by admin | Aug 31, 2019 | Automation Testing, Fixed, Blog |
Nowadays, we have umpteen number of testing frameworks developed using Python and most of them don’t fit everyone’s requirement, through extensive research we have a found a testing framework which is comprehensive and has all the required features to maintain your automated test cases. It is Test Junkie which is still in the Alpha stage. This framework was developed by Artur Spirin . In this blog article, we will see what are all the distinct features of Test Junkie.
ListenersIn Cucumber, we use hooks like beforeScenario & afterScenario. Similarly, in Test Junkie, we have many listeners for Test and Suite.
Test Listeners: on_in_progress, on_success, on_failure, on_error, on_ignore, on_cancel, on_skip, & on_complete.
Suite Listeners: on_class_in_progress, on_before_class_failure, on_before_class_error, on_after_class_failure, on_after_class_error, on_class_skip, on_class_cancel, on_class_ignore, on_class_complete, on_before_group_failure, on_before_group_error, on_after_group_failure, & on_after_group_error.
from test_junkie.listener import Listener
class MyTestListener(Listener):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
Listener.__init__(self, **kwargs)
...
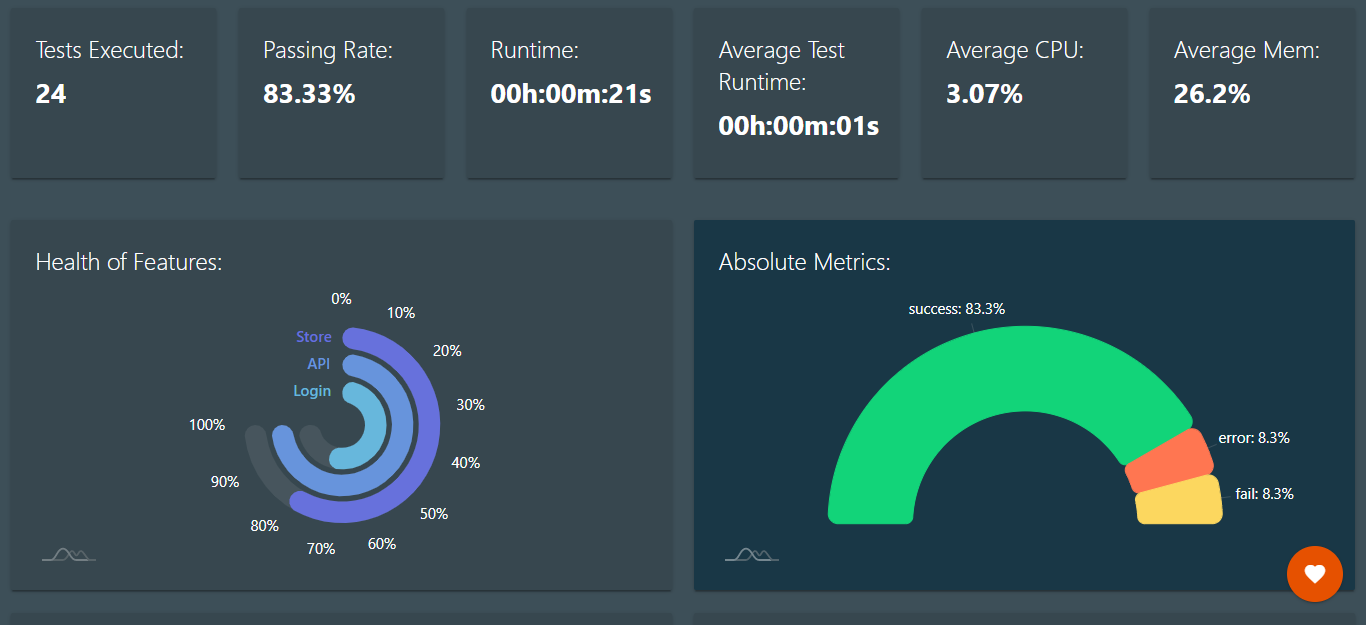
Test ReportingIn Test Junkie, you can report the test execution in HTML, XML, and JSON. Using monitor_resources parameter, you can enable monitoring of the MEM & CPU usage during test execution. Test Junkie generates a beautiful HTML report as shown below.
Advanced Test Suite Example
from test_junkie.decorators import Suite, test, afterTest, beforeTest, beforeClass, afterClass
from test_junkie.meta import meta, Meta
@Suite(parameters=[{"login": "[email protected]", "password": "example", "admin": True},
{"login": "[email protected]", "password": "example", "admin": False}])
class LoginSuite:
@beforeClass()
def before_class(self, suite_parameter): # yes, we just parameterized this function, seen that anywhere else?
# Lets assume we have some code here to login with
# username . . . suite_parameter["login"]
# password . . . suite_parameter["password"]
# This is our, hypothetical, pre-requirement before we run the tests
# If this step were to fail, the tests would have been ignored
pass
@afterClass()
def after_class(self):
# Here, generally, we would have clean up logic.
# For the sake of this example, lets assume we logout
# from the account that we logged into during @beforeClass()
# no `suite_parameter` in method signature,
# logout process would likely be the same irrespective of the account
pass
@test(parameters=["page_url_1", "page_url_2", "page_url_3"])
def validate_user_login_in_header(self, parameter, suite_parameter):
# Lets assume that in this test case we are going to be validating
# the header. We need to make sure that email that user logged in with
# is displayed on every page so we will make this test parameterized.
# By doing so we will know exactly which pages pass/fail without
# writing any extra logic in the test itself to log all the failures
# and complete testing all the pages which would be required if you
# were to use a loop inside the test case for instance.
# Now we would use something like Webdriver to open the parameter in order to land on the page
# and assert that suite_parameter["username"] in the expected place
pass
@test(parameters=["admin_page_url_1", "admin_page_url_2"])
def validate_access_rights(self, parameter, suite_parameter):
# Similar to the above test case, but instead we are validating
# access right privileges for different user groups.
# Using same principal with the parameterized test approach.
# Now we would also use Webdriver to open the parameter in order to land on the page
# and assert that the page is accessible if suite_parameter["admin"] is True
@Suite(pr=[LoginSuite],
parameters=[{"login": "[email protected]", "password": "example", "user_id": 1},
{"login": "[email protected]", "password": "example", "user_id": 2}])
class EditAccountCredentialsSuite:
"""
It is risky to run this suite with the LoginSuite above because if
the suites happen to run in parallel and credentials get updated
it can cause the LoginSuite to fail during the login process.
Therefore, we are going to restrict this suite using the `pr` property, this will insure that
LoginSuite and EditAccountCredentialsSuite will never run in parallel thus removing any risk
when you run Test Junkie in multi-threaded mode.
"""
@test(priority=1, retry=2) # this test, in case of failure, will be retried twice
def reset_password(self, suite_parameter): # this test is now parameterised with parameters from the suite
# Lets assume in this test we will be resetting password of the
# username . . . suite_parameter["login"]
# and then validate that the hash value gets updated in the database
# We will need to know login when submitting the passowrd reset request, thus we need to make sure that
# we don't run this test in parallel with edit_login() test bellow.
# We will use decorator properties to prioritize this test over anything else in this suite
# which means it will get kicked off first and then we will disable parallelized mode for the
# edit_login() test so it will have to wait for this test to finish.
pass
@test(parallelized=False, meta=meta(expected="Able to change account login"))
def edit_login(self, suite_parameter):
# Lets assume in this test we will be changing login for . . . suite_parameter["login"]
# with the current number of tests and settings, this test will run last
Meta.update(self, suite_parameter=suite_parameter, name="Edit Login: {}".format(suite_parameter["login"]))
# Making this call, gives you option to update meta from within the test case
# make sure, when making this call, you did not override suite_parameter with a different value
# or update any of its content
@afterClass()
def after_class(self, suite_parameter):
# Will reset everything back to default values for the
# user . . . suite_parameter["user_id"]
# and we know the original value based on suite_parameter["login"]
# This will insure other suites that are using same credentials, wont be at risk
pass
@Suite(listener=MyTestListener, # This will assign a dedicated listener that you created
retry=2, # Suite will run up to 2 times but only for tests that did not pass
owner="Chuck Norris", # defined the owner of this suite, has effects on the reporting
feature="Analytics", # defines a feature that is being tested by the tests in this suite,
# has effects on the reporting and can be used by the Runner
# to run regression only for this feature
meta=meta(name="Example", # sets meta, most usable for custom reporting, accessible in MyTestListener
known_failures_ticket_ids=[1, 2, 3])) # can use to reference bug tickets for instance in your reporting
class ExampleTestSuite:
@beforeTest()
def before_test(self):
pass
@afterTest()
def after_test(self):
pass
@test(component="Datatable", # defines the component that this test is validating,
# has effects on the reporting and can be used by the Runner
# to run regression only for this component
tags=["table", "critical", "ui"], # defines tags that this test is validating,
# has effects on the reporting and can be used by the Runner
# to run regression only for specific tags
)
def something_to_test1(self, parameter):
pass
@test(skip_before_test=True, # if you don't want to run before_test for s specific test in the suite, no problem
skip_after_test=True) # also no problem, you are welcome!
def something_to_test2(self):
pass
Command Line InterfaceTest Junkie comes with three features in Command Line execution. First one is run command which allows to execute your tests. The second one is audit command which to quickly scan existing codebase and aggregate test data based on the audit query. The last one is config command is to let you easily persist test configuration for later use with other commands like run & audit
In Conclusion:
Reviewing a testing framework helps the test automation community to understand the framework features quickly. We, at Codoid, urge our testers to explore latest tools/frameworks to improve our automation testing services. Test Junkie is still Alpha phase. Once it is released, it will be the most popular Python testing framework.

by admin | Aug 30, 2019 | Automation Testing, Fixed, Blog |
Automated software testing schedules have the ability to increase the depth and expand the scope of software testing while elevating the quality of software applications and packages. Today, test automation frameworks are deployed to execute thousands of different complex test cases during every test run, thus providing expansive testing coverage, which would be impossible with manual testing. For instance, certain automated testing tools can playback pre-recorded and predefined actions, compare the results to the expected behavior of a software package, and report the success or failure of these manual tests to the software testing experts. Automation also boosts the repeatability of tests, which can be extended to perform tasks impossible with manual testing. These facts help leading software testing companies to promote automated software testing as an essential component of successful software development projects, while also measuring its success across a range of projects.
Test Management Tools
Testing engineers offering automation testing services should identify ‘candidates’ for automation during the process of defining test cases and testing scenarios. The salient features of a test management tool are flexibility and ease of use. Further, a good quality tool should be able to help testers identify any bugs in the project. Additionally, a test management tool should have the ability to execute various automation tests and scripts in batches or position these in the testing pipeline for scheduled testing or on-demand.

What to Automate
An intelligent automated testing strategy should be able to answer the questions: ‘where to automate’ and ‘what to automate’. Testing engineers must answer these queries to denote the layer of an application that must undergo automated testing. However, testing engineers offering automation testing services must bear in mind that although automated testing requires higher initial investment, it can yield a significantly higher return on investment. Therefore, teams of software testing experts should have answers to the questions mentioned to enable a better focus on their automation efforts.
Tool Selection
The correct automation tool is critical to ensure the success of automation testing. Hence, test engineers must, for instance, work to determine which tool could enable the automated testing of a desktop application. Further, factors such as language support, tool support, the availability of newer versions of a tool, support for API automation, and more, must be considered during the tool selection process. These factors can and should influence commercial decisions to purchase tools for firms that offer test automation services. Certain complexities may arise when a company engaged in automation testing services negotiates the process of tool selection in specific circumstances.
Environment Stability
Test automation thrives in stable testing environments. Hence, test engineers performing test automation services must consider factors such as dependency, availability and the up-time of a test environment. Testers should take a special interest in managing test infrastructure – such as hardware servers, application servers, networking, firewalls, software components required for testing, build software required for testing releases and more. Further, they must manage test environments such as database clusters, UAT, Pre-production, and the data required for testing. Additionally, testers must remain aware that test environments differ from production environments in several ways – these include operating systems, configuration, software versions, patches, and others. Therefore, the wider the gap between test and production environments, the greater the probability the delivered product will feature a range of bugs and defects.
Data Usage
Data and its appropriate usage are critical to devising a correct approach to automation. The complications associated with data bring up several unexpected challenges in automation testing. Therefore, testing engineers must find the means to randomly generate or obtain varied data input combinations as part of reinforcing their efforts towards test automation. For instance, data can be sourced from tables, files or APIs. Further, engineers must make qualitative judgments such as whether sourcing a certain type of data would affect the performance of scripts, and others.
In Conclusion
A well-calibrated and prudent approach to testing automation can elevate the quality of testing in software testing scenarios. Testers with the ability to put together a unique approach to test automation would be more successful in their chosen domain of work. Companies must partner with a leading software testing company to get the best service, experts, and top testing tools. Connect with us for all these features and more.

by admin | Aug 28, 2019 | Mobile App Testing, Fixed, Blog |
The highly fragmented and ultra-competitive market for mobile applications offers significant business opportunities for idea generators, developers, and testers alike. Consequently, the QA testing cycle designed by mobile testing services engineers is undergoing compression in terms of timelines. Efficiency has emerged as the cornerstone of mobile app testing services, and this metric has the ability to enable developers and testers of mobile apps to meet customer expectations. Non-functional testing such as security and usability testing play an important role in ensuring the success of contemporary mobile apps.
Planning
Engineers offering mobile app testing services must design a plan for mobile app testing processes. Such plans define the types of testing they wish to execute, the testing methodology, manual and/or automated testing processes, KPI specifications, number of testers in a schedule, and other such information. These queries, when answered before the start of a testing project helps make the app testing process faster and more efficient. Some engineers create a test plan that describes the scope of testing, test strategy, objectives, effort, schedule, and the required testing resources.

Continuous Testing
Market research indicates mobile app testing schedules follow weekly release builds, followed by bi-weekly releases. This pace of testing reveals that mobile testing services are eagerly embracing continuous integration and continuous deployment techniques and practices. The efficiency factor undergoes significant boosts when testers implement continuous testing systems and processes. This implies executing automated tests regularly to generate instant feedback on testing outcomes and implementing remediation. Additionally, continuous mobile app testing services hinge on configuring error reporting to identify all the glitches during production. Further, continuous testing includes beta testing to detect bugs while a mobile app is in production (but not yet released to all users)
Automated App Testing
This form of software testing can be run frequently, since it enables mobile testing services engineers to focus on exploratory, security, or usability testing. The benefits of mobile app automation testing extends to fewer errors in testing schedules, the ability to schedule testing in the absence of human talent, faster test execution, and more. Further, mobile app testing services can save time and money when they opt for this form of mobile app testing. The preparation for such testing includes monetary investments to buy licenses for automated testing tools, writing scripts, and setting up an appropriate test environment. Experts in the realm of test automation corroborate that this form of testing reaps rich rewards given constrained timelines imposed on mobile testing services.
Test in the Cloud
Cloud computing excels in providing test environments for mobile testing services. The cloud offers effective fits for all types of testing enterprises ranging from start-ups to legacy businesses. Companies that invest in cloud-based mobile app testing can automate tests on hundreds of digital devices, each running on a different platform. Additionally, cloud-based mobile app testing allows developers and testers around the world to communicate and connect to mobile devices via the Internet. Cloud technology also offers testers seamless access to a range of devices with different OS platforms, versions, network carriers, and others. Also, simulators and emulators available in the cloud empower testers to perform actions such as swiping, double-tapping, zoom, scrolling, rotate inside a virtual app. Further, such forms of mobile app testing services allow faster detection of performance issues inside mobile applications.
Resource Allocation
Leaders of mobile app testing services must adjust testing resources in tune with project requirements. This could involve hiring extra numbers of QA testing engineers or outsourcing specific segments of mobile app testing services. Some companies may choose to enhance their competitiveness by hiring remote software testers. Team management is a vital aspect of optimizing the available test resources, and therefore, it would make sense to hire expert managers who would be able boost the mileage of mobile testing services.
In Conclusion
It is critical for mobile app testing teams to attain and sustain higher levels of efficiency, thereby presenting a definitive ROI for clients and customers. Refining and extending such testing paradigms can help bring a larger number of highly functional mobile apps to the market. We are amongst the leaders in the realm of mobile app testing and a very large gamut of testing services. Connect with us to gain all the advantages from our experts.
by admin | Aug 2, 2019 | Automation Testing, Fixed, Blog |
The norms of evolution in technology emphasize a shift from the manual to the automated. Software testing services are no exception and hence automation testing services are gaining ground within the industry. This shift is largely powered by a well-grounded view that test automation services help unearth a larger number of glitches in software applications and products. The very essence of automation has enabled it to emerge as a more reliable testing method, which the industry seems more than willing to emulate.
Is Automation Testing Necessary?
The answer is an emphatic yes and since automation testing represents the future of software testing processes and services. Intelligently framed testing scripts that would create accurate and repeatable automated tests across multiple mobile devices, platforms, and environments will most likely dominate the software testing industry in the years to come.

Effortless and Efficient Testing
Expert testers vouch for the efficacy of test automation services, saying that it offers seamless execution of software testing systems and principles. This approach, however, must be complemented by the clarity of the objective of the testing regime and the ability of software testing engineers to manage the rigors of such a testing method. The testers should be able to determine the purpose of a test script and only then consider automating to affect speedier and more efficient testing. Such practices drive a transition from manual testing systems to automation-driven regimes in the long term.
Storable, Customizable, and Reusable Scripts
Software testing systems evolved from manual practices to automated testing, being driven by the efforts and intelligence of human testers. Transitioning from a manual regime to automation testing services requires a graded and calibrated approach. It is possible to attain a middle ground when testers automate certain tests, which makes their execution more efficient. Benefits accrue since automated testing tools have the ability to playback pre-recorded and predefined actions, compare results with expected outcomes, and report the actual outcomes to the testing team. It is possible to repeat and extend automated tests to perform tasks, which would not be possible with manual testing.
Evaluating Tests
Testing managers understand the critical nature of automated software testing as an essential component of successful development projects. However, the existence and rationale of a test script must undergo interrogation before implementing it into an automated regime. A test scenario should merit testing in different ways to ensure the satisfactory coverage of a given set-up. The evaluation process must include queries designed to satisfy the curiosity of the tester regarding likely outcomes. It is important to ensure that the efforts focus on reviewing, refining, and tightening the repository of test scripts to retain a high degree of relevance.
Regular and Rigorous Evaluation
Test suites need regular evaluation by the creators of test automation services. Being able to extract significant value from the information created by executing various tests is necessary for the success of the project. This is a marked departure from mechanistic testing regimes dominated by legacy testing scripts. Therefore, providers of automation testing should invest time and effort to frame automated tests that conform to client requirements and can add value to the process of modern software development.
In Conclusion
Automated software testing regimens offer distinctive benefits by way of faster feedback, reduced business expenses, accelerated results, higher levels of testing efficiency, comprehensive test coverage, the early detection of defects, and thoroughness in testing outcomes. However, the transition from manual to automation testing services must have clear lines of thought and inquiry and must be complemented by a robust assessment of the benefits afforded by each script. Connect with us to leverage on our experience and expertise in the realm of automation testing services, and a much more.
by admin | Aug 5, 2019 | QA Outsourcing, Fixed, Blog |
As a business practice, the phenomenon of outsourcing emerged roughly two decades ago on the global stage. This model of conducting business allows commercial operators to lower expenditure on fixed costs and control various items of variable costs; these actions can drive significant savings that add to the bottom line of a sponsor business.
While most outsourced tasks are time-consuming, the choice to invest in outsourcing allows enterprises to refine and improve business focus. The QA Outsourcing initiative concerns the outsourcing of software testing duties and responsibilities. We examine the principles that underlie the decision to outsource software testing.
Deep Knowledge
QA Outsourcing teams must have access to deep pools of technical knowhow and knowledge. This should emerge as a deciding factor that governs business decisions such as selecting testing vendors for QA Outsourcing projects. This implies testers working on a QA Outsourcing project must be fluent in ERP and CRM systems, document management systems, the specifics of operating an intranet, supplier portals, customer portals, and data warehousing techniques and technologies. In addition, software testing professionals must have experience in terms of testing the building blocks of multiple types of software applications and platforms. Therefore, sponsor businesses must remain fully aware of the capabilities of QA Outsourcing vendors prior to signing a contract with a vendor.
International Standards
Further to the above, QA Outsourcing vendors must have high levels of engagement with international standards and regulations that govern different industries. In line with this, testing professionals must be familiar with specific standards and regulations (such as FATCA, AML, PCI DSS, and Basel III) when testing software applications for the financial services and banking industries. Significant levels of knowledge and expertise should ensure testing professionals are able to navigate the complicated software applications while bearing in mind the required standards and regulations.
Multi-Vendor Strategy or a Single Vendor with All Round Abilities
The decision to pursue QA Outsourcing for software testing services must be informed by an active choice in the number of vendors. Experts in the software testing domain admit a single vendor system can create complications during the lifetime of an outsourcing contract. The credentials presented by a single vendor may appear tailored to suit the contours of a QA Outsourcing work contract; however, such credentials may prove inadequate when the sponsor business allots testing assignments based on novel (or emerging) software technologies. This scenario encourages sponsor businesses to consider the services of multiple QA Outsourcing vendors, each offering services suited to specific software technologies. This approach to QA Outsourcing could prove beneficial in the long term when we consider the business interests of the sponsor organization. That said organizations must consider the complexities and complications that may arise from a multi-vendor strategy. Team management skills assume importance, as does the ability to track the services rendered by multiple QA Outsourcing vendors. It would make more business sense to take on the services of a vendor with all inclusive testing abilities, backed by an expert team with in-depth knowledge of all industries.
Vendor Management
A successful QA Outsourcing strategy hinges on the expert management of the services offered by a vendor (or multiple vendors). Business managers working on behalf of the sponsor organization must assess the efficacy of vendor performance at regular intervals. Such actions must include devising strategies to improve vendor performance, anticipating process disruptions in QA Outsourcing processes, drive higher levels of co-operation from a vendor’s management team, penalize inefficient vendors, institute best practices in the work processes of individual vendors, and more. These actions, when summed under the title of vendor management, allow higher levels of achievement in the QA Outsourcing paradigm.
In Conclusion
The ideas presented can act as lodestones that guide modern organizations in the domain of QA Outsourcing activities, and the top brass and leaders of such organizations must effect timely course corrections in such collaborations. Intelligent business operators must deal with challenges that emerge in such collaborations on a real-time basis in order to gain the maximum mileage from such business decisions. In addition, sponsor organizations must share best practices with outsourced software testing organizations, while closely monitoring the progress registered by the vendor(s). The net outcomes of such actions can spell success for the collaboration and could lead to more wide-ranging business collaborations in the future. Leave all your QA and testing worries to a renowned and expert team – connect with us.

by admin | Aug 4, 2019 | E-Learning Testing, Fixed, Blog |
Modern quality assurance systems focus on preventing mistakes and defects in the processes that end in the creation of products and services. The intent is to avoid problems when delivering products or services to customers. The modules of e-learning courses are no exception – they must be tested regularly to ensure quality in digital learning design. A solid e-learning testing process reduces work for reviewers since it eliminates bugs and errors before the release of content, thereby improving the learner experience.
Gaining Inputs from Stakeholders
A key aspect of e-learning domain testing involves reviews of the course materials by personnel not directly connected to developing an e-learning project. Co-workers, colleagues, and managers can help detect errors in the course material. Errors may include typos, spelling mistakes, punctuation, grammar, the layout and relevance of images, text alignments, brand guidelines, and more. Engineers working for an e-learning testing company can use this technique to improve the quality of course material and user experience.
Review Cycles
A large number of review cycles can trigger setbacks for an e-learning testing project. Therefore, project leaders must plan to ensure the optimum number of review cycles that would match the requirements. Once managed, review cycles can contribute significantly to the successful development of an e-learning domain testing exercise. Hence, instructional designers and project managers must ensure learning objectives are covered adequately in each review cycle.
Specific Feedback
Testing engineers of an e-learning testing company benefit when they receive clear instructions on the quantum and quality of feedback expected from them. Appropriate types and levels of feedback allow stakeholders to gain a clear view of progress in a project. When reviewing a storyboard, for instance, the feedback must focus on content, while the review of a prototype should focus on functionality and design.
A Review App to Track Feedback
Every activity in the e-learning domain testing generates elements that comprise a feedback cycle. Digital devices, such as apps, can be deployed to help reviewers gain swift and first-hand feedback. There are specific apps which enable QA professionals conducting e-learning testing to review digital modules and provide usable feedback for testers. The app also serves to track feedback over time, thus expanding the scope for receiving and incorporating relevant feedback into the work schedules of testers.
Stakeholder Satisfaction
Multiple stakeholders can drive an e-learning project, and it is therefore imperative that e-learning testing professionals can manage stakeholder expectations consistently and efficiently. Defining the needs of stakeholders, analyzing their influence and interests, the subsequent actions and reviews also serve to drive quality assurance in the e-learning domain testing projects. The leaders of an e-learning testing company must remember these aspects before commencing testing regimens.
Reviewers Play a Critical Role
It is the responsibility of content reviewers to finalize the shape and scope of content in the early phases of a project. This enables quality assurance personnel to commence e-learning testing through various mechanisms. Reviewers must leverage their professional experience to provide direction to testing engineers, thus enabling the creation of robust e-learning modules.
In Conclusion
Testers must focus on the design and functionality of e-learning modules, while reviewers work to ensure flawless, updated content. Companies delivering such modules would benefit from the services of top-line professionals and experts in this realm. Connect with our team to elevate the quality and user experience of your e-learning material and software.