by Rajesh K | Oct 30, 2025 | Mobile App Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
Appium 3 is finally here and while it may not be a revolutionary leap like the upgrade from Appium 1 to 2, it introduces significant refinements that every QA engineer, automation tester, and mobile developer should understand. This release brings substantial improvements for mobile app testing, making it more efficient, secure, and compatible with modern testing frameworks. The update focuses on modernization, cleaner architecture, and stronger W3C compliance, ensuring that Appium remains the go-to framework for cross-platform mobile automation in 2025 and beyond. In today’s rapidly evolving test automation ecosystem, frameworks must keep pace with modern Node.js environments, updated web standards, and tighter security expectations. Appium 3 accomplishes all three goals with precision. It streamlines deprecated behaviors, removes old endpoints, and enhances both stability and developer experience. In short, it’s a major maintenance release that makes your automation setup leaner, faster, and more future-proof.
In this blog, we’ll dive into everything new in Appium 3, including:
- Key highlights and breaking changes
- Updated Node.js requirements
- Deprecated endpoints and W3C compliance
- New feature flag rules
- The newly built-in Appium Inspector plugin
- Migration steps from Appium 2
- Why upgrading matters for your QA team
Let’s unpack each update in detail and explore why Appium 3 is an essential step forward for mobile test automation.
Key Highlights and New Features in Appium 3
1. A Leaner Core and Modernized Dependencies
Appium 3 introduces a leaner core by removing outdated and redundant code paths. The framework now runs on Express 5, the latest version of the Node.js web framework, which supports async/await, improved middleware handling, and better performance overall.
This shift not only reduces startup time but also improves request handling efficiency, particularly in large-scale CI/CD pipelines.
Why it matters:
- Reduced server overhead during startup
- Cleaner request lifecycle management
- Smoother parallel execution in CI systems
2. Updated Node.js and npm Requirements
Appium 3 enforces modern Node.js standards by increasing the minimum supported versions:
- Node.js: v20.19.0 or higher
- npm: v10 or higher
Older environments will no longer launch Appium 3. This change ensures compatibility with new JavaScript language features and secure dependency management.
Action Step:
Before installing, make sure your environment is ready:
# Optional: Clean setup
appium setup reset
npm install -g appium
By aligning Appium with current Node.js versions, the ecosystem becomes more predictable, minimizing dependency conflicts and setup errors.
3. Removal of Deprecated Endpoints (Goodbye JSONWP)
Appium 3 fully drops the JSON Wire Protocol (JSONWP) that was partially supported in previous versions. All communication between clients and servers now follows W3C WebDriver standards exclusively.
Key changes:
- Legacy JSONWP endpoints have been completely removed.
- Certain endpoints are now driver-specific (e.g., UiAutomator2, XCUITest).
- The rest are consolidated under new
/appium/ endpoint paths.
Action Step:
If you’re using client libraries (Java, Python, JavaScript, etc.), verify that they’re updated to the latest version supporting W3C-only mode.
Pro Tip: Use your test logs to identify deprecated endpoints before upgrading. Fixing them early will save debugging time later.
4. Feature Flag Prefix is Now Mandatory
In Appium 2, testers could enable insecure features globally using simple flags like:
appium --allow-insecure=adb_shell
However, this global approach is no longer supported. In Appium 3, you must specify a driver prefix for each flag:
# For specific drivers
appium --allow-insecure=uiautomator2:adb_shell
# For all drivers (wildcard)
appium --allow-insecure=*:adb_shell
Why it matters:
This helps ensure secure configurations in multi-driver or shared testing environments.
5. Session Discovery Now Requires a Feature Flag
In earlier versions, testers could retrieve session details using:
Appium 3 replaces this with:
This endpoint is now protected by a feature flag and requires explicit permission:
appium --allow-insecure=*:session_discovery
Additionally, the response includes a newly created field that shows the session’s creation timestamp, a useful addition for debugging and audit trails.
Pro Tip: Ensure your Appium Inspector is version 2025.3.1+ to support this endpoint.
6. Built-In Appium Inspector Plugin
The most user-friendly enhancement in Appium 3 is the built-in Inspector plugin. You can now host Appium Inspector directly from your Appium server without needing a separate desktop app.
Setup is simple:
appium plugin install inspector
Then, launch the Appium server and access the Inspector directly via your browser.
Benefits:
- Simplifies setup across teams
- Reduces dependency on local environments
- Makes remote debugging easier
For QA teams working in distributed setups or CI environments, this built-in feature is a game-changer.
7. Sensitive Data Masking for Security
Security takes a big leap forward in Appium 3. When sending sensitive data such as passwords or API keys, clients can now use the HTTP header:
X-appium-Is-Sensitive: true
Why it matters:
This simple header greatly enhances security and is especially useful when logs are shared or stored in cloud CI tools.
8. Removal of Unzip Logic from Core
Appium 3 removes its internal unzip logic used for handling file uploads like .apk or .ipa. That functionality now lives within the respective drivers, reducing duplication and improving maintainability.
Action Step:
This ensures all drivers are upgraded to handle uploads correctly.
Appium 2 vs Appium 3
| S. No |
Feature/Aspect |
Appium 2 |
Appium 3 |
| 1 |
Node.js Support |
Supported Node.js 14, 16, 18. |
Requires Node.js 18 or higher. Node.js 16 is end-of-life (EOL). |
| 2 |
Architecture |
Driver-based architecture, where drivers (e.g., XCUITest, Espresso) are installed separately via the CLI. |
Builds on the same driver-based architecture but updates core dependencies. |
| 3 |
Underlying HTTP Library |
Used a legacy version of the appium-base-driver with an older HTTP stack. |
Upgraded to use @appium/base-driver version 9.x+, which uses a modern Express.js framework and body-parser. |
| 4 |
Default Port |
Default server port was 4723. |
Default server port remains 4723. |
| 5 |
CLI Commands |
Uses appium driver and appium plugin commands for extensibility. |
Continues to use the same CLI system. Commands are unchanged. |
| 6 |
Primary Goal |
To modularize Appium and move away from the monolithic “all-in-one” structure of Appium 1. |
To modernize the core, update dependencies, drop support for EOL technologies (like Node.js 16), and improve stability. |
| 7 |
Migration Effort |
A significant shift from Appium 1.x, requiring new installation and driver management. |
Minimal from Appium 2.x. For most users, updating the Appium package and ensuring Node.js >=18 is the main step. |
Migration Guide: From Appium 2 to Appium 3
If you’re upgrading from Appium 2, follow this checklist to ensure a smooth transition.
Step 1: Verify Environment Versions
- Node.js ≥ 20.19
- npm ≥ 10
- Latest Appium 2.x installed
Step 2: Install Appium 3
npm uninstall -g appium
npm install -g appium@latest
Step 3: Update Drivers
Step 4: Update Feature Flags
appium --allow-insecure=uiautomator2:adb_shell
appium --allow-insecure=*:adb_shell
Step 5: Update Endpoints
/sessions → /appium/sessions
appium --allow-insecure=*:session_discovery
Step 6: Update Client Libraries
Ensure Java, Python, and JS bindings are compatible with W3C-only mode.
Step 7: Implement Sensitive Data Masking
X-appium-Is-Sensitive: true
Step 8: Validate Setup
Run smoke tests on both Android and iOS devices to ensure full compatibility. Validate CI/CD and device farm integrations.
Why Upgrading to Appium 3 Matters
Upgrading isn’t just about staying current; it’s about future-proofing your automation infrastructure.
Key Benefits:
- Performance: A leaner core delivers faster server startup and stable execution.
- Security: Sensitive data is masked automatically in logs.
- Compliance: Full W3C alignment ensures consistent test behavior across drivers.
- Simplified Maintenance: The Inspector plugin and modular file handling streamline setup.
- Scalability: With Express 5 and Node.js 20+, Appium 3 scales better in cloud or CI environments.
In short, Appium 3 is designed for modern QA teams aiming to stay compliant, efficient, and secure.
Appium 3 in Action
Consider a large QA team managing 100+ mobile devices across Android and iOS. Previously, each tester had to install the Appium Inspector separately, manage local setups, and handle inconsistent configurations. With Appium 3’s Inspector plugin, the entire team can now access a web-hosted Inspector instance running on the Appium server.
This not only saves time but ensures that all testers work with identical configurations. Combined with sensitive data masking, it also strengthens security during CI/CD runs on shared infrastructure.
Conclusion
Appium 3 might not look revolutionary on the surface, but it represents a major step toward a more stable, compliant, and secure testing framework. By cleaning up legacy code, enforcing W3C-only standards, and introducing the Inspector plugin, Appium continues to be the preferred tool for modern mobile automation.If you’re still on Appium 2, now’s the perfect time to upgrade. Follow the migration checklist, verify your flags and endpoints, and start enjoying smoother test execution and better performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Is Appium 3 backward-compatible with Appium 2 scripts?
Mostly yes, but deprecated JSONWP endpoints and unscoped feature flags must be updated.
-
Do I need to reinstall all drivers?
Yes, run appium driver update after installation to ensure compatibility
-
What if I don’t prefix the feature flags?
Appium 3 will throw an error and refuse to start. Always include the driver prefix.
-
Can I keep using Appium 2 for now?
Yes, but note that future drivers and plugins will focus on Appium 3.
-
Where can I find official documentation?
Check the Appium 3 Release Notes and Appium Migration Guide.

by Rajesh K | Oct 23, 2025 | Automation Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
As software development accelerates toward continuous delivery and deployment, testing frameworks are being reimagined to meet modern demands. Teams now require tools that deliver speed, reliability, and cross-browser coverage while maintaining clean, maintainable code. It is in this evolving context that the Playwright + TypeScript + Cucumber BDD combination has emerged as a revolutionary solution for end-to-end (E2E) test automation. This trio is not just another stack; it represents a strategic transformation in how automation frameworks are designed, implemented, and scaled. At Codoid Innovation, this combination has been successfully adopted to deliver smarter, faster, and more maintainable testing solutions. The synergy between Playwright’s multi-browser power, TypeScript’s strong typing, and Cucumber’s behavior-driven clarity allows teams to create frameworks that are both technically advanced and business-aligned.
In this comprehensive guide, both the “why” and the “how” will be explored, from understanding the future-proof nature of Playwright + TypeScript to implementing the full setup step-by-step and reviewing the measurable outcomes achieved through this modern approach.
The Evolution of Test Automation: From Legacy to Modern Frameworks
For many years, Selenium WebDriver dominated the automation landscape. While it laid the foundation for browser automation, its architecture has often struggled with modern web complexities such as dynamic content, asynchronous operations, and parallel execution.
Transitioning toward Playwright + TypeScript was therefore not just a technical choice, but a response to emerging testing challenges:
- Dynamic Web Apps: Modern SPAs (Single Page Applications) require smarter wait mechanisms.
- Cross-Browser Compatibility: QA teams must now validate across Chrome, Firefox, and Safari simultaneously.
- CI/CD Integration: Automation has become integral to every release pipeline.
- Scalability: Code maintainability is as vital as functional coverage.
These challenges are elegantly solved when Playwright, TypeScript, and Cucumber BDD are combined into a cohesive framework.
Why Playwright and TypeScript Are the Future of E2E Testing
Playwright’s Power
Developed by Microsoft, Playwright is a Node.js library that supports Chromium, WebKit, and Firefox, the three major browser engines. Unlike Selenium, Playwright offers:
- Built-in auto-wait for elements to be ready
- Native parallel test execution
- Network interception and mocking
- Testing of multi-tab and multi-context applications
- Support for headless and headed modes
Its API is designed to be fast, reliable, and compatible with modern JavaScript frameworks such as React, Angular, and Vue.
TypeScript’s Reliability
TypeScript, on the other hand, adds a layer of safety and structure to the codebase through static typing. When used with Playwright, it enables:
- Early detection of code-level errors
- Intelligent autocompletion in IDEs
- Better maintainability for large-scale projects
- Predictable execution with strict type checking
By adopting TypeScript, automation code evolves from being reactive to being proactive, preventing issues before they occur.
Cucumber BDD’s Business Readability
Cucumber uses Gherkin syntax to make tests understandable for everyone, not just developers. With lines like Given, When, and Then, both business analysts and QA engineers can collaborate seamlessly.
This approach ensures that test intent aligns with business value, a critical factor in agile environments.
The Ultimate Stack: Playwright + TypeScript + Cucumber BDD
| Sno |
Aspect |
Advantage |
| 1 |
Cross-Browser Execution |
Run on Chromium, WebKit, and Firefox seamlessly |
| 2 |
Type Safety |
TypeScript prevents runtime errors |
| 3 |
Test Readability |
Cucumber BDD enhances collaboration |
| 4 |
Speed |
Playwright runs tests in parallel and headless mode |
| 5 |
Scalability |
Modular design supports enterprise growth |
| 6 |
CI/CD Friendly |
Easy integration with Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and Azure |
Such a framework is built for the future, efficient for today’s testing challenges, yet adaptable for tomorrow’s innovations.
Step-by-Step Implementation: Building the Framework
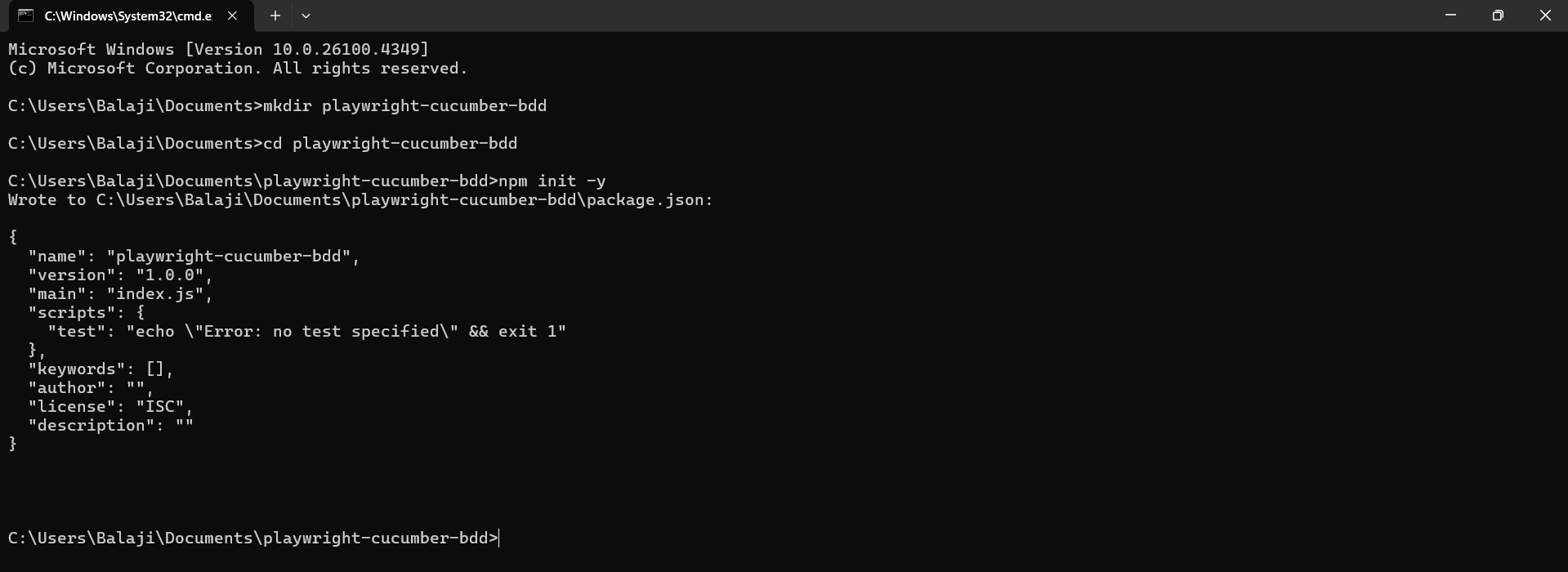
Step 1: Initialize the Project
mkdir playwright-cucumber-bdd
cd playwright-cucumber-bdd
npm init -y
This command creates a package.json file and prepares the environment for dependency installation.
Step 2: Install Required Dependencies
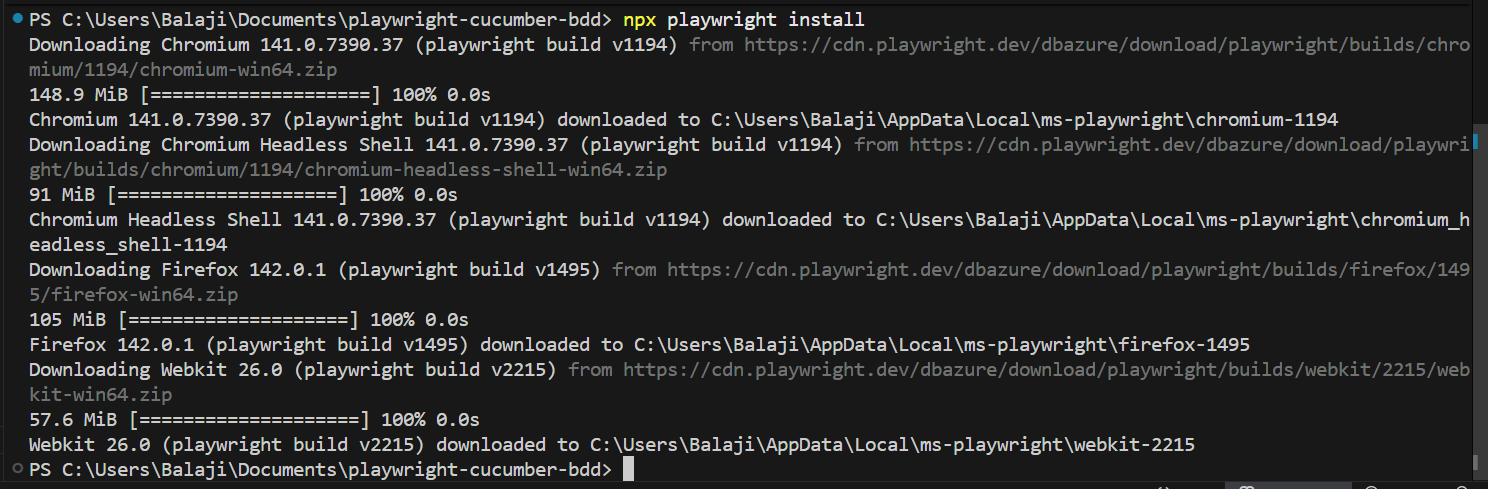
npm install playwright @cucumber/cucumber typescript ts-node @types/node --save-dev
npx playwright install
These libraries form the backbone of the framework.
Step 3: Organize Folder Structure
A clean directory layout enhances clarity and maintainability:
playwright-cucumber-bdd/
│
├── features/
│ ├── login.feature
│
├── steps/
│ ├── login.steps.ts
│
├── pages/
│ ├── login.page.ts
│
├── support/
│ ├── hooks.ts
│
├── tsconfig.json
└── cucumber.json
This modular layout ensures test scalability and easier debugging.
Step 4: Configure TypeScript
File: tsconfig.json
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ESNext",
"module": "commonjs",
"strict": true,
"esModuleInterop": true,
"moduleResolution": "node",
"outDir": "./dist",
"types": ["node", "@cucumber/cucumber"]
},
"include": ["steps/**/*.ts"]
}
This ensures strong typing, modern JavaScript features, and smooth compilation.
Step 5: Write the Feature File
File: features/login.feature
Feature: Login functionality
@Login
Scenario: Verify login and homepage load successfully
Given I navigate to the SauceDemo login page
When I login with username "standard_user" and password "secret_sauce"
Then I should see the products page
This test scenario defines the business intent clearly in natural language.
Step 6: Implement Step Definitions
File: steps/login.steps.ts
import { Given, When, Then } from "@cucumber/cucumber";
import { chromium, Browser, Page } from "playwright";
import { LoginPage } from "../pages/login.page";
import { HomePage } from "../pages/home.page";
let browser: Browser;
let page: Page;
let loginPage: LoginPage;
let homePage: HomePage;
Given('I navigate to the SauceDemo login page', async () => {
browser = await chromium.launch({ headless: false });
page = await browser.newPage();
loginPage = new LoginPage(page);
homePage = new HomePage(page);
await loginPage.navigate();
});
When('I login with username {string} and password {string}', async (username: string, password: string) => {
await loginPage.login(username, password);
});
Then('I should see the products page', async () => {
await homePage.verifyHomePageLoaded();
await browser.close();
});
These definitions bridge the gap between business logic and automation code.
Step 7: Define Page Objects
File: pages/login.page.ts
import { Page } from "playwright";
export class LoginPage {
private usernameInput = '#user-name';
private passwordInput = '#password';
private loginButton = '#login-button';
constructor(private page: Page) {}
async navigate() {
await this.page.goto('https://www.saucedemo.com/');
}
async login(username: string, password: string) {
await this.page.fill(this.usernameInput, username);
await this.page.fill(this.passwordInput, password);
await this.page.click(this.loginButton);
}
}
File: pages/home.page.ts
import { Page } from "playwright";
import { strict as assert } from "assert";
export class HomePage {
private inventoryContainer = '.inventory_list';
private titleText = '.title';
constructor(private page: Page) {}
async verifyHomePageLoaded() {
await this.page.waitForSelector(this.inventoryContainer);
const title = await this.page.textContent(this.titleText);
assert.equal(title, 'Products', 'Homepage did not load correctly');
}
}
This modular architecture supports reusability and clean code management.
Step 8: Configure Cucumber
File: cucumber.json
{
"default": {
"require": ["steps/**/*.ts", "support/hooks.ts"],
"requireModule": ["ts-node/register"],
"paths": ["features/**/*.feature"],
"format": ["progress"]
}
}
This configuration ensures smooth execution across all feature files.
Step 9: Add Hooks for Logging and Step Tracking
File: support/hooks.ts
(Refer to earlier code in your document, included verbatim here)
These hooks enhance observability and make debugging intuitive.
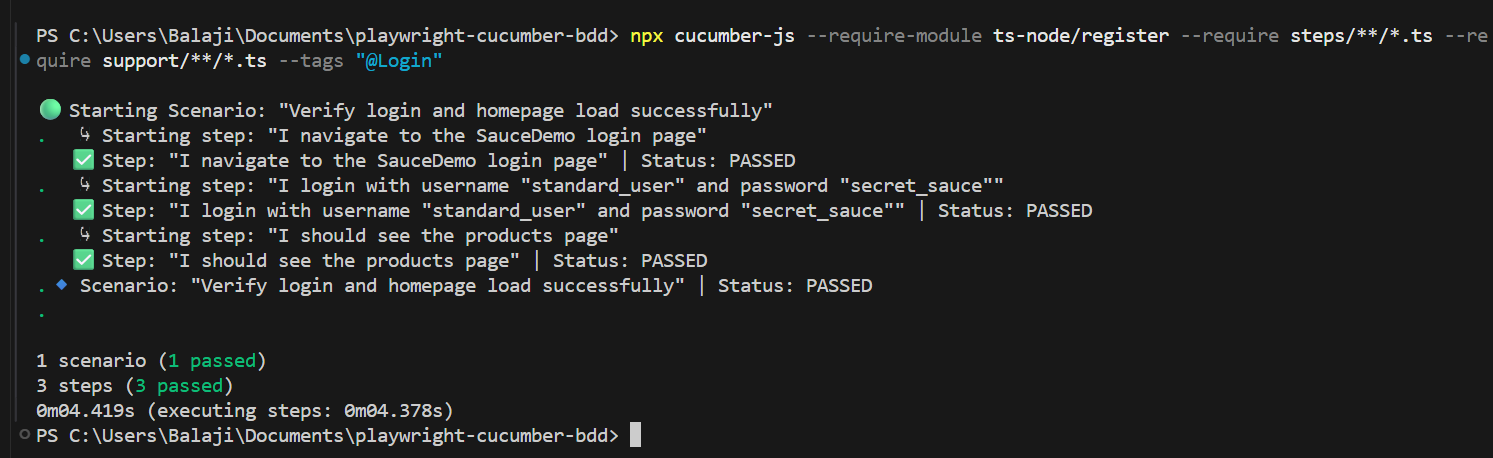
Step 10: Execute the Tests
npx cucumber-js --require-module ts-node/register --require steps/**/*.ts --require support/**/*.ts --tags "@Login"
Run the command to trigger your BDD scenario.
Before and After Outcomes: The Transformation in Action
At Codoid Innovation, teams that migrated from Selenium to Playwright + TypeScript observed measurable improvements:
| Sno |
Metric |
Before Migration (Legacy Stack) |
After Playwright + TypeScript Integration |
| 1 |
Test Execution Speed |
~12 min per suite |
~7 min per suite |
| 2 |
Test Stability |
65% pass rate |
95% consistent pass rate |
| 3 |
Maintenance Effort |
High |
Significantly reduced |
| 4 |
Code Readability |
Low (JavaScript) |
High (TypeScript typing) |
| 5 |
Collaboration |
Limited |
Improved via Cucumber BDD |
Best Practices for a Scalable Framework
- Maintain a modular Page Object Model (POM).
- Use TypeScript interfaces for data-driven testing.
- Run tests in parallel mode in CI/CD for faster feedback.
- Store test data externally to improve maintainability.
- Generate Allure or Extent Reports for actionable insights.
Conclusion
The combination of Playwright + TypeScript + Cucumber represents the future of end-to-end automation testing. It allows QA teams to test faster, communicate better, and maintain cleaner frameworks, all while aligning closely with business goals. At Codoid Innovation, this modern framework has empowered QA teams to achieve new levels of efficiency and reliability. By embracing this technology, organizations aren’t just catching up, they’re future-proofing their quality assurance process.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Is Playwright better than Selenium for enterprise testing?
Yes. Playwright’s auto-wait and parallel execution features drastically reduce flakiness and improve speed.
-
Why should TypeScript be used with Playwright?
TypeScript’s static typing minimizes errors, improves code readability, and makes large automation projects easier to maintain.
-
How does Cucumber enhance Playwright tests?
Cucumber enables human-readable test cases, allowing collaboration between business and technical stakeholders.
-
Can Playwright tests be integrated with CI/CD tools?
Yes. Playwright supports Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and Azure DevOps out of the box.
-
What’s the best structure for Playwright projects?
A modular folder hierarchy with features, steps, and pages ensures scalability and maintainability.

by Rajesh K | Oct 16, 2025 | Software Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
The question of how to balance API vs UI testing remains a central consideration in software quality assurance. This ongoing discussion is fueled by the distinct advantages each approach offers, with API testing often being celebrated for its speed and reliability, while UI testing is recognized as essential for validating the complete user experience. It is widely understood that a perfectly functional API does not guarantee a flawless user interface. This fundamental disconnect is why a strategic approach to test automation must be considered. For organizations operating in fast-paced environments, from growing tech hubs in India to global enterprise teams, the decision of where to invest testing effort has direct implications for release velocity and product quality. The following analysis will explore the characteristics of both testing methodologies, evaluate their respective strengths and limitations, and present a hybrid framework that is increasingly being adopted to maximize test coverage and efficiency.
What the Global QA Community Says: Wisdom from the Trenches
Before we dive into definitions, let’s ground ourselves in the real-world experiences shared by QA professionals globally. Specifically, the Reddit conversation provides a goldmine of practical insights into the API vs UI testing dilemma:
- On Speed and Reliability: “API testing is obviously faster and more reliable for pure logic testing,” one user stated, a sentiment echoed by many. This is the foundational advantage that hasn’t changed for years.
- On the Critical UI Gap: A crucial counterpoint was raised: “Retrieving the information you expect on the GET call does not guarantee that it’s being displayed as it should on the user interface.” In essence, this single sentence encapsulates the entire reason UI testing remains indispensable.
- On Practical Ratios: Perhaps the most actionable insight was the suggested split: “We typically do maybe 70% API coverage for business logic and 30% browser automation for critical user journeys.” Consequently, this 70/30 rule serves as a valuable heuristic for teams navigating the API vs UI testing decision.
- On Tooling Unification: A modern trend was also highlighted: “We test our APIs directly, but still do it in Playwright, browser less. Just use the axios library.” As a result, this move towards unified frameworks is a defining characteristic of the 2025 testing landscape.
With these real-world voices in mind, let’s break down the two approaches central to the API vs UI testing debate.
What is API Testing? The Engine of the Application
API (Application Programming Interface) testing involves sending direct requests to your application’s backend endpoints, be it REST, GraphQL, gRPC, or SOAP, and validating the responses. In other words, it’s about testing the business logic, data structures, and error handling without the overhead of a graphical user interface. This form of validation is foundational to modern software architecture, ensuring that the core computational engine of your application performs as expected under a wide variety of conditions.
In practice, this means:
- Sending a POST /login request with credentials and validating the 200 OK response and a JSON Web Token.
- Checking that a GET /users/123 returns a 404 Not Found for an invalid ID.
- Verifying that a PUT /orders/456 with malformed data returns a precise 422 Unprocessable Entity error.
- Stress-testing a payment gateway endpoint with high concurrent traffic to validate performance SLAs.
For teams practicing test automation in Hyderabad or Chennai, the speed of these tests is a critical advantage, allowing for rapid feedback within CI/CD pipelines. Thus, mastering API testing is a key competency for any serious automation engineer, enabling them to validate complex business rules with precision and efficiency that UI tests simply cannot match.
What is UI Testing? The User’s Mirror
On the other hand, UI testing, often called end-to-end (E2E) or browser automation, uses tools like Playwright, Selenium, or Cypress to simulate a real user’s interaction with the application. It controls a web browser, clicking buttons, filling forms, and validating what appears on the screen. This process is fundamentally about empathy—seeing the application through the user’s eyes and ensuring that the final presentation layer is not just functional but also intuitive and reliable.
This is where you catch the bugs your users would see:
- A “Submit” button that’s accidentally disabled due to a JavaScript error.
- A pricing calculation that works in the API but displays incorrectly due to a frontend typo.
- A checkout flow that breaks on the third step because of a misplaced CSS class.
- A responsive layout that completely breaks on a mobile device, even though all API calls are successful.
For a software testing service in Bangalore validating a complex fintech application, this UI testing provides non-negotiable, user-centric confidence that pure API testing cannot offer. It’s the final gatekeeper before the user experiences your product, catching issues that exist in the translation between data and design.
The In-Depth Breakdown: Pros, Cons, and Geographic Considerations
The Unmatched Advantages of API Testing
- Speed and Determinism: Firstly, API tests run in milliseconds, not seconds. They bypass the slowest part of the stack: the browser rendering engine. This is a universal benefit, but it’s especially critical for QA teams in India working with global clients across different time zones, where every minute saved in the CI pipeline accelerates the entire development cycle.
- Deep Business Logic Coverage: Additionally, you can easily test hundreds of input combinations, edge cases, and failure modes. This is invaluable for data-intensive applications in sectors like e-commerce and banking, which are booming in the Indian market. You can simulate scenarios that would be incredibly time-consuming to replicate through the UI.
- Resource Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness: No browser overhead means lower computational costs. For instance, for startups in Pune or Mumbai, watching their cloud bill, this efficiency directly impacts the bottom line. Running thousands of API tests in parallel is financially feasible, whereas doing the same with UI tests would require significant infrastructure investment.
Where API Tests Fall Short
However, the Reddit commenter was right: the perfect API response means nothing if the UI is broken. In particular, API tests are blind to:
- Visual regressions and layout shifts.
- JavaScript errors that break user interactivity.
- Performance issues with asset loading or client-side rendering.
- Accessibility issues that can only be detected by analyzing the rendered DOM.
The Critical Role of UI Testing
- End-to-End User Confidence: Conversely, there is no substitute for seeing the application work as a user would. This builds immense confidence before a production deployment, a concern for every enterprise QA team in Delhi or Gurgaon managing mission-critical applications. This holistic validation is what ultimately protects your brand’s reputation.
- Catching Cross-Browser Quirks: Moreover, the fragmented browser market in India, with a significant share of legacy and mobile browsers, makes cross-browser testing via UI testing a necessity, not a luxury. An application might work perfectly in Chrome but fail in Safari or on a specific mobile device.
The Well-Known Downsides of UI Testing
- Flakiness and Maintenance: As previously mentioned, the Reddit thread was full of lamentations about brittle tests. A simple CSS class change can break a dozen tests, leading to a high maintenance burden. This is often referred to as “test debt” and can consume a significant portion of a QA team’s bandwidth.
- Speed and Resource Use: Furthermore, spinning up multiple browsers is slow and resource-intensive. A comprehensive UI test suite can take hours to run, making it difficult to maintain the rapid feedback cycles that modern development practices demand.
The Business Impact: Quantifying the Cost of Getting It Wrong
To truly understand the stakes, it’s crucial to frame the API vs UI testing decision in terms of its direct business impact. The choice isn’t merely technical; it’s financial and strategic.
- The Cost of False Negatives: Over-reliance on flaky UI tests that frequently fail for non-critical reasons can lead to “alert fatigue.” Teams start ignoring failure notifications, and genuine bugs slip into production. The cost of a production bug can be 100x more expensive to fix than one caught during development.
- The Cost of Limited Coverage: Relying solely on API testing creates a false sense of security. A major UI bug that reaches users—such as a broken checkout flow on an e-commerce site during a peak sales period—can result in immediate revenue loss and long-term brand damage.
- The Cost of Inefficiency: Maintaining two separate, siloed testing frameworks for API and UI tests doubles the maintenance burden, increases tooling costs, and requires engineers to context-switch constantly. This inefficiency directly slows down release cycles and increases time-to-market.
Consequently, the hybrid model isn’t just a technical best practice; it’s a business imperative. It optimizes for both speed and coverage, minimizing both the direct costs of test maintenance and the indirect costs of software failures.
The Winning Hybrid Strategy for 2025: Blending the Best of Both
Ultimately, the API vs UI testing debate isn’t “either/or.” The most successful global teams use a hybrid, pragmatic approach. Here’s how to implement it, incorporating the community’s best ideas.
1. Embrace the 70/30 Coverage Rule
As suggested on Reddit, aim for roughly 70% of your test coverage via API tests and 30% via UI testing. This ratio is not dogmatic but serves as an excellent starting point for most web applications.
- The 70% (API): All business logic, data validation, CRUD operations, error codes, and performance benchmarks. This is your high-velocity, high-precision testing backbone.
- The 30% (UI): The “happy path” for your 3-5 most critical user journeys (e.g., User Signup, Product Purchase, Dashboard Load). This is your confidence-building, user-centric safety net.
2. Implement API-Assisted UI Testing
This is a game-changer for efficiency. Specifically, use API calls to handle the setup and teardown of your UI tests. This advanced testing approach, perfected by Codoid’s automation engineers, dramatically cuts test execution time while making tests significantly more reliable and less prone to failure.
Example: Testing a Multi-Step Loan Application
Instead of using the UI to navigate through a lengthy loan application form multiple times, you can use APIs to pre-populate the application state.
// test-loan-application.spec.js
import { test, expect } from '@playwright/test';
test('complete loan application flow', async ({ page, request }) => {
// API SETUP: Create a user and start a loan application via API
const apiContext = await request.newContext();
const loginResponse = await apiContext.post('https://api.finance-app.com/auth/login', {
data: { username: 'testuser', password: 'testpass' }
});
const authToken = (await loginResponse.json()).token;
// Use the token to pre-fill the first two steps of the application via API
await apiContext.post('https://api.finance-app.com/loan/application', {
headers: { 'Authorization': `Bearer ${authToken}` },
data: {
step1: { loanAmount: 50000, purpose: 'home_renovation' },
step2: { employmentStatus: 'employed', annualIncome: 75000 }
}
});
// Now, start the UI test from the third step where user input is most critical
await page.goto('https://finance-app.com/loan/application?step=3');
// Fill in the final details and submit via UI
await page.fill('input[name="phoneNumber"]', '9876543210');
await page.click('text=Submit Application');
// Validate the success message appears in the UI
await expect(page.locator('text=Application Submitted Successfully')).toBeVisible();
});
This pattern slashes test execution time and drastically reduces flakiness, a technique now standard for high-performing teams engaged in the API vs UI testing debate.
3. Adopt a Unified Framework like Playwright
The Reddit user who mentioned using “Playwright, browserless” identified a key 2025 trend. In fact, modern frameworks like Playwright allow you to write both API and UI tests in the same project, language, and runner.
Benefits for a Distributed Team:
- Reduced Context Switching: As a result, engineers don’t need to juggle different tools for API vs UI testing.
- Shared Logic: For example, authentication helpers, data fixtures, and environment configurations can be shared.
- Consistent Reporting: Get a single, unified view of your test health across both API and UI layers.
The 2025 Landscape: What’s New and Why It Matters Now
Looking ahead, the tools and techniques are evolving, making this hybrid approach to API vs UI testing more powerful than ever.
- AI-Powered Test Maintenance: Currently, tools are now using AI to auto-heal broken locators in UI tests. When a CSS selector changes, the AI can suggest a new, more stable one, mitigating the primary pain point of UI testing. This technology is rapidly moving from experimental to mainstream, promising to significantly reduce the maintenance burden that has long plagued UI automation.
- API Test Carving: Similarly, advanced techniques can now monitor UI interactions and automatically “carve out” the underlying API calls, generating a suite of API tests from user behavior. This helps ensure your API coverage aligns perfectly with actual application use and can dramatically accelerate the creation of a comprehensive API test suite.
- Shift-Left and Continuous Testing: Furthermore, API tests are now integrated into the earliest stages of development. For Indian tech hubs serving global clients, this “shift-left” mentality is crucial for competing on quality and speed within the broader context of test automation in 2025. Developers are increasingly writing API tests as part of their feature development, with QA focusing on complex integration scenarios and UI flows.
Building a Future-Proof QA Career in the Era of Hybrid Testing
For individual engineers, the API vs UI testing discussion has direct implications for skill development and career growth. The market no longer values specialists in only one area; the most sought-after professionals are those who can navigate the entire testing spectrum.
The most valuable skills in 2025 include:
- API Testing Expertise: Deep knowledge of REST, GraphQL, authentication mechanisms, and performance testing at the API level.
- Modern UI Testing Frameworks: Proficiency with tools like Playwright or Cypress that support reliable, cross-browser testing.
- Programming Proficiency: The ability to write clean, maintainable code in languages like JavaScript, TypeScript, or Python to create robust automation frameworks.
- Performance Analysis: Understanding how to measure and analyze the performance impact of both API and UI changes.
- CI/CD Integration: Skills in integrating both API and UI tests into continuous integration pipelines for rapid feedback.
In essence, the most successful QA professionals are those who refuse to be pigeonholed into the API vs UI testing dichotomy and instead master the art of strategically applying both.
Challenges & Pitfalls: A Practical Guide to Navigation
Despite the clear advantages, implementing a hybrid strategy comes with its own set of challenges. Being aware of these pitfalls is the first step toward mitigating them.
| S. No |
Challenge |
Impact |
Mitigation Strategy |
| 1 |
Flaky UI Tests |
Erodes team confidence, wastes investigation time |
Erodes team confidence, wastes investigation time
Implement robust waiting strategies, use reliable locators, quarantine flaky tests |
| 2 |
Test Data Management |
Inconsistent test results, false positives/failures |
Use API-based test data setup, ensure proper isolation between tests |
| 3 |
Overlapping Coverage |
Wasted effort, increased maintenance |
Clearly define the responsibility of each test layer; API for logic, UI for E2E flow |
| 4 |
Tooling Fragmentation |
High learning curve, maintenance overhead |
Adopt a unified framework like Playwright that supports both API and UI testing |
| 5 |
CI/CD Pipeline Complexity |
Slow feedback, resource conflicts |
Parallelize test execution, run API tests before UI tests, use scalable infrastructure |
Conclusion
In conclusion, the conversation on Reddit didn’t end with a winner. It ended with a consensus: the most effective QA teams are those that strategically blend both methodologies. The hybrid testing strategy is the definitive answer to the API vs UI testing question.
Your action plan for 2025:
- Audit Your Tests: Categorize your existing tests. How many are pure API? How many are pure UI? Is there overlap?
- Apply the 70/30 Heuristic: Therefore, strategically shift logic-level validation to API tests. Reserve UI tests for critical, user-facing journeys.
- Unify Your Tooling: Evaluate a framework like Playwright that can handle both your API and UI testing needs, simplifying your stack and empowering your team.
- Implement API-Assisted Setup: Immediately refactor your slowest UI tests to use API calls for setup, and watch your pipeline times drop.
Finally, the goal is not to pit API testing against UI testing. The goal is to create a resilient, efficient, and user-confident testing strategy that allows your team, whether you’re in Bengaluru or Boston, to deliver quality at speed. The future belongs to those who can master the balance, not those who rigidly choose one side of a false dichotomy.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the main difference between API and UI testing?
API testing focuses on verifying the application's business logic, data responses, and performance by directly interacting with backend endpoints. UI testing validates the user experience by simulating real user interactions with the application's graphical interface in a browser.
-
Which is more important for my team in 2025, API or UI testing?
Neither is universally "more important." The most effective strategy is a hybrid approach. The blog recommends a 70/30 split, with 70% of coverage dedicated to API tests for business logic and 30% to UI tests for critical user journeys, ensuring both speed and user-centric validation.
-
Why are UI tests often considered "flaky"?
UI tests are prone to flakiness because they depend on the stability of the frontend code (HTML, CSS, JavaScript). Small changes like a modified CSS class can break selectors, and tests can be affected by timing issues, network latency, or browser quirks, leading to inconsistent results.
-
What is "API-Assisted UI Testing"?
This is an advanced technique where API calls are used to set up the application's state (e.g., logging in a user, pre-filling form data) before executing the UI test. This dramatically reduces test execution time and minimizes flakiness by bypassing lengthy UI steps.
-
Can one tool handle both API and UI testing?
Yes, modern frameworks like Playwright allow you to write both API and UI tests within the same project. This unification reduces context-switching for engineers, enables shared logic (like authentication), and provides consistent reporting.

by Rajesh K | Oct 7, 2025 | AI Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
For years, the promise of test automation has been quietly undermined by a relentless reality: the burden of maintenance. As a result, countless hours are spent by engineering teams not on building new features or creative test scenarios, but instead on a frustrating cycle of fixing broken selectors after every minor UI update. In fact, it is estimated that up to 40% of test maintenance effort is consumed solely by this tedious task. Consequently, this is often experienced as a silent tax on productivity and a drain on team morale. This is precisely the kind of challenge that the Stagehand framework was built to overcome. But what if a different approach was taken? For instance, what if the browser could be spoken to not in the complex language of selectors, but rather in the simple language of human intent?
Thankfully, this shift is no longer a theoretical future. On the contrary, it is being delivered today by Stagehand, an AI-powered browser automation framework that is widely considered the most significant evolution in testing technology in a decade. In the following sections, a deep dive will be taken into how Stagehand is redefining automation, how it works behind the scenes, and how it can be practically integrated into a modern testing strategy with compelling code examples.
The Universal Pain Point: Why the Old Way is Felt by Everyone
To understand the revolution, the problem must first be appreciated. Let’s consider a common login test. In a robust traditional framework like Playwright, it is typically written as follows:
// Traditional Playwright Script - Fragile and Verbose
const { test, expect } = require('@playwright/test');
test('user login', async ({ page }) => {
await page.goto("https://example.com/login");
// These selectors are a single point of failure
await page.fill('input[name="email"]', '[email protected]');
await page.fill('input[data-qa="password-input"]', 'MyStrongPassword!');
await page.click('button#login-btn.submit-button');
await page.waitForURL('**/dashboard');
// Assertion also relies on a specific selector
const welcomeMessage = await page.textContent('.user-greeting');
expect(welcomeMessage).toContain('Welcome, Test User');
});
While effective in a controlled environment, this script is inherently fragile in a dynamic development lifecycle. Consequently, when a developer changes an attribute or a designer tweaks a class, the test suite is broken. As a result, automated alerts are triggered, and valuable engineering time is redirected from development to diagnostic maintenance. In essence, this cycle is not just inefficient; it is fundamentally at odds with the goal of rapid, high-quality software delivery.
It is precisely this core problem that is being solved by Stagehand, where rigid, implementation-dependent selectors are replaced with intuitive, semantic understanding.
What is Stagehand? A New Conversation with the Browser
At its heart, Stagehand is an AI-powered browser automation framework that is built upon the reliable foundation of Playwright. Essentially, its revolutionary premise is simple: the browser can be controlled using natural language instructions. In practice, it is designed for both developers and AI agents, seamlessly blending the predictability of code with the adaptability of AI.
For comparison, the same login test is reimagined with Stagehand as shown below:
import asyncio
from stagehand import Stagehand, StagehandConfig
async def run_stagehand_local():
config = StagehandConfig(
env="LOCAL",
model_name="ollama/mistral",
model_client_options={"provider": "ollama"},
headless=False
)
stagehand = Stagehand(config=config)
await stagehand.init()
page = stagehand.page
await page.act("Go to https://the-internet.herokuapp.com/login")
await page.act("Enter 'tomsmith' in the Username field")
await page.act("Enter 'SuperSecretPassword!' in the Password field")
await page.act("Click the Login button and wait for the Secure Area page to appear")
title = await page.title()
print("Login successful" if "Secure Area" in title else "Login failed")
await stagehand.close()
asyncio.run(run_stagehand_local())
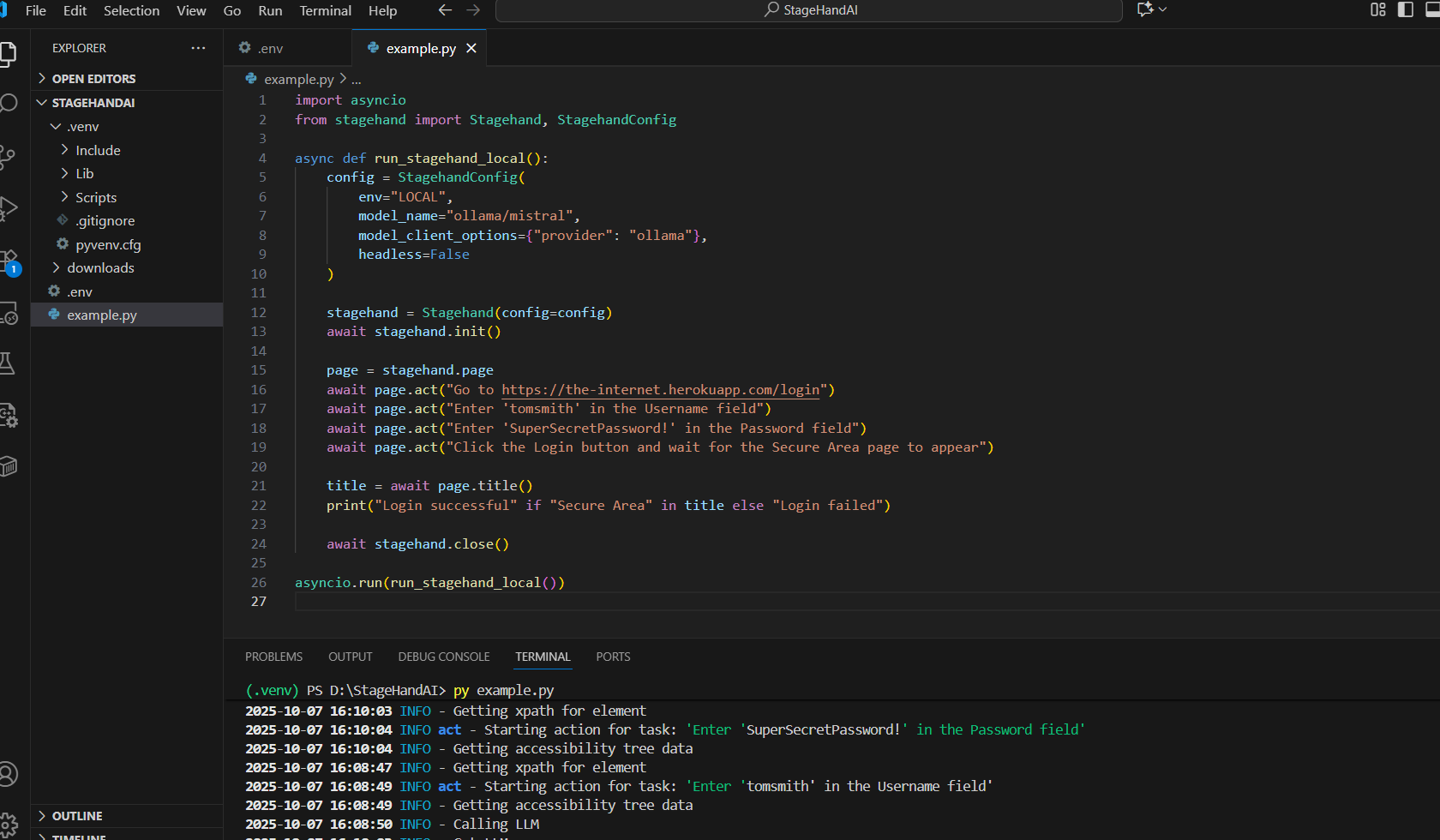
The difference is immediately apparent. Specifically, the test is transformed from a low-level technical script into a human-readable narrative. Therefore, tests become:
- More Readable: What is being tested can be understood by anyone, from a product manager to a new intern, without technical translation.
- More Resilient: Elements are interacted with based on their purpose and label, not a brittle selector, thereby allowing them to withstand many front-end changes.
- Faster to Write: Less time is spent hunting for selectors, and more time is invested in defining meaningful user behaviors and acceptance criteria.
Behind the Curtain: The Intelligent Three-Layer Engine
Of course, this capability is not magic; on the contrary, it is made possible by a sophisticated three-layer AI engine:
- Instruction Understanding & Parsing: Initially, the natural language command is parsed by an AI model. Subsequently, the intent is identified, and key entities’ actions, targets, and data are broken down into atomic, executable steps.
- Semantic DOM Mapping & Analysis: Following this, the webpage is scanned, and a semantic map of all interactive elements is built. In other words, elements are understood by their context, labels, and relationships, not just their HTML tags.
- Adaptive Action Execution & Validation: Finally, the action is intelligently executed. Additionally, built-in waits and retries are included, and the action is validated to ensure the expected outcome was achieved.
A Practical Journey: Implementing Stagehand in Real-World Scenarios
Installation and Setup
Firstly, Stagehand must be installed. Fortunately, the process is straightforward, especially for teams already within the Python ecosystem.
# Install Stagehand via pip for Python
pip install stagehand
# Playwright dependencies are also required
pip install playwright
playwright install
Real-World Example: An End-to-End E-Commerce Workflow
Now, let’s consider a user journey through an e-commerce site: searching for a product, filtering, and adding it to the cart. This workflow can be automated with the following script:
import asyncio
from stagehand import Stagehand
async def ecommerce_test():
browser = await Stagehand.launch(headless=False)
page = await browser.new_page()
try:
print("Starting e-commerce test flow...")
# 1. Navigate to the store
await page.act("Go to https://example-store.com")
# 2. Search for a product
await page.act("Type 'wireless headphones' into the search bar and press Enter")
# 3. Apply a filter
await page.act("Filter the results by brand 'Sony'")
# 4. Select a product
await page.act("Click on the first product in the search results")
# 5. Add to cart
await page.act("Click the 'Add to Cart' button")
# 6. Verify success
await page.act("Go to the shopping cart")
page_text = await page.text_content("body")
if "sony" in page_text.lower() and "wireless headphones" in page_text.lower():
print("TEST PASSED: Correct product successfully added to cart.")
else:
print("TEST FAILED: Product not found in cart.")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Test execution failed: {e}")
finally:
await browser.close()
asyncio.run(ecommerce_test())
This script demonstrates remarkable resilience. For instance, if the “Add to Cart” button is redesigned, the AI’s semantic understanding allows the correct element to still be found and clicked. As a result, this adaptability is a game-changer for teams dealing with continuous deployment and evolving UI libraries.
Weaving Stagehand into the Professional Workflow
It is important to note that Stagehand is not meant to replace existing testing frameworks. Instead, it is designed to enhance them. Therefore, it can be seamlessly woven into a professional setup, combining the structure of traditional frameworks with the adaptability of AI.
Example: A Structured Test with Pytest
For example, Stagehand can be integrated within a Pytest structure for organized and reportable tests.
# test_stagehand_integration.py
import pytest
import asyncio
from stagehand import Stagehand
@pytest.fixture(scope="function")
async def browser_setup():
browser = await Stagehand.launch(headless=True)
yield browser
await browser.close()
@pytest.mark.asyncio
async def test_user_checkout(browser_setup):
page = await browser_setup.new_page()
# Test Steps are written as a user story
await page.act("Navigate to the demo store login page")
await page.act("Log in with username 'test_user'")
await page.act("Search for 'blue jeans' and select the first result")
await page.act("Select size 'Medium' and add it to the cart")
await page.act("Proceed to checkout and fill in shipping details")
await page.act("Enter test payment details and place the order")
# Verification
confirmation_text = await page.text_content("body")
assert "order confirmed" in confirmation_text.lower()
This approach, often called Intent-Driven Automation, focuses on the what rather than the how. Consequently, tests become more valuable as living documentation and are more resilient to the underlying code changes.
The Strategic Imperative: Weighing the Investment
Given these advantages, adopting a new technology is a strategic decision. Therefore, the advantages offered by Stagehand must be clearly understood.
A Comparative Perspective
| Aspect |
Traditional Automation |
Stagehand AI Automation |
Business Impact |
| Locator Dependency |
High – breaks on UI changes. |
None – adapts to changes. |
Reduced maintenance costs & faster releases. |
| Code Verbosity |
High – repetitive selectors. |
Minimal – concise language. |
Faster test creation. |
| Maintenance Overhead |
High – “test debt” accumulates. |
Low – more stable over time. |
Engineers focus on innovation. |
| Learning Curve |
Steep – requires technical depth. |
Gentle – plain English is used. |
Broader team contribution. |
The Horizon: What Comes Next?
Furthermore, Stagehand is just the beginning. Looking ahead, the future of QA is being shaped by AI, leading us toward:
- Self-Healing Tests: Scripts that can adjust themselves when failures are detected.
- Intelligent Test Generation: Critical test paths are suggested by AI based on analysis of the application.
- Context-Aware Validation: Visual and functional changes are understood in context, distinguishing bugs from enhancements.
Ultimately, these tools will not replace testers but instead will empower them to focus on higher-value activities like complex integration testing and user experience validation.
Conclusion: From Maintenance to Strategic Innovation
In conclusion, Stagehand is recognized as more than a tool; in fact, it is a fundamental shift in the philosophy of test automation. By leveraging its power, the gap between human intention and machine execution is being bridged, thereby allowing test suites to be built that are not only more robust but also more aligned with the way we naturally think about software. The initial setup is straightforward, and the potential for reducing technical debt is profound. Therefore, by integrating Stagehand, a team is not just adopting a new library,it is investing in a future where tests are considered valuable, stable assets that support rapid innovation rather than hindering it.
In summary, the era of struggling with selectors is being left behind. Meanwhile, the era of describing behavior and intent has confidently arrived.
Is your team ready to be transformed?
The first step is easily taken: pip install stagehand. From there, a new, more collaborative, and more efficient chapter in test automation can be begun.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
How do I start a browser automation project with Stagehand?
Getting started with Stagehand is easy. You can set up a new project with the command npx create-browser-app. This command makes the basic structure and adds the necessary dependencies. If you want advanced features or want to use it for production, you will need an api key from Browserbase. The api key helps you connect to a cloud browser with browserbase.
-
What makes Stagehand different from other browser automation tools?
Stagehand is different because it uses AI in every part of its design. It is not like old automation tools. You can give commands with natural language, and it gives clear results. This tool works within a modern AI browser automation framework and can be used with other tools. The big feature is that it lets you watch and check prompts. You can also replay sessions. All of this happens with its link to Browserbase.
-
Is there a difference between Stagehand and Stagehand-python?
Yes, there is a simple difference here. Stagehand is the main browser automation framework. Stagehand-python is the official software development kit in Python. It is made so you can use Python to interact with the main Stagehand framework. With Stagehand-python, people who work with Python can write browser automation scripts in just a few lines of code. This lets them use all the good features that Stagehand offers for browser automation.
by Rajesh K | Sep 28, 2025 | Artificial Intelligence, Blog, Latest Post |
Imagine being asked to test a computer that doesn’t always give you the same answer twice, even when you ask the same question. That, in many ways, is the daily reality when testing Quantum AI. Quantum AI is transforming industries like finance, healthcare, and logistics. It promises drug discovery breakthroughs, smarter trading strategies, and more efficient supply chains. But here’s the catch: all of this potential comes wrapped in uncertainty. Results can shift because qubits behave in ways that don’t always align with our classical logic.
For testers, this is both daunting and thrilling. Our job is not just to validate functionality but to build trust in systems that behave unpredictably. In this blog, we’ll walk through the different types of Quantum AI and explore how testing adapts to this strange but exciting new world.
Highlights of this blog:
- Quantum AI blends quantum mechanics and artificial intelligence, making systems faster and more powerful than classical AI.
- Unlike classical systems, results in Quantum AI are probabilistic, so testers validate probability ranges instead of exact outputs.
- The main types are Quantum Machine Learning, Quantum-Native Algorithms, and Hybrid Models, each requiring unique testing approaches.
- Noise and error correction are critical challenges—testers must ensure resilience and stability in real-world environments.
- Applications span finance, healthcare, and logistics, where trust, accuracy, and reproducibility are vital.
- Hybrid systems let industries use Quantum AI today, but testers must focus on integration, security, and reliability.
- Ultimately, testers ensure that Quantum AI is not just powerful but also credible, consistent, and ready for real-world adoption.
Understanding Quantum AI
To test Quantum AI effectively, you must first understand what makes it different. Traditional computers use bits, which can be either 0 or 1. Quantum computers, on the other hand, use qubits. Thanks to the principles of superposition and entanglement, qubits can be 0, 1, or both at the same time.
From a testing perspective, this has huge implications. Instead of simply checking whether the answer is “correct,” we need to check whether the answer falls within an expected probability distribution. For example, if a system is supposed to return 70% “yes” and 30% “no,” we need to validate that distribution across many runs.
This is a completely different mindset from classical testing. It forces us to ask: how do we define correctness in a probabilistic world?
Defining Quantum AI Concepts for Testers
Superposition and Test Design
Superposition means that qubits can hold multiple states at once. For testers, this translates to designing test cases that validate consistency across probability ranges rather than exact outputs.
Entanglement and Integration Testing
Entangled qubits remain connected even when separated. If one qubit changes, the other responds instantly. Testers need to check that entangled states remain stable across workloads and integrations. Otherwise, results may drift unexpectedly.
Noise and Error Correction
Quantum AI is fragile. Qubits are easily disrupted by environmental “noise.” Testers must therefore validate whether error-correction techniques work under real-world conditions. Stress testing becomes less about load and more about resilience in noisy environments.
How Quantum AI Differs from Classical AI – QA Viewpoint
In classical AI testing, we typically focus on:
- Accuracy of predictions
- Performance under load
- Security and compliance
With Quantum AI, these remain important, but we add new layers:
- Non-determinism: Results may vary from run to run.
- Hardware dependency: Noise levels in qubits can impact accuracy.
- Scalability challenges: Adding more qubits increases complexity exponentially.
This means that testers need new strategies and tools. Instead of asking, “Is this answer correct?” we ask, “Is this answer correct often enough, and within an acceptable margin of error?”
Core Types of Quantum AI
1. Quantum Machine Learning (QML)
Quantum Machine Learning applies quantum principles to enhance traditional machine learning models. For instance, quantum neural networks can analyze larger datasets faster by leveraging qubit superposition.
Tester’s Focus in QML:
- Training Validation: Do quantum-enhanced models actually converge faster and more accurately?
- Dataset Integrity: Does mapping classical data into quantum states preserve meaning?
- Pattern Recognition: Are the patterns identified by QML models consistent across test datasets?
Humanized Example: Imagine training a facial recognition system. A classical model might take days to train, but QML could reduce that to hours. As testers, we must ensure that the speed doesn’t come at the cost of misidentifying faces.
2. Quantum-Native Algorithms
Unlike QML, which adapts classical models, quantum-native algorithms are built specifically for quantum systems. Examples include Grover’s algorithm for search and Shor’s algorithm for factorization.
Tester’s Focus in Quantum Algorithms:
- Correctness Testing: Since results are probabilistic, we run tests multiple times to measure statistical accuracy.
- Scalability Checks: Does the algorithm maintain performance as more qubits are added?
- Noise Tolerance: Can it deliver acceptable results even in imperfect hardware conditions?
Humanized Example: Think of Grover’s algorithm like searching for a needle in a haystack. Normally, you’d check each piece of hay one by one. Grover’s algorithm helps you check faster, but as testers, we need to confirm that the “needle” found is indeed the right one, not just noise disguised as success.
3. Hybrid Quantum-Classical Models
Because we don’t yet have large, error-free quantum computers, most real-world applications use hybrid models—a blend of classical and quantum systems.
Tester’s Focus on Hybrid Systems:
- Integration Testing: Are data transfers between classical and quantum components seamless?
- Latency Testing: Is the handoff efficient, or do bottlenecks emerge?
- Security Testing: Are cloud-based quantum services secure and compliant?
- End-to-End Validation: Does the hybrid approach genuinely improve results compared to classical-only methods?
Humanized Example: Picture a logistics company. The classical system schedules trucks, while the quantum processor finds the best delivery routes. Testers need to ensure that these two systems talk to each other smoothly and don’t deliver conflicting outcomes.
Applications of Quantum AI – A QA Perspective
Finance
In trading and risk management, accuracy is everything. Testers must ensure that quantum-driven insights don’t just run faster but also meet regulatory standards. For example, if a quantum model predicts market shifts, testers validate whether those predictions hold across historical datasets.
Healthcare
In drug discovery, Quantum AI can simulate molecules at atomic levels. However, testers must ensure that results are reproducible. In personalized medicine, fairness testing becomes essential—do quantum models provide accurate recommendations for diverse populations?
Logistics
Quantum AI optimizes supply chains, but QA must confirm scalability. Can the model handle global datasets? Can it adapt when delivery routes are disrupted? Testing here involves resilience under dynamic conditions.
Leading Innovators in Quantum AI – And What Testers Should Know
- Google Quantum AI: Pioneering processors and quantum algorithms. Testers focus on validating hardware-software integration.
- IBM Quantum: Offers quantum systems via the cloud. Testers must assess latency and multi-tenant security.
- SAS: Developing hybrid quantum-classical tools. Testers validate enterprise compatibility.
- D-Wave: Specializes in optimization problems. Testers validate real-world reliability.
Universities and Research Labs also play a key role, and testers working alongside these groups often serve as the bridge between theory and practical reliability.
Strengths and Limitations of Hybrid Systems – QA Lens
Strengths:
- Allow industries to adopt Quantum AI without waiting for perfect hardware.
- Let testers practice real-world validation today.
- Combine the best of both classical and quantum systems.
Limitations:
- Integration is complex and error-prone.
- Noise in quantum hardware still limits accuracy.
- Security risks emerge when relying on third-party quantum cloud providers.
From a QA standpoint, hybrid systems are both an opportunity and a challenge. They give us something to test now, but they also highlight the imperfections we must manage.
Expanding the QA Framework for Quantum AI
Testing Quantum AI requires rethinking traditional QA strategies:
- Probabilistic Testing: Accepting that results may vary, so validation is based on statistical confidence levels.
- Resilience Testing: Stress-testing quantum systems against noise and instability.
- Comparative Benchmarking: Always comparing quantum results to classical baselines to confirm real benefits.
- Simulation Testing: Using quantum simulators on classical machines to test logic before deploying on fragile quantum hardware.
Challenges for Testers in Quantum AI
- Tool Gaps: Few standardized QA tools exist for quantum systems.
- Result Variability: Harder to reproduce results consistently.
- Interdisciplinary Knowledge: Testers must understand both QA principles and quantum mechanics.
- Scalability Risks: As qubits scale, so does the complexity of testing.
Conclusion
Quantum AI is often hailed as revolutionary, but revolutions don’t succeed without trust. That’s where testers come in. We are the guardians of reliability in a world of uncertainty. Whether it’s validating quantum machine learning models, probing quantum-native algorithms, or ensuring hybrid systems run smoothly, testers make sure Quantum AI delivers on its promises.
As hardware improves and algorithms mature, testing will evolve too. New frameworks, probabilistic testing methods, and resilience checks will become the norm. The bottom line is simple: Quantum AI may redefine computing, but testers will define its credibility.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What’s the biggest QA challenge in Quantum AI?
Managing noise and non-deterministic results while still ensuring accuracy and reproducibility.
-
How can testers access Quantum AI platforms?
By using cloud-based platforms from IBM, Google, and D-Wave to run tests on actual quantum hardware.
-
How does QA add value to Quantum AI innovation?
QA ensures correctness, validates performance, and builds the trust required for Quantum AI adoption in sensitive industries like finance and healthcare.

by Rajesh K | Sep 25, 2025 | Software Testing, Blog, Latest Post |
Blockchain technology has emerged as one of the most transformative innovations of the past decade, impacting industries such as finance, healthcare, supply chain, insurance, and even gaming. Unlike conventional applications, blockchain systems are built on decentralization, transparency, and immutability. These properties create trust between participants but also make software testing significantly more complex and mission-critical. Consider this: A small bug in a mobile app might cause inconvenience, but a flaw in a blockchain application could lead to irreversible financial loss, regulatory penalties, or reputational damage. The infamous DAO hack in 2016 is a classic example of an exploit in a smart contract that drained nearly $50 million worth of Ether, shaking the entire Ethereum ecosystem. Such incidents highlight why blockchain testing is not optional; it is the backbone of security, trust, and adoption.
As more enterprises adopt blockchain to handle sensitive data, digital assets, and business-critical workflows, QA engineers and developers must adapt their testing strategies. Unlike traditional testing, blockchain QA requires validating distributed consensus, immutable ledgers, and on-chain smart contracts, all while ensuring performance and scalability.
In this blog, we’ll explore the unique challenges, methodologies, tools, vulnerabilities, and best practices in blockchain testing. We’ll also dive into real-world risks, emerging trends, and a roadmap for QA teams to ensure blockchain systems are reliable, secure, and future-ready.
- Blockchain testing is essential to guarantee the security, performance, and reliability of decentralized applications (dApps).
- Unique challenges such as decentralization, immutability, and consensus mechanisms make blockchain testing more complex than traditional software testing.
- Effective testing strategies must combine functional, security, performance, and scalability testing for complete coverage.
- Smart contract testing requires specialized tools and methodologies since vulnerabilities are permanent once deployed.
- A structured blockchain testing plan not only ensures resilience but also builds trust among users.
Understanding Blockchain Application Testing
At its core, blockchain application testing is about validating whether blockchain-based systems are secure, functional, and efficient. But unlike traditional applications, where QA focuses mainly on UI, API, and backend systems, blockchain testing requires additional dimensions:
- Transaction validation – Ensuring correctness and irreversibility.
- Consensus performance – Confirming that nodes agree on the same state.
- Smart contract accuracy – Validating business logic encoded into immutable contracts.
- Ledger synchronization – Guaranteeing consistency across distributed nodes.
For example, in a fintech dApp, every transfer must not only update balances correctly but also synchronize across multiple nodes instantly. Even a single mismatch could undermine trust in the entire system. This makes end-to-end testing mandatory rather than optional.
What Makes Blockchain Testing Unique?
Traditional QA practices are insufficient for blockchain because of its fundamental differences:
- Decentralization – Multiple independent nodes must reach consensus, unlike centralized apps with a single authority.
- Immutability – Data, once written, cannot be rolled back. Testing must catch every flaw before deployment.
- Smart Contracts – Logic executed directly on-chain. Errors can lock or drain funds permanently.
- Consensus Mechanisms – Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, and Byzantine Fault Tolerance must be stress-tested against malicious attacks and scalability issues.
For example, while testing a banking application, a failed transaction can simply be rolled back in a traditional system. In blockchain, the ledger is final, meaning a QA miss could result in lost assets for thousands of users. This makes blockchain testing not just technical but also financially and legally critical.
Key Differences from Traditional Software Testing
| S. No |
Traditional Testing |
Blockchain Testing |
| 1 |
Centralized systems with one authority |
Decentralized, multi-node networks |
| 2 |
Data can be rolled back or altered |
Immutable ledger, no rollback |
| 3 |
Focus on UI, APIs, and databases |
Includes smart contracts, consensus, and tokens |
| 4 |
Regression testing is straightforward |
Requires adversarial, network-wide tests |
The table highlights why QA teams must go beyond standard skills and develop specialized blockchain expertise.
Core Components in Blockchain Testing
Blockchain testing typically validates three critical layers:
- Distributed Ledger – Ensures ledger synchronization, transaction finality, and fault tolerance.
- Smart Contracts – Verifies correctness, resilience, and security of on-chain code.
- Token & Asset Management – Tests issuance, transfers, double-spend prevention, and compliance with standards like ERC-20, ERC-721, and ERC-1155.
Testing across these layers ensures both infrastructure stability and business logic reliability.
Building a Blockchain Testing Plan
A structured blockchain testing plan should cover:
- Clear Objectives – Security, scalability, or functional correctness.
- Test Environments – Testnets like Ethereum Sepolia or private setups like Ganache.
- Tool Selection – Frameworks (Truffle, Hardhat), auditing tools (Slither, MythX), and performance tools (Caliper, JMeter).
- Exit Criteria – No critical vulnerabilities, 100% smart contract coverage, and acceptable TPS benchmarks.
Types of Blockchain Application Testing
1. Functional Testing
Verifies that wallets, transactions, and block creation follow the expected logic. For example, ensuring that token transfers correctly update balances across all nodes.
2. Security Testing
Detects vulnerabilities like:
- Reentrancy attacks (e.g., DAO hack)
- Integer overflows/underflows
- Sybil or 51% attacks
- Data leakage risks
Security testing is arguably the most critical part of blockchain QA.
3. Performance & Scalability Testing
Evaluates throughput, latency, and network behavior under load. For example, Ethereum’s network congestion in 2017 during CryptoKitties highlighted the importance of stress testing.
4. Smart Contract Testing
Includes unit testing, fuzzing, and even formal verification of contract logic. Since contracts are immutable once deployed, QA teams must ensure near-perfect accuracy.
Common Smart Contract Bugs
- Reentrancy Attacks – Attackers repeatedly call back into a contract before state changes are finalized. Example: The DAO hack (2016).
- Integer Overflow/Underflow – Incorrect arithmetic operations can manipulate balances.
- Timestamp Manipulation – Miners influencing block timestamps for unfair advantages.
- Unchecked External Calls – Allowing malicious external contracts to hijack execution.
- Logic Errors – Business rule flaws leading to unintended outcomes.
Each of these vulnerabilities has caused millions in losses, underlining why QA cannot skip deep smart contract testing.
Tools for Blockchain Testing
- Automation Frameworks – Truffle, Hardhat, Foundry
- Security Audits – Slither, MythX, Manticore
- Performance Tools – Hyperledger Caliper, JMeter
- UI/Integration Testing – Selenium, Cypress
These tools together ensure end-to-end testing coverage.
Blockchain Testing Lifecycle
- Requirement Analysis & Planning
- Test Environment Setup
- Test Case Execution
- Defect Logging & Re-testing
- Regression & Validation
This lifecycle ensures a structured QA approach across blockchain systems.
QA Automation in Blockchain Testing
Automation is vital for speed and consistency:
- Unit tests for smart contracts
- Regression testing
- API/dApp integration
- High-volume transaction validation
But manual testing is still needed for exploratory testing, audits, and compliance validation.
Blockchain Testing Challenges
- Decentralization & Immutability – Difficult to simulate real-world multi-node failures.
- Consensus Testing – Verifying forks, validator fairness, and 51% attack resistance.
- Regulatory Compliance – Immutability conflicts with GDPR’s “right to be forgotten.”
Overcoming Blockchain Testing Problems
- Data Integrity – Use hash validations and fork simulations.
- Scalability – Stress test early, optimize smart contracts, and explore Layer-2 solutions.
- Security – Combine static analysis, penetration testing, and third-party audits.
Best Practices for Blockchain Testing
- Achieve end-to-end coverage (unit → integration → regression).
- Foster collaborative testing across dev, QA, and compliance teams.
- Automate pipelines via CI/CD for consistent quality.
- Adopt a DevSecOps mindset by embedding security from the start.
The Future of Blockchain Testing
Looking ahead, blockchain QA will evolve with new technologies:
- AI & Machine Learning – AI-driven fuzz testing to detect vulnerabilities faster.
- Continuous Monitoring – Real-time dashboards for blockchain health.
- Quantum Threat Testing – Preparing for quantum computing’s potential to break cryptography.
- Cross-chain Testing – Ensuring interoperability between Ethereum, Hyperledger, Solana, and others.
QA teams must stay ahead, as future attacks will be more sophisticated and regulations will tighten globally.
Conclusion
Blockchain testing is not just a QA activity; it is the foundation of trust in decentralized systems. Unlike traditional apps, failures in blockchain cannot be undone, making thorough and proactive testing indispensable. By combining automation with human expertise, leveraging specialized tools, and embracing best practices, organizations can ensure blockchain systems are secure, scalable, and future-ready. As adoption accelerates across industries, mastering blockchain testing will separate successful blockchain projects from costly failures.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Why is blockchain testing harder than traditional app testing?
Because it involves decentralized systems, immutable ledgers, and high-value transactions where rollbacks are impossible.
-
Can blockchain testing be done without real cryptocurrency?
Yes, developers can use testnets and private blockchains with mock tokens.
-
What tools are best for smart contract auditing?
Slither, MythX, and Manticore are widely used for security analysis.
-
How do QA teams ensure compliance with regulations?
By validating GDPR, KYC/AML, and financial reporting requirements within blockchain flows.
-
What’s the most common blockchain vulnerability?
Smart contract flaws, especially reentrancy attacks and integer overflows.
-
Will automation replace manual blockchain QA?
Not entirely does automation cover repetitive tasks, but audits and compliance checks still need human expertise