without being integrated with a project management tool or change management system. The best known Project management tools that are widely used in the market are Jira, HP ALM etc. As we know that JIRA is one of the systems which is used mostly in the industry, we consider the fact that integration matters. This helps us right from the tracking of the requirements to document the scenarios, writing test cases, managing defects and projecting reports to share with stakeholders.
Testing consumes a lot of manpower and time in the software development life cycle. Organizations look for anything that can reduce this manual effort and time which in turn will reduce the cost of overall development. Test automation saves time and effort because, unlike some project activities, it is repeated, sometimes the test execution has to happen frequently, so the test management tools with in-built support for automation will help the team to achieve testing in a short period of time.
This is one of the most essential features that a Test Management Tool should have, that it supports the reusability of test cases, user scenarios, and test stories. This will allow the existing test resources to be utilized again in various test projects. This will help in reducing the cost and time invested in test management, and the testing teams will be more productive. Most of the projects which adopts Agile methodology have automation testing practice, it would be good for the testers to follow BDD (Behaviour Driven Development) model to design automated tests. Having the test management tool that supports BDD tools like behave, Cucumber, Specflow etc, will reduce rewriting test cases by automation engineers.
The upside of deployment automation is that it allows delivery of new functionality to users within minutes whenever it’s needed, as well as instant feedback will be given to the DevOps team that, in turn, allows them to respond rapidly to customer/ stakeholder demand in order to speed up the release of high-quality software. Tools like Jenkins, Teamcity and Bamboos help to achieve CI/ CD.
A tool that offers test results information in personalized dashboards will make everyone’s work easier. Dashboards should be flexible because different types of user have different needs when it comes to analyzing test results. Project Managers will look for results/ destination and the developers will look for the metrics/ Journey. The data can be diced and sliced to offer even greater insight into things such as the effectiveness of the development process and the existence of any high risk areas.
Below are some of the best test management tools that can help testers.
TestRail It assists you to track and manage your software testing efforts and tracks individual test status, projects and milestones with active reports. It performs most of the tasks that are performed by Xray. It has no automation support and there is no requirements planning feature to associate the test cases and traceability.
Zephyr Majority of the developers have the knowledge that Jira is used for bug tracker that aims to control the development process with bugs, tasks, and agile cards. Zephyr is one of the numerous Jira’s plugins out spreading Jira’s capacities.
Using a combo of these two tools will enable you to attain things such as: creating test plan, test cases, executing tests, executing tests, producing reports. It has few limitations like, it doesn’t support CI Integration.
PractitestIt is a prominent cloud-based test management tool which assists project development teams to manage and organize their testing processes while giving management/ stakeholder a simple and clear view of their project status every time. It is best for Agile Teams as it supports Manual and Automation testing. The only disadvantage is that it is not budget friendly.
The testing team can make the testing process more efficient and produce better results with the help of the right test management tool that satisfies the needs of the team and budget.

by admin | Mar 17, 2020 | Software Testing, Fixed, Blog |
On this planet everything that is developed should be tested, officially or unofficially. In our rota, we tend to do a lot of testing but we don’t realize because they are part and parcel of daily routines. In a similar profession, the information technology stream adopted the testing domain as one of their power to ensure that the application or software designed working as intended and it serves the purpose.
In this blog we are going to give the knowledge related software testing from the very basic level even a novice will be able to follow.
One must brainstorm themselves to get the motivation of being a software tester. Being an art testing requires some of below skillset.
Intelligence
Out of box thinking
Disciplinary and punctual actions
Planning
Leadership abilities
The mentioned skills were quite common for any profession but when it comes to the point of testing they play an additional role but are mandatory to possess. We keep everything crossed for you to choose to test as your profession, be ready to break the system in a procedural manner and ensure that you are of great help to your team always to launch a perfect flawless product.
Understanding the SDLC
As a pre-requisite, we would strongly recommend one to give yourself a walkthrough on SDLC (software testing life cycle), while going through the below content. A blog can still be understood without SDLC knowledge but it’s recommended as that way you connect the dots while undergoing discovery learning to understand better.
What is software testing?
Software testing a process of identifying the bugs present in the software by validating all possible scenarios that are applicable to the software. In this formal process, we design test cases basis the understanding of the application then executes to deem the correctness of the software
Why is software testing required?
For an illustration, let’s consider that a bank has launched one of its internet banking system applications into production for use without testing. It is evident that customers are going to initiate transactions and apply for various services that are offered by the system.
There is a high probability for the customer-friendly scenarios could fail, which in turn cause the bank to lose its reputation and trust in the market and it’s very expensive for the bank to correct the mistake and re-work on the application
1. Initiated transactions might get failed due to various reason
2. Fund would have not credited at the receiving end
3. Can’t be able to query about the balance?
4. Can’t apply for cheque leaves through the internet banking system.
In the above discussion, it’s a software imagine its software component that performs some physical actions based on the input such as airbag release system in the car, automotive alarms elevators, and lift..etc. failing which can cost lives. So we need to keep the mindset in such a way that, if the application or a working software is not tested we are going to see a huge amount of loss which is difficult to recover from. So we know why testing is essential now, great understanding!!!
Principles of testing
There are a few principles that must be learned which explain the reasoning of testing in all possible views, why wait? Let’s see them quickly
Early testing is beneficial
How early we start to test, that early we can stabilize the system also it’s true that early bugs are cheaper than bugs that are identified late in the business. When we say cheaper if we can identify and fix them early we can avoid doing late regression testing and that as well helps to meet the deadlines. So we should adopt a process that helps us proceed with test activities early in the software life cycle.
Error absence is the fallacy
Though the intention is to test as much as we can and identify all possible bugs, we can guarantee that system if bug-free and 100% flawless. We might have misbehavior seen at a very low level that might not have caught up in our test scope or an unfortunate miss. Despite the principle, we should always ensure that we don’t cover any bug present in customer use cases.
Exhaustive testing can’t be conducted
As part of the testing phase in the software development life cycle, we will conduct various levels and types of testing, but it’s still difficult to cover all the scenarios including positive and negative. Given the timelines for the testing phase we should understand the prioritized edge tests also we need to apply the proper test case techniques to make sure a few test cases will give more coverage.
Pesticide paradox (redundant test case)
We should be continuously reviewing the test cases in order to ensure we have powerful tests and no more duplicates present. If the same tests are being executed again and again we end up identifying no defects. Every time there is an operational change or enhancement in the module, we should build the tests accordingly.
Defect clustering
In any software system, every component has to be treated and tested thoroughly, it could be that most of the defects might be happening in smaller components or from a module which we don’t even think of. We should always focus on the integration pieces and also focus on edge cases as that gives confidence that either boundary are working.
Testing shows the presence of defects
It’s evident that only testing allows us to find defects, how much diligence we possess while testing that much defect rate can be achieved and in turn can help the business to make the application more stable within the nominal time.
Testing is situational dependent
We should keep changing the mindset and the game plan when we are supposed to test different applications or different software. The same strategy will not help us to find the bugs and which will cause so many complexities within the domain. For an illustration, the plan that’s applied for testing a banking-related application may not be useful to test the retail application or insurance application as the requirements and usage are significantly varying.
Software testing life cycle
STLC is a part of SDLC, it’s one of the phases which is executed after completion of development. It’s essential to understand the phases involved in the testing life cycle as that helps us apply the right testing approach. The steps involved in STLC are
Requirement analysis understanding
In this phase, the goal is to analyze the requirements thoroughly to understand the functionality. Any clarification that would be required should be clarified by discussing with the business analysts or the subject matter experts.
Test plan
Once the requirements are understood we should plan for proper testing. We should also define the scope as what comes into the scope and what can’t be. We should also plan the number of resources that would be required also the timelines.
Test case design
Basis the understanding the test case design should be commenced. By following the proper test case development techniques also keeping the type of test in scope we should have the test cases designed. Since the tests designed are going to be executed for finding the defects. Hence proper understanding of the design techniques are needed.
Test data preparation
Test data plays an important role in the execution front. Based on the test data the test execution flow changes, hence apparently we can believe that test data has the ability to drive the test case. We should identify possible combinations of negative and positive scenarios. Test data plays a major role in automation as well, in a pure data-driven or hybrid framework, we can execute the same test with different sets of inputs than writing them as a separate test case. Test data can be maintained in Database or in excel spreadsheet or in any other known form.
Test execution
Once the designing of the test cases and identification of test data is done we need to execute the test cases. Any underlying bugs present in the system can possibly be found in this phase. Due diligence is required while executing the tests as we need to catch up with minor cosmetic bugs as well. Every execution report should be shared with all the stakeholders for their reference and also help with understanding the progress of the test
Test closure
As a test closure activity we will share the final results observed during the execution phase in a detailed format. We will put in graphs, bar charts and presentations so that the higher management can actually understand the status better. Also, the sign-off documents, test risk assessments, and test completion reports are being circulated to get the approval from all business stakeholders.
Test case development techniques
While writing the test cases it’s essential to adopt the techniques to be smart enough also to ensure the coverage with a minimum set of test cases as possible. If the techniques are not followed we end up writing invalid tests also test cases might appear as redundant ones.
Given the two major classifications of testing, we have respective test case techniques designed as well
White box testing techniques
As discussed above it’s a test designed or executed on the structure or design of an application and proper understanding of the code and system is a must.
Statement coverage
Let’s consider a developer is conducting a unit testing, the developer must have a thorough understanding of what that module or component should do? Also, the developer must aware of the code that has been written. Predominantly with the help of this technique, we try to get rid of any unreachable code that’s available in the system. Ideally, the statement coverage is equal to the number of statements being written.
Eg.
Main(){
If(a>0&&b>0){
If(a>b){
Print is bigger;
Else
Print b is bigger;
}
Else{
Print error message saying, negative values are not allowed;
}
}
The statement coverage for the above program is 9, as there are 9 statements.
Decision coverage
The decision coverage mechanism of a white box testing technique ensures that we make proper conditional calls and don’t miss any edge cases. The decision coverage is equal to the number of decisions we have in the system.
Eg:
Main(){
If(a>0&&b>0){
If(a>b){
Print is bigger;
Else
Print b is bigger;
}
Else{
Print error message saying, negative values are not allowed;
}
}
In the above snippet we are making two decisions as to whether or not both the given numbers are non-negative integers then considering a decision as which number is bigger
So the decision coverage for the snippet is equaled to 2
Path coverage
Path coverage ensure that how many use cases and flows can be derived based on the given inputs. Also, we need to ensure that all possible paths are covered to ensure that the system is not open to breaking in any scenario. This can be understood by drawing some UML, flow chart diagrams.
Black box testing techniques
As we already discussed above that black box is a manual validation and test cases are mainly focused to test the functional validation. These techniques will help us to do some permutations and combinations and identify the test cases based on the edge cases or doing some partitioning
Boundary value analysis
In this technique based on the condition, the boundary values such one immediate left and one immediate right boundary values are tested to ensure the state transition is happening properly on the conditional edge.
Eg lets consider that a person whose age is 18 or above only can vote and below age group, people can’t cast their vote.
In order to test this condition we will understand the deciding factor age as “18” as it’s mentioned then identify one value just below 17 and one above 19 as boundary values to test that critical conditional logic.
Equivalence partitioning
This is another technique, which will help us to avoid the number of test cases but gives more coverage in this testing. In this technique based on the condition, we will partition the negative and positive slots and then pick one of those values to test. The lore is that, if the test case is behaving as expected for one value it is understood rest other values would be passed from the same slot.
Eg: let’s consider the same example as above that person with 18 or above can vote and rest can’t
We will identify three partitions as
Age- 0<=17- negative slot
Age- 18= positive slot
Age- 19 to any greater value- positive slot
We will pick any one test data from each classification then with the help of 3 test cases all the scenarios can be covered.
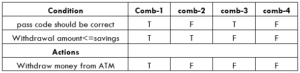
Decision tables
When we have multiple combinations of inputs to test, if we choose to write test cases for all the values it becomes an overhead. Then forming a table with all the conditions and actions put in would help better to identify the cases.
Eg: let’s consider a scenario of withdrawing money from the automated teller machine.
The machine will dispense money only when
Cond-1 user put incorrect passcode
Cond-2 withdrawal money should be lesser or equal to the savings balance.
Action / Goal: Withdraw money from the teller machine.
The above requirement can be converted into a decision table as,
State transition testing
In this technique we need to understand the state flow of the use case then come up with a design flow diagram. This flow can help us derive how many flows and how many are positive and negative. In order to do this, we must have proper knowledge of the application.
Use case testing
Use case tests are designed to be more customer-specific test. The test case is written in the form of a user guide where the steps are written in a procedural format. This gives more insight on the test procedure as it talks about the actors, events n pre and post conditions in specific.
Eg: let’s consider a login scenario into an application
Actor
Actor is the person who performs that events
Pre-condition
Actor should own a good network provision
Actor should be on the login page to be able to enter credentials
Events
Steps are addressed as events, the events involved in this step are
Enter the username and password
Click on the login button
Alternatives
This says what other actions can be possible when actor on that page.
The actor can look for help link or actor can try signing up if the account is not created yet.
Exceptions
These are the problems that user might encounter during the execution of events
Application might be throwing an error upon entering the credentials
After the clicking the login button, occurrence of any HTTP error
Post- actions
These are the subsequent actions executed after the completion of events.
Logging out from the application
Performing any business functionality with in the application
Conclusion
We reckon it’s a vague discussion, but every piece in this is important to be a competitive and distinguished tester. Adopting these fundamentals will help us test the applications with due diligence and with enhanced coverage. How much its the fact that the principles have to be understood, in the same fashion we must apply the sense to determine what technique to be used and when. I keep everything crossed for every reader to be a successful tester.
Thanks for reading!!! More we know more we grow.

by admin | Mar 11, 2020 | Software Testing, Fixed, Blog |
Software testers are considered to be the gate-keeper of the quality and hence are very vital to the success of any software. Still, this ever-evolving career option Software Testing is surrounded by many myths and misconceptions. Let us unveil the reality behind them:
MYTH: Fighting against the bugs is the only Bull’s Eye
REALITY: To most of us, even the tasks of a software tester are ambiguous. Some of us say the core task is to make the software bug-free but it is not at all the truth. Software testers have a huge list of functions to be performed, including checking the interoperability, inter-browser acceptance, smooth working, security against malicious codes, and fighting against the bugs. So making the software bug-free is just one of the tasks. There is indeed a bigger picture beyond this little point.
Also, even if the software is fully protected against the bugs, there may be other issues hampering the smooth functioning of the software viz, server crashes in the period of huge traffic on the site or some browsers not supporting the software, some users are unable to access or transact through it, and much more
MYTH: Software Testing is inferior to Software Development
REALITY: This myth is too harsh to be real for software testers who actually put in so much effort day and night to ensure the quality of the software. So in reality, both the professions go complementary. Developers are not able to launch their software into the market until it is duly tested by the testers to get certain about the security and QA of the software. So the developers are dependent on testers.
Also, vice versa is true. The testers have to work according to the codes and programs used by the developers during the development stage. The testers have to gather information about bottlenecks in the software, which can only be known by its creators. So the testers are dependent on developers.
Hence, none of them are inferior or superior to each other.
MYTH: Software Testing requires no specialized qualification or less expertise
REALITY: This is one of the biggest misconceptions that we think that any person from an engineering background can join a team of QA Analysts. In order to fully understand the system and debug the root cause of any issue, testers need to know about the underlying database structure and the different technologies used.
Apart from that some testing activities like white box testing, automated testing, security testing, etc requires specialized programming language and/or a particular tool’s expertise.
MYTH: Automation can eliminate manual testing requirement
REALITY: This is a misconception not only in the context of software testing but all technology-related fields. We believe that with the increase in automation, human intervention will decrease but this is not the case. Even automated techniques require a human application and continuous monitoring by expert personnel. So automation testing can never substitute manual testing techniques completely, rather the integration of both in the right proportion will bring greater results.
MYTH:Testing does not contribute to value addition
REALITY: It is not necessary that value addition happens only when some new software is designed. Testing the software also contributes to the cycle of value addition by enhancing its quality and improving its durability.
Without ideal testing, launching a new software can prove to be worthless, in that case even the primary value addition will become a zero. So testing is secondary but immensely affects the value addition of the primary activities like software designing so it is a part of value addition itself. So testing is never an extra expense, it bears fruits if done in the right way.
MYTH: Testing may lead to delay in launching new software
REALITY: It is true that testing is time-consuming but the time spent on it never goes worthless. Testing should be considered as a part of development only instead of considering it as an extra activity. Thus, time utilized in testing or QA is counted in the process of designing and development itself. Moreover, automated techniques have reduced the wastage of time in lengthy manual methods so we can not conclude that testing leads to any delay in launching if new software.
MYTH: Software once tested is perfect forever
REALITY: Software testing is a continuous process. As and when there are changes in any coding or programming of the software, testing is required to risk-proof those changes, even if they are minor. With increasing users of your site, there may emerge new issues related to the performance of software, so testing is required at every step.
It is not only done once before it is launched, rather the process continues even after years of its initial designing and introduction in the market. The malicious codes or worms can come up any time to damage your software, so it is a whole-time job.

Conclusion
If any of these myths were stopping you to choose software testing as a career, so clear your minds and be confident about your choice. And if you are already a software tester and you had wrong notions about your tasks, I hope this article will show you the true picture and help you work with more efficiency.
Author Bio
Kuldeep Rana is the founder of ArtOfTesting, a software testing tutorial blog. He is a QA professional with a demonstrated history of working in the e-commerce, education and technology domain. He is skilled in test automation, performance testing, big data, and CI-CD.

by admin | Mar 4, 2020 | Software Testing, Fixed, Blog |
In this blog we are going to discuss what test strategy is all about, why test strategy is required when we would require a test strategy document and finally about how to write Test strategy document
What is a Test Strategy
A Test strategy is a static document that describes how the testing activity will be done. This is like a handbook to stakeholders which describes the test approach that we undertake, how we manage risk as well as how we do testing and what all levels of testing along with entry and exit criteria of each activity. This will be a generic document that the testing team would refer to prepare their test plan for every project.
Test strategy act as a guidelines/plan at the global Organization/Business Unit level whereas Test plan will be specific to project and always we should ensure that we are not deviating from what we commit in Test strategy
Why Test Strategy is required
It gives an Organization a standard approach about how Quality is ensured in the SDLC. When there is any typical risk involved in a program, how to mitigate those risk and how can those risks be handled. When every project adopt to the same standard, quality improvement will be witnessed across the Organization and hence Test strategy is important
When do we need a Test Strategy
Below could be some of the circumstances which would require Test Strategy.
When an Organization is forming a separate QA wing
When there is a change in QA Organization from normal QA model to TCoE / QCoE where the operating model and structure is changed
When QA leadership changes who comes with different perception
When Organization is adopting different tool approach for Automation / Performance etc
Contents of Test Strategy
Below are the contents of Test Strategy document
1) Brief Introduction about programs covered in this Strategy
2) Testing Scope and Objective
3) Test Planning / Timeline
4) TEM Strategy
5) TDM Strategy
6) Performance Strategy
7) Automation Strategy
8) Release and Configuration Management
9) Test schedule, cycles, and reporting
10) Risk and Mitigation
11) Assumptions
Brief Introduction about programs covered in this Strategy
This section covers the overall scope this Test strategy is going to be covered with. Important engagement and programs which will run based on this Test strategy.
Testing Scope and Objective
This section describes the following
What will be the different levels of testing conducted like Integration, System, E2E, etc
The process of review and approval of each stage
Roles and Responsibility
Defect process and procedure till final Test sign off
Test Planning and Timeline
This section covers in-brief the following
What are the programs going to be executed
What is the timeline that each program is going to constitute
What will be the infrastructure and tooling needs to support this program
Different Environment that will be used
TEM Strategy
Prior section describes the overall requirement and this section describes in detail about the Test Environment Strategy and covers the following
1) How to book Environment for project purpose including booking 3rd party Environment
2) Assess to Environment to users for project requirement
3) Environment integration and stability management
4) Test data refresh co-ordination
5) Post release Environment validation
6) Support and co-ordination requirement
TDM Strategy
Similar to Environment, different project test teams would require different data requirement and some would need to mock up live data. This section in TDM strategy would provide the below information
What are the forms to be filled and agreement to be in place to serve this data need
What type of data to be loaded and when it will be available
Who will be the point of contact for each program
If any 3rd party Vendor support is required, this would describe in detail of that
Performance Strategy
Based on various programs and its schedules listed in the prior section, performance strategy would describe how Performance Testing requirements would be fulfilled and what their tool strategy, license model is and team availability. If the team also does Performance Engineering, it would describe in detail about how it is performed
It cover details about Requirement phase (How NFR requirement will be gathered from stakeholders, Proof of concept procedure, how critical scenarios are defined.), Testing phase (How testable scripts are created, how data setup is done), Analysis and Recommendation (How performance issues are reported, sign off procedure)
Automation Testing Strategy
Similar to Performance Strategy, Automation strategy would describe how requirements are defined, tool strategy, license model, etc and also elaborate how the Automation team conducts feasibility approach till defining framework, developing scripts till execution and Continuous Testing if it is in-scope
Release and Configuration Management
This section describe the following areas of Release and configuration management
Overall release and configuration strategy
QA deployment and release calendar
How different Test assets are loaded and tracked
Co-ordination of QA Deployment
How QA audit is conducted
How production deployment is co-ordinated by the QA team
Change Management for any CR post-release is managed
Test schedule, cycles and reporting
This section details out about each program, its schedules, Test timeline, Test cycles and how reporting will be carried out.
Risk and Mitigation
This section describes overall risk management and risk mitigation process along with how it will be tracked and reported.
It also classifies various risk levels like Project level and program level risk and describes how it will be handled during the execution phase
Assumption and Dependencies
During Test strategy development the timeline of program etc are in a predictive stage as it could be for a period of 1-5 years and hence there is going to be a lot of assumption which should be listed in this section. Also, there are different teams which Testing team has to co-ordinate with like TEM, TDM, vendors, etc which needs to be called out in advance in the assumption and dependencies as any change in Project-level / Program level scope will have an adverse impact and it has to be called out in strategy as assumption and dependencies
How to write Test Strategy document
For now we have covered about what Test strategy is all about, why it is important and looked in detail about the contents of the Test strategy, it is now easier to define how to write better Test strategy document.
Before writing Test strategy we need to collect few information which is listed below:
List of programs that need to be handled in this stream
Programs and its releases objective and basic requirement it is going to meet
Criteria for Environment and Data management requirement
Timeline of each releases and it’s key stakeholders
Third party integration and vendor management details
Information about Test type and release frequency
Tool requirements/procurement process understanding
Basic assumption and dependency with outside QA Organization
This information will be collected by Program Test Manager after discussing with Key stakeholders of the program.
The collected information has to be discussed internally within the QA team Managers and assign responsibility to detail out further requirements to refine the Test Strategy.
If the program is going to be from the QA Transformation perspective, then further information has to be collected on the key QA levers that are going to run the program run differently.
After identifying the key levers, assign the responsibility of each lever to a dedicated person so that Strategy can be further fine-tuned and can be circulated to wider group.