by admin | Nov 26, 2019 | Mobile App Testing, Fixed, Blog |
We live in a world where smartphones consume people, our eyes glued to the various apps on the phone. The only way to stand out against the 1000’s apps released every day is through the usability of your app. A good UI/UX can help you discover ways to interact and engage with your users. An app’s success is highly dependent on the usability of a mobile app’s user interface (UI), and it should carry precedence over its user experience (UX).
Usability is an important aspect of the overall relationship between the user and the product. It focuses only on the efficiency and simplicity of achieving the goals of the app. Pay attention to the little things that can make or break the success of your app. If you’re a mobile app testing services company, you must consider these three aspects: efficiency, easiness to learn, and user satisfaction while optimizing your mobile app usability.
In today’s modern-day mobile apps are plagued by multiple usability issues. Let’s discuss a few:
1. Developers need to design apps to fit each mobile brand and model due to different screen sizes and resolutions, even if it’s the same operating system.
2. An organized and intuitive design that avoids unnecessary deep navigation is critical. When a user navigates your app, they need to understand how to do what they want quickly.
3. The constant battle between information vs. speed can leave some apps desiring for better function and balance.
4. Users access their device one-handed and on the go with their opposable thumb, so scrolling is inevitable, that’s why apps must prioritize within the limits of their screen.
5. It is imperative to design apps with both portrait and landscape modes as they go for development separately as two different applications, so you should adapt it suitably.
6. A self-explanatory app succeeds better than others in the market. Statistics show that 20% of users abandon an app within 3-7 days due to complexities.
7. Content should be relevant and presented concisely with the right font and size. Pop-ups can provide additional information and increase the conversion rate with users.
8. Auto-fill/suggestion is a prerequisite and a powerful way to improve user experience in apps these days. Registrations through email or social media and one-click payments are preferred.
9. Include qualitative analytical tools to combat unresponsive gesture issues into your testing. It can provide insights into how users browse, click, and interact within the app.
10. User feedback and optimization are crucial to maintaining a well-updated app. Small sample groups can detect 85% of usability issues, so A/B testing is a must.
In conclusion,A successful mobile app must be intuitive, and it should take little to no time for a user to become familiar with the interface. As per International Standards like ISO 9241–11, usability is the capability of the product to be understood, learned, and operated. To reach all potential customers, you would need both kinds of apps – Android and iOS. As a mobile testing services company, Codoid ensures all apps are developed to meet high standards of approval. We can help your app break through a saturated market and head in the right direction towards success. Contact us if you’re ready to discover a flexible approach to usability testing and want to maintain the stellar quality of your mobile app.
“Don’t forget an excellent usability score helps convert users into loyal and long-term customers.”

by admin | Nov 19, 2019 | Mobile App Testing, Fixed, Blog |
Customers today want to experience the best of technology through devices, apps, and surfing online information, without wasting time and expending too much effort. Efficiency and speed are the top priorities and hence customers are drawn towards websites and mobile applications that consistently deliver on these two counts. It is all about the customer now – the user! This is why we as an expert Software Testing Company are consistently building UI (User Interface) and UX (User Experience) testing capability.
The whole premise and perspective of any business would be to enhance profitability by increasing the user base and retaining existing users. A company would aim to ensure that users focus on and use its products rather than that of competition. It is necessary therefore to approach business intelligently and from the perspective of the users, such that service and products align with their expectations. If users hear positive comments they would buy or download the product and would then use it, and form their own opinion. Hence while a new user might first buy a product basis other customer reviews, remaining a customer would depend on the interface and experience they have. Every new user is either a potential brand ambassador or someone who would write a scathing review or might never use a company’s product ever again. It makes sense therefore to ensure that users love your product and efficiency and usefulness are the criteria. Websites and applications must achieve these goals in order for customers to continue using and recommending them to others and this is why user testing becomes critical.
UX testing helps a business to identify the purpose for which customers use the product, and how they use the product to achieve that purpose. Customers expect maximum value from products, and they will question and stop using anything that does not achieve their purpose. Any responsible business will ensure that the websites and applications they produce will bring happiness and top notch usability for their customers. As leading Mobile App Testing Services expert we understand the importance of usability testing to enable businesses to give customers exactly what they expect and need.
Usability testing enables companies to deal with some core issues such as:
- Identification of damaged or severed links
- Bridging content and language gaps
- Fixing page errors
- Ensuring uniformity across sites and applications thereby enhancing the message and image of a brand
- Resolving poor page design layout
UX Testing Benefits
Cost effectiveness and money saving – Ensuring that users get the product they expect and need is necessary in order to save time and money rectifying a sub-standard product that fails to hit home with users. It makes more sense to partner with UI UX testing experts who would ensure that the product that goes out is of the best quality. Through usability testing never have to waste resources on redesign or code factoring later on.
Enhancing Conversion Rates – Usability testing enhances user experiences for websites, which is a proven factor to raise conversion rates by up to 75% – an extremely critical factor for any business. Applications and software solutions too must be able to increase conversions and long-term engagement. Usability testing also ensures that users can provide feedback on the software created. When users are included in the process, they are less likely to criticize and more amenable to providing new ideas with regard to functionality and improvements.
Creating Brand Awareness and Loyalty – A uniform brand experience is necessary to create a good impression on users. Software and applications should be simple, recognizable, unique, and have high quality – and this must be consistent across platforms, devices, and applications. Intuitive, interactive, and easy to navigate user interfaces keep users loyal to a brand and encourage them to spread the word of mouth to others. In addition, uniformity ensures that users and current non-users are able to identify the brand from the look and feel of the websites, software, and applications.
At Codoid we have an expert team that completely understands and is equipped to use all the techniques and tools required to find and fix bugs and ensure that software, applications, and websites are and remain of top quality. Diligence in documentation is extremely important to report bugs and capture recommendations of the solutions. Usability testing is an ongoing process and cannot be done all at once – regular testing across mobile devices and operating systems to ensure compatibility and a holistic user experience is the core of usability testing. Connect with us to create the right testing strategy, which will help to achieve the digital objectives for your business.

by admin | Oct 13, 2019 | Mobile App Testing, Fixed, Blog |
Mobile usability goes a long way in enhancing end-user app acceptance. But usability starts with the user, and users differ in terms of knowledge, interests, goals, and so on. This article discusses some core usability characteristics that matter to customers, and how test engineers can understand and achieve them.
Smartphone applications have been booming since the advent of iPhones and Android phones. There are more than 2,200,000 iOS and 2,600,000 android apps available as on Feb 2019. While a few apps go viral and get downloaded thousands of times, many do not generate even a few users. Apps can flop because the content is not interesting, but there’s another prevalent (and avoidable) reason for failure: because they are too difficult to be used on a mobile device.

Usability starts with the user, and users differ in terms of knowledge, interests, goals, and so on. As test engineers, we must ask questions about the app users, their mobile tasks, the environments they work in, the types of devices they use, and how tech-savvy they are. Clearly, usability is an important attribute to account for. This article discusses some core usability characteristics that matter to customers, and how test engineers can understand and achieve them.
The type of users and how they will interact with your product have to be taken into consideration for each app.
As Software test engineers, we must understand that mobile applications differ from traditional desktop and web-based apps in a number of ways. Correspondingly, the test focus areas also differ. Many areas require special attention, but let’s restrict our discussion to the below five elements:
- Functionality
- Context
- Range of devices
- Data entry methods
- Multimodality
Context can be defined as the totality of a consumer’s mobile experience. This includes the situational, attitudinal, and preferential habits of the user. Mobile context is constrained by factors such as screen sizes, users’ fingers, location, posture, and network connectivity. Mobile context also includes various capabilities like automatic orientation detection, dynamic location detection, the compass, and accelerometers. Let us take the example of a mobile context with respect to location. Say you ask your application to display a list of Chinese restaurants. A good application will locate your geographical positioning and give you a list of nearby places, along with reviews of other users in the same geography, and specific eating options depending on the time of the day. Results should be targeted, contextual, and valuable.
Another focus area is the various supported device models for the application. An application may work fine on one device but then crash or fail on another. For example, Zomato is a restaurant guide app with great features and UI. However, the app crashes on Android 4.3. A Software tester has a prime responsibility in verifying these nuances, keeping an optimized test matrix in mind. Next up are data entry methods. We understand that mobile devices, especially smart devices, support a lot of data entry methods, including a stylus, touch, voice recognition, gestures, and so on. Test engineers must ensure that the application responds well to each potential entry point.
Multimodality combines voice and touch as input and displays visual screens and spoken responses as output—for example, a navigation application that provides spoken responses as audio aids for the driver and visual displays as directions. Testers need to examine input and output to be sure both audio and visual components function properly.
Taking into account the many variables that need to be considered from the mobile usability angle, Codoid recommends the following practices which come in handy when creating a testing strategy.
Start early. Testing should begin at the requirements analysis phase. Most usability issues are related to design, and if you can catch them upfront when you review the designs as wireframes or mockups, it will mean less trouble down the road.
Work iteratively. Testing regularly makes it a lot easier to support small incremental changes throughout the lifespan of the application. Usability should be considered in all stages throughout the development lifecycle because every change in design and every interaction with the product prototype has an impact.
Adopt usability in conjunction with other testing types. You need to think about combinatorial elements in usability testing. For example, functionality and usability can cause a conflict; a functional designer might want to make the product feature-rich, whereas the usability engineer’s focus is to keep the application simple and intuitive. Usability studies need to be performed collaboratively, keeping in mind the performance, security, localization, functionality, and accessibility aspects of the application.
Check in after launch. Usability studies should continue after the product launches. Checking the app store, studying the ratings and reviews by users, and analyzing competition are all valuable practices in enhancing the usability of the application.
Use productivity tools. Usability testing for mobile apps is still largely done manually, and there is room to use productivity tools to make the effort more effective. There are many handy productivity tools available for a variety of usability factors, including testing the application across multiple devices for optimum screen resolution. At the end you get a report with screenshots for each selected device, indicating the screen resolution effectiveness. Another tool creates heat maps to help find areas where users’ focus lingers the most. These visible indicators help realign UI if needed. And recording software shows where participants tapped and scrolled and how they navigated from page to page, helping gauge the level of workflow intuitiveness.
Go to the source to discover user expectations. Reading about usability is one thing, but interacting with people who have special accessibility needs is invaluable. It opens your eyes to their requirements and reveals some big coverage gaps you may have.
Talk like a human, not a programmer. Emotional intelligence factors are gaining attention. When you talk about end-users, don’t talk about them as entities, but as real people with emotions. If you want to account for an emotional angle in your testing strategy and you don’t know where to start, usability is a good place to consider.
Testing, testing, testing. While it is good to have a well-etched strategy, it’s better to set aside time for exploratory testing. Most often, usability issues surface when you try operating your product in an exploratory way. Invite groups to come to test your app and think of creative ways to maximize test coverage.
In Conclusion
In essence, mobile usability goes a long way in enhancing end-user app acceptance. This industry is still evolving by the day, but the practices discussed above will give you a head start in building usable mobile applications.
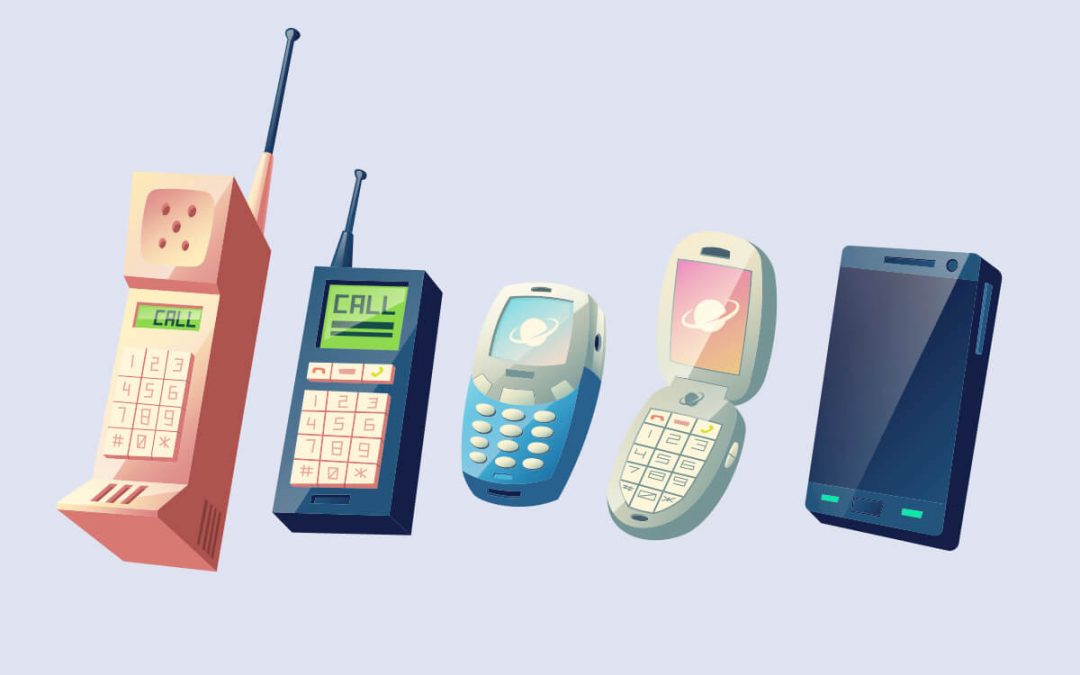

by admin | Oct 27, 2019 | Mobile App Testing, Fixed, Blog |
The advances of smartphones continue to grow constantly, the improvement of mobile technology has allowed us more options in how we approach both our work and leisure activities. Over the past 23 years, smartphones have changed the way we live our lives. From checking the weather updates to efficiently running a business, we often rely on these small powerful devices to complete our daily tasks with ease. Since their first introduction, smartphones have consistently evolved to meet our growing needs in the form of faster wireless connections, sharper images, greater memory storage, etc.
In 1926, during an interview for “Collier” magazine, legendary scientist and inventor Nikola Tesla described a piece of technology that would revolutionize the lives of its users. Here’s the quote:
When wireless is perfectly applied, the whole earth will be converted into a huge brain, which in fact it is, all things being particles of a real and rhythmic whole. We shall be able to communicate with one another instantly, irrespective of distance. Not only this, but through television and telephony we shall see and hear one another as perfectly as though we were face to face, despite intervening distances of thousands of miles; and the instruments through which we shall be able to do he will be amazingly simple compared with our present telephone. A man will be able to carry one in his vest pocket.

While Tesla might not have chosen to call this instrument a smartphone, his foresight was spot on. The history and evolution of the smartphone are important to understand because it gives us a glimpse of where we’ve come from, and of what’s coming. That goes for improvements in technology as well as consumer trends. So let’s take a look at just how far we’ve come.
The World’s First Smartphone
The device had many of the modern elements we attribute to current smartphones and mobile devices. Highlights included:
- Touch screen
- Email
- Fax
- Notes and Calendar
- Apps and other widgets that would become widespread decades later.
The Simon was advanced for its time but has nothing on the smartphones of today. It only had a small monochrome LCD screen and a one-hour battery life. Clearly, though, Simon created a great launching pad for others to innovate.
BlackBerry
Blackberry’s first wireless handheld computer, RIM 850, is announced in July 1999,The device garnered popularity in the business world with its ability to connect people by having some key features like
- Calendar
- Music
- A full keyboard
- Advanced security
- Internet access
Apple unveils iPhone in 2007
Apple had already begun transforming how people use portable technology with the iPod, and the stage was set for them to unveil their latest device in 2007. Among some of the groundbreaking features was an expansive and responsive display from which to check email, stream video, play audio, and browse the internet with a mobile browser that loaded full websites, much like what’s experienced on personal computers. Apple’s iOS operating system allowed for a wide range of intuitive gesture-based commands and eventually, a rapidly-growing warehouse of downloadable third-party applications.
Steve Jobs says it’s “a revolutionary and magical product that is literally five years ahead of any other mobile phone.” Apple’s version took it to a whole other level as a full-blown multimedia powerhouse, enabling users to play games, watch movies, chat, share content, and stay connected to all the possibilities that we’re all still constantly rediscovering.
Evolution of Android:
Andy Rubin was developing his own version of a mobile OS called Android. After being purchased by Google, the first Android phone was released in 2008. Android has become the world’s most popular operating system in 2011, by the start of 2012, Android officially ruled the smartphone market share worldwide. The reason behind its popularity is that the OS is open-source, it allows the developers to play with the code allowing them to modify the code as per their needs. At present Android has one of the largest communities of Application Developers writing and developing a large number of mobile applications that extend the functionality of the device.

The Change:
Now that we’ve seen how smartphones have changed the way we communicate over the last 20+ years, let’s evaluate some of the big ways smartphones have changed the way we do business:
1. Creation of the “right now” culture Smartphones give us access to the world’s database of information within seconds. This has raised consumer expectations when it comes to immediate gratification. Not only do people expect prompt responses to communications, but they also want to access the purchasing process for any good or service easily and instantaneously.
2. Farewell to office space well, not entirely. But thanks to smartphones, telecommuting is a realistic way of operating for many. Thanks to tools like Slack, FaceTime, Skype, you can access a virtual desk on your smartphone from anywhere in the world.
3. Advertisers delight Smartphones (and the apps that are on them) opened up a completely new space for advertisers to serve content. The revenue generated from mobile ads is substantial and becoming the bread and butter for many businesses.
4. Social butterflies nearly 80% of all time spent on social media is on mobile devices. This radical change has resulted in millions of businesses flocking to social media and pouring their time and energy into interacting with customers through that space.

by admin | Sep 15, 2019 | Mobile App Testing, Fixed, Blog |
Mobile application development has become cumbersome so does Mobile app testing. Not because of development complexity. But, because of the intense market competition in delivering niche and user-friendly apps in the market.
Let’s through some light on the market research data
On an average 88.7 apps are installed on the smartphones in the US. But, roughly 24.7 of them are used on a monthly basis. Which amounts to an average of 7.6 apps on a daily basis. The humongous difference in the usage of mobile apps is attributed to the following reasons: remaining mobile apps have either FAILED to impress and engage the users because of inadequate & improper mobile app testing strategy, improper research, poor UI/UX, etc.
Let’s delve deeper into this topic and jot down the major factors determining the success of your mobile app:
1. Unseemly Buyer Research Buyer research needs to be the most crucial and inevitable step in developing a mobile application, for all OS’s like Android, iOS, etc. One must do the following due diligence while doing research:
- Do thorough market research.
- Understand your buyer who is most likely interested in your mobile app.
- Do demographic research of your mobile app users as well.
- Arrive at a conclusion based on your research data and ascertain which gender is most likely to use your mobile app.
- Further broaden your research by conducting surveys throughout the complete spectrum of your network.
- Be a part of various forums, online communities where people talk about the latest mobile apps.
2. Competitor Analysis Competitor analysis is as important as using your market and audience research data effectively, your app would eventually crash if you develop it without possessing a thorough knowledge about your competitors.
Who your competitors are:
- The top 50 mobile apps in different Stores
- Mobile apps with similar functionality
- Apps with similar ideas
- Apps which fall under the same segment
Analyzing your competitors the following manner:
- How well your competitors have fared well so for on the app idea?
- Major functionalities covered
- Check their app compatibility in all possible OS like Android, iOS etc.
- Compare the app downloads data and reviews efficiently
- App users review data
- Ascertain their marketing strategy
After having done with your competitor analysis, you can work on developing a mobile application that can outsmart your competitor in all aspects with ease. Ignoring any of the above crucial steps could put your mobile app at a bigger risk of failing.
3. Bad Mobile app ideation Most developers have a conviction that their app ideas are path-breaking and will work amazingly well. But in reality, not all app ideas succeed. Research says that 49% of developers develop apps based on their own requirements which usually turns out to be unsuccessful.
Ponder over the following pointers before bringing your app idea into reality:
- Is your app idea niche and unique
- Is your app idea a need of the hour?
- Does is intent to solve any of the users’ needs?
- Unique ness of your app idea from your competitors.
You should have a foolproof system prepared in place for your app idea else it is likely to fail.
4. Inadequate Mobile App testing The need for Mobile app testing is obvious, but getting adequate coverage, with the plethora of Android versions and devices available in the market it can be a cumbersome task. There are simulators, but software running on a server might not show the same performance limitations.
For instance, one thread of a mobile app might try to read a database at the same time another thread is trying to modify the same database. “It’s a timing mismatch problem,” “If they don’t hit at the exact moment in time, the issue doesn’t surface. It can be overcome with a very simple log statement.” A simulator often will not illustrate the same fundamental performance limitations of a mobile device, so the race condition isn’t apparent.

There are a host of other services that can run pairings of different devices and variations of operating systems and make them available, but that would most likely be more expensive compared to a simulator. Apparently, our choice is based on the trade-off between budgets and needs. Mobile app testing should be looked at benchmarking against industry standards and user expectations to ensure that the expectations of the developers and users are in sync. Mobile testing should be done on a continuous basis. As a thumb rule one must monitor performance, look for user feedback suggesting problems, and then fix things as soon as possible for the best possible outcome.
5. Ill-timed App Development Strategy Sans proper strategy, even big Mobile app players in the industry would not have been successful.
App development strategy got to be perfect in all facets:
- How your app development should be devised?
- Turnaround time of your design strategy
- What technology stack to be used in the app development?
- How much time does it take for successful mobile app testing?
- When do you plan to launch the app?
All the above points make a perfect app development strategy. Any minor deviations in any of the above estimations, your app is sure to hit the failure road.
6. Bad UI/UX This is the biggest reason why most mobile apps crash. User interface (UI) is one of the striking aspects that not only attract the users but also keep them engaged. UI is ideally considered as the first impression of your mobile app. while launching your mobile app, you have your app screenshots prepared to put them on the Stores. And, that is where your users will make an effort to read the app description below. If your UI seems improper in the screenshots, Eventually that will end up in no downloads resulting in a great failure. Amazing user interface and user experience define the success of your app and poor UI/UX can fail your app.
Some UX factors that lead to mobile app failures:
- Low resolution images
- Poor loading time
- Broken sign up or login functionality
- Broken app navigation
- Irrelevant implementation of micro interactions
- Tiny or too big fonts
- Poor connectivity to social profiles
- No actions on clickable elements
- Inappropriate spacing between touch points
- Too much of page scrolling
7. Arbitrary Development Process Let’s learn how an arbitrary development process leads to mobile application failure.
- How to formulate the right designing strategy for the mobile app
- Which functionality to be developed first?
- How many hours of dedicated effort to be put in while developing a certain functionality?
- Which designer/developer to utilize?
- How to finalize the app designs?
- How much time is needed for end to end mobile testing?
All the above things need to be followed religiously to make sure your mobile app does not fail.
8. Ignorance of Rigorous mobile testing
While designing and developing a mobile app is considered very important. Mobile app testing is equally important. Mobile app testing is required to check whether your mobile app has any exceptions and bugs or not. A mobile app that is launched without proper testing, fails for sure. There are several types of testing to be executed in order to see your mobile app has no bugs.
- Each functionality needs to be tested as and when developed
- With each new developed functionality, don’t forget to check whether the earlier functionality works fine.
- Mobile testing is required to check whether each and every app integrations are working properly.
- Usability of your mobile app should to be tested
- Compatibility testing to be done without fail.
- Need to check whether the app works at the users’ end before going live
This is not limited to just mobile testing alone. The process after testing is even considered. The differentiating factor here is what measures we take after getting any bugs or exceptions. So, test your apps rigorously to avoid failure.
9. Inept App Launch Plan You cannot just develop an app and launch it directly on the Apple App Store or Google Play Store. Well, if you do this or if you have done this earlier, you would surely get a big failure hit for your app.
Without letting your target audience know about your app, how are you going to get the downloads?
10. Middling Monetization Strategy Designing, developing, testing, and successfully launching your app does not pay you anything. These are just the investments that you make. How the success of your mobile app is measured? Clearly, with the money coming in, from your app. If your mobile app is not able to make you money, then there are chances that your app has flaws and is at risk of failure. If you have noticed in the Apple App Store and Google Play Store, most of the apps are free and if you are looking to charge your audience, you need to be more careful. So, how will you earn money out of your mobile app? Well, this needs a solid, foolproof monetization strategy to work on.
Conclusion
Mobile apps are a great way of doing business. But, it is equally important to make sure that it does not fail. Because if it fails, it will be beyond revival. So carefully consider the above-mentioned reasons why your mobile app can fail. Also, ensure to follow the mobile app tips given along with them to avoid the same. So make sure you approach the Best Mobile App Testing Services Company to test your Mobile Apps.

by admin | Sep 11, 2019 | Mobile App Testing, Fixed, Blog |
Mobile app testing is a comparatively more complicated process than desktop or web app testing given the numerous challenges faced by mobile app testers. Some of these challenges include device variations, device fragmentation, OS fragmentation, rapid release schedules, several testing tools, unexpected customer app use cases, network compatibility, battery/power consumption, and offline functioning, among others.
In addition to these challenges, there are some added challenges that mobile app testers have and could possibly encounter in 2019. The top 7 additional mobile testing challenges in 2019 are listed below:
Tackling App Performance Issues
It is pertinent in present times that mobile app testing must focus on the delivery of quality apps to users. If there are performance issues affecting the user experience with an app, mobile device users are likely to opt for a competing app. Therefore, it is a challenge for testers to enhance the user experience by tackling app performance issues such as long time to load and run an app, inconsistent performance, poor responsiveness, and incompatibility with different networks or platforms.
Greater Need for Shift Left Testing
To ensure comprehensive testing of a mobile app, testing companies need to incorporate Shift Left Testing (test early and test often approach) in their mobile testing strategy. The Shift Left Testing process enables the mobile app testers to test an app in the early stages of its development rather than testing it only before release. The use of Shift Left Testing mechanism is a challenge because it requires the deft use of automated testing tools so that the testing of an app can be performed alongside its development.

Continuous Mobile Testing Requirements
The DevOps and Agile scenarios are paving the way for faster development of apps and frequent addition of new features to existing apps. Continuous Mobile Testing requirements pose a challenge even for a top mobile testing company because of the emphasis on continuous mobile testing skills of the testers. It is imperative for mobile app testers to be experts at Agile testing in order to make continuous testing a part of the continuous integration process for updating an app with new features and functionalities.
Focus on Social Media Testing
The increasing focus on social media is emerging as another big challenge for mobile app testers in the current year – 2019. It is crucial for testers to acquire social media testing skills because the present-day mobile app users trust social media reviews more than any other data. Hence, with all mobile apps now necessitating interface with the social media, testers should be proficient in running an app by different social media platforms when they test the app at various development stages.
Global Testing of Apps
In present times, almost all mobile apps, irrespective of the operating system and functionality, are developed for mobile phone users across the globe. Given this reality, it is a challenging task for the testers at a mobile app development company to test an app globally, on a range of networks, from one location. To overcome the challenge of global testing, mobile app companies generally outsource the testing tasks, but the results of the testing may sometimes not be desirable from the perspective of global usage.
Lack of Suitable Testing Tools
Mobile app development companies often lack the right testing tools that can enable their testers to test their app for use on smart devices. Due to the unavailability of suitable testing tools, testers are not able to get adequate test coverage while testing an app on a variety of mobile devices. Without the knowledge and use of proper testing tools, testers fail to capitalize on automated testing because of which there are delays in testing and, eventually, also in the release of the app to the market.
Coping Up With App Marketing Schedules
The rise of app store and in-app advertising has made it difficult for mobile app testers to cope up with the marketing schedules of the app marketers. With market app advertising on the increase, testers at most of the leading mobile testing companies have limited time to test the app exhaustively. Since a shorter testing time is becoming a challenge in mobile app testing, it is vital for mobile app companies to put a testing plan in place when they start the development of an app.
In Conclusion:
The astounding pace of mobile app development has made mobile app testing a very critical process since the users of smartphones demand well-designed, responsive, engaging, and feature-rich mobile apps. To overcome the challenges for mobile testing in 2019, mobile app testers should build top-notch app testing strategies based on a broad understanding of the different areas of mobile testing like technology, devices, usability, and user experience. Connect with us – we keep abreast with all the latest technologies, tools, and methodologies to glide past these challenges.